Deck 9: Chemistry of Fire and Heat
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/19
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 9: Chemistry of Fire and Heat
1
Explain the differences between a bomb calorimeter and a cone calorimeter.
The answer should include the following information: Bomb calorimeters convert fuel to gaseous products that are confined within a sealed container at high pressures. Cone calorimeters measure the heat of combustion of ignitable materials by monitoring the decrease in oxygen in the air collected above a burning sample. Bomb calorimeters do not provide information about time, while cone calorimeters do.
2
Determine how much heat is required to increase the temperature of a 495.0 g sample of acetone from 58°C to its autoignition temperature of 465°C, given that the specific heat capacity of acetone is 1.20 J/g·°C.
2.4 × 105 J
3
What physical process is happening between points E and F? 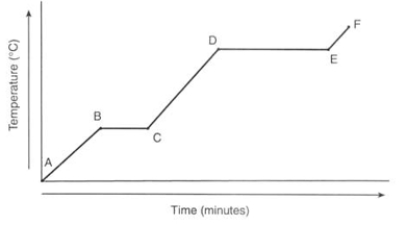
A) Heat energy converts the solid water into liquid water.
B) Solid water is being heated, resulting in the temperature of the solid increasing.
C) Liquid water is being heated, resulting in the temperature of the liquid increasing.
D) Gaseous water is being heated, resulting in the temperature of the gas increasing.

A) Heat energy converts the solid water into liquid water.
B) Solid water is being heated, resulting in the temperature of the solid increasing.
C) Liquid water is being heated, resulting in the temperature of the liquid increasing.
D) Gaseous water is being heated, resulting in the temperature of the gas increasing.
Gaseous water is being heated, resulting in the temperature of the gas increasing.
4
Calculate the specific heat capacity in J/kg·°C of an unknown metal in a 3.76 kg block that requires 1.83 × 104 J of heat to raise the temperature from 23.8°C to 61.2°C.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 19 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Compounds with which type of intermolecular force will tend to have large heats of vaporization?
A) dipole-dipole
B) dipole-induced dipole
C) dispersion
D) hydrogen bonding
A) dipole-dipole
B) dipole-induced dipole
C) dispersion
D) hydrogen bonding

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 19 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
A 0.500 g sample of TNT (C7H5N2O6) is ignited in a bomb calorimeter and the temperature of 610 mL of water increases from 20.0°C to 23.0°C. What is the heat of combustion (J/g) of the TNT?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 19 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Convert 76.2 Calories to kilojoules.
A) 0.0000182 kJ
B) 0.000319 kJ
C) 18.2 kJ
D) 319 kJ
A) 0.0000182 kJ
B) 0.000319 kJ
C) 18.2 kJ
D) 319 kJ

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 19 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
A 28.4 g sample of aluminum, initially at 39.4°C, heated 50.0 g of water from 22.0°C to 24.0°C upon being submerged in the water. Determine the specific heat of aluminum, given that the specific heat of water is 4.184 J/g·°C.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 19 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Which element is oxidized in the following reaction? 10I- + 16H+ + 2MnO4- → 5I2 + 2Mn2+ + 8H2O
A) H
B) I
C) Mn
D) O
A) H
B) I
C) Mn
D) O

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 19 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
What physical process is happening between points B and C? 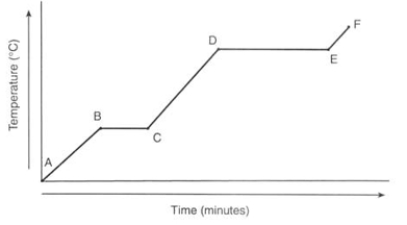
A) Heat energy converts the solid water into liquid water.
B) Heat energy converts the liquid water into gaseous water.
C) Solid water is being heated, resulting in the temperature of the solid increasing.
D) Liquid water is being heated, resulting in the temperature of the liquid increasing.
E) Gaseous water is being heated, resulting in the temperature of the gas increasing.

A) Heat energy converts the solid water into liquid water.
B) Heat energy converts the liquid water into gaseous water.
C) Solid water is being heated, resulting in the temperature of the solid increasing.
D) Liquid water is being heated, resulting in the temperature of the liquid increasing.
E) Gaseous water is being heated, resulting in the temperature of the gas increasing.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 19 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Write and balance the equation for the complete combustion of pentane.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 19 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Which element is reduced in the following reaction? 4Ag(s) + 2H2S(g) + O2(g) → 2Ag2S(s) + 2H2O(g)
A) Ag
B) H
C) O
D) S
Enter the appropriate word(s) to complete the statement.
A) Ag
B) H
C) O
D) S
Enter the appropriate word(s) to complete the statement.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 19 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Indicate whether the following statement is true or false
Temperature is a measure of the heat content of a body.
Temperature is a measure of the heat content of a body.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 19 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
In which type of reaction do the products have more energy than the reactants?
A) endothermic
B) exothermic
A) endothermic
B) exothermic

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 19 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Write and balance the equation for the complete combustion of C6H14.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 19 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
What is the oxidation number of Mn in the compound Mn2S3?
A) +3/2
B) +2
C) +3
D) +6
A) +3/2
B) +2
C) +3
D) +6

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 19 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
What is the initial temperature of a 13.5 g sample of gold if it raises the temperature of 60.0 g of water from 19.5°C to 20.5°C upon submersion? The specific heat of gold is 0.13 J/g·°C and of water is 4.184 J/g·°C.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 19 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
What is the oxidation number of Hg in Hg2Cl2?
A) -2
B) -1
C) +1
D) +2
A) -2
B) -1
C) +1
D) +2

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 19 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Convert the heat of combustion of ethanol, 7.1 Cal/g, to J/g.
A) 1.7 × 10-3 J/g
B) 3.0 × 10-2 J/g
C) 1.7 × 103 J/g
D) 3.0 × 104 J/g
A) 1.7 × 10-3 J/g
B) 3.0 × 10-2 J/g
C) 1.7 × 103 J/g
D) 3.0 × 104 J/g

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 19 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



