Deck 28: Wages,Unions,and Labor
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/134
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 28: Wages,Unions,and Labor
1
The closed shop was prohibited by the
A) Norris-LaGuardia Act.
B) Clayton Act.
C) Wagner Act.
D) Taft-Hartley Act.
E) none of the above
A) Norris-LaGuardia Act.
B) Clayton Act.
C) Wagner Act.
D) Taft-Hartley Act.
E) none of the above
D
2
Unions often encourage the buying public to "look for the union label" primarily because
A) they feel that only U.S. and/or union-made goods are of high quality.
B) they feel that it is un-American to buy goods from foreign producers.
C) doing so may increase demand for the product they produce, which in turn may increase the wage rate paid to union employees.
D) they realize that Americans are too busy to take time to gather all the important information about a product and these labels are a way of informing the buying public that union-made goods are well made.
A) they feel that only U.S. and/or union-made goods are of high quality.
B) they feel that it is un-American to buy goods from foreign producers.
C) doing so may increase demand for the product they produce, which in turn may increase the wage rate paid to union employees.
D) they realize that Americans are too busy to take time to gather all the important information about a product and these labels are a way of informing the buying public that union-made goods are well made.
C
3
A union shop is an organization that
A) requires individuals to join a union within a certain period of time after becoming employed.
B) requires individuals to be members of the union before they can be hired.
C) is legal in all fifty states.
D) is set up by labor unions to train new entrants and inform members of jobs in different states.
E) a and c
A) requires individuals to join a union within a certain period of time after becoming employed.
B) requires individuals to be members of the union before they can be hired.
C) is legal in all fifty states.
D) is set up by labor unions to train new entrants and inform members of jobs in different states.
E) a and c
A
4
Unions generally call for __________ the barriers against foreign trade,as a way of __________ the elasticity of demand for union labor.
A) lowering; increasing
B) lowering; decreasing
C) raising; increasing
D) raising; decreasing
A) lowering; increasing
B) lowering; decreasing
C) raising; increasing
D) raising; decreasing

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 134 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Which of the following is a possible objective of labor unions?
A) employment for all union members
B) maximizing the total (union) wage bill
C) maximizing income for a limited number of union members
D) a and b
E) a, b, and c
A) employment for all union members
B) maximizing the total (union) wage bill
C) maximizing income for a limited number of union members
D) a and b
E) a, b, and c

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 134 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
A closed shop is an organization
A) that is closed on holidays.
B) in which an employee must belong to the union before he or she can work.
C) that does not require workers to be union members in order to be hired, but does require them to join the union within a certain period of time after becoming employed.
D) set up by the federal government to train ex-convicts to become productive workers.
E) none of the above
A) that is closed on holidays.
B) in which an employee must belong to the union before he or she can work.
C) that does not require workers to be union members in order to be hired, but does require them to join the union within a certain period of time after becoming employed.
D) set up by the federal government to train ex-convicts to become productive workers.
E) none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 134 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
In collective bargaining,
A) union members act together as a single unit.
B) each union member represents herself in labor-management negotiations.
C) the objective of the union is to increase its bargaining power with management.
D) a and c
E) b and c
A) union members act together as a single unit.
B) each union member represents herself in labor-management negotiations.
C) the objective of the union is to increase its bargaining power with management.
D) a and c
E) b and c

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 134 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Right-to-work laws
A) say that everyone has the right to work and that it is the responsibility of the government to make available employment opportunities.
B) ensure that employers cannot prevent persons from gaining employment simply because they are members of a union.
C) allow everyone to gain employment at a firm without being a union member but also require that once hired the employee must join the union.
D) make it illegal to require union membership for purposes of employment.
A) say that everyone has the right to work and that it is the responsibility of the government to make available employment opportunities.
B) ensure that employers cannot prevent persons from gaining employment simply because they are members of a union.
C) allow everyone to gain employment at a firm without being a union member but also require that once hired the employee must join the union.
D) make it illegal to require union membership for purposes of employment.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 134 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Exhibit 28-2
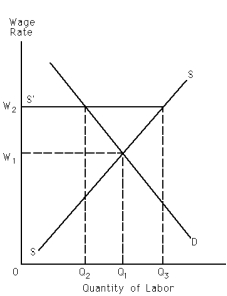
Refer to Exhibit 28-2.One of the things that the labor union probably can do to convince management that the supply curve is S'S instead of SS is
A) make a credible threat of a strike.
B) ask workers to take a cut in fringe benefits.
C) try to maximize the wage bill to the union.
D) try to maximize membership in the union.

Refer to Exhibit 28-2.One of the things that the labor union probably can do to convince management that the supply curve is S'S instead of SS is
A) make a credible threat of a strike.
B) ask workers to take a cut in fringe benefits.
C) try to maximize the wage bill to the union.
D) try to maximize membership in the union.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 134 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Exhibit 28-l
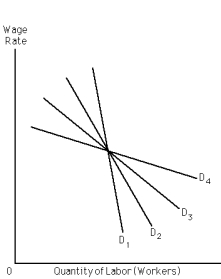
Refer to Exhibit 28-l.Four demand curves for labor are displayed: D?,D?,D?,and D?. Which provides the least pronounced wage-employment tradeoff?
A) D1
B) D2
C) D3
D) D4

Refer to Exhibit 28-l.Four demand curves for labor are displayed: D?,D?,D?,and D?. Which provides the least pronounced wage-employment tradeoff?
A) D1
B) D2
C) D3
D) D4

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 134 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Unions are interested in increasing the productivity of their members because as their productivity rises,the __________ their labor __________ and their wages __________.
A) demand for; falls; rise.
B) demand for; rises; rise.
C) supply of; rises; rise.
D) supply of; falls; rise.
A) demand for; falls; rise.
B) demand for; rises; rise.
C) supply of; rises; rise.
D) supply of; falls; rise.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 134 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Labor unions generally favor
A) import restrictions.
B) strict immigration laws.
C) increasing the minimum wage.
D) a and c
E) a, b, and c
A) import restrictions.
B) strict immigration laws.
C) increasing the minimum wage.
D) a and c
E) a, b, and c

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 134 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
If a union seeks to maximize the total wage bill received by its members,then it should negotiate the
A) highest possible wage rate.
B) wage rate at which all of its members are employed.
C) wage rate that maximizes the firm's profits.
D) wage rate at which the elasticity of demand for workers is 1.
E) wage rate at which the elasticity of demand for workers is at its highest.
A) highest possible wage rate.
B) wage rate at which all of its members are employed.
C) wage rate that maximizes the firm's profits.
D) wage rate at which the elasticity of demand for workers is 1.
E) wage rate at which the elasticity of demand for workers is at its highest.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 134 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
If union action leads to a rise in the relative price of factors that are substitutes for union labor,
A) the supply of union labor falls.
B) the quantity demanded of union labor falls.
C) the demand for union labor rises.
D) the supply of union labor rises.
A) the supply of union labor falls.
B) the quantity demanded of union labor falls.
C) the demand for union labor rises.
D) the supply of union labor rises.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 134 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Union training programs are meant to shift the __________ labor to the __________.
A) demand curve for; left
B) demand curve for; right
C) supply curve of; left
D) supply curve of; right
A) demand curve for; left
B) demand curve for; right
C) supply curve of; left
D) supply curve of; right

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 134 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Sometimes labor unions try to increase the demand for the product they produce.They do so because the demand for labor is derived; and the __________ the demand for the product labor produces,the __________labor and the __________ wages will be,ceteris paribus.
A) higher; greater the supply of; lower
B) higher; lower the demand for; higher
C) higher; higher the demand for; higher
D) lower; higher the demand for; higher
A) higher; greater the supply of; lower
B) higher; lower the demand for; higher
C) higher; higher the demand for; higher
D) lower; higher the demand for; higher

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 134 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
If a union seeks to maximize the total wage bill received by its members,then it
A) should seek to establish the highest possible wage rate.
B) should seek to establish the lowest possible wage rate.
C) will find that this cannot be done under any circumstances.
D) none of the above
A) should seek to establish the highest possible wage rate.
B) should seek to establish the lowest possible wage rate.
C) will find that this cannot be done under any circumstances.
D) none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 134 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Exhibit 28-2

Refer to Exhibit 28-2.The union wants management to believe the supply curve of labor is S'S instead of SS.What does supply curve S'S represent?
A) It represents a situation where management cannot hire workers for less than W2, and if the firm wants to hire more workers than it hires at equilibrium, it will have to pay a wage between W1 and W2.
B) It represents a situation where management cannot hire workers for more than W2, and if the firm wants to hire more workers than Q2 it will have to pay more than W1.
C) It represents a situation where management cannot hire workers for less than W2, and if the firm wants to hire more than Q3 workers it will have to pay more than W2.
D) It represents a situation where management cannot hire Q1 - Q2 workers for less than W2, but that Q3 - Q1 workers can be hired for less.

Refer to Exhibit 28-2.The union wants management to believe the supply curve of labor is S'S instead of SS.What does supply curve S'S represent?
A) It represents a situation where management cannot hire workers for less than W2, and if the firm wants to hire more workers than it hires at equilibrium, it will have to pay a wage between W1 and W2.
B) It represents a situation where management cannot hire workers for more than W2, and if the firm wants to hire more workers than Q2 it will have to pay more than W1.
C) It represents a situation where management cannot hire workers for less than W2, and if the firm wants to hire more than Q3 workers it will have to pay more than W2.
D) It represents a situation where management cannot hire Q1 - Q2 workers for less than W2, but that Q3 - Q1 workers can be hired for less.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 134 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Exhibit 28-l

Refer to Exhibit 28-l.Four demand curves for labor are displayed: D?,D?,D?,and D?.Which provides the most pronounced wage-employment tradeoff?
A) D1
B) D2
C) D3
D) D4

Refer to Exhibit 28-l.Four demand curves for labor are displayed: D?,D?,D?,and D?.Which provides the most pronounced wage-employment tradeoff?
A) D1
B) D2
C) D3
D) D4

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 134 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
A single buyer in a factor market is known as a
A) monopoly.
B) monopsony.
C) oligopsony.
D) pure buyer.
A) monopoly.
B) monopsony.
C) oligopsony.
D) pure buyer.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 134 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Exhibit 28-3
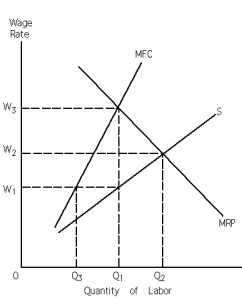
Refer to Exhibit 28-3.Consider the monopsony setting.In the absence of collective bargaining,what wage rate does the profit-maximizing monopsonist pay?
A) W1
B) W2
C) W3
D) none of the above

Refer to Exhibit 28-3.Consider the monopsony setting.In the absence of collective bargaining,what wage rate does the profit-maximizing monopsonist pay?
A) W1
B) W2
C) W3
D) none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 134 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
If a firm is a monopsonist,then it faces
A) a downward sloping demand curve for its product, and its marginal revenue curve will lie below its demand curve.
B) a horizontal marginal factor cost curve.
C) an upward sloping factor supply curve, and its marginal factor cost curve will lie above the factor supply curve.
D) an upward sloping factor supply curve, and its marginal factor cost curve will coincide with the factor supply curve.
E) an upward-sloping factor supply curve, and its marginal factor cost curve will lie below the factor supply curve.
A) a downward sloping demand curve for its product, and its marginal revenue curve will lie below its demand curve.
B) a horizontal marginal factor cost curve.
C) an upward sloping factor supply curve, and its marginal factor cost curve will lie above the factor supply curve.
D) an upward sloping factor supply curve, and its marginal factor cost curve will coincide with the factor supply curve.
E) an upward-sloping factor supply curve, and its marginal factor cost curve will lie below the factor supply curve.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 134 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
If a labor union successfully practices collective bargaining against a monopsonist,then
A) product price will decrease.
B) both wages and employment may rise.
C) both wages and employment may fall.
D) workers will probably receive a wage further away from their marginal revenue products.
E) b and d
A) product price will decrease.
B) both wages and employment may rise.
C) both wages and employment may fall.
D) workers will probably receive a wage further away from their marginal revenue products.
E) b and d

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 134 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
If a monopsonist is hiring factors,it will choose to hire that quantity at which __________ and pay a wage rate that is __________.
A) MR = MC; equal to labor's MRP
B) the supply curve of labor intersects the demand curve for labor; equal to labor's MRP
C) MRP = MFC; equal to labor's MRP
D) MRP = MFC; less than labor's MRP
E) the supply curve of labor intersects the demand curve for labor; less than MFC
A) MR = MC; equal to labor's MRP
B) the supply curve of labor intersects the demand curve for labor; equal to labor's MRP
C) MRP = MFC; equal to labor's MRP
D) MRP = MFC; less than labor's MRP
E) the supply curve of labor intersects the demand curve for labor; less than MFC

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 134 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Which of the following comes closest to being a monopsony?
A) a car manufacturer in Detroit
B) a McDonald's in a big city
C) a coal company who employees all of the workers in a given town
D) a farmer who hires labor
A) a car manufacturer in Detroit
B) a McDonald's in a big city
C) a coal company who employees all of the workers in a given town
D) a farmer who hires labor

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 134 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Labor unions have caused
A) the fraction of national income that goes to labor (union and nonunion, combined) to increase.
B) the fraction of national income that goes to labor (union and nonunion, combined) to decrease.
C) almost no change in the fraction of national income that goes to labor (union and nonunion, combined).
D) the fraction of national income that goes to profits to rise.
A) the fraction of national income that goes to labor (union and nonunion, combined) to increase.
B) the fraction of national income that goes to labor (union and nonunion, combined) to decrease.
C) almost no change in the fraction of national income that goes to labor (union and nonunion, combined).
D) the fraction of national income that goes to profits to rise.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 134 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
If a firm is a monopsony,then it
A) can pay any price it wants for the factors that it hires.
B) will have to pay the same price to each factor owner that supplies its factor.
C) will have to pay a higher price to purchase additional units of a factor.
D) need not lower the price of its product to induce buyers to purchase additional quantities.
A) can pay any price it wants for the factors that it hires.
B) will have to pay the same price to each factor owner that supplies its factor.
C) will have to pay a higher price to purchase additional units of a factor.
D) need not lower the price of its product to induce buyers to purchase additional quantities.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 134 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Suppose the marginal revenue product of individuals who work in the union sector is greater than that of individuals who work in the nonunion sector.Normally,we would expect labor to move from the nonunionized sector to the unionized sector-from where it is worth less to where it is worth more.But if this cannot happen,owing to the supply-restraining efforts of the union,then
A) wages in the nonunion sector will rise.
B) wages in the union sector will fall.
C) there will be a misallocation of labor---not all labor will be employed where it is most valuable.
D) workers in the union sector will move to the nonunion sector.
A) wages in the nonunion sector will rise.
B) wages in the union sector will fall.
C) there will be a misallocation of labor---not all labor will be employed where it is most valuable.
D) workers in the union sector will move to the nonunion sector.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 134 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
To lower the elasticity of demand for labor,a labor union might attempt to
A) decrease the availability of substitutes for the products union workers produce.
B) increase the availability of substitutes for the products union workers produce.
C) increase the availability of substitute factors for union labor.
D) a and c
E) b and c
A) decrease the availability of substitutes for the products union workers produce.
B) increase the availability of substitutes for the products union workers produce.
C) increase the availability of substitute factors for union labor.
D) a and c
E) b and c

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 134 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Exhibit 28-3

Refer to Exhibit 28-3.In the absence of collective bargaining,if the profit-maximizing monopsonist were to pay workers what their services were worth to it,it would pay
A) W1.
B) W2.
C) W3.
D) some wage rate between W2 and W3.

Refer to Exhibit 28-3.In the absence of collective bargaining,if the profit-maximizing monopsonist were to pay workers what their services were worth to it,it would pay
A) W1.
B) W2.
C) W3.
D) some wage rate between W2 and W3.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 134 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Research by H.Gregg Lewis shows that over the period 1929-1979,
A) the average wage of union members was 10 to 15 percent higher than that of comparable nonunion labor.
B) the average wage of union members was 10 to 15 percent lower than that of comparable nonunion labor.
C) labor unions increased productivity.
D) labor unions decreased productivity.
E) none of the above
A) the average wage of union members was 10 to 15 percent higher than that of comparable nonunion labor.
B) the average wage of union members was 10 to 15 percent lower than that of comparable nonunion labor.
C) labor unions increased productivity.
D) labor unions decreased productivity.
E) none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 134 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Which of the following is true?
A) The orthodox view of labor unions predicts that unionization of a firm will result in improvements in productivity and efficiency.
B) The labor-union-as-collective-voice view of labor unions predicts that unionization of a firm will result in decreases in productivity and efficiency.
C) The traditional view of labor unions supports the formation of unions as a counterweight to firms' factor-hiring power.
D) The labor-union-as-collective-voice view of labor unions supports efforts to decrease the unions' role as "monopolizer of labor."
E) none of the above
A) The orthodox view of labor unions predicts that unionization of a firm will result in improvements in productivity and efficiency.
B) The labor-union-as-collective-voice view of labor unions predicts that unionization of a firm will result in decreases in productivity and efficiency.
C) The traditional view of labor unions supports the formation of unions as a counterweight to firms' factor-hiring power.
D) The labor-union-as-collective-voice view of labor unions supports efforts to decrease the unions' role as "monopolizer of labor."
E) none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 134 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Which of the following is not consistent with the view of labor unions as a collective voice?
A) Unions reduce job exiting.
B) Labor productivity declines as a result of labor unions
C) The worker turnover rate is reduced by labor unions.
D) Workers feel more secure in their jobs as a result of labor unions.
A) Unions reduce job exiting.
B) Labor productivity declines as a result of labor unions
C) The worker turnover rate is reduced by labor unions.
D) Workers feel more secure in their jobs as a result of labor unions.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 134 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Assuming the wage-employment tradeoff exists,if labor in a particular geographic area is homogeneous and the unionized workers successfully negotiate a higher wage rate,then
A) nonunion workers will also experience an increase in their wages.
B) nonunion workers will not be affected by what happens in the unionized labor market.
C) the nonunion labor market will experience an increase in the number of workers, and this will cause wage rates to decrease in this market.
D) nonunion workers will become members of the union that has just negotiated a wage increase because they want higher wages.
A) nonunion workers will also experience an increase in their wages.
B) nonunion workers will not be affected by what happens in the unionized labor market.
C) the nonunion labor market will experience an increase in the number of workers, and this will cause wage rates to decrease in this market.
D) nonunion workers will become members of the union that has just negotiated a wage increase because they want higher wages.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 134 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
The marginal factor cost of labor for a monopsonist is
A) equal to the wage rate because if the monopsonist wants to hire another worker, it can do so at the old wage rate.
B) less than the wage rate because if the monopsonist wants to hire another worker, it has to raise the wage rate paid to all workers.
C) less than the wage rate because if the monopsonist wants to hire another worker, it has to lower the wage rate paid to all workers.
D) greater than the wage rate because if the monopsonist wants to hire another worker, it has to raise the wage rate paid to all workers.
A) equal to the wage rate because if the monopsonist wants to hire another worker, it can do so at the old wage rate.
B) less than the wage rate because if the monopsonist wants to hire another worker, it has to raise the wage rate paid to all workers.
C) less than the wage rate because if the monopsonist wants to hire another worker, it has to lower the wage rate paid to all workers.
D) greater than the wage rate because if the monopsonist wants to hire another worker, it has to raise the wage rate paid to all workers.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 134 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Which of the following is true for a monopsony?
A) It cannot buy additional units of a factor without increasing the price it pays for the factor.
B) It can buy additional units of a factor without increasing the price it pays for the factor.
C) The supply of labor it faces is the industry supply of labor.
D) a and c
E) b and c
A) It cannot buy additional units of a factor without increasing the price it pays for the factor.
B) It can buy additional units of a factor without increasing the price it pays for the factor.
C) The supply of labor it faces is the industry supply of labor.
D) a and c
E) b and c

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 134 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
A possible objective of labor unions is
A) employment for all their members.
B) minimizing the total wage bill.
C) maximizing income for all union members.
D) all of the above
E) none of the above
A) employment for all their members.
B) minimizing the total wage bill.
C) maximizing income for all union members.
D) all of the above
E) none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 134 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
In a perfectly competitive industry,do higher wages for labor union members diminish profits?
A) Yes, in the short run, but not in the long run, in which some firms exit the industry because of higher costs.
B) Yes, in the long run, but not in the short run, because profits are always fixed in the short run.
C) No, higher wage costs can affect profits only if they affect labor productivity and this doesn't happen.
D) No, because higher labor costs usually bring more firms into the industry and this effect dampens price rises.
A) Yes, in the short run, but not in the long run, in which some firms exit the industry because of higher costs.
B) Yes, in the long run, but not in the short run, because profits are always fixed in the short run.
C) No, higher wage costs can affect profits only if they affect labor productivity and this doesn't happen.
D) No, because higher labor costs usually bring more firms into the industry and this effect dampens price rises.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 134 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Exhibit 28-3

Refer to Exhibit 28-3.Consider the monopsony setting.In the absence of collective bargaining,what quantity of labor does the profit-maximizing monopsonist hire?
A) Q1
B) Q2
C) Q3
D) none of the above

Refer to Exhibit 28-3.Consider the monopsony setting.In the absence of collective bargaining,what quantity of labor does the profit-maximizing monopsonist hire?
A) Q1
B) Q2
C) Q3
D) none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 134 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
The traditional (or orthodox)view of labor unions is that they
A) positively impact productivity and efficiency.
B) negatively impact productivity and efficiency.
C) drive an artificial wedge between the wages of comparable labor in the union and nonunion sectors of the labor market.
D) a and c
E) b and c
A) positively impact productivity and efficiency.
B) negatively impact productivity and efficiency.
C) drive an artificial wedge between the wages of comparable labor in the union and nonunion sectors of the labor market.
D) a and c
E) b and c

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 134 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
Exhibit 28-5

Refer to Exhibit 28-5.In which of the following cases has the increase in the wage from W? to W? been brought about by a country-wide legalization of union shops?
A) (1)
B) (2)
C) (3)
D) none of the above

Refer to Exhibit 28-5.In which of the following cases has the increase in the wage from W? to W? been brought about by a country-wide legalization of union shops?
A) (1)
B) (2)
C) (3)
D) none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 134 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Exhibit 28-4
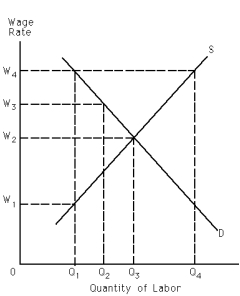
Refer to Exhibit 28-4.If a labor union successfully organizes the labor market and sets the wage rate at W?,the amount of unemployment in this market will be equal to
A) Q4 - Q3.
B) zero.
C) Q3 - Q1.
D) Q2 - Q3.
E) Q4 - Q1.

Refer to Exhibit 28-4.If a labor union successfully organizes the labor market and sets the wage rate at W?,the amount of unemployment in this market will be equal to
A) Q4 - Q3.
B) zero.
C) Q3 - Q1.
D) Q2 - Q3.
E) Q4 - Q1.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 134 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
To increase the demand for union labor,a labor union might attempt to
A) increase the demand for the products produced by union labor.
B) decrease substitute factor prices.
C) decrease the marginal physical product productivity of union labor.
D) a and b
E) all of the above
A) increase the demand for the products produced by union labor.
B) decrease substitute factor prices.
C) decrease the marginal physical product productivity of union labor.
D) a and b
E) all of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 134 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
If,through collective bargaining,a union is able to raise the wage above the existing competitive equilibrium wage,
A) fewer workers will be employed than before the wage increase.
B) more workers will be employed than before the wage increase.
C) the same number of workers will be employed as before the wage increase.
D) the number of workers that will be employed is not related to the wage increase.
A) fewer workers will be employed than before the wage increase.
B) more workers will be employed than before the wage increase.
C) the same number of workers will be employed as before the wage increase.
D) the number of workers that will be employed is not related to the wage increase.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 134 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
"Collective bargaining" refers to
A) negotiations between labor unions and management about wage rates and other issues.
B) negotiations among labor unions over jurisdictional control.
C) negotiations between labor, management, and government over the drafting of labor laws.
D) b and c
E) none of the above
A) negotiations between labor unions and management about wage rates and other issues.
B) negotiations among labor unions over jurisdictional control.
C) negotiations between labor, management, and government over the drafting of labor laws.
D) b and c
E) none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 134 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
A monopsony,as compared to a perfectly competitive firm,pays __________ wage and hires __________ labor.
A) a higher; less
B) a higher; more
C) a lower; less
D) a lower; more
E) the same; the same amount of
A) a higher; less
B) a higher; more
C) a lower; less
D) a lower; more
E) the same; the same amount of

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 134 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
Exhibit 28-7

Refer to Exhibit 28-7.As the firm increases employment from 30 to 40 workers,its total labor cost
A) decreases by $190.
B) increases by $160.
C) increases by $60.
D) increases by $100.

Refer to Exhibit 28-7.As the firm increases employment from 30 to 40 workers,its total labor cost
A) decreases by $190.
B) increases by $160.
C) increases by $60.
D) increases by $100.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 134 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
Exhibit 28-6
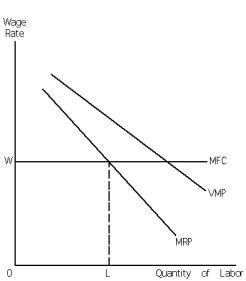
Refer to Exhibit 28-6.L and W are the equilibrium quantity of labor employed and the wage rate respectively.A person arguing that a worker is being exploited if she is paid less than the value of her marginal product would say that the exhibit is an illustration of the fact that
A) perfect competition entails labor exploitation.
B) monopoly entails labor exploitation.
C) monopoly entails no labor exploitation.
D) monopsony entails labor exploitation.
E) monopsony entails no labor exploitation.

Refer to Exhibit 28-6.L and W are the equilibrium quantity of labor employed and the wage rate respectively.A person arguing that a worker is being exploited if she is paid less than the value of her marginal product would say that the exhibit is an illustration of the fact that
A) perfect competition entails labor exploitation.
B) monopoly entails labor exploitation.
C) monopoly entails no labor exploitation.
D) monopsony entails labor exploitation.
E) monopsony entails no labor exploitation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 134 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
In a monopsony model of the labor market,as more labor is hired,the marginal factor cost of labor
A) decreases.
B) becomes zero.
C) remains constant.
D) increases.
E) becomes identical to the wage rate.
A) decreases.
B) becomes zero.
C) remains constant.
D) increases.
E) becomes identical to the wage rate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 134 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
In a monopsony model of the labor market,the firm finds that (over a range)as more workers are hired,the wage rate
A) increases.
B) decreases.
C) remains constant.
D) remains identical to the marginal factor cost per worker.
E) b and d
A) increases.
B) decreases.
C) remains constant.
D) remains identical to the marginal factor cost per worker.
E) b and d

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 134 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
Exhibit 28-4

Refer to Exhibit 28-4.If a labor union successfully organizes the labor market and sets the wage rate at W?,the quantity of labor hired will be
A) Q1.
B) Q2.
C) Q3.
D) Q4.
E) cannot be determined

Refer to Exhibit 28-4.If a labor union successfully organizes the labor market and sets the wage rate at W?,the quantity of labor hired will be
A) Q1.
B) Q2.
C) Q3.
D) Q4.
E) cannot be determined

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 134 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
A monopsonist's wage rate is
A) the same as marginal factor cost.
B) greater than marginal factor cost.
C) less than marginal factor cost.
D) the same as marginal revenue product.
E) a and d
A) the same as marginal factor cost.
B) greater than marginal factor cost.
C) less than marginal factor cost.
D) the same as marginal revenue product.
E) a and d

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 134 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
Exhibit 28-5

Refer to Exhibit 28-5.In case (3),with a rise in the wage rate from W? to W?,the wage bill will rise if
A) Q1 x W3 > Q2 x W1.
B) (Q3 - Q2) x W3 > Q1 x W1.
C) (W2-W1) x Q2 > (Q1 - Q2) x W1.
D) (W2 - W3) x Q2 > (W2 - W3) x (Q3 - Q2).

Refer to Exhibit 28-5.In case (3),with a rise in the wage rate from W? to W?,the wage bill will rise if
A) Q1 x W3 > Q2 x W1.
B) (Q3 - Q2) x W3 > Q1 x W1.
C) (W2-W1) x Q2 > (Q1 - Q2) x W1.
D) (W2 - W3) x Q2 > (W2 - W3) x (Q3 - Q2).

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 134 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
A firm that is the sole buyer in a factor market is known as a
A) monopolist.
B) public employee union.
C) monopsonist.
D) perfect competitor.
A) monopolist.
B) public employee union.
C) monopsonist.
D) perfect competitor.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 134 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
To increase the wages of its members,a labor union might attempt to
A) lower the elasticity of demand for its labor.
B) increase the demand for union labor.
C) increase the supply of union labor.
D) a and b
E) all of the above
A) lower the elasticity of demand for its labor.
B) increase the demand for union labor.
C) increase the supply of union labor.
D) a and b
E) all of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 134 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
Exhibit 28-5

Refer to Exhibit 28-5.In case (1),with a rise in the wage rate from W? to W?,the wage bill will fall if
A) (Q1 - Q2) x W1 > (W2 - W1) x Q2.
B) (Q3 - Q2) x W3 > (W2 - W3) x Q2.
C) W2 x Q2 > Q3 x W1.
D) (W1 - W3) x Q2 > (W2 - W1) x Q2.

Refer to Exhibit 28-5.In case (1),with a rise in the wage rate from W? to W?,the wage bill will fall if
A) (Q1 - Q2) x W1 > (W2 - W1) x Q2.
B) (Q3 - Q2) x W3 > (W2 - W3) x Q2.
C) W2 x Q2 > Q3 x W1.
D) (W1 - W3) x Q2 > (W2 - W1) x Q2.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 134 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
Exhibit 28-5

For a union to be successful in increasing the total wage bill received by its members by forcing up the wage rate,the demand curve for labor needs to be
A) elastic.
B) perfectly elastic.
C) unitary elastic.
D) inelastic.

For a union to be successful in increasing the total wage bill received by its members by forcing up the wage rate,the demand curve for labor needs to be
A) elastic.
B) perfectly elastic.
C) unitary elastic.
D) inelastic.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 134 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
Exhibit 28-5

Refer to Exhibit 28-5.In which case or cases does the increase in the wage rate from W? to W? definitely cause the total wage bill to rise?
A) (1)
B) (2)
C) (3)
D) (1) and (2)
E) (1) and (3)

Refer to Exhibit 28-5.In which case or cases does the increase in the wage rate from W? to W? definitely cause the total wage bill to rise?
A) (1)
B) (2)
C) (3)
D) (1) and (2)
E) (1) and (3)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 134 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
Exhibit 28-5

Refer to Exhibit 28-5.In which of the following cases has the increase in the wage from W? to W? been brought about by a prolonged successful training program undertaken by the union for the benefit of its members?
A) (1)
B) (2)
C) (3)
D) none of the above

Refer to Exhibit 28-5.In which of the following cases has the increase in the wage from W? to W? been brought about by a prolonged successful training program undertaken by the union for the benefit of its members?
A) (1)
B) (2)
C) (3)
D) none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 134 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
Exhibit 28-6

Unions typically argue that state right-to-work laws
A) are unfair.
B) constrain unions' abilities to control the supply of labor in a market.
C) are inconsistent with the Taft-Hartley Act.
D) legalize union shops.

Unions typically argue that state right-to-work laws
A) are unfair.
B) constrain unions' abilities to control the supply of labor in a market.
C) are inconsistent with the Taft-Hartley Act.
D) legalize union shops.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 134 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
Exhibit 28-7

Refer to Exhibit 28-7.As the firm increases employment from 50 to 60 workers,by how much does total labor cost increase?
A) $160
B) $40
C) $60
D) $200

Refer to Exhibit 28-7.As the firm increases employment from 50 to 60 workers,by how much does total labor cost increase?
A) $160
B) $40
C) $60
D) $200

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 134 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
Exhibit 28-8
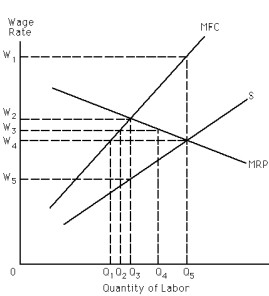
Refer to Exhibit 28-8.An effective price floor set at W? would
A) increase employment from Q1 to Q2.
B) increase employment from Q3 to Q4.
C) decrease employment from Q5 to Q2.
D) decrease employment from Q5 to Q4.

Refer to Exhibit 28-8.An effective price floor set at W? would
A) increase employment from Q1 to Q2.
B) increase employment from Q3 to Q4.
C) decrease employment from Q5 to Q2.
D) decrease employment from Q5 to Q4.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 134 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
Which of the following is true?
A) The lower the elasticity of demand for cars, the higher the elasticity of demand for the workers that produce cars.
B) The higher the elasticity of demand for cars, the lower the elasticity of demand for the workers that produce cars.
C) The lower the elasticity of demand for cars, the lower the elasticity of demand for the workers that produce cars.
D) The fewer the substitute factors for union labor, the higher the elasticity of demand for union labor.
E) c and d
A) The lower the elasticity of demand for cars, the higher the elasticity of demand for the workers that produce cars.
B) The higher the elasticity of demand for cars, the lower the elasticity of demand for the workers that produce cars.
C) The lower the elasticity of demand for cars, the lower the elasticity of demand for the workers that produce cars.
D) The fewer the substitute factors for union labor, the higher the elasticity of demand for union labor.
E) c and d

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 134 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
Exhibit 28-8

Refer to Exhibit 28-8.What is the total wage bill of the profit- maximizing monoposonist?
A) W5 x Q3
B) W4 x Q5
C) W3 x Q2
D) W2 x Q3

Refer to Exhibit 28-8.What is the total wage bill of the profit- maximizing monoposonist?
A) W5 x Q3
B) W4 x Q5
C) W3 x Q2
D) W2 x Q3

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 134 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
Which of the following will make the cutback in union labor for a given wage increase smaller?
A) an increase in the number of substitutes for union labor
B) an increase in the elasticity of demand for the product that labor produces
C) a decrease in the elasticity of demand for the product that labor produces
D) an increase in the total revenue for the product that labor produces
E) a decrease in the total revenue for the product that labor produces
A) an increase in the number of substitutes for union labor
B) an increase in the elasticity of demand for the product that labor produces
C) a decrease in the elasticity of demand for the product that labor produces
D) an increase in the total revenue for the product that labor produces
E) a decrease in the total revenue for the product that labor produces

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 134 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
Exhibit 28-7

Refer to Exhibit 28-7.The marginal factor cost of increasing employment from 20 to 30 workers
A) is $14.
B) is $8.
C) is $7.
D) is $120.
E) is $100.

Refer to Exhibit 28-7.The marginal factor cost of increasing employment from 20 to 30 workers
A) is $14.
B) is $8.
C) is $7.
D) is $120.
E) is $100.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 134 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
Exhibit 28-8

Refer to Exhibit 28-8.Suppose that initially there is no collective bargaining and the monoposonist maximizes profit.Then the workers form a union and negotiate a wage of W?.What will happen to the total wage bill?
A) It will definitely rise.
B) It will definitely fall.
C) It will definitely stay the same.
D) It may rise, fall, or remain the same.

Refer to Exhibit 28-8.Suppose that initially there is no collective bargaining and the monoposonist maximizes profit.Then the workers form a union and negotiate a wage of W?.What will happen to the total wage bill?
A) It will definitely rise.
B) It will definitely fall.
C) It will definitely stay the same.
D) It may rise, fall, or remain the same.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 134 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
Exhibit 28-8

Refer to Exhibit 28-8.If the monopsonist could perfectly discriminate by paying each worker a different wage rate,the number of workers employed would be
A) Q1.
B) Q2.
C) Q3.
D) Q4.
E) Q5.

Refer to Exhibit 28-8.If the monopsonist could perfectly discriminate by paying each worker a different wage rate,the number of workers employed would be
A) Q1.
B) Q2.
C) Q3.
D) Q4.
E) Q5.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 134 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
Exhibit 28-7

Refer to Exhibit 28-7.For technological reasons,this monopsonist can hire labor only in increments of 10 workers.The profit-maximizing number of workers is
A) 10.
B) 20.
C) 30.
D) 40.
E) 50.

Refer to Exhibit 28-7.For technological reasons,this monopsonist can hire labor only in increments of 10 workers.The profit-maximizing number of workers is
A) 10.
B) 20.
C) 30.
D) 40.
E) 50.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 134 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
Most likely,if a labor union wanted to employ all its membership it would negotiate for a __________ than if it wanted to maximize the income of a limited number of union members.
A) wage that discounted for fixed costs
B) higher wage
C) wage that accounted for a percentage of sales revenues
D) lower wage
E) none of the above
A) wage that discounted for fixed costs
B) higher wage
C) wage that accounted for a percentage of sales revenues
D) lower wage
E) none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 134 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
The lower the elasticity of demand for labor,
A) the larger the cutback in labor for a given wage increase.
B) the smaller the cutback in labor for a given wage increase.
C) the higher the wage rate that a labor union receives for its membership.
D) the lower the wage rate that a labor union receives for its membership.
E) the more members of a given union.
A) the larger the cutback in labor for a given wage increase.
B) the smaller the cutback in labor for a given wage increase.
C) the higher the wage rate that a labor union receives for its membership.
D) the lower the wage rate that a labor union receives for its membership.
E) the more members of a given union.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 134 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
Exhibit 28-8

Refer to Exhibit 28-8.If the profit-maximizing monopsonist were to pay its workers what the marginal worker's services are worth to it,the wage rate would be
A) W1.
B) W2.
C) W3.
D) W4.
E) W5.

Refer to Exhibit 28-8.If the profit-maximizing monopsonist were to pay its workers what the marginal worker's services are worth to it,the wage rate would be
A) W1.
B) W2.
C) W3.
D) W4.
E) W5.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 134 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
Exhibit 28-8

Refer to Exhibit 28-8.In the absence of collective bargaining,what quantity of labor would the profit-maximizing monoposonist hire?
A) Q1
B) Q2
C) Q3
D) Q4
E) Q5

Refer to Exhibit 28-8.In the absence of collective bargaining,what quantity of labor would the profit-maximizing monoposonist hire?
A) Q1
B) Q2
C) Q3
D) Q4
E) Q5

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 134 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
Exhibit 28-7

Refer to Exhibit 28-7.For each quantity of labor hired (after the first worker),marginal factor cost (MFC)will
A) be less than column (2).
B) exceed column (2).
C) be less than column (3).
D) exceed column (3).
E) b and d

Refer to Exhibit 28-7.For each quantity of labor hired (after the first worker),marginal factor cost (MFC)will
A) be less than column (2).
B) exceed column (2).
C) be less than column (3).
D) exceed column (3).
E) b and d

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 134 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
If a labor union tries to reduce the availability of substitutes for the product it sells,it is attempting to affect the __________ for labor.But if it tries to increase substitute factor prices,it is attempting to affect the __________ labor.
A) elasticity of demand; supply of
B) demand; elasticity of demand for
C) elasticity of demand; demand for
D) demand; supply of
E) none of the above
A) elasticity of demand; supply of
B) demand; elasticity of demand for
C) elasticity of demand; demand for
D) demand; supply of
E) none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 134 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
Exhibit 28-9
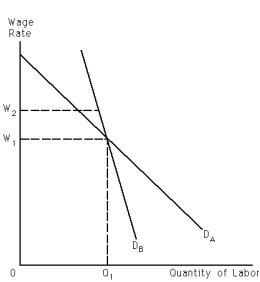
Refer to Exhibit 28-9.Let DA and DB represent demand for labor curves facing unions A and B,respectively.As a result of their efforts,both unions succeed in increasing the wage rate from W? to W?.In terms of the wage-employment trade-off,the wage increase
A) had a larger impact on employment for union A than for union B.
B) had a larger impact on employment for union B than for union A.
C) had the same impact on employment in both unions.
D) cannot be determined without further information.

Refer to Exhibit 28-9.Let DA and DB represent demand for labor curves facing unions A and B,respectively.As a result of their efforts,both unions succeed in increasing the wage rate from W? to W?.In terms of the wage-employment trade-off,the wage increase
A) had a larger impact on employment for union A than for union B.
B) had a larger impact on employment for union B than for union A.
C) had the same impact on employment in both unions.
D) cannot be determined without further information.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 134 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
Exhibit 28-7

Refer to Exhibit 28-7.The marginal factor cost of increasing employment from 40 to 50 workers is
A) $120.
B) $18.
C) $14.
D) $160.
E) $15

Refer to Exhibit 28-7.The marginal factor cost of increasing employment from 40 to 50 workers is
A) $120.
B) $18.
C) $14.
D) $160.
E) $15

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 134 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
Labor unions try to meet their objectives by influencing the elasticity of demand for labor and the demand for labor.To influence these factors,they try to do all the following except
A) reduce the availability of substitutes for the product they produce.
B) reduce the availability of substitute factors.
C) increase demand for the product they produce.
D) increase substitute factor prices.
E) reduce the nonmoney benefits of substitute factors.
A) reduce the availability of substitutes for the product they produce.
B) reduce the availability of substitute factors.
C) increase demand for the product they produce.
D) increase substitute factor prices.
E) reduce the nonmoney benefits of substitute factors.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 134 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
Which of the following statements is true?
A) The fewer the substitute factors for union labor, the higher the elasticity of demand for union labor, and the smaller the cutback in union labor for any given wage increase.
B) The fewer the substitute factors for union labor, the lower the elasticity of demand for union labor, and the larger the cutback in union labor for any given wage increase.
C) The more the substitute factors for union labor, the higher the elasticity of demand for union labor, and the smaller the cutback in union labor for any given wage increase.
D) The more the substitute factors for union labor, the higher the elasticity of demand for union labor, and the larger the cutback in union labor for any given wage increase.
E) none of the above
A) The fewer the substitute factors for union labor, the higher the elasticity of demand for union labor, and the smaller the cutback in union labor for any given wage increase.
B) The fewer the substitute factors for union labor, the lower the elasticity of demand for union labor, and the larger the cutback in union labor for any given wage increase.
C) The more the substitute factors for union labor, the higher the elasticity of demand for union labor, and the smaller the cutback in union labor for any given wage increase.
D) The more the substitute factors for union labor, the higher the elasticity of demand for union labor, and the larger the cutback in union labor for any given wage increase.
E) none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 134 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
Exhibit 28-8

Refer to Exhibit 28-8.In the absence of collective bargaining,what wage rate would the profit-maximizing monoposonist pay?
A) W1
B) W2
C) W3
D) W4
E) W5

Refer to Exhibit 28-8.In the absence of collective bargaining,what wage rate would the profit-maximizing monoposonist pay?
A) W1
B) W2
C) W3
D) W4
E) W5

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 134 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



