Deck 25: Monopolistic Competition, Oligopoly, and Game Theory
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/167
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 25: Monopolistic Competition, Oligopoly, and Game Theory
1
In a monopolistic competitive market,which of the following factors probably does not give rise to product differentiation?
A) packaging of the product
B) brand names
C) loyalty of customers to a particular producer
D) quality difference
E) the small number of sellers
A) packaging of the product
B) brand names
C) loyalty of customers to a particular producer
D) quality difference
E) the small number of sellers
E
2
One of the ways in which monopolistic competitors differ from perfect competitors is that
A) perfect competitors produce the quantity of output at which marginal revenue equals marginal cost and monopolistic competitors do not.
B) perfect competitors produce a homogeneous product and monopolistic competitors do not.
C) there is easy entry and exit for a perfect competitor, but not for a monopolistic competitor.
D) a and c
E) b and c
A) perfect competitors produce the quantity of output at which marginal revenue equals marginal cost and monopolistic competitors do not.
B) perfect competitors produce a homogeneous product and monopolistic competitors do not.
C) there is easy entry and exit for a perfect competitor, but not for a monopolistic competitor.
D) a and c
E) b and c
B
3
The monopolistic competitive firm faces a(n)__________ demand curve.
A) horizontal
B) vertical
C) downward-sloping
D) upward-sloping
A) horizontal
B) vertical
C) downward-sloping
D) upward-sloping
C
4
Some monopolistic competitive firms earn positive economic profits in the long run because
A) there are high barriers to entry in monopolistic competition.
B) they have successfully differentiated their products from their competitors' products.
C) there is easy entry and exit.
D) b and c
E) none of the above
A) there are high barriers to entry in monopolistic competition.
B) they have successfully differentiated their products from their competitors' products.
C) there is easy entry and exit.
D) b and c
E) none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 167 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Which of the following industries is the best real-world example of monopolistic competition?
A) soft drinks
B) electricity generation
C) automobiles
D) computer software
A) soft drinks
B) electricity generation
C) automobiles
D) computer software

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 167 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Compared to a monopolistic competitor,a monopolist produces a good with __________ substitutes and so has a __________ elastic demand curve.
A) fewer; more
B) fewer; less
C) more; more
D) more; less
A) fewer; more
B) fewer; less
C) more; more
D) more; less

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 167 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
The perfectly competitive firm charges a price equal to __________ while the monopolistic competitor firm charges a price __________.
A) marginal revenue; equal to marginal cost
B) marginal cost; greater than marginal cost
C) marginal revenue; greater than marginal revenue
D) average fixed cost; greater than average total cost
E) b and c
A) marginal revenue; equal to marginal cost
B) marginal cost; greater than marginal cost
C) marginal revenue; greater than marginal revenue
D) average fixed cost; greater than average total cost
E) b and c

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 167 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Which of the following statements is false?
A) The monopolistic competitor is a price searcher.
B) The monopolistic competitor produces an output at which price is greater than marginal cost.
C) The demand curve facing a monopolistic competitor is less elastic than the demand curve facing a monopolist.
D) There are many substitutes in a monopolistic competitive industry.
A) The monopolistic competitor is a price searcher.
B) The monopolistic competitor produces an output at which price is greater than marginal cost.
C) The demand curve facing a monopolistic competitor is less elastic than the demand curve facing a monopolist.
D) There are many substitutes in a monopolistic competitive industry.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 167 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Does the monopolistic competitive firm exhibit resource-allocative efficiency?
A) No, because at its chosen quantity of output, price does not equal the lowest possible average total cost.
B) Yes, because at its chosen quantity of output, price equals marginal cost.
C) No, because at its chosen quantity of output, price is greater than marginal cost.
D) Yes, because at its chosen quantity of output, price is less than marginal cost.
A) No, because at its chosen quantity of output, price does not equal the lowest possible average total cost.
B) Yes, because at its chosen quantity of output, price equals marginal cost.
C) No, because at its chosen quantity of output, price is greater than marginal cost.
D) Yes, because at its chosen quantity of output, price is less than marginal cost.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 167 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
The relationship between a monopolistic competitor's marginal revenue curve and its demand curve is that the
A) two curves coincide and are horizontal at the market price.
B) marginal revenue curve lies above the demand curve and the demand curve is horizontal at the market price.
C) marginal revenue curve lies below the demand curve and both are downward sloping.
D) two curves coincide and are downward sloping to the right.
E) marginal revenue curve lies above the demand curve and both are downward sloping.
A) two curves coincide and are horizontal at the market price.
B) marginal revenue curve lies above the demand curve and the demand curve is horizontal at the market price.
C) marginal revenue curve lies below the demand curve and both are downward sloping.
D) two curves coincide and are downward sloping to the right.
E) marginal revenue curve lies above the demand curve and both are downward sloping.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 167 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
The demand curve facing a monopolistic competitor will be more elastic than the demand curve facing a monopolist because
A) there are barriers to exit for the monopolist, but not for the monopolistic competitor.
B) the monopolistic competitor attains resource-allocative efficiency, but the monopolist does not.
C) there are substitute goods for what the monopolistic competitor produces, but not for what the monopolist produces.
D) the monopolist is a price searcher, but the monopolistic competitor is not.
A) there are barriers to exit for the monopolist, but not for the monopolistic competitor.
B) the monopolistic competitor attains resource-allocative efficiency, but the monopolist does not.
C) there are substitute goods for what the monopolistic competitor produces, but not for what the monopolist produces.
D) the monopolist is a price searcher, but the monopolistic competitor is not.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 167 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Which of the following is one of the assumptions upon which the theory of monopolistic competition is built?
A) There are many sellers.
B) There are few buyers.
C) It is difficult to enter the industry.
D) Each firm in the industry produces a homogeneous product.
A) There are many sellers.
B) There are few buyers.
C) It is difficult to enter the industry.
D) Each firm in the industry produces a homogeneous product.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 167 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
The monopolistic competitive firm produces the output at which
A) price equals marginal cost.
B) marginal revenue equals marginal cost.
C) there is resource allocative efficiency.
D) average total cost is at a minimum.
A) price equals marginal cost.
B) marginal revenue equals marginal cost.
C) there is resource allocative efficiency.
D) average total cost is at a minimum.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 167 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Which of the following is not an assumption of the theory of monopolistic competition?
A) There are high barriers to entry.
B) There are many sellers and few buyers.
C) Each firm in the industry produces and sells a homogeneous product.
D) a and b
E) all of the above
A) There are high barriers to entry.
B) There are many sellers and few buyers.
C) Each firm in the industry produces and sells a homogeneous product.
D) a and b
E) all of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 167 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Which of the following statements is false?
A) The monopolistic competitor is a price searcher.
B) The monopolistic competitor produces a product that differs slightly from the products of the other firms in the industry.
C) The monopolistic competitor faces a horizontal demand curve.
D) The monopolistic competitor produces an output at which price is greater than marginal cost.
A) The monopolistic competitor is a price searcher.
B) The monopolistic competitor produces a product that differs slightly from the products of the other firms in the industry.
C) The monopolistic competitor faces a horizontal demand curve.
D) The monopolistic competitor produces an output at which price is greater than marginal cost.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 167 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
The demand curve facing a monopolistic competitive firm will be __________ than the demand curve facing a perfectly competitive firm,because the price elasticity of demand for the monopolistic competitive firm's product is __________ than that for the perfectly competitive firm.
A) steeper; greater
B) flatter; greater
C) steeper; less
D) flatter; less
A) steeper; greater
B) flatter; greater
C) steeper; less
D) flatter; less

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 167 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Which of the following is an example of a monopolistic competitor?
A) General Motors
B) a wheat farmer in Iowa
C) a long-distance telephone company
D) a family-owned Italian restaurant
A) General Motors
B) a wheat farmer in Iowa
C) a long-distance telephone company
D) a family-owned Italian restaurant

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 167 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
In a monopolistic competitive industry,
A) each firm in the industry produces a slightly differentiated product.
B) there are barriers to entry.
C) there are barriers to exit.
D) there are few sellers.
A) each firm in the industry produces a slightly differentiated product.
B) there are barriers to entry.
C) there are barriers to exit.
D) there are few sellers.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 167 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
The monopolistic competitive firm faces a __________ demand curve and therefore is a price __________.
A) downward-sloping; searcher.
B) horizontal; taker.
C) downward-sloping; taker.
D) horizontal; searcher.
A) downward-sloping; searcher.
B) horizontal; taker.
C) downward-sloping; taker.
D) horizontal; searcher.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 167 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
If a monopolistic competitive firm raises its price,then
A) it should expect to lose all of its customers because there are many other sellers of the product.
B) this is a trick question because the firm does not have the ability to change its price.
C) it should expect to lose some, but not all, of its customers.
D) it will be able to increase its profits.
E) it can sell all it wants because it faces a horizontal demand curve.
A) it should expect to lose all of its customers because there are many other sellers of the product.
B) this is a trick question because the firm does not have the ability to change its price.
C) it should expect to lose some, but not all, of its customers.
D) it will be able to increase its profits.
E) it can sell all it wants because it faces a horizontal demand curve.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 167 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
There are few sellers and many buyers in the
A) perfectly competitive market structure.
B) monopolistic competitive market structure.
C) oligopoly market structure.
D) monopoly market structure.
A) perfectly competitive market structure.
B) monopolistic competitive market structure.
C) oligopoly market structure.
D) monopoly market structure.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 167 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
A firm in a monopolistic competitive market will produce a level of output at which
A) P < MR.
B) P = MR.
C) P > MR.
D) P = MC.
A) P < MR.
B) P = MR.
C) P > MR.
D) P = MC.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 167 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Why can't an economist say for certain that a monopolistic competitive firm will always earn zero economic profits in the long run?
A) Barriers to entry exist.
B) The very large number of buyers indicates that there will always be demand for the firm's product.
C) The firms in the industry do not produce identical products.
D) The firms practice price competition, so at least some firms will always be charging a lower price than other firms and will sell more as a result.
E) The firms face a horizontal demand curve.
A) Barriers to entry exist.
B) The very large number of buyers indicates that there will always be demand for the firm's product.
C) The firms in the industry do not produce identical products.
D) The firms practice price competition, so at least some firms will always be charging a lower price than other firms and will sell more as a result.
E) The firms face a horizontal demand curve.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 167 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
The excess capacity theorem states that a monopolistic competitor
A) will produce an output level smaller than the one that would minimize its unit costs.
B) will produce an output level where MR > MC.
C) generally does not attain long run equilibrium, and thus charges a higher price than it should.
D) typically produces too much of a good at too low a quality.
A) will produce an output level smaller than the one that would minimize its unit costs.
B) will produce an output level where MR > MC.
C) generally does not attain long run equilibrium, and thus charges a higher price than it should.
D) typically produces too much of a good at too low a quality.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 167 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Interdependence implies that each firm in an industry
A) is independent of one another and are essentially price takers.
B) is aware that its actions influence the others and that the actions of the other firms affect it.
C) is so large and powerful that they do not need to consider how their actions will affect their rivals.
D) must depend on the other firms to maintain consumers' interest in their "mutual" product.
A) is independent of one another and are essentially price takers.
B) is aware that its actions influence the others and that the actions of the other firms affect it.
C) is so large and powerful that they do not need to consider how their actions will affect their rivals.
D) must depend on the other firms to maintain consumers' interest in their "mutual" product.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 167 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Total industry sales are $800 million.The four largest firms have sales of $320 million,$226 million,$98 million,and $42 million.The industry's four-firm concentration ratio is
A) 0.86.
B) 0.68.
C) 0.39.
D) 0.14.
A) 0.86.
B) 0.68.
C) 0.39.
D) 0.14.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 167 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Total industry sales are $80 million.The top four firms (A,B,C,and D)account for sales of $15 million,$3.2 million,$1.3 million and $0.4 million,respectively.What is the four-firm concentration ratio?
A) 9.40
B) 0.25
C) 0.75
D) 0.20
A) 9.40
B) 0.25
C) 0.75
D) 0.20

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 167 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Which of the following is an assumption of the theory of oligopoly?
A) There are barriers to entry.
B) There are many sellers and many buyers.
C) Firms produce and sell either homogeneous or differentiated products.
D) a and c
E) none of the above
A) There are barriers to entry.
B) There are many sellers and many buyers.
C) Firms produce and sell either homogeneous or differentiated products.
D) a and c
E) none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 167 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
If a perfectly competitive firm and a monopolistic competitor in long run equilibrium face the same demand and cost curves,then the competitive firm will produce a
A) greater output and charge a lower price than the monopolistic competitor.
B) greater output, but charge the same price as the monopolistic competitor.
C) greater output and charge a higher price than the monopolistic competitor.
D) smaller output and charge a lower price than the monopolistic competitor.
E) smaller output and charge a higher price than the monopolistic competitor.
A) greater output and charge a lower price than the monopolistic competitor.
B) greater output, but charge the same price as the monopolistic competitor.
C) greater output and charge a higher price than the monopolistic competitor.
D) smaller output and charge a lower price than the monopolistic competitor.
E) smaller output and charge a higher price than the monopolistic competitor.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 167 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Generally,the monopolistic competitor is in long run equilibrium when
A) MR = MC and P = ATC.
B) P = MC = ATC.
C) P = MC and P > ATC.
D) MR = MC = ATC.
E) b and d
A) MR = MC and P = ATC.
B) P = MC = ATC.
C) P = MC and P > ATC.
D) MR = MC = ATC.
E) b and d

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 167 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Which of the following statements is true?
A) Monopolistic competitive firms will earn economic profits in the long run because of their ability to control the price of the product.
B) Monopolistic competitive firms that earn economic profits in the short run commonly will find their profits competed away in the long run.
C) Monopolistic competitive firms will earn zero economic profits in both the short and the long run.
D) Monopolistic competitive firms must earn economic profits in the long run, or they will shut down.
E) Monopolistic competitive firms must earn economic profits in the short run, or they will shut down.
A) Monopolistic competitive firms will earn economic profits in the long run because of their ability to control the price of the product.
B) Monopolistic competitive firms that earn economic profits in the short run commonly will find their profits competed away in the long run.
C) Monopolistic competitive firms will earn zero economic profits in both the short and the long run.
D) Monopolistic competitive firms must earn economic profits in the long run, or they will shut down.
E) Monopolistic competitive firms must earn economic profits in the short run, or they will shut down.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 167 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
If a perfectly competitive firm and a monopolistic competitive firm face the same demand and cost curves,then
A) the perfectly competitive firm will attain resource-allocative efficiency, but the monopolistic competitive firm will not.
B) the perfectly competitive firm will attain resource-allocative efficiency, but the monopolistic competitive firm may or may not, depending upon the demand for its product.
C) the perfectly competitive firm will not attain resource-allocative efficiency, but the monopolistic competitive firm will.
D) both the perfectly competitive firm and the monopolistic competitive firm will attain resource-allocative efficiency.
E) neither the perfectly competitive firm nor the monopolistic competitive firm will attain resource-allocative efficiency.
A) the perfectly competitive firm will attain resource-allocative efficiency, but the monopolistic competitive firm will not.
B) the perfectly competitive firm will attain resource-allocative efficiency, but the monopolistic competitive firm may or may not, depending upon the demand for its product.
C) the perfectly competitive firm will not attain resource-allocative efficiency, but the monopolistic competitive firm will.
D) both the perfectly competitive firm and the monopolistic competitive firm will attain resource-allocative efficiency.
E) neither the perfectly competitive firm nor the monopolistic competitive firm will attain resource-allocative efficiency.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 167 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
In long run equilibrium,the monopolistic competitor will most likely
A) be earning zero economic profit.
B) be operating at the lowest point on its average total cost curve.
C) charge a price that is equal to marginal revenue.
D) charge a price that is equal to marginal cost.
E) c and d
A) be earning zero economic profit.
B) be operating at the lowest point on its average total cost curve.
C) charge a price that is equal to marginal revenue.
D) charge a price that is equal to marginal cost.
E) c and d

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 167 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
____________________ constitute(s)perhaps the most significant barrier to entry into an oligopolistic market is
A) Patent rights
B) Exclusive ownership of essential resources
C) Legal barriers
D) Economies of scale
E) Copyrights
A) Patent rights
B) Exclusive ownership of essential resources
C) Legal barriers
D) Economies of scale
E) Copyrights

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 167 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
The percentage of sales accounted for by X number of firms in the industry is called the
A) concentration ratio.
B) oligopoly rate.
C) interdependence rate.
D) market power index.
A) concentration ratio.
B) oligopoly rate.
C) interdependence rate.
D) market power index.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 167 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
In what industry structure is the interdependence of firms a key characteristic?
A) perfect competition
B) monopolistic competition
C) oligopoly
D) monopoly
A) perfect competition
B) monopolistic competition
C) oligopoly
D) monopoly

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 167 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Some economists contend that a monopolistic competitor tends to produce too __________ output,charges a price that is too __________ and __________ its present plant size.
A) little; low; underutilizes
B) little; high; underutilizes
C) much; low; overutilizes
D) much; high; overutilizes
E) much; low; underutilizes
A) little; low; underutilizes
B) little; high; underutilizes
C) much; low; overutilizes
D) much; high; overutilizes
E) much; low; underutilizes

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 167 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
A concentration ratio indicates the
A) number of firms in an industry.
B) number of large firms in an industry compared to the number of large firms in another related industry.
C) percentage of total sales accounted for by the (for example) four largest firms.
D) percentage of sellers in an industry relative to the number of buyers.
E) percentage of sellers in an industry protected by barriers to entry relative to the number of sellers that wish to enter.
A) number of firms in an industry.
B) number of large firms in an industry compared to the number of large firms in another related industry.
C) percentage of total sales accounted for by the (for example) four largest firms.
D) percentage of sellers in an industry relative to the number of buyers.
E) percentage of sellers in an industry protected by barriers to entry relative to the number of sellers that wish to enter.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 167 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
"In equilibrium,a monopolistic competitor will produce an output level that is less than the level that would minimize its average total costs." This is a statement of the
A) law of diminishing returns.
B) law of second best.
C) law of variable proportions.
D) excess capacity theorem.
A) law of diminishing returns.
B) law of second best.
C) law of variable proportions.
D) excess capacity theorem.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 167 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
If a perfectly competitive firm and a monopolistic competitor in long run equilibrium face exactly the same demand and cost curves,then there is high probability that
A) the former will earn zero economic profits, but the latter will earn positive economic profits.
B) both will earn zero economic profits, but the former will attain lower unit costs than the latter.
C) both will earn zero economic profits, but the latter will attain lower unit costs than the former.
D) both firms will earn zero economic profits, and attain the lowest possible unit costs.
E) neither firm will earn zero economic profits, but both will attain the lowest possible unit costs.
A) the former will earn zero economic profits, but the latter will earn positive economic profits.
B) both will earn zero economic profits, but the former will attain lower unit costs than the latter.
C) both will earn zero economic profits, but the latter will attain lower unit costs than the former.
D) both firms will earn zero economic profits, and attain the lowest possible unit costs.
E) neither firm will earn zero economic profits, but both will attain the lowest possible unit costs.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 167 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
The concentration ratio provides a measure of the extent to which an industry
A) produces a useful product.
B) is dominated by a small number of firms.
C) is earning economic profits.
D) is earning accounting profits.
A) produces a useful product.
B) is dominated by a small number of firms.
C) is earning economic profits.
D) is earning accounting profits.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 167 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
A monopolistic competitive firm maximizes profits by producing at the point where
A) total revenue is at a maximum.
B) marginal revenue equals average cost.
C) marginal revenue equals marginal cost.
D) price equals marginal revenue.
E) b and d
A) total revenue is at a maximum.
B) marginal revenue equals average cost.
C) marginal revenue equals marginal cost.
D) price equals marginal revenue.
E) b and d

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 167 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
Which of the following is not a condition of a contestable market?
A) There is easy entry into and costless exit from the market.
B) New firms entering the market can produce the product at the same cost as current firms.
C) Firms exiting the market can easily dispose of their fixed assets by selling them elsewhere.
D) New firms entering the market produce a higher-quality product than existing firms.
A) There is easy entry into and costless exit from the market.
B) New firms entering the market can produce the product at the same cost as current firms.
C) Firms exiting the market can easily dispose of their fixed assets by selling them elsewhere.
D) New firms entering the market produce a higher-quality product than existing firms.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 167 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
If you were to rank the four market structures in terms of lowest concentration ratio to highest concentration ratio,which of the following rankings would be correct?
A) oligopoly, monopoly, perfect competition, monopolistic competition
B) monopoly, oligopoly, monopolistic competition, perfect competition
C) perfect competition, monopolistic competition, oligopoly, monopoly
D) monopolistic competition, perfect competition, oligopoly, monopoly
E) monopolistic competition, oligopoly, perfect competition, monopoly
A) oligopoly, monopoly, perfect competition, monopolistic competition
B) monopoly, oligopoly, monopolistic competition, perfect competition
C) perfect competition, monopolistic competition, oligopoly, monopoly
D) monopolistic competition, perfect competition, oligopoly, monopoly
E) monopolistic competition, oligopoly, perfect competition, monopoly

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 167 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
A cartel is an organization of firms
A) dominated by one firm, which is usually referred to as the price leader.
B) that attempts to increase total (or industry) demand for their product.
C) that reduces output and increases price in an effort to increase joint profits.
D) that deliberately attempts to disrupt the market for political reasons.
A) dominated by one firm, which is usually referred to as the price leader.
B) that attempts to increase total (or industry) demand for their product.
C) that reduces output and increases price in an effort to increase joint profits.
D) that deliberately attempts to disrupt the market for political reasons.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 167 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
According to the contestable markets theory,
A) even if an industry is comprised of a small number of firms, this is not sufficient evidence that the firms perform in a noncompetitive way.
B) profits cannot be zero in an industry if the number of sellers in the industry is small.
C) if a market is contestable, inefficient producers are more likely to survive than if the market is not contestable.
D) b and c
E) a, b, and c
A) even if an industry is comprised of a small number of firms, this is not sufficient evidence that the firms perform in a noncompetitive way.
B) profits cannot be zero in an industry if the number of sellers in the industry is small.
C) if a market is contestable, inefficient producers are more likely to survive than if the market is not contestable.
D) b and c
E) a, b, and c

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 167 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
Which of the following is not a necessary condition for the contestable market theory?
A) There are no barriers to entry.
B) Exit from an industry is costless.
C) All firms in an industry have the same costs of production.
D) All of the above are necessary conditions.
A) There are no barriers to entry.
B) Exit from an industry is costless.
C) All firms in an industry have the same costs of production.
D) All of the above are necessary conditions.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 167 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
Which of the following statements is false?
A) On occasion, governments have helped to create and maintain cartels.
B) Once a cartel agreement has been made, cartel members have an incentive to cheat on the agreement.
C) A single cartel member may be better off with a cartel agreement that all members abide by (including itself) than with no cartel agreement at all.
D) Cartels are easy to form and to maintain.
A) On occasion, governments have helped to create and maintain cartels.
B) Once a cartel agreement has been made, cartel members have an incentive to cheat on the agreement.
C) A single cartel member may be better off with a cartel agreement that all members abide by (including itself) than with no cartel agreement at all.
D) Cartels are easy to form and to maintain.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 167 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
How does contestable markets theory challenge orthodox market structure theory?
A) Contestable markets theory argues that firms do not maximize sales; orthodox market structure theory argues that they do.
B) Orthodox market structure theory places much greater weight than contestable markets theory on the number of firms in an industry as a major factor in determining a firm's behavior.
C) Contestable markets theory emphasizes product differentiation; orthodox market structure theory does not.
D) Contestable markets theory emphasizes nonprice competition; orthodox market structure theory does not.
A) Contestable markets theory argues that firms do not maximize sales; orthodox market structure theory argues that they do.
B) Orthodox market structure theory places much greater weight than contestable markets theory on the number of firms in an industry as a major factor in determining a firm's behavior.
C) Contestable markets theory emphasizes product differentiation; orthodox market structure theory does not.
D) Contestable markets theory emphasizes nonprice competition; orthodox market structure theory does not.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 167 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
An industry is composed of 20 firms,all with equal sales.The eight-firm concentration ratio in this industry is
A) 0.40.
B) 0.32.
C) 2.00.
D) This cannot be determined from the information given.
A) 0.40.
B) 0.32.
C) 2.00.
D) This cannot be determined from the information given.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 167 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
The key behavioral assumption of the cartel theory is that oligopolists in an industry
A) try to maximize sales instead of profits.
B) act as if they are perfect competitors.
C) act in a manner consistent with there being only one firm in the industry.
D) try to create a demand for their products by way of advertising.
E) none of the above
A) try to maximize sales instead of profits.
B) act as if they are perfect competitors.
C) act in a manner consistent with there being only one firm in the industry.
D) try to create a demand for their products by way of advertising.
E) none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 167 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
The major economic objective of cartels is to
A) impose their political will on others.
B) restrict output, push up price, and increase profits.
C) reduce costs.
D) develop new ways of doing things.
E) b and d
A) impose their political will on others.
B) restrict output, push up price, and increase profits.
C) reduce costs.
D) develop new ways of doing things.
E) b and d

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 167 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
In the long run,new firms will enter a monopolistic competitive industry until
A) minimum average total cost is achieved.
B) all firms are incurring losses.
C) economic profits in the industry are zero.
D) a and b
A) minimum average total cost is achieved.
B) all firms are incurring losses.
C) economic profits in the industry are zero.
D) a and b

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 167 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
The assumption that precludes economic profits in monopolistic competition in the long run is that
A) there are many buyers and sellers.
B) the firms produce a homogeneous product.
C) there is easy entry and exit in this market structure.
D) buyers and sellers have all relevant information.
A) there are many buyers and sellers.
B) the firms produce a homogeneous product.
C) there is easy entry and exit in this market structure.
D) buyers and sellers have all relevant information.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 167 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
In long run equilibrium,a monopolistic competitive firm's price will
A) exceed ATC, but equal MC.
B) exceed both MC and ATC.
C) be less than both MC and ATC.
D) exceed MC, but equal ATC.
A) exceed ATC, but equal MC.
B) exceed both MC and ATC.
C) be less than both MC and ATC.
D) exceed MC, but equal ATC.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 167 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
The "prisoner's dilemma" game illustrates a case in which
A) individually rational behavior leads to a collectively inefficient outcome.
B) what is irrational individual behavior turns out to be ultra-irrational group behavior.
C) the whole is greater than the sum of the parts.
D) none of the above
A) individually rational behavior leads to a collectively inefficient outcome.
B) what is irrational individual behavior turns out to be ultra-irrational group behavior.
C) the whole is greater than the sum of the parts.
D) none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 167 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
The demand curve facing a firm in monopolistic competition is downward sloping,because the firm
A) sells a differentiated product.
B) is the entire industry by itself.
C) is small relative to the market.
D) b and c
E) none of the above
A) sells a differentiated product.
B) is the entire industry by itself.
C) is small relative to the market.
D) b and c
E) none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 167 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
In the real-world,which of these industries is most clearly an oligopoly?
A) wheat
B) electricity generation
C) cereal breakfast foods
D) restaurants
A) wheat
B) electricity generation
C) cereal breakfast foods
D) restaurants

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 167 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
If the firms of an industry form a cartel,their goal is to
A) collectively increase output and thereby earn higher profits.
B) cut back on output and raise the price of their product to earn higher profits.
C) maintain a constant level of output, but increase price to earn higher profits.
D) maintain a constant price level, but increase output to earn higher profits.
A) collectively increase output and thereby earn higher profits.
B) cut back on output and raise the price of their product to earn higher profits.
C) maintain a constant level of output, but increase price to earn higher profits.
D) maintain a constant price level, but increase output to earn higher profits.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 167 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
Concentration ratios are not perfect guides to industry concentration,because they
A) do not take into account foreign competition and competition from substitute goods.
B) take into account foreign competition and competition from substitute goods.
C) do not take into account advertising expenditures.
D) do not take into account tax payments.
A) do not take into account foreign competition and competition from substitute goods.
B) take into account foreign competition and competition from substitute goods.
C) do not take into account advertising expenditures.
D) do not take into account tax payments.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 167 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
The theory of contestable markets concludes that
A) a small number of firms in an industry is strong evidence that they will perform in a noncompetitive way.
B) even if the number of sellers in an industry is small, profits can be zero in the industry.
C) inefficient producers can survive in a contestable market.
D) a firm in a contestable market will sell at a price above marginal cost.
E) all of the above
A) a small number of firms in an industry is strong evidence that they will perform in a noncompetitive way.
B) even if the number of sellers in an industry is small, profits can be zero in the industry.
C) inefficient producers can survive in a contestable market.
D) a firm in a contestable market will sell at a price above marginal cost.
E) all of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 167 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
The theory of oligopoly assumes
A) a few sellers and many buyers.
B) a few buyers and many sellers.
C) significant barriers to entry.
D) a and c
E) b and c
A) a few sellers and many buyers.
B) a few buyers and many sellers.
C) significant barriers to entry.
D) a and c
E) b and c

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 167 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
The monopolistic competitive firm will most likely earn a normal profit in the long run because of
A) product differentiation.
B) many buyers and sellers.
C) easy entry and exit.
D) b and c
A) product differentiation.
B) many buyers and sellers.
C) easy entry and exit.
D) b and c

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 167 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
The profit-maximizing monopolistic competitor produces where price
A) equals marginal cost and marginal revenue.
B) is less than marginal cost and marginal revenue.
C) is greater than both marginal cost and marginal revenue.
D) equals marginal cost and is less than marginal revenue.
E) equals marginal cost and is greater than marginal revenue.
A) equals marginal cost and marginal revenue.
B) is less than marginal cost and marginal revenue.
C) is greater than both marginal cost and marginal revenue.
D) equals marginal cost and is less than marginal revenue.
E) equals marginal cost and is greater than marginal revenue.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 167 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
The monopolistic competitor's demand curve is
A) perfectly elastic because of the many buyers and sellers in the market.
B) downward sloping because of product differentiation.
C) perfectly elastic because of identical products.
D) downward sloping because of the few buyers and sellers in the market.
E) none of the above
A) perfectly elastic because of the many buyers and sellers in the market.
B) downward sloping because of product differentiation.
C) perfectly elastic because of identical products.
D) downward sloping because of the few buyers and sellers in the market.
E) none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 167 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
In the prisoner's dilemma,each prisoner would be best off if
A) both confess.
B) one confesses but the other does not.
C) one confesses, regardless of what the other does.
D) neither confesses.
A) both confess.
B) one confesses but the other does not.
C) one confesses, regardless of what the other does.
D) neither confesses.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 167 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
Exhibit 25-3
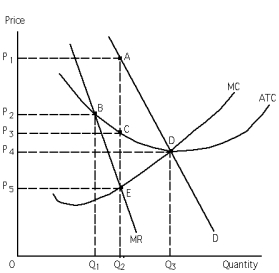
Refer to Exhibit 25-3.Profits of this profit maximizing monopolistic competitor is represented by the area
A) 0P4DQ3.
B) P5P3CE.
C) P3P1AC.
D) 0Q1 times P2P4.
E) 0Q1 times P2P5.

Refer to Exhibit 25-3.Profits of this profit maximizing monopolistic competitor is represented by the area
A) 0P4DQ3.
B) P5P3CE.
C) P3P1AC.
D) 0Q1 times P2P4.
E) 0Q1 times P2P5.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 167 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
In the prisoner's dilemma,both prisoners end up __________,which turns out to be __________ confessed.
A) confessing; better for them than if they had both not
B) confessing; worse for them than if they had both not
C) not confessing; better for them than if they had both
D) not confessing; worse for them than if they had both
A) confessing; better for them than if they had both not
B) confessing; worse for them than if they had both not
C) not confessing; better for them than if they had both
D) not confessing; worse for them than if they had both

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 167 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
Which of the following is not correct about contestable markets?
A) There is easy entry into and costless exit from the market.
B) New firms entering the market can produce the product at the same cost as current firms.
C) Firms exiting the market can easily dispose of their fixed assets by selling them elsewhere.
D) Firms already in the market have technological advantages.
E) b and c
A) There is easy entry into and costless exit from the market.
B) New firms entering the market can produce the product at the same cost as current firms.
C) Firms exiting the market can easily dispose of their fixed assets by selling them elsewhere.
D) Firms already in the market have technological advantages.
E) b and c

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 167 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
Exhibit 25-3

Refer to Exhibit 25-3.What level of output is productively efficient?
A) Q1
B) Q2
C) Q3
D) It is not labeled on the diagram.
E) It is not determinable without more information.

Refer to Exhibit 25-3.What level of output is productively efficient?
A) Q1
B) Q2
C) Q3
D) It is not labeled on the diagram.
E) It is not determinable without more information.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 167 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
Exhibit 25-3

Refer to Exhibit 25-3.Which of the following points represents the profit-maximizing quantity and price of a monopolistic competitor?
A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D
E) E

Refer to Exhibit 25-3.Which of the following points represents the profit-maximizing quantity and price of a monopolistic competitor?
A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D
E) E

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 167 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
If a market is contestable,then
A) a cartel will form in the industry.
B) economic profits are small or zero.
C) firms face a vertical demand curve.
D) there is a dominant firm in the market.
E) none of the above
A) a cartel will form in the industry.
B) economic profits are small or zero.
C) firms face a vertical demand curve.
D) there is a dominant firm in the market.
E) none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 167 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
The profit-maximizing oligopolist produces where
A) price equals marginal cost.
B) marginal revenue equals marginal cost.
C) price is greater than average total cost.
D) a and b
E) b and c
A) price equals marginal cost.
B) marginal revenue equals marginal cost.
C) price is greater than average total cost.
D) a and b
E) b and c

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 167 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
Concentration ratios are used to determine
A) the number of firms in an industry.
B) the potential for entry into an industry.
C) the degree of product differentiation.
D) the extent (degree) of oligopoly.
E) none of the above
A) the number of firms in an industry.
B) the potential for entry into an industry.
C) the degree of product differentiation.
D) the extent (degree) of oligopoly.
E) none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 167 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
The theory of contestable markets places more emphasis than orthodox market structure theories on
A) the number of sellers in an industry.
B) the type of product produced in an industry.
C) the issue of entry into and exit from an industry.
D) who has access to relevant information.
A) the number of sellers in an industry.
B) the type of product produced in an industry.
C) the issue of entry into and exit from an industry.
D) who has access to relevant information.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 167 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
It has been argued that as a result of not producing the quantity of output where unit cost is minimized,the monopolistic competitive firm charges too __________ a price and produces too __________ output.
A) high; little
B) low; little
C) high; much
D) low; much
A) high; little
B) low; little
C) high; much
D) low; much

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 167 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
The profit-maximizing monopolistic competitor produces at the level of output where
A) price equals marginal cost and marginal revenue.
B) marginal cost equals marginal revenue, but not price.
C) price equals marginal revenue, but not marginal cost.
D) price equals marginal cost, but not marginal revenue.
A) price equals marginal cost and marginal revenue.
B) marginal cost equals marginal revenue, but not price.
C) price equals marginal revenue, but not marginal cost.
D) price equals marginal cost, but not marginal revenue.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 167 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
The monopolistic competitor is a price
A) taker, because of the many buyers and sellers in the market.
B) searcher, because of product differentiation.
C) taker, because of identical products.
D) searcher, because of the few buyers and sellers in the market.
E) searcher, because of the few buyers and sellers in the market and product differentiation.
A) taker, because of the many buyers and sellers in the market.
B) searcher, because of product differentiation.
C) taker, because of identical products.
D) searcher, because of the few buyers and sellers in the market.
E) searcher, because of the few buyers and sellers in the market and product differentiation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 167 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
The theory of monopolistic competition assumes
A) the production of a slightly differentiated product.
B) significant barriers to entry.
C) many buyers and sellers.
D) a and c
E) all of the above
A) the production of a slightly differentiated product.
B) significant barriers to entry.
C) many buyers and sellers.
D) a and c
E) all of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 167 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
It has been argued that because the monopolistic competitive firm faces a downward-sloping demand curve,in long run equilibrium it
A) underutilizes its plant size.
B) has excess capacity.
C) produces an output smaller than the one that would minimize its costs of production.
D) a and b
E) all of the above
A) underutilizes its plant size.
B) has excess capacity.
C) produces an output smaller than the one that would minimize its costs of production.
D) a and b
E) all of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 167 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



