Deck 31: Market Failure: Externalities, Public Goods, and Asymmetric Information
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/185
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 31: Market Failure: Externalities, Public Goods, and Asymmetric Information
1
Suppose the production of a good results in negative externalities.If output is at the intersection of the demand curve and the marginal social cost curve,then
A) the socially optimal level of output will be produced.
B) society will incur a net social cost.
C) society will want less output produced, and producers will be willing to satisfy this desire at a price that society deems acceptable.
D) b and c
A) the socially optimal level of output will be produced.
B) society will incur a net social cost.
C) society will want less output produced, and producers will be willing to satisfy this desire at a price that society deems acceptable.
D) b and c
A
2
Exhibit 31-1
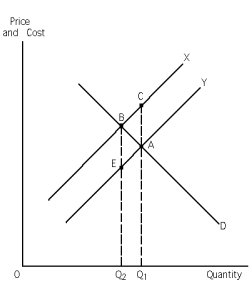
Refer to Exhibit 31-l.If the exhibit represents a negative externality situation,the benefit of expanding output from Q? to Q? is the area of
A) ABC.
B) Q2BCQ1.
C) Q2BAQ1.
D) Q2EAQ1.

Refer to Exhibit 31-l.If the exhibit represents a negative externality situation,the benefit of expanding output from Q? to Q? is the area of
A) ABC.
B) Q2BCQ1.
C) Q2BAQ1.
D) Q2EAQ1.
C
3
Negative externalities arising from the production of a good
A) cause an increase in the demand for the good.
B) cause a decrease in the demand for the good.
C) impose costs on third parties.
D) bring private costs into equality with social costs.
A) cause an increase in the demand for the good.
B) cause a decrease in the demand for the good.
C) impose costs on third parties.
D) bring private costs into equality with social costs.
C
4
Sometimes,when goods are produced and consumed,side effects are felt by people who are not directly involved in the market exchanges.In general,these side effects are called
A) Coase effects.
B) externalities.
C) public goods.
D) internalities.
E) none of the above
A) Coase effects.
B) externalities.
C) public goods.
D) internalities.
E) none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 185 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Suppose the production of a good results in negative externalities.If all costs are taken into account,then
A) output will occur at the socially optimal level.
B) the price of the product will be higher than if all costs are not taken into account.
C) more output will be produced than if all costs are not taken into account.
D) a and b
E) a, b, and c
A) output will occur at the socially optimal level.
B) the price of the product will be higher than if all costs are not taken into account.
C) more output will be produced than if all costs are not taken into account.
D) a and b
E) a, b, and c

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 185 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Which of the following situations probably would not yield a negative externality?
A) a rock concert in the quad next to the library
B) one person who is smoking cigarettes in a closed room where several other people are present
C) a tutor quietly instructs a student in economics as a bystander willingly listens in without the tutor knowing it
D) mowing your lawn early on a Saturday morning when you live in a densely populated neighborhood
E) All of the above situations would yield negative externalities.
A) a rock concert in the quad next to the library
B) one person who is smoking cigarettes in a closed room where several other people are present
C) a tutor quietly instructs a student in economics as a bystander willingly listens in without the tutor knowing it
D) mowing your lawn early on a Saturday morning when you live in a densely populated neighborhood
E) All of the above situations would yield negative externalities.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 185 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Market failure is a situation in which
A) the market does not provide the ideal or optimal amount of a particular good.
B) there are too many buyers but not enough sellers.
C) prices are too high for "average" people to buy necessities.
D) there is a question over the quality of a product for sale.
A) the market does not provide the ideal or optimal amount of a particular good.
B) there are too many buyers but not enough sellers.
C) prices are too high for "average" people to buy necessities.
D) there is a question over the quality of a product for sale.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 185 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Exhibit 31-1

Refer to Exhibit 31-l.If the exhibit represents a negative externality situation,the private cost of expanding output from Q? to Q? is the area of
A) ABC.
B) Q2BCQ1.
C) Q2BAQ1.
D) Q2EAQ1.

Refer to Exhibit 31-l.If the exhibit represents a negative externality situation,the private cost of expanding output from Q? to Q? is the area of
A) ABC.
B) Q2BCQ1.
C) Q2BAQ1.
D) Q2EAQ1.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 185 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Exhibit 31-1

Refer to Exhibit 31-1.If the exhibit represents a negative externality situation,then what is Q??
A) It is the quantity of output at which marginal social costs

Refer to Exhibit 31-1.If the exhibit represents a negative externality situation,then what is Q??
A) It is the quantity of output at which marginal social costs

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 185 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
A side effect of an action that adversely affects the well-being of others is called a
A) complement.
B) supplement.
C) negative externality.
D) marginal cost.
A) complement.
B) supplement.
C) negative externality.
D) marginal cost.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 185 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
A negative externality is
A) a type of tax.
B) a type of subsidy.
C) a type of money price.
D) linked to external costs.
E) linked to external benefits.
A) a type of tax.
B) a type of subsidy.
C) a type of money price.
D) linked to external costs.
E) linked to external benefits.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 185 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Exhibit 31-1

Refer to Exhibit 31-1.If the exhibit represents a negative externality situation,the triangle ABC is representative of
A) social failure.
B) optimal failure.
C) market failure.
D) socially optimal output.
E) none of the above

Refer to Exhibit 31-1.If the exhibit represents a negative externality situation,the triangle ABC is representative of
A) social failure.
B) optimal failure.
C) market failure.
D) socially optimal output.
E) none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 185 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
When a negative externality exists,
A) external costs are necessarily greater than private costs.
B) social costs equal private costs.
C) social costs are less than private costs.
D) social costs are greater than private costs.
E) none of the above
A) external costs are necessarily greater than private costs.
B) social costs equal private costs.
C) social costs are less than private costs.
D) social costs are greater than private costs.
E) none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 185 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Suppose the production of a good results in negative externalities.If all costs are taken into account,then
A) output will be at a lower level than if all costs are not taken into account.
B) output will be at a lower level than the socially optimal level.
C) the marginal private cost curve will lie above and to the left of the marginal social cost curve.
D) a and b
E) a, b, and c
A) output will be at a lower level than if all costs are not taken into account.
B) output will be at a lower level than the socially optimal level.
C) the marginal private cost curve will lie above and to the left of the marginal social cost curve.
D) a and b
E) a, b, and c

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 185 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
If society is experiencing a net social cost from the production of a good,this implies that
A) the socially optimal level of output is being produced and society is willing to accept the costs that result.
B) producers would rather produce the output at which marginal social cost equals the demand for the good.
C) negative externalities are involved in the production of this good.
D) none of the above
A) the socially optimal level of output is being produced and society is willing to accept the costs that result.
B) producers would rather produce the output at which marginal social cost equals the demand for the good.
C) negative externalities are involved in the production of this good.
D) none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 185 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Exhibit 31-1

Refer to Exhibit 31-1.This graph represents a negative externality situation.Given this,which of the two curves,X or Y,represents marginal social costs and why?
A) Curve X, because if there is a negative externality, external costs are associated with it: social costs = external costs + private costs, therefore the marginal social cost curve must lie above the marginal private cost curve.
B) Curve Y, because if there is a negative externality, negative external costs are associated with it: social costs = negative external costs + private costs, therefore the marginal social cost curve must lie below the marginal private cost curve.
C) Curve X, because if there is a negative externality, external benefits are associated with it: social costs = external benefits + private costs, therefore the marginal social cost curve must lie above the marginal private cost curve.
D) Curve Y, because if there is a negative externality, negative external benefits are associated with it: social costs = negative external benefits + private costs, therefore the marginal social cost curve must lie below the marginal private cost curve.

Refer to Exhibit 31-1.This graph represents a negative externality situation.Given this,which of the two curves,X or Y,represents marginal social costs and why?
A) Curve X, because if there is a negative externality, external costs are associated with it: social costs = external costs + private costs, therefore the marginal social cost curve must lie above the marginal private cost curve.
B) Curve Y, because if there is a negative externality, negative external costs are associated with it: social costs = negative external costs + private costs, therefore the marginal social cost curve must lie below the marginal private cost curve.
C) Curve X, because if there is a negative externality, external benefits are associated with it: social costs = external benefits + private costs, therefore the marginal social cost curve must lie above the marginal private cost curve.
D) Curve Y, because if there is a negative externality, negative external benefits are associated with it: social costs = negative external benefits + private costs, therefore the marginal social cost curve must lie below the marginal private cost curve.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 185 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
When negative externalities are connected with the production of a good,
A) market output will be greater than the socially optimal output.
B) private costs and social costs are equal.
C) the government should subsidize the production of the good.
D) there will be a shortage of the good.
A) market output will be greater than the socially optimal output.
B) private costs and social costs are equal.
C) the government should subsidize the production of the good.
D) there will be a shortage of the good.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 185 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Suppose the production of a good results in negative externalities.If society produces the output consistent with the intersection of the demand curve and the marginal private cost curve,then
A) the socially optimal level of output will be produced.
B) society will incur a net social cost.
C) society will want more output produced, and producers will be willing to satisfy this desire at a price that society deems acceptable.
D) all of the above
E) There is not enough information to answer this question.
A) the socially optimal level of output will be produced.
B) society will incur a net social cost.
C) society will want more output produced, and producers will be willing to satisfy this desire at a price that society deems acceptable.
D) all of the above
E) There is not enough information to answer this question.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 185 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
A consequence of a negative externality is that social costs __________ private costs,and the socially optimal level of output __________.
A) equal; is not equal to social costs or private costs
B) do not equal; is obtained
C) do not equal; is not obtained
D) equal; is obtained
E) equal; is not obtained
A) equal; is not equal to social costs or private costs
B) do not equal; is obtained
C) do not equal; is not obtained
D) equal; is obtained
E) equal; is not obtained

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 185 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
In which of the following situations would a negative externality most likely be involved?
A) It is night and Kenneth is sitting in his easy chair reading a novel by John Grisham. The lamp he is reading by has only a 40-watt light bulb. He is having a hard time reading.
B) Alyson lives near an airport. At five o'clock in the morning every day she can hear the airplanes taking off and it awakens her.
C) Lucy went to a fancy restaurant last night and ordered the most expensive meal on the menu. She hated it.
D) Richard is taking an economics class from Professor Franklin. Professor Franklin often says things that confuse Richard.
A) It is night and Kenneth is sitting in his easy chair reading a novel by John Grisham. The lamp he is reading by has only a 40-watt light bulb. He is having a hard time reading.
B) Alyson lives near an airport. At five o'clock in the morning every day she can hear the airplanes taking off and it awakens her.
C) Lucy went to a fancy restaurant last night and ordered the most expensive meal on the menu. She hated it.
D) Richard is taking an economics class from Professor Franklin. Professor Franklin often says things that confuse Richard.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 185 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Exhibit 31-1

Refer to Exhibit 31-1.If the exhibit represents a negative externality situation,the net social cost of expanding output from Q? to Q? is the area of
A) ABC.
B) BEA.
C) Q2BAQ1.
D) Q2EAQ1.

Refer to Exhibit 31-1.If the exhibit represents a negative externality situation,the net social cost of expanding output from Q? to Q? is the area of
A) ABC.
B) BEA.
C) Q2BAQ1.
D) Q2EAQ1.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 185 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Suppose the production of a good results in positive externalities.If output occurs at the intersection of the marginal social benefits curve and the supply curve,then
A) output will be at the socially optimal level.
B) the price of the product will be the same as it was when all benefits were not taken into account.
C) more output will be produced than if all benefits were not taken into account.
D) a and c
E) a, b, and c
A) output will be at the socially optimal level.
B) the price of the product will be the same as it was when all benefits were not taken into account.
C) more output will be produced than if all benefits were not taken into account.
D) a and c
E) a, b, and c

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 185 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Given a positive externality,the marginal private benefit curve lies to the __________ of the demand curve,with the market output __________ the socially optimal output.
A) right; above
B) right; below
C) left; above
D) left; below
A) right; above
B) right; below
C) left; above
D) left; below

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 185 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
In which of the following situations would a positive externality most likely be involved?
A) Shawn is sitting at home one day when she gets a telephone call, informing her that she has won $10,000 in a contest she entered three months ago.
B) There are eight houses in the neighborhood where Rodney lives. Rodney likes nice-looking yards, and last week his neighbors began to beautify their yards.
C) Willy needs eight hours of sleep each night to feel good. Last night he got eight hours of sleep.
D) Patrick received an A on a biology exam. He is feeling better about his chances of getting admitted to medical school.
A) Shawn is sitting at home one day when she gets a telephone call, informing her that she has won $10,000 in a contest she entered three months ago.
B) There are eight houses in the neighborhood where Rodney lives. Rodney likes nice-looking yards, and last week his neighbors began to beautify their yards.
C) Willy needs eight hours of sleep each night to feel good. Last night he got eight hours of sleep.
D) Patrick received an A on a biology exam. He is feeling better about his chances of getting admitted to medical school.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 185 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Exhibit 31-2
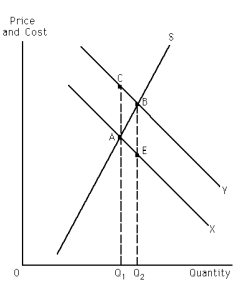
Refer to Exhibit 31-2.If the exhibit represents a positive externality situation,the private cost of expanding output from Q? to Q? is the area of
A) Q1ABQ2.
B) Q1AEQ2.
C) Q1CBQ2.
D) ABE.

Refer to Exhibit 31-2.If the exhibit represents a positive externality situation,the private cost of expanding output from Q? to Q? is the area of
A) Q1ABQ2.
B) Q1AEQ2.
C) Q1CBQ2.
D) ABE.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 185 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Which of the following statements is false?
A) A positive externality is internalized if the person that generated the externality incorporates into his or her own private cost-benefit calculations the external benefits that third parties receive.
B) Internalizing externalities is not the same as adjusting for externalities.
C) An externality has been completely internalized if the socially optimal output emerges.
D) Assigning property rights is one way to internalize externalities.
A) A positive externality is internalized if the person that generated the externality incorporates into his or her own private cost-benefit calculations the external benefits that third parties receive.
B) Internalizing externalities is not the same as adjusting for externalities.
C) An externality has been completely internalized if the socially optimal output emerges.
D) Assigning property rights is one way to internalize externalities.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 185 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Exhibit 31-1

Refer to Exhibit 31-1.If the exhibit represents a negative externality situation,the social cost of expanding output from Q? to Q? is the area of
A) ABC.
B) Q2BCQ1.
C) Q2BAQ1.
D) Q2EAQ1.

Refer to Exhibit 31-1.If the exhibit represents a negative externality situation,the social cost of expanding output from Q? to Q? is the area of
A) ABC.
B) Q2BCQ1.
C) Q2BAQ1.
D) Q2EAQ1.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 185 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Exhibit 31-2

Refer to Exhibit 31-2.If the exhibit represents a positive externality situation,the social benefit of expanding output from Q? to Q? is the area of
A) Q1ABQ2.
B) Q1AEQ2.
C) Q1CBQ2.
D) ABE.

Refer to Exhibit 31-2.If the exhibit represents a positive externality situation,the social benefit of expanding output from Q? to Q? is the area of
A) Q1ABQ2.
B) Q1AEQ2.
C) Q1CBQ2.
D) ABE.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 185 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Suppose the production of a good results in positive externalities.If output occurs at the intersection of the marginal social benefits curve and the supply curve,then
A) output will be at a higher level than if all benefits were not taken into account.
B) output will be at a lower level than the socially optimal level.
C) the marginal private benefit curve will lie above and to the right of the marginal social benefit curve.
D) there will be underproduction.
E) all of the above
A) output will be at a higher level than if all benefits were not taken into account.
B) output will be at a lower level than the socially optimal level.
C) the marginal private benefit curve will lie above and to the right of the marginal social benefit curve.
D) there will be underproduction.
E) all of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 185 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
The side effect of an action that increases the well-being of others is called
A) an augmentation.
B) an elasticity.
C) a passive benefit.
D) a positive externality.
A) an augmentation.
B) an elasticity.
C) a passive benefit.
D) a positive externality.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 185 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Exhibit 31-2

Refer to Exhibit 31-2.If the exhibit represents a positive externality situation,the net social benefit of expanding output from Q? to Q? is the area of
A) Q1ABQ2.
B) Q1AEQ2.
C) CBA.
D) ABE.

Refer to Exhibit 31-2.If the exhibit represents a positive externality situation,the net social benefit of expanding output from Q? to Q? is the area of
A) Q1ABQ2.
B) Q1AEQ2.
C) CBA.
D) ABE.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 185 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
When positive externalities are involved,the market is said to
A) fail, because it underproduces the good connected with the positive externality.
B) fail, because it overproduces the good connected with the positive externality.
C) succeed, because it produces the socially optimal quantity of the good connected with the positive externality.
D) be "in optimum," because the equilibrium fully adjusts for the positive externality.
A) fail, because it underproduces the good connected with the positive externality.
B) fail, because it overproduces the good connected with the positive externality.
C) succeed, because it produces the socially optimal quantity of the good connected with the positive externality.
D) be "in optimum," because the equilibrium fully adjusts for the positive externality.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 185 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Which of the following statements is true?
A) When production of a good yields positive externalities but output is currently at the market level, then a change in output to the socially optimal level will certainly be for the worse.
B) When production of a good yields negative externalities but output is currently at the market level, then a change in output to the socially optimal level will cause benefits to increase by an amount greater than costs will increase.
C) When production of a good yields positive externalities but output is currently at the market level, then a change in output to the socially optimal level will cause benefits to increase by an amount less than costs will increase.
D) a, b, and c
E) none of the above
A) When production of a good yields positive externalities but output is currently at the market level, then a change in output to the socially optimal level will certainly be for the worse.
B) When production of a good yields negative externalities but output is currently at the market level, then a change in output to the socially optimal level will cause benefits to increase by an amount greater than costs will increase.
C) When production of a good yields positive externalities but output is currently at the market level, then a change in output to the socially optimal level will cause benefits to increase by an amount less than costs will increase.
D) a, b, and c
E) none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 185 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Exhibit 31-2

Refer to Exhibit 31-2.If Exhibit 30-2 exhibits a positive externality situation,then what is Q??
A) It is the quantity of output at which marginal social benefits (MSB) equal marginal private benefits (MPB).
B) It is the quantity of output at which MPB > MSB.
C) It is the market output-the quantity of output that exists if the external benefits associated with the positive externality are not taken into account.
D) It is the socially optimal output-the quantity of output that exists if the external benefits associated with the positive externality are taken into account.
E) none of the above

Refer to Exhibit 31-2.If Exhibit 30-2 exhibits a positive externality situation,then what is Q??
A) It is the quantity of output at which marginal social benefits (MSB) equal marginal private benefits (MPB).
B) It is the quantity of output at which MPB > MSB.
C) It is the market output-the quantity of output that exists if the external benefits associated with the positive externality are not taken into account.
D) It is the socially optimal output-the quantity of output that exists if the external benefits associated with the positive externality are taken into account.
E) none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 185 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Suppose the production of a good results in positive externalities.If output occurs at the intersection of the supply curve and the marginal social benefits curve,then
A) the socially optimal level of output will be produced.
B) society will incur a net social cost.
C) society will want less produced, and producers will be willing to satisfy that desire.
D) there is market failure.
A) the socially optimal level of output will be produced.
B) society will incur a net social cost.
C) society will want less produced, and producers will be willing to satisfy that desire.
D) there is market failure.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 185 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
When a positive externality exists,
A) external benefits are necessarily greater than private benefits.
B) social benefits are greater than private benefits.
C) social benefits are less than private benefits.
D) social benefits equal private benefits.
E) none of the above
A) external benefits are necessarily greater than private benefits.
B) social benefits are greater than private benefits.
C) social benefits are less than private benefits.
D) social benefits equal private benefits.
E) none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 185 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Exhibit 31-2

Refer to Exhibit 31-2.If the exhibit represents a positive externality situation,the private benefit of expanding output from Q? to Q? is the area of
A) Q1ABQ2.
B) Q1AEQ2.
C) Q1CBQ2.
D) ABE.

Refer to Exhibit 31-2.If the exhibit represents a positive externality situation,the private benefit of expanding output from Q? to Q? is the area of
A) Q1ABQ2.
B) Q1AEQ2.
C) Q1CBQ2.
D) ABE.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 185 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Exhibit 31-2

Refer to Exhibit 31-2.This graph represents a positive externality situation.Given this,which of the two curves,X or Y,represents marginal social benefits and why?
A) Curve X, because if there is a positive externality, negative external benefits are associated with it: social costs external benefits - private benefits, therefore the marginal social benefit curve must lie below the marginal private benefit curve.
B) Curve X, because if there is a positive externality, external benefits are associated with it: social benefits = external benefits + private benefits, therefore the marginal social benefit curve must lie below the marginal private benefit curve.
C) Curve Y, because if there is a positive externality, external costs are associated with it: social benefits = external costs + private benefits, therefore the marginal social benefit curve must lie above the marginal private benefit cost curve.
D) Curve Y, because if there is a positive externality, external benefits are associated with it: social benefits = external benefits + private benefits, therefore the marginal social benefit curve must lie above the marginal private benefit curve.

Refer to Exhibit 31-2.This graph represents a positive externality situation.Given this,which of the two curves,X or Y,represents marginal social benefits and why?
A) Curve X, because if there is a positive externality, negative external benefits are associated with it: social costs external benefits - private benefits, therefore the marginal social benefit curve must lie below the marginal private benefit curve.
B) Curve X, because if there is a positive externality, external benefits are associated with it: social benefits = external benefits + private benefits, therefore the marginal social benefit curve must lie below the marginal private benefit curve.
C) Curve Y, because if there is a positive externality, external costs are associated with it: social benefits = external costs + private benefits, therefore the marginal social benefit curve must lie above the marginal private benefit cost curve.
D) Curve Y, because if there is a positive externality, external benefits are associated with it: social benefits = external benefits + private benefits, therefore the marginal social benefit curve must lie above the marginal private benefit curve.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 185 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Samantha is given a flu shot by her doctor.This reduces the probability that she will get the flu and it also reduces the probability that others will get the flu,too.The latter is an example of a
A) negative externality.
B) positive externality.
C) substitute good.
D) complementary good.
A) negative externality.
B) positive externality.
C) substitute good.
D) complementary good.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 185 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
When negative externalities are involved,the market is said to
A) fail, because it underproduces the good connected with the negative externality.
B) fail, because it overproduces the good connected with the negative externality.
C) succeed, because it produces the socially optimal quantity of the good connected with the negative externality.
D) be "in optimum," because the equilibrium fully adjusts for the negative externality.
A) fail, because it underproduces the good connected with the negative externality.
B) fail, because it overproduces the good connected with the negative externality.
C) succeed, because it produces the socially optimal quantity of the good connected with the negative externality.
D) be "in optimum," because the equilibrium fully adjusts for the negative externality.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 185 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
Which of the following statements is true?
A) A tax applied to an activity that generates a negative externality always brings about the socially optimal level of output.
B) A subsidy applied to an activity that generates a positive externality always brings about the socially optimal level of output.
C) a and b
D) none of the above
A) A tax applied to an activity that generates a negative externality always brings about the socially optimal level of output.
B) A subsidy applied to an activity that generates a positive externality always brings about the socially optimal level of output.
C) a and b
D) none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 185 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
An externality is internalized if
A) the person(s) or group that generated the externality incorporate into their own private cost-benefit calculations the external benefits (in the case of a positive externality) or the external costs (in the case of a negative externality) that third parties bear.
B) people are made aware of it and realize that social benefits are less than private benefits (in the case of a positive externality) and that social costs are less than private costs (in the case of a negative externality).
C) the person(s) or group that generated the externality do not incorporate into their own private cost-benefit calculations the external benefits (in the case of a positive externality) or the external costs (in the case of a negative externality) that third parties bear.
D) b and c
E) none of the above
A) the person(s) or group that generated the externality incorporate into their own private cost-benefit calculations the external benefits (in the case of a positive externality) or the external costs (in the case of a negative externality) that third parties bear.
B) people are made aware of it and realize that social benefits are less than private benefits (in the case of a positive externality) and that social costs are less than private costs (in the case of a negative externality).
C) the person(s) or group that generated the externality do not incorporate into their own private cost-benefit calculations the external benefits (in the case of a positive externality) or the external costs (in the case of a negative externality) that third parties bear.
D) b and c
E) none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 185 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
If the consumption of a good by one person reduces the amount of it that can be consumed by others,the good is
A) excludable.
B) nonexcludable.
C) rivalrous in consumption.
D) nonrivalrous in consumption.
A) excludable.
B) nonexcludable.
C) rivalrous in consumption.
D) nonrivalrous in consumption.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 185 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
Externalities can be internalized through voluntary agreements as long as
A) transaction costs are low relative to expected benefits.
B) transaction costs are high relative to expected benefits.
C) the agreement is a short-run agreement.
D) the agreement is a long-run agreement.
A) transaction costs are low relative to expected benefits.
B) transaction costs are high relative to expected benefits.
C) the agreement is a short-run agreement.
D) the agreement is a long-run agreement.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 185 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Which of the following is not a method to internalize or adjust for externalities?
A) persuasion
B) assignment of property rights
C) unilateral transfers
D) voluntary agreements
A) persuasion
B) assignment of property rights
C) unilateral transfers
D) voluntary agreements

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 185 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
The Coase theorem states that
A) positive externalities are directly related to the weather-the better the weather, the more positive externalities.
B) in the case of trivial or zero transaction costs, negative externalities are more likely to appear.
C) when transaction costs are high, positive externalities will be minimized.
D) in the case of trivial or zero transaction costs, the property rights assignment does not matter to the resource-allocative outcome.
A) positive externalities are directly related to the weather-the better the weather, the more positive externalities.
B) in the case of trivial or zero transaction costs, negative externalities are more likely to appear.
C) when transaction costs are high, positive externalities will be minimized.
D) in the case of trivial or zero transaction costs, the property rights assignment does not matter to the resource-allocative outcome.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 185 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
Suppose a particular production process results in a large amount of pollution and the government decides to impose a tax to correct for this externality,such that the socially optimal output will be produced.The tax will have the effect of shifting the
A) marginal private benefit curve to the right.
B) marginal social benefit curve to the right.
C) marginal private cost curve to the left.
D) marginal social cost curve to the left.
E) marginal private cost curve to the right.
A) marginal private benefit curve to the right.
B) marginal social benefit curve to the right.
C) marginal private cost curve to the left.
D) marginal social cost curve to the left.
E) marginal private cost curve to the right.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 185 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
Which of the following statements is true?
A) The lower transaction costs are, the more likely individuals will solve negative externality problems through a voluntary exchange.
B) The higher transaction costs are, the more likely individuals will solve negative externality problems through a voluntary exchange.
C) Coase agrees with Pigou that taxing those activities associated with negative externalities is a good idea.
D) a and c
E) none of the above
A) The lower transaction costs are, the more likely individuals will solve negative externality problems through a voluntary exchange.
B) The higher transaction costs are, the more likely individuals will solve negative externality problems through a voluntary exchange.
C) Coase agrees with Pigou that taxing those activities associated with negative externalities is a good idea.
D) a and c
E) none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 185 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
Some pollution may be preferable to zero pollution because
A) attempting to decrease the level of pollution to zero may cause significant losses in society's welfare.
B) we really do not have that much pollution.
C) the nation's citizens are against government's involvement in solving the pollution problem.
D) no form of regulation that has been shown to be effective at solving the pollution problem.
A) attempting to decrease the level of pollution to zero may cause significant losses in society's welfare.
B) we really do not have that much pollution.
C) the nation's citizens are against government's involvement in solving the pollution problem.
D) no form of regulation that has been shown to be effective at solving the pollution problem.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 185 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
A good is a nonexcludable if
A) its consumption by one person does not reduce its consumption by others.
B) it is impossible to prevent people from obtaining the benefits of the good once it has been produced.
C) no negative externalities are associated with its production and consumption.
D) it is free in the first place; that is, it is so abundant that people can get all they want at zero price.
A) its consumption by one person does not reduce its consumption by others.
B) it is impossible to prevent people from obtaining the benefits of the good once it has been produced.
C) no negative externalities are associated with its production and consumption.
D) it is free in the first place; that is, it is so abundant that people can get all they want at zero price.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 185 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
The Coase theorem is significant because it
A) implies that no transaction costs are associated with solving externalities.
B) shows that property rights can be assigned.
C) shows that under certain conditions externalities can be corrected in the market without resorting to nonmarket means.
D) a and b
A) implies that no transaction costs are associated with solving externalities.
B) shows that property rights can be assigned.
C) shows that under certain conditions externalities can be corrected in the market without resorting to nonmarket means.
D) a and b

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 185 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
If private property rights were established in the air,there would probably be
A) more air pollution.
B) less air pollution.
C) the same amount of air pollution that exists without private property rights in the air.
D) better weather.
A) more air pollution.
B) less air pollution.
C) the same amount of air pollution that exists without private property rights in the air.
D) better weather.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 185 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
The Coase theorem
A) shows that under certain conditions the market can internalize externalities.
B) states that economic units should specialize in the production of those goods in which they have a comparative advantage.
C) asserts that the firm should produce that output at which marginal cost is equal to marginal revenue.
D) holds that the firm should produce that output at which marginal factor cost is equal to marginal revenue product.
A) shows that under certain conditions the market can internalize externalities.
B) states that economic units should specialize in the production of those goods in which they have a comparative advantage.
C) asserts that the firm should produce that output at which marginal cost is equal to marginal revenue.
D) holds that the firm should produce that output at which marginal factor cost is equal to marginal revenue product.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 185 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
Which of the following statements is false?
A) Externalities can sometimes be internalized through individual voluntary agreements.
B) It would be a relatively easy matter to establish property rights in the air.
C) Persuasion can be used in some cases to internalize externalities.
D) Taxes and subsidies are sometimes used as corrective devices for market failures.
A) Externalities can sometimes be internalized through individual voluntary agreements.
B) It would be a relatively easy matter to establish property rights in the air.
C) Persuasion can be used in some cases to internalize externalities.
D) Taxes and subsidies are sometimes used as corrective devices for market failures.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 185 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
If private property rights were established in the oceans,there would probably be
A) more ocean pollution.
B) less ocean pollution.
C) the same amount of ocean pollution that exists without private property rights in the ocean.
D) more ocean voyages on cruise ships.
A) more ocean pollution.
B) less ocean pollution.
C) the same amount of ocean pollution that exists without private property rights in the ocean.
D) more ocean voyages on cruise ships.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 185 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
The primary difference between private goods and public goods is that
A) private goods are consumed by private individuals whereas public goods are not consumed by private individuals.
B) private goods often yield externalities but public goods do not.
C) property rights can be assigned to public goods but not to private goods.
D) public goods are nonrivalrous in consumption whereas private goods are rivalrous in consumption.
A) private goods are consumed by private individuals whereas public goods are not consumed by private individuals.
B) private goods often yield externalities but public goods do not.
C) property rights can be assigned to public goods but not to private goods.
D) public goods are nonrivalrous in consumption whereas private goods are rivalrous in consumption.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 185 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
Which of the following statements is not an example of the use of persuasion to correct (or adjust for)an externality?
A) Maggie asks her neighbor to keep his dog quiet at night.
B) An environmental group conducts a sit-in at a chemical factory to demand that the firm stop polluting rivers.
C) A judicial court imposes a fine on a reckless driver.
D) All of the above are examples of the use of persuasion to correct (or adjust for) an externality.
A) Maggie asks her neighbor to keep his dog quiet at night.
B) An environmental group conducts a sit-in at a chemical factory to demand that the firm stop polluting rivers.
C) A judicial court imposes a fine on a reckless driver.
D) All of the above are examples of the use of persuasion to correct (or adjust for) an externality.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 185 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
In the early West,many of the open lands were overgrazed.This was largely because
A) landowners charged ranchers a fee to graze their cattle.
B) the lands were unowned.
C) a government policy in effect at the time subsidized cattle production.
D) none of the above
A) landowners charged ranchers a fee to graze their cattle.
B) the lands were unowned.
C) a government policy in effect at the time subsidized cattle production.
D) none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 185 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
Which of the following statements is false?
A) A subsidy can be used to internalize a negative externality; a tax can be used to internalize a positive externality.
B) Ronald Coase stressed the reciprocal nature of externalities.
C) One way to deal with negative externalities is for government to apply regulations directly to the activity that generates the externalities.
D) Simply because taxes and subsidies are sometimes used to adjust for negative and positive externalities, respectively, it does not necessarily follow that the socially optimal level of output will be reached.
A) A subsidy can be used to internalize a negative externality; a tax can be used to internalize a positive externality.
B) Ronald Coase stressed the reciprocal nature of externalities.
C) One way to deal with negative externalities is for government to apply regulations directly to the activity that generates the externalities.
D) Simply because taxes and subsidies are sometimes used to adjust for negative and positive externalities, respectively, it does not necessarily follow that the socially optimal level of output will be reached.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 185 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
If a person who generates a negative externality incorporates into his or her private cost-benefit calculations the effects that this externality will have on third parties,the externality has been
A) substituted.
B) accommodated.
C) compounded.
D) internalized.
A) substituted.
B) accommodated.
C) compounded.
D) internalized.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 185 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
Marginal social costs are equal to
A) marginal private costs + external costs.
B) marginal private costs - external costs.
C) marginal private costs + internal costs.
D) marginal private costs - internal costs.
A) marginal private costs + external costs.
B) marginal private costs - external costs.
C) marginal private costs + internal costs.
D) marginal private costs - internal costs.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 185 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
Marginal social benefits are equal to
A) marginal private benefits + marginal internal benefits.
B) marginal private benefits - marginal internal benefits.
C) marginal private benefits + marginal external benefits.
D) marginal private benefits - marginal external benefits.
A) marginal private benefits + marginal internal benefits.
B) marginal private benefits - marginal internal benefits.
C) marginal private benefits + marginal external benefits.
D) marginal private benefits - marginal external benefits.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 185 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
It seems quite possible that cigarette companies concealed information about the effect of smoking on health,causing cigarette prices to be __________ and cigarette sales to be __________ than would have been the case under symmetric information.
A) higher; higher
B) higher; lower
C) lower; higher
D) lower; lower
A) higher; higher
B) higher; lower
C) lower; higher
D) lower; lower

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 185 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
According to the Coase theorem,externalities
A) must usually be internalized by taxation or subsidy.
B) can be internalized by the market under certain conditions.
C) result when firms fail to maximize profits.
D) cannot be internalized if property rights are assigned.
E) are not relevant to the issue of market failure.
A) must usually be internalized by taxation or subsidy.
B) can be internalized by the market under certain conditions.
C) result when firms fail to maximize profits.
D) cannot be internalized if property rights are assigned.
E) are not relevant to the issue of market failure.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 185 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
When marginal private cost is less than marginal social cost,
A) a public good exists.
B) a negative externality exists.
C) a positive externality exists.
D) negative economic profits are made.
E) a and d
A) a public good exists.
B) a negative externality exists.
C) a positive externality exists.
D) negative economic profits are made.
E) a and d

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 185 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
Generally,negative externalities result in
A) too much of a good being produced.
B) the socially optimal output of a good being produced.
C) too little of a good being produced.
D) either a or c
E) any of the above
A) too much of a good being produced.
B) the socially optimal output of a good being produced.
C) too little of a good being produced.
D) either a or c
E) any of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 185 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
A side effect of an action that affects the well-being of third parties is
A) a marginal cost.
B) a marginal private benefit.
C) an externality.
D) a and b
E) all of the above
A) a marginal cost.
B) a marginal private benefit.
C) an externality.
D) a and b
E) all of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 185 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
A positive externality exists when
A) a person's or group's actions cause a benefit that is felt by others.
B) a person's or group's actions cause a cost that is felt by others.
C) market output is less than socially optimal output.
D) a and c
E) b and c
A) a person's or group's actions cause a benefit that is felt by others.
B) a person's or group's actions cause a cost that is felt by others.
C) market output is less than socially optimal output.
D) a and c
E) b and c

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 185 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
If a negative externality exists,__________ for the socially optimal output to be reached.
A) supply needs to increase
B) supply needs to decrease
C) demand needs to increase
D) b and c
E) none of the above
A) supply needs to increase
B) supply needs to decrease
C) demand needs to increase
D) b and c
E) none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 185 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
A positive externality exists when
A) marginal social costs are less than marginal private costs.
B) marginal social costs are greater than marginal private costs.
C) marginal social benefits are less than marginal private benefits.
D) marginal social benefits are greater than marginal private benefits.
E) a and d
A) marginal social costs are less than marginal private costs.
B) marginal social costs are greater than marginal private costs.
C) marginal social benefits are less than marginal private benefits.
D) marginal social benefits are greater than marginal private benefits.
E) a and d

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 185 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
Which of the following is an example of a negative externality?
A) Bad weather reduces the size of the wheat crop.
B) A reduction in the size of the wheat crop causes the income of wheat farmers to fall.
C) Smoking harms the health of nonsmokers who are nearby.
D) Smoking harms the health of the smoker.
E) all of the above
A) Bad weather reduces the size of the wheat crop.
B) A reduction in the size of the wheat crop causes the income of wheat farmers to fall.
C) Smoking harms the health of nonsmokers who are nearby.
D) Smoking harms the health of the smoker.
E) all of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 185 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
Asymmetric information exists when
A) both parties to an exchange have all relevant facts about that exchange.
B) a good that is either nonrivalrous or nonexcludable is being sold on a market.
C) the two parties to an exchange differ in what they know about the good being exchanged.
D) neither party to an exchange is knowledgeable about the quality of the good being exchanged.
A) both parties to an exchange have all relevant facts about that exchange.
B) a good that is either nonrivalrous or nonexcludable is being sold on a market.
C) the two parties to an exchange differ in what they know about the good being exchanged.
D) neither party to an exchange is knowledgeable about the quality of the good being exchanged.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 185 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
If an asymmetry of information is removed and laborers' preferences change against employment,this will shift the equilibrium in the labor market to the
A) northwest.
B) northeast.
C) southwest.
D) southeast.
A) northwest.
B) northeast.
C) southwest.
D) southeast.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 185 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
Market failure is a situation in which
A) negative economic profits persist in the long run.
B) negative economic profits exist in the short run.
C) the market does not provide the ideal or optimal amount of a particular good.
D) both a and b
E) a, b, and c
A) negative economic profits persist in the long run.
B) negative economic profits exist in the short run.
C) the market does not provide the ideal or optimal amount of a particular good.
D) both a and b
E) a, b, and c

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 185 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
If the government does not provide it,the quantity of a nonexcludable good that private firms will choose to produce is
A) zero.
B) more than the optimal amount.
C) the optimal amount.
D) optimal only if property rights are assigned.
E) optimal only if the industry is competitive.
A) zero.
B) more than the optimal amount.
C) the optimal amount.
D) optimal only if property rights are assigned.
E) optimal only if the industry is competitive.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 185 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
Generally,positive externalities result in
A) too much of a good being produced.
B) the socially optimal output of a good being produced.
C) too little of a good being produced.
D) either a or c
E) any of the above
A) too much of a good being produced.
B) the socially optimal output of a good being produced.
C) too little of a good being produced.
D) either a or c
E) any of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 185 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
The government's provision of nonexcludable public goods such as national defense is accepted because
A) government is more efficient than private firms at producing goods.
B) the market fails to produce nonexcludable public goods as a result of the free-rider problem.
C) people do not value public goods such as national defense very highly.
D) a and c
E) all of the above
A) government is more efficient than private firms at producing goods.
B) the market fails to produce nonexcludable public goods as a result of the free-rider problem.
C) people do not value public goods such as national defense very highly.
D) a and c
E) all of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 185 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
A negative externality exists when
A) a person's or group's actions cause a benefit that is felt by others.
B) a person's or group's actions cause a cost that is felt by others.
C) market output is less than socially optimal output.
D) a and c
E) b and c
A) a person's or group's actions cause a benefit that is felt by others.
B) a person's or group's actions cause a cost that is felt by others.
C) market output is less than socially optimal output.
D) a and c
E) b and c

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 185 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
A __________ good is one that once produced and provided to one person,provides benefits to other persons.
A) consumption
B) investment
C) private
D) public
A) consumption
B) investment
C) private
D) public

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 185 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
A negative externality exists when
A) marginal social costs are less than marginal private costs.
B) marginal social costs are greater than marginal private costs.
C) marginal social benefits are less than marginal private benefits.
D) marginal social benefits are greater than marginal private benefits.
E) b and c
A) marginal social costs are less than marginal private costs.
B) marginal social costs are greater than marginal private costs.
C) marginal social benefits are less than marginal private benefits.
D) marginal social benefits are greater than marginal private benefits.
E) b and c

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 185 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



