Deck 4: Chemical Bonds
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/189
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 4: Chemical Bonds
1
Which of the following pairs is isoelectronic?
A) Ar and Ne
B) Ar and Na+
C) Ar and F-
D) Ar and S2-
A) Ar and Ne
B) Ar and Na+
C) Ar and F-
D) Ar and S2-
Ar and S2-
2
The number of protons in a sodium ion, Na+, is
A) 10.
B) 11.
C) 12.
D) 23.
A) 10.
B) 11.
C) 12.
D) 23.
11.
3
All of the following pairs are isoelectronic EXCEPT
A) Ne and Rn.
B) Rb+ and Sr2+.
C) Ne and Mg2+.
D) F- and Ne.
A) Ne and Rn.
B) Rb+ and Sr2+.
C) Ne and Mg2+.
D) F- and Ne.
Ne and Rn.
4
A sodium ion, Na+, has the same electron configuration as a(n)
A) sodium atom.
B) chlorine atom.
C) neon atom.
D) argon atom.
A) sodium atom.
B) chlorine atom.
C) neon atom.
D) argon atom.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Which molecule is NOT likely to exist?
A) N2
B) Br2
C) CI4
D) Ar2
A) N2
B) Br2
C) CI4
D) Ar2

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
The number of protons in a chloride ion, Cl-, is
A) 16.
B) 17.
C) 18.
D) 35.
A) 16.
B) 17.
C) 18.
D) 35.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Mg2+ has the same electronic structure as
A) Ne.
B) Mg.
C) C.
D) Ar.
A) Ne.
B) Mg.
C) C.
D) Ar.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
When barium reacts with iodine, barium ions, Ba2+, and iodide ions, I-, are formed. In this reaction, iodine atoms
A) lose electrons.
B) gain electrons.
C) lose protons.
D) gain protons.
A) lose electrons.
B) gain electrons.
C) lose protons.
D) gain protons.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
A chloride ion, Cl- has the same electron configuration as a(n)
A) sodium atom.
B) chlorine atom.
C) neon atom.
D) argon atom.
A) sodium atom.
B) chlorine atom.
C) neon atom.
D) argon atom.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
The inertness of the noble gases is due to
A) the outermost shell has six electrons.
B) the number of protons and neutrons.
C) the bonds they form with other elements.
D) the outermost shell has an octet of electrons, except for helium which has two electrons.
A) the outermost shell has six electrons.
B) the number of protons and neutrons.
C) the bonds they form with other elements.
D) the outermost shell has an octet of electrons, except for helium which has two electrons.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Which of the following molecules is NOT likely to exist?
A) CO2
B) HCl
C) CCl4
D) RnH
A) CO2
B) HCl
C) CCl4
D) RnH

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
All of the following species are isoelectronic to Mg2+ EXCEPT
A) Li+.
B) Na+.
C) Ne.
D) O2-.
A) Li+.
B) Na+.
C) Ne.
D) O2-.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
The number of electrons in a sodium ion, Na+, is
A) 10.
B) 11.
C) 12.
D) 23.
A) 10.
B) 11.
C) 12.
D) 23.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
When calcium reacts with iodine, calcium ions, Ca2+, and iodide ions, I-, are formed. In this reaction, calcium atoms
A) lose electrons.
B) gain electrons.
C) lose protons.
D) gain protons.
A) lose electrons.
B) gain electrons.
C) lose protons.
D) gain protons.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
The nature of bonding forces in matter influences which of the following observable properties of the matter?
A) the optical property
B) the state of the matter at room temperature
C) the strength and rigidity
D) all of the above
A) the optical property
B) the state of the matter at room temperature
C) the strength and rigidity
D) all of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
The number of electrons in a chloride ion, Cl-, is
A) 16.
B) 17.
C) 18.
D) 35.
A) 16.
B) 17.
C) 18.
D) 35.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
The number of electrons in a sulfide ion, S2-, is
A) 16.
B) 14.
C) 18.
D) 32.
A) 16.
B) 14.
C) 18.
D) 32.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
The noble gases are inert. This means they
A) undergo very few chemical reactions.
B) exist as gases at room temperature.
C) undergo many chemical reactions.
D) lose and gain electrons easily.
A) undergo very few chemical reactions.
B) exist as gases at room temperature.
C) undergo many chemical reactions.
D) lose and gain electrons easily.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Noble gases are unreactive because of their electronic structures. The kind of reasoning that states "if other elements could be made to achieve noble gas electronic structures they would be more stable" is called
A) logic.
B) inductive reasoning.
C) deductive reasoning.
D) critical thinking.
A) logic.
B) inductive reasoning.
C) deductive reasoning.
D) critical thinking.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
When atoms lose or gain electrons in chemical reactions they form
A) new atoms.
B) noble gases.
C) nucleons.
D) ions.
A) new atoms.
B) noble gases.
C) nucleons.
D) ions.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
An anion is
A) an element that has lost protons.
B) an element that has gained protons.
C) an element that has lost electrons.
D) an element that have gained electrons.
A) an element that has lost protons.
B) an element that has gained protons.
C) an element that has lost electrons.
D) an element that have gained electrons.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
An element with 7 electrons in its outer shell is in which group on the periodic table?
A) Group 5A
B) Group 7A
C) Group 6A
D) Group 2A
A) Group 5A
B) Group 7A
C) Group 6A
D) Group 2A

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
An electron-dot structure is a convenient method of representing
A) valence electrons of an atom.
B) core electrons of an atom.
C) all electrons of the atom.
D) the complete electron configuration of the atom.
A) valence electrons of an atom.
B) core electrons of an atom.
C) all electrons of the atom.
D) the complete electron configuration of the atom.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
When a freshly cut piece of sodium metal, Na, is dropped into a flask with chlorine gas, a violent reaction takes place creating a new compound. This compound
A) has properties that are more like Na than Cl.
B) has properties that are totally unlike either Na or Cl.
C) has properties that more like Cl than Na.
D) has properties that are like both Cl and Na.
A) has properties that are more like Na than Cl.
B) has properties that are totally unlike either Na or Cl.
C) has properties that more like Cl than Na.
D) has properties that are like both Cl and Na.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Which is the electron dot structure of magnesium?
A) Mg
B)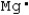
C)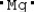
D)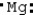
A) Mg
B)
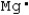
C)
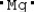
D)
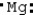

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Which is the electron dot structure of nitrogen?
A)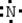
B)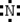
C)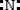
D)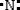
A)
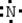
B)
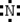
C)
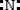
D)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
In a Lewis formula, the dots represent
A) all the electrons in the atoms.
B) the valence electrons in all the atoms.
C) only the electrons that are being transferred or shared.
D) whatever number of electrons are needed to satisfy the octet rule.
A) all the electrons in the atoms.
B) the valence electrons in all the atoms.
C) only the electrons that are being transferred or shared.
D) whatever number of electrons are needed to satisfy the octet rule.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Which is the electron dot structure of oxygen?
A)
B)
C)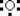
D)
A)

B)

C)
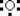
D)


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
The attraction between positive and negative ions is known as a(n)
A) covalent bond.
B) crystal bond.
C) ionic bond.
D) molecular bond.
A) covalent bond.
B) crystal bond.
C) ionic bond.
D) molecular bond.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Why do chemists use the Lewis symbols to represent chlorine and sodium rather than drawing the electron diagrams of each element before and after the reaction?
A) Lewis symbols are easier to use.
B) Lewis symbols are more scientific.
C) Lewis symbols are more accurate.
D) Lewis symbols are more abstract.
A) Lewis symbols are easier to use.
B) Lewis symbols are more scientific.
C) Lewis symbols are more accurate.
D) Lewis symbols are more abstract.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
When ions arrange themselves in an orderly structure, that structure is known as a
A) crystal.
B) dipole.
C) molecule.
D) tetrahedron.
A) crystal.
B) dipole.
C) molecule.
D) tetrahedron.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Where does an element X with the electron dot structure 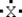 fit in the periodic table?
fit in the periodic table?
A) Group 1A
B) Group 2A
C) Group 3A
D) Group 5A
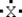 fit in the periodic table?
fit in the periodic table?A) Group 1A
B) Group 2A
C) Group 3A
D) Group 5A

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
From the periodic table, the number of valence electrons for most of the main group elements may be determined directly from the
A) atomic number.
B) group number.
C) period number.
D) nucleon number.
A) atomic number.
B) group number.
C) period number.
D) nucleon number.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
How many dots will appear in the Lewis dot structure for an element from in Group 1A of the periodic table?
A) five
B) eight
C) one
D) four
A) five
B) eight
C) one
D) four

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Which is the electron dot structure of calcium?
A) Ca
B)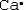
C)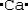
D)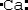
A) Ca
B)
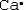
C)
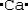
D)
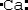

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
With respect to chemical bonding, which particles play the least active role?
A) nucleons
B) core electrons
C) valence electrons
D) All play equal roles.
A) nucleons
B) core electrons
C) valence electrons
D) All play equal roles.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Which of the noble gases does NOT have an octet of electrons in its outer shell?
A) He
B) Ne
C) Ar
D) Kr
A) He
B) Ne
C) Ar
D) Kr

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
With respect to chemical bonding, which particles play the most active role?
A) protons
B) neutrons
C) valence electrons
D) core electrons
A) protons
B) neutrons
C) valence electrons
D) core electrons

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
When magnesium combines with bromine, the bond formed is best classified as
A) ionic.
B) polar covalent
C) metallic.
D) nonpolar covalent.
A) ionic.
B) polar covalent
C) metallic.
D) nonpolar covalent.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Which is the electron dot structure of sulfur?
A)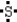
B)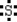
C)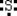
D) 2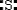
A)
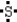
B)
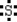
C)
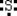
D) 2

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
When calcium reacts with chlorine, the reaction involves a
A) transfer of electrons from Ca to Cl.
B) transfer of electrons from Cl to Ca.
C) sharing of electrons between Ca and Cl.
D) creation of electrons.
A) transfer of electrons from Ca to Cl.
B) transfer of electrons from Cl to Ca.
C) sharing of electrons between Ca and Cl.
D) creation of electrons.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Which pair of atoms would form an ionic bond?
A) Na and Mg
B) Ca and S
C) Cl and Br
D) N and N
A) Na and Mg
B) Ca and S
C) Cl and Br
D) N and N

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
A nitride ion is
A) N+.
B) N3+.
C) N2-.
D) N3-.
A) N+.
B) N3+.
C) N2-.
D) N3-.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
In reactions to form ionic compounds, metals generally
A) lose electrons.
B) gain electrons.
C) become non-metals.
D) do not react.
A) lose electrons.
B) gain electrons.
C) become non-metals.
D) do not react.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
An oxide ion is
A) O+.
B) O2+.
C) O-.
D) O2-.
A) O+.
B) O2+.
C) O-.
D) O2-.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
Calcium reacts with chloride to form
A) CaCl.
B) CaCl2.
C) Ca2Cl.
D) Ca2Cl3.
A) CaCl.
B) CaCl2.
C) Ca2Cl.
D) Ca2Cl3.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
A sodium ion is
A) Na+.
B) Na2+.
C) Na-.
D) Na2-.
A) Na+.
B) Na2+.
C) Na-.
D) Na2-.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
A iodide ion is
A) I+.
B) I2+.
C) I-.
D) I2-.
A) I+.
B) I2+.
C) I-.
D) I2-.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
Which substance has ionic bonds?
A) O2
B) BaO
C) H2O
D) OF2
A) O2
B) BaO
C) H2O
D) OF2

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
Chlorine forms monatomic ions with a charge of
A) 1-.
B) 1+.
C) 2-.
D) 2+.
A) 1-.
B) 1+.
C) 2-.
D) 2+.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
In reactions to form ionic compounds, nonmetals generally
A) lose electrons.
B) gain electrons.
C) become metals.
D) do not react.
A) lose electrons.
B) gain electrons.
C) become metals.
D) do not react.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
Potassium reacts with iodine to form
A) KI.
B) K2I.
C) KI2.
D) K2I3.
A) KI.
B) K2I.
C) KI2.
D) K2I3.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
Which atom is least likely to form an ion?
A) bromine, Br
B) phosphorus, P
C) aluminum, Al
D) carbon, C
A) bromine, Br
B) phosphorus, P
C) aluminum, Al
D) carbon, C

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
Oxygen forms monatomic ions with a charge of
A) 2+.
B) 3+.
C) 1-.
D) 2-.
A) 2+.
B) 3+.
C) 1-.
D) 2-.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
Which atom is least likely to form an ion?
A) chlorine
B) sodium
C) carbon
D) oxygen
A) chlorine
B) sodium
C) carbon
D) oxygen

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
When magnesium reacts with chlorine, the reaction involves a
A) transfer of electrons from Mg to Cl.
B) transfer of electrons from Cl to Mg.
C) sharing of electrons between Mg and Cl.
D) creation of electrons.
A) transfer of electrons from Mg to Cl.
B) transfer of electrons from Cl to Mg.
C) sharing of electrons between Mg and Cl.
D) creation of electrons.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
Which substance has ionic bonds?
A) K2S
B) SO3
C) CI4
D) N2
A) K2S
B) SO3
C) CI4
D) N2

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
Magnesium reacts with oxygen to form
A) MgO.
B) Mg2O.
C) MgO2.
D) Mg3O2.
A) MgO.
B) Mg2O.
C) MgO2.
D) Mg3O2.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
Which substance has ionic bonds?
A) Br2
B) NH3
C) H2O
D) LiI
A) Br2
B) NH3
C) H2O
D) LiI

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
When magnesium combines with oxygen, the reaction involves a
A) transfer of electrons from Mg to O.
B) transfer of electrons from O to Mg.
C) sharing of electrons between Mg and O.
D) conversion of protons into electrons.
A) transfer of electrons from Mg to O.
B) transfer of electrons from O to Mg.
C) sharing of electrons between Mg and O.
D) conversion of protons into electrons.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
The cation formed when a sodium atom loses an electron is called the
A) sodide ion.
B) sodate ion.
C) sodium ion.
D) soda ion.
A) sodide ion.
B) sodate ion.
C) sodium ion.
D) soda ion.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
The formula of aluminum oxide is
A) AlO.
B) AlO2.
C) AlO3.
D) Al2O3.
A) AlO.
B) AlO2.
C) AlO3.
D) Al2O3.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
The anion formed when nitrogen gains three electrons is called the
A) nitride ion.
B) nitrite ion.
C) nitrogide ion.
D) nitro ion.
A) nitride ion.
B) nitrite ion.
C) nitrogide ion.
D) nitro ion.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
Which is the electron dot structure for nitrogen, N2?
A)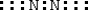
B)
C)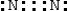
D)
A)
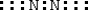
B)

C)
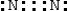
D)


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
The anion formed when oxygen gains two electrons is called the
A) oxygen ion.
B) oxyide ion.
C) oxide ion.
D) oxy ion.
A) oxygen ion.
B) oxyide ion.
C) oxide ion.
D) oxy ion.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
Covalent bonds generally form between
A) ions.
B) metals.
C) metals and nonmetals.
D) nonmetals.
A) ions.
B) metals.
C) metals and nonmetals.
D) nonmetals.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
Which of the following is a binary compound?
A) HCN
B) O2
C) LiBr
D) Na2SO4
A) HCN
B) O2
C) LiBr
D) Na2SO4

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
The name of the compound with the formula AlCl3 is
A) aluminum(III) chloride.
B) aluminum trichloride.
C) monoaluminum trichlorine.
D) aluminum chloride.
A) aluminum(III) chloride.
B) aluminum trichloride.
C) monoaluminum trichlorine.
D) aluminum chloride.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
The prefix which means seven is
A) hexa.
B) hepta.
C) octa.
D) tetra.
A) hexa.
B) hepta.
C) octa.
D) tetra.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
The formula of magnesium nitride is
A) Mg3N2.
B) Mg2N3.
C) Mg2N.
D) MgN.
A) Mg3N2.
B) Mg2N3.
C) Mg2N.
D) MgN.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
An ionic bond is formed when electrons are
A) transferred.
B) shared.
C) split.
D) destroyed.
A) transferred.
B) shared.
C) split.
D) destroyed.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
In a molecule of nitrogen, N2, the nitrogen atoms are bonded to each other by
A) an ionic bond.
B) a single covalent bond.
C) a double covalent bond.
D) a triple covalent bond.
A) an ionic bond.
B) a single covalent bond.
C) a double covalent bond.
D) a triple covalent bond.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
The formula for the compound calcium bromide is
A) CaBr.
B) Ca2Br.
C) CaBr2.
D) Ca3Br2.
A) CaBr.
B) Ca2Br.
C) CaBr2.
D) Ca3Br2.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
For which atom is it difficult to predict the most probable ionic charge using the periodic table?
A) H
B) Fe
C) O
D) Ne
A) H
B) Fe
C) O
D) Ne

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
A covalent bond is formed when a pair of electrons is
A) transferred.
B) shared.
C) split.
D) destroyed.
A) transferred.
B) shared.
C) split.
D) destroyed.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
How many electrons are there in a double bond?
A) 1
B) 2
C) 4
D) 6
A) 1
B) 2
C) 4
D) 6

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
If two atoms from the same element share three pairs of electrons in forming a molecule the bond is called a
A) single covalent bond.
B) double covalent bond.
C) triple covalent bond.
D) coordinate covalent bond.
A) single covalent bond.
B) double covalent bond.
C) triple covalent bond.
D) coordinate covalent bond.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
The name of the compound S2O3 is
A) disulfur oxide.
B) disulfur trioxide.
C) sulfur oxide.
D) sulfur trioxide.
A) disulfur oxide.
B) disulfur trioxide.
C) sulfur oxide.
D) sulfur trioxide.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
For which atom is it difficult to predict the most probable ionic charge using the periodic table?
A) Co
B) K
C) Al
D) Br
A) Co
B) K
C) Al
D) Br

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
Octet means
A) stable electrons.
B) valence electrons.
C) eight.
D) filled shell.
A) stable electrons.
B) valence electrons.
C) eight.
D) filled shell.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



