Deck 21: Introduction to Statistical Analysis
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/31
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 21: Introduction to Statistical Analysis
1
Which group of numbers is the best example of a normally distributed data set? 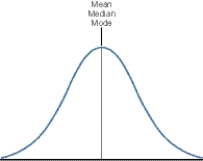
A)1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 10, 10, 10, 10
B)2, 2, 2, 2, 4, 8, 8, 8, 9
C)3, 4, 4, 5, 5, 5, 6, 6, 7
D)1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9

A)1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 10, 10, 10, 10
B)2, 2, 2, 2, 4, 8, 8, 8, 9
C)3, 4, 4, 5, 5, 5, 6, 6, 7
D)1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9
3, 4, 4, 5, 5, 5, 6, 6, 7
2
There are four data sets:
A: 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 10, 10, 10, 10
B: 2, 2, 2, 2, 4, 8, 8, 8, 9
C: 3, 4, 4, 5, 5, 5, 6, 6, 7
D: 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9
What is the mean of the four individual data sets?
A)5, 5, 5, 5
B)1, 4, 5, 5
C)1, 2, 5, 5
D)5
A: 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 10, 10, 10, 10
B: 2, 2, 2, 2, 4, 8, 8, 8, 9
C: 3, 4, 4, 5, 5, 5, 6, 6, 7
D: 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9
What is the mean of the four individual data sets?
A)5, 5, 5, 5
B)1, 4, 5, 5
C)1, 2, 5, 5
D)5
5, 5, 5, 5
3
A null hypothesis is stated. The null hypothesis is, "There is no difference between one baby aspirin every day and no baby aspirin at all in prevention of myocardial infarction." What are the implications of this statement, concerning the null hypothesis and Type II error?
A)Accepting the null hypothesis when it actually is true means that the researcher has made a Type II error in concluding that there is no difference between one baby aspirin every day and no baby aspirin in the prevention of myocardial infarction.
B)Making the statement is itself a Type II error.
C)Whether the null hypothesis is true or not makes no difference in terms of Type II error.
D)Whether or not the researcher rejects the null hypothesis makes no difference, in terms of Type II error.
E)Accepting the null hypothesis when it actually is true means that the researcher concludes that there is no difference between one baby aspirin and no baby aspirin every day in the prevention of myocardial infarction, and there is no error.
F)Accepting the null hypothesis when it actually is false means that the researcher concludes that there is no difference between one baby aspirin and no baby aspirin every day in the prevention of myocardial infarction, when there actually is a difference. The researcher has therefore made a Type II error.
A)Accepting the null hypothesis when it actually is true means that the researcher has made a Type II error in concluding that there is no difference between one baby aspirin every day and no baby aspirin in the prevention of myocardial infarction.
B)Making the statement is itself a Type II error.
C)Whether the null hypothesis is true or not makes no difference in terms of Type II error.
D)Whether or not the researcher rejects the null hypothesis makes no difference, in terms of Type II error.
E)Accepting the null hypothesis when it actually is true means that the researcher concludes that there is no difference between one baby aspirin and no baby aspirin every day in the prevention of myocardial infarction, and there is no error.
F)Accepting the null hypothesis when it actually is false means that the researcher concludes that there is no difference between one baby aspirin and no baby aspirin every day in the prevention of myocardial infarction, when there actually is a difference. The researcher has therefore made a Type II error.
Accepting the null hypothesis when it actually is true means that the researcher concludes that there is no difference between one baby aspirin and no baby aspirin every day in the prevention of myocardial infarction, and there is no error.
Accepting the null hypothesis when it actually is false means that the researcher concludes that there is no difference between one baby aspirin and no baby aspirin every day in the prevention of myocardial infarction, when there actually is a difference. The researcher has therefore made a Type II error.
Accepting the null hypothesis when it actually is false means that the researcher concludes that there is no difference between one baby aspirin and no baby aspirin every day in the prevention of myocardial infarction, when there actually is a difference. The researcher has therefore made a Type II error.
4
A researcher conducts a statistical test that reveals that the four groups analyzed differed. The researcher wants to discover which one or ones of the four differed from the others. The researcher must then perform a post hoc analysis. What will this involve?
A)Design of a second research study, using a new sample
B)Descriptive statistics about the sample demographics
C)Qualitative research generating new themes and ideas
D)A second statistical test using the original data
A)Design of a second research study, using a new sample
B)Descriptive statistics about the sample demographics
C)Qualitative research generating new themes and ideas
D)A second statistical test using the original data

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 31 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
If beta, , is the probability of making a Type II error, what is 1 minus ?
A)Alpha [ ]
B)A relationship exists
C)The power of the study
D)The likelihood that the null hypothesis is incorrect
E)The probability of not making a Type II error
A)Alpha [ ]
B)A relationship exists
C)The power of the study
D)The likelihood that the null hypothesis is incorrect
E)The probability of not making a Type II error

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 31 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
A researcher designs a study to measure the effect on patient satisfaction of the nurse stating to the patient at least once a day, "You're a good person." The researcher sets the alpha (Type I error) for the study at p < 0.10 because the intervention costs nothing, it needs very little time to enact, and it is harmless. If the alpha is set at 0.10, what is the effect on the beta [ ], and on Type II error?
A)Beta [ ] stays the same.
B)Type II error becomes less likely.
C)Type II error becomes more likely.
D)Beta [ ] decreases.
E)Beta [ ] increases as well.
F)Type II error stays the same.
A)Beta [ ] stays the same.
B)Type II error becomes less likely.
C)Type II error becomes more likely.
D)Beta [ ] decreases.
E)Beta [ ] increases as well.
F)Type II error stays the same.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 31 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
If a researcher wishes to predict with 97.5% accuracy, the level of significance would be:
A)0.05.
B)0.01.
C)0.25.
D)0.025.
A)0.05.
B)0.01.
C)0.25.
D)0.025.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 31 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Which of the illustrations of distribution curves demonstrates the least amount of variation in the scores? 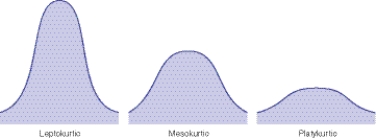
A)The least amount of variation would be in the first curve.
B)The least amount of variation would be in the second curve.
C)The least amount of variation would be in the third curve.
D)The amount of variation can't be defined by the curve.

A)The least amount of variation would be in the first curve.
B)The least amount of variation would be in the second curve.
C)The least amount of variation would be in the third curve.
D)The amount of variation can't be defined by the curve.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 31 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
A researcher states in an article that a new experimental treatment, trialed in the outpatient setting in a tri-physician practice in northern Oregon, produces better outcomes than the control treatment for patients with COPD. The p-value given is p < 0.05. What does this mean?
A)There is better than a 95% chance that at the research site mentioned in the article, the experimental treatment really does produce better outcomes for patients with COPd.
B)The probability of error is 95%.
C)There is very little chance that the intervention is effective-less than a 5% chance, in fact.
D)There is better than a 95% chance that the experimental treatment will produce better outcomes for all COPD patients.
E)There is less than a 5% chance that the researcher has reached this conclusion in error.
A)There is better than a 95% chance that at the research site mentioned in the article, the experimental treatment really does produce better outcomes for patients with COPd.
B)The probability of error is 95%.
C)There is very little chance that the intervention is effective-less than a 5% chance, in fact.
D)There is better than a 95% chance that the experimental treatment will produce better outcomes for all COPD patients.
E)There is less than a 5% chance that the researcher has reached this conclusion in error.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 31 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
What is 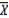 the symbol for?
the symbol for?
A)Sample mean
B)Population mean
C)Population variance
D)Sample variance
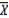 the symbol for?
the symbol for?A)Sample mean
B)Population mean
C)Population variance
D)Sample variance

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 31 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
A researcher reports that the heights of men aged 53 living in Rapid City, South Dakota, is between 5'7" and 6'0" and that the confidence interval is calculated at the p < 0.05 level. What does this mean?
A)If the heights of men in Rapid City, South Dakota, do not fall within the confidence interval at least 5% of the time, a Type I error has occurred.
B)If a 53-yr-old man in Rapid City, South Dakota, is measured, there is a 95% chance that his height will fall in the 5'7" through 6'0" interval.
C)Ninety-five percent of the 53-year-old men living in Rapid City, South Dakota, are between 5'7" and 6'0".
D)The heights of the men in the sample were all between 5'7" and 6'0", and the sample was representative of 95% of the men in town.
A)If the heights of men in Rapid City, South Dakota, do not fall within the confidence interval at least 5% of the time, a Type I error has occurred.
B)If a 53-yr-old man in Rapid City, South Dakota, is measured, there is a 95% chance that his height will fall in the 5'7" through 6'0" interval.
C)Ninety-five percent of the 53-year-old men living in Rapid City, South Dakota, are between 5'7" and 6'0".
D)The heights of the men in the sample were all between 5'7" and 6'0", and the sample was representative of 95% of the men in town.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 31 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
A null hypothesis is stated. The null hypothesis is, "There is no difference between 10 mcg and 20 mcg of vitamin D3, in prevention of osteoporosis." What are the implications of this statement, concerning the null hypothesis and Type I error?
A)Rejecting the null hypothesis when it actually is false means that the researcher has made a Type I error in concluding that there is a difference between 10 and 20 mcg of vitamin D3 in preventing osteoporosis.
B)Making the statement is itself a Type I error.
C)Whether the null hypothesis is true or not makes no difference, in terms of Type I error.
D)Whether or not the researcher rejects the null hypothesis makes no difference, in terms of Type I error.
E)Rejecting the null hypothesis when it actually is false means that the researcher concludes that there is a difference between 10 and 20 mcg of vitamin D3 in preventing osteoporosis, and there is no error.
F)Rejecting the null hypothesis when it actually is true means that there is no difference between 10 and 20 mcg of vitamin D3 in preventing osteoporosis, but the researcher thinks there is, and has made a Type I error.
A)Rejecting the null hypothesis when it actually is false means that the researcher has made a Type I error in concluding that there is a difference between 10 and 20 mcg of vitamin D3 in preventing osteoporosis.
B)Making the statement is itself a Type I error.
C)Whether the null hypothesis is true or not makes no difference, in terms of Type I error.
D)Whether or not the researcher rejects the null hypothesis makes no difference, in terms of Type I error.
E)Rejecting the null hypothesis when it actually is false means that the researcher concludes that there is a difference between 10 and 20 mcg of vitamin D3 in preventing osteoporosis, and there is no error.
F)Rejecting the null hypothesis when it actually is true means that there is no difference between 10 and 20 mcg of vitamin D3 in preventing osteoporosis, but the researcher thinks there is, and has made a Type I error.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 31 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
A researcher who has conducted experimental research finds that in the researcher's 145-person hospital study, the patients who are ambulated on the evening of abdominal surgery are less likely than the control group to develop postoperative pneumonia. What does the researcher infer?
A)The control group resembled the experimental group in all important characteristics.
B)Early ambulation and pneumonia are strongly related.
C)Evening-of-surgery ambulation will prevent some cases of postoperative pneumonia in abdominal surgery patients.
D)Careful support of the abdomen is important for postoperative ambulation in patients who have had abdominal surgery.
A)The control group resembled the experimental group in all important characteristics.
B)Early ambulation and pneumonia are strongly related.
C)Evening-of-surgery ambulation will prevent some cases of postoperative pneumonia in abdominal surgery patients.
D)Careful support of the abdomen is important for postoperative ambulation in patients who have had abdominal surgery.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 31 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
There are four data sets:
A: 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 10, 10, 10, 10
B: 2, 2, 2, 2, 4, 8, 8, 8, 9
C: 3, 4, 4, 5, 5, 5, 6, 6, 7
D: 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9
What is the mode of the four individual data sets?
A)5, 5, 5, 5
B)1, 4, 5, 5
C)1, 2, 5, none
D)1
A: 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 10, 10, 10, 10
B: 2, 2, 2, 2, 4, 8, 8, 8, 9
C: 3, 4, 4, 5, 5, 5, 6, 6, 7
D: 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9
What is the mode of the four individual data sets?
A)5, 5, 5, 5
B)1, 4, 5, 5
C)1, 2, 5, none
D)1

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 31 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
In this illustration of a negatively skewed curve, identify which line represents the mode. 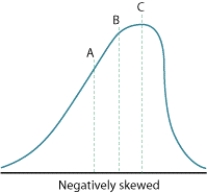
A)A
B)B
C)C

A)A
B)B
C)C

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 31 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
In statistical hypothesis testing, which of the following occur before the data are collected?
A)The beta (Type II error) is set.
B)A power analysis is conducted.
C)The null hypothesis is accepted or rejected.
D)The alpha (Type I error) is set.
E)The primary null hypothesis is stated.
A)The beta (Type II error) is set.
B)A power analysis is conducted.
C)The null hypothesis is accepted or rejected.
D)The alpha (Type I error) is set.
E)The primary null hypothesis is stated.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 31 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
One hundred students took an examination; the mean of the test was 45%, and the median 38%; 70 students scored below the mean, but 3 scored more than 96%. This would represent what type of distribution?
A)Normal
B)Positively skewed
C)Negatively skewed
D)Leptokurtic
A)Normal
B)Positively skewed
C)Negatively skewed
D)Leptokurtic

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 31 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
There are four data sets:
A: 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 10, 10, 10, 10
B: 2, 2, 2, 2, 4, 8, 8, 8, 9
C: 3, 4, 4, 5, 5, 5, 6, 6, 7
D: 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9
What is the median of the four individual data sets?
A)5, 5, 5, 5
B)1, 4, 5, 5
C)1, 2, 5, 5
D)5
A: 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 10, 10, 10, 10
B: 2, 2, 2, 2, 4, 8, 8, 8, 9
C: 3, 4, 4, 5, 5, 5, 6, 6, 7
D: 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9
What is the median of the four individual data sets?
A)5, 5, 5, 5
B)1, 4, 5, 5
C)1, 2, 5, 5
D)5

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 31 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Where would one find approximately 95% of the scores in the following example if scores are normally distributed? "Scores ranged from 30 to 68, M = 45, SD = 7."
A)Between 37 and 61
B)Between 38 and 52
C)Between 31 and 59
D)Between 30 and 68
A)Between 37 and 61
B)Between 38 and 52
C)Between 31 and 59
D)Between 30 and 68

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 31 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
In the illustration, what is this particular distribution called? 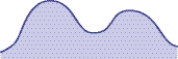
A)Bimodal
B)Normal
C)Camelesque
D)Negatively skewed

A)Bimodal
B)Normal
C)Camelesque
D)Negatively skewed

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 31 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Which of the following are true about Type II error?
A)It is more likely to occur when p < 0.01 rather than when p < 0.05.
B)It is extremely likely to occur when p < 0.001.
C)It occurs when the null hypothesis is true but rejected.
D)It is a possibility only when there are statistically nonsignificant results in a study.
E)It is a possibility only when there are statistically significant results in a study.
A)It is more likely to occur when p < 0.01 rather than when p < 0.05.
B)It is extremely likely to occur when p < 0.001.
C)It occurs when the null hypothesis is true but rejected.
D)It is a possibility only when there are statistically nonsignificant results in a study.
E)It is a possibility only when there are statistically significant results in a study.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 31 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Which of the following should a reader of a research article be able to do, in order to decide whether the article's statistics are correctly selected and applied?
A)Understand the discussion section of the article.
B)Make a judgment as to whether the author's interpretations of the data are correct.
C)Make some judgment about whether the statistical procedures used were the correct ones for the level of measurement used for the study variables.
D)Make some judgment about whether the statistical procedures used were the correct ones for the research question.
E)Agree with the study's stated limitations.
F)Find the names of the statistical procedures the author used.
A)Understand the discussion section of the article.
B)Make a judgment as to whether the author's interpretations of the data are correct.
C)Make some judgment about whether the statistical procedures used were the correct ones for the level of measurement used for the study variables.
D)Make some judgment about whether the statistical procedures used were the correct ones for the research question.
E)Agree with the study's stated limitations.
F)Find the names of the statistical procedures the author used.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 31 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Why can Type I error and Type II error not be both present for one given hypothesis?
A)Power analysis makes one type of error less likely.
B)One refers to rejecting the null hypothesis when it is true and the other to accepting it when it is false.
C)As beta rises, alpha falls.
D)The researcher sets both the alpha level and the beta level.
E)Qualitative research does not use power analysis.
A)Power analysis makes one type of error less likely.
B)One refers to rejecting the null hypothesis when it is true and the other to accepting it when it is false.
C)As beta rises, alpha falls.
D)The researcher sets both the alpha level and the beta level.
E)Qualitative research does not use power analysis.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 31 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
A teacher administers an examination. The examination seemed relatively easy for the students, and the majority of the scores are at the high end of the scale, although several students received low scores. In statistical terms this represents what?
A)Positive skew
B)Negative skew
C)Asymmetrical distribution
D)Symmetrical distribution
E)A normal curve
F)A non-normal curve
A)Positive skew
B)Negative skew
C)Asymmetrical distribution
D)Symmetrical distribution
E)A normal curve
F)A non-normal curve

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 31 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
A researcher is attempting to decide whether to hire a statistician to assist with the statistical aspects of the study. If the researcher cannot perform all of the following for a quantitative study, why should a statistician be contacted?
A)Provide sample demographics using descriptive statistics.
B)Perform reliability testing of the study instruments.
C)Design and perform analyses to answer research questions and test hypotheses.
D)Design and perform an exploratory analysis of the data.
E)Hand-compute all statistical calculations.
F)Prepare the data for analysis.
G)Perform a power analysis.
H)Interpret the results obtained by all statistical computations.
A)Provide sample demographics using descriptive statistics.
B)Perform reliability testing of the study instruments.
C)Design and perform analyses to answer research questions and test hypotheses.
D)Design and perform an exploratory analysis of the data.
E)Hand-compute all statistical calculations.
F)Prepare the data for analysis.
G)Perform a power analysis.
H)Interpret the results obtained by all statistical computations.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 31 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
A researcher is concerned about the power of a study. The researcher's planned interventional study examines the effect upon depression of instituting twice-yearly trips with the Road Scholar travel program for widows and widowers who have, 1 to 2 years before, lost a spouse to a long illness. What strategies could make Type II error less likely?
A)Decreasing the effect size
B)Increasing the alpha from 0.05 to 0.10
C)Increasing the beta from 0.20 to 0.30
D)Decreasing the beta from 0.20 to 0.10
E)Decreasing the alpha from 0.05 to 0.025
F)Increasing the sample size
A)Decreasing the effect size
B)Increasing the alpha from 0.05 to 0.10
C)Increasing the beta from 0.20 to 0.30
D)Decreasing the beta from 0.20 to 0.10
E)Decreasing the alpha from 0.05 to 0.025
F)Increasing the sample size

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 31 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Findings can be statistically significant but clinically not significant. Which of the following studies with statistically significant findings exemplify this?
A)Seventy-five seconds of UV light daily can completely reverse the symptoms of allergic dermatitis.
B)Eating a cup of salad greens daily increases one's life expectancy by 2 years.
C)Petting a cat for 5 minutes daily increases one's endorphin levels.
D)Exercise Program Delta causes weight loss of 6.3 pounds per year in morbidly obese women.
E)Talking to a crying baby calms the baby more than ignoring it; picking up the baby calms it more than talking to it.
F)Medication R15B, taken daily from age 13, completely controls cystic acne by age 23.
A)Seventy-five seconds of UV light daily can completely reverse the symptoms of allergic dermatitis.
B)Eating a cup of salad greens daily increases one's life expectancy by 2 years.
C)Petting a cat for 5 minutes daily increases one's endorphin levels.
D)Exercise Program Delta causes weight loss of 6.3 pounds per year in morbidly obese women.
E)Talking to a crying baby calms the baby more than ignoring it; picking up the baby calms it more than talking to it.
F)Medication R15B, taken daily from age 13, completely controls cystic acne by age 23.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 31 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
A measured value is within two standard deviations of the mean but not within one standard deviation, and it is greater than the mean. The distribution is very close to a normal distribution. What does this signify?
A)This particular value is not an outlier.
B)In the data set, almost 2/3 of the values are closer to the mean than this one is.
C)The data point falls within the majority of the measured values, in terms of its closeness to the mean.
D)In the data set, at least 4% of the values are further from the mean than this particular value is.
E)In this data set, between 65% and 95% of the values are smaller in value than this one is.
A)This particular value is not an outlier.
B)In the data set, almost 2/3 of the values are closer to the mean than this one is.
C)The data point falls within the majority of the measured values, in terms of its closeness to the mean.
D)In the data set, at least 4% of the values are further from the mean than this particular value is.
E)In this data set, between 65% and 95% of the values are smaller in value than this one is.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 31 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Which of the following are true in a skewed distribution?
A)Mean, mode, and median are not equal.
B)The curve is asymmetrical.
C)There is bimodal distribution.
D)There is no mode.
E)More than 50% of the values lie to one side of the mean.
A)Mean, mode, and median are not equal.
B)The curve is asymmetrical.
C)There is bimodal distribution.
D)There is no mode.
E)More than 50% of the values lie to one side of the mean.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 31 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Why might nonparametric statistical methods be used for analysis?
A)The level of measurement of the variables is nominal.
B)The researcher prefers to use these statistical tests.
C)The null hypothesis is absent.
D)The sample is small or lacks a normal distribution.
A)The level of measurement of the variables is nominal.
B)The researcher prefers to use these statistical tests.
C)The null hypothesis is absent.
D)The sample is small or lacks a normal distribution.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 31 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
A data set shows that the mean, median, and mode are the same. This means which of the following?
A)The distribution is bimodal.
B)The data are normally distributed.
C)The variables are dichotomous.
D)All data points are identical.
E)The kurtosis is symmetrical.
F)This may describe the normal curve.
A)The distribution is bimodal.
B)The data are normally distributed.
C)The variables are dichotomous.
D)All data points are identical.
E)The kurtosis is symmetrical.
F)This may describe the normal curve.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 31 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



