Deck 39: Agriculture: Problems, Policies, and Unintended Effects
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/149
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 39: Agriculture: Problems, Policies, and Unintended Effects
1
During the twentieth century,the U.S.farm sector experienced
A) large increases in its ability to produce output.
B) relatively little improvement in its ability to produce output.
C) a marked decrease in its ability to produce output.
D) relatively stable demand for its output.
E) increasing relative prices for its output.
A) large increases in its ability to produce output.
B) relatively little improvement in its ability to produce output.
C) a marked decrease in its ability to produce output.
D) relatively stable demand for its output.
E) increasing relative prices for its output.
A
2
Suppose iceberg lettuce has an income elasticity of demand of 0.35.A 10 percent increase in income causes the quantity demanded of iceberg lettuce to _______________ by ______________ percent.
A) rise; 3.5
B) rise; 28.57
C) fall; 28.57
D) fall; 3.5
A) rise; 3.5
B) rise; 28.57
C) fall; 28.57
D) fall; 3.5
A
3
If the demand curve for agricultural products is inelastic,then it would be in the best interest of farmers as a group to
A) increase output and thereby receive greater revenues.
B) cause the price of their product to decrease.
C) find some way to decrease the quantities of output that are placed on the market for sale.
D) petition the government to find a way to decrease the demand for their product.
E) a and b
A) increase output and thereby receive greater revenues.
B) cause the price of their product to decrease.
C) find some way to decrease the quantities of output that are placed on the market for sale.
D) petition the government to find a way to decrease the demand for their product.
E) a and b
C
4
Suppose the price elasticity of demand of for soy beans is 0.85. When the price of soybeans rises by 20 percent,the quantity demanded of soybeans falls by approximately _____________ percent.
A) 0.024
B) 26.67
C) 23.53
D) 17.00
A) 0.024
B) 26.67
C) 23.53
D) 17.00

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 149 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Studies show that,in the United States,
A) price elasticity of demand for agricultural products has hovered around 3.2 for many years.
B) as real income has been increasing, the per-capita demand for food has been decreasing.
C) as real income has been increasing, the per-capita demand for food has been increasing by much more.
D) none of the above
A) price elasticity of demand for agricultural products has hovered around 3.2 for many years.
B) as real income has been increasing, the per-capita demand for food has been decreasing.
C) as real income has been increasing, the per-capita demand for food has been increasing by much more.
D) none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 149 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
If the demand for a particular farm product is inelastic between price P? and P? (where P? > P?),farmers as a group would want to sell their product at the
A) higher price, but an individual farmer would rather sell his product at the lower price.
B) higher price, and an individual farmer would rather sell his product at the higher price, too.
C) lower price, but an individual farmer would rather sell his product at the higher price.
D) lower price, and an individual farmer would rather sell his product at the lower price, too.
A) higher price, but an individual farmer would rather sell his product at the lower price.
B) higher price, and an individual farmer would rather sell his product at the higher price, too.
C) lower price, but an individual farmer would rather sell his product at the higher price.
D) lower price, and an individual farmer would rather sell his product at the lower price, too.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 149 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
If we assume that the income elasticity of demand for food has been around 0.2 and that agricultural producers have become increasingly more productive,we can conclude that
A) prices of food have increased.
B) supply increases have been less than demand decreases.
C) as consumers' real incomes have been increasing over the years, they have been spending absolutely less on food.
D) prices of food have been stable.
E) none of the above
A) prices of food have increased.
B) supply increases have been less than demand decreases.
C) as consumers' real incomes have been increasing over the years, they have been spending absolutely less on food.
D) prices of food have been stable.
E) none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 149 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Increased productivity in the agricultural sector during much of the twentieth century shifted the
A) demand curve for farm products rightward.
B) supply curve of farm products leftward.
C) demand curve for farm products leftward.
D) supply curve of farm products rightward.
A) demand curve for farm products rightward.
B) supply curve of farm products leftward.
C) demand curve for farm products leftward.
D) supply curve of farm products rightward.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 149 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
During much of the 20th century,agricultural product prices
A) rose relative to other prices.
B) fell relative to other prices.
C) neither rose nor fell relative to other prices.
D) rose as agricultural productivity increased.
A) rose relative to other prices.
B) fell relative to other prices.
C) neither rose nor fell relative to other prices.
D) rose as agricultural productivity increased.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 149 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Which of the following best describes the agricultural sector for much of the 20th century and today?
A) high productivity, price elasticity of demand less than 1, income elasticity of demand greater than 1
B) low productivity, price elasticity of demand greater than 1, income elasticity of demand less than 1
C) high productivity, price elasticity of demand less than 1, income elasticity of demand less than 1
D) low productivity, price elasticity of demand less than 1, income elasticity of demand greater than 1
A) high productivity, price elasticity of demand less than 1, income elasticity of demand greater than 1
B) low productivity, price elasticity of demand greater than 1, income elasticity of demand less than 1
C) high productivity, price elasticity of demand less than 1, income elasticity of demand less than 1
D) low productivity, price elasticity of demand less than 1, income elasticity of demand greater than 1

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 149 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Increased productivity in the agricultural sector is not always a benefit to farmers because it is accompanied by
A) lower prices and if demand is inelastic, lower prices mean lower revenues.
B) higher prices and if demand is elastic, higher prices mean lower revenues.
C) lower prices and if demand is elastic, lower prices mean lower revenues.
D) higher prices and if demand is inelastic, higher prices mean lower revenues.
A) lower prices and if demand is inelastic, lower prices mean lower revenues.
B) higher prices and if demand is elastic, higher prices mean lower revenues.
C) lower prices and if demand is elastic, lower prices mean lower revenues.
D) higher prices and if demand is inelastic, higher prices mean lower revenues.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 149 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Evidence seems to indicate that the demand for many agricultural products
A) has increased much more than supply over the years.
B) is relatively elastic.
C) is relatively inelastic.
D) is relatively income elastic.
E) b and d
A) has increased much more than supply over the years.
B) is relatively elastic.
C) is relatively inelastic.
D) is relatively income elastic.
E) b and d

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 149 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Studies show that as real income has been rising in the United States,the per-capita demand for food has been increasing by
A) much less, which means the demand for food is income inelastic.
B) much more, which means the demand for food is income elastic.
C) much more, which means the demand for food is income inelastic.
D) as much, which means the demand for food is unit elastic.
E) none of the above
A) much less, which means the demand for food is income inelastic.
B) much more, which means the demand for food is income elastic.
C) much more, which means the demand for food is income inelastic.
D) as much, which means the demand for food is unit elastic.
E) none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 149 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
If the demand curve for agricultural products is inelastic and farmers as a group become more productive,then prices of agricultural goods will __________ and total revenue earned by farmers will __________.
A) decrease; increase
B) decrease; decrease
C) increase; increase
D) increase; decrease
E) We cannot answer this question without knowing how inelastic the demand curve is.
A) decrease; increase
B) decrease; decrease
C) increase; increase
D) increase; decrease
E) We cannot answer this question without knowing how inelastic the demand curve is.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 149 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
With a price elasticity of demand of 0.45,when the price of soybeans falls by 10 percent,the quantity demanded of soybeans rises by approximately _____________ percent.
A) 4.50
B) 45.0
C) 0.45
D) 0.56
A) 4.50
B) 45.0
C) 0.45
D) 0.56

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 149 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
In 2000,farmers in the United States represented approximately what percentage of the population?
A) 8 percent
B) 25 percent
C) 1 percent
D) 5 percent
A) 8 percent
B) 25 percent
C) 1 percent
D) 5 percent

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 149 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Which of the following statements is true?
A) Bad weather isn't always that bad for farmers' incomes.
B) An individual farmer would probably increase his revenues if he experienced good weather and other farmers experienced bad weather.
C) Price elasticity of demand is a relevant factor to a farmer's income.
D) a and b
E) a, b, and c
A) Bad weather isn't always that bad for farmers' incomes.
B) An individual farmer would probably increase his revenues if he experienced good weather and other farmers experienced bad weather.
C) Price elasticity of demand is a relevant factor to a farmer's income.
D) a and b
E) a, b, and c

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 149 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Suppose farmers get together and decide to be less productive.They want to do this so that they can shift the supply curve of farm products leftward and raise the price.They must be assuming that the demand curve between the current price and the higher price is
A) inelastic.
B) elastic.
C) unit elastic.
D) There is not enough information to answer this question.
A) inelastic.
B) elastic.
C) unit elastic.
D) There is not enough information to answer this question.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 149 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
If the demand curve for agricultural products is elastic and farmers as a group become more productive,then prices of agricultural goods will __________ and total revenue earned by farmers will __________.
A) decrease; increase
B) decrease; decrease
C) increase; increase
D) increase; decrease
E) We cannot answer this question without knowing how elastic the demand curve is.
A) decrease; increase
B) decrease; decrease
C) increase; increase
D) increase; decrease
E) We cannot answer this question without knowing how elastic the demand curve is.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 149 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Suppose farmers get together and decide to be less productive.They want to do this so that they can shift the supply curve of farm products leftward and raise the price.What are the thoughts of a profit-maximizing farmer most likely to be once this agreement has been made?
A) If I break the agreement while everyone else holds to it, I can make myself better off.
B) I am happy that we decided to be unproductive; I can't be unproductive by myself.
C) I will definitely hold to the agreement.
D) Everyone will break the agreement but me.
A) If I break the agreement while everyone else holds to it, I can make myself better off.
B) I am happy that we decided to be unproductive; I can't be unproductive by myself.
C) I will definitely hold to the agreement.
D) Everyone will break the agreement but me.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 149 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Suppose 100 bushels of X are produced at a target price of $7 per bushel,but consumers will only buy 100 bushels at $3 a bushel.What is the total deficiency payment to farmers?
A) $400
B) $600
C) $300
D) $100
A) $400
B) $600
C) $300
D) $100

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 149 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Exhibit 39-1
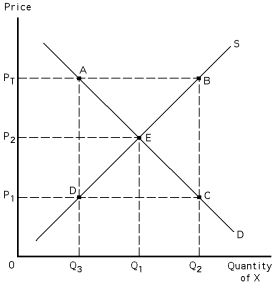
Refer to Exhibit 39-1.Given the target price PT,what is the quantity supplied?
A) Q1
B) Q2
C) Q3
D) Q3 - Q1

Refer to Exhibit 39-1.Given the target price PT,what is the quantity supplied?
A) Q1
B) Q2
C) Q3
D) Q3 - Q1

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 149 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
In the acreage allotment program,a farmer's acreage allotment is sometimes based on a farmer's
A) history of production.
B) income.
C) location.
D) b and c
E) none of the above
A) history of production.
B) income.
C) location.
D) b and c
E) none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 149 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Which of the following is not an effect of an agricultural price support?
A) a surplus
B) fewer exchanges
C) higher prices paid by consumers
D) government purchase and storage of surplus
E) higher-quality products
A) a surplus
B) fewer exchanges
C) higher prices paid by consumers
D) government purchase and storage of surplus
E) higher-quality products

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 149 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Under an acreage allotment program,
A) the government sets a limit on the quantity of a product that a farmer is allowed to bring to market, which is intended to cause farmers to cut back on the number of acres they cultivate.
B) farmers are paid to take part of their land out of cultivation.
C) farmers are given limits as to the number of acres that can be farmed.
D) farmers are paid the difference between the market price of their product and a governmentally determined price that would maintain an established price parity.
E) the government establishes a minimum price that farmers will be paid for their product, which causes the farmers to cut back on the number of acres planted.
A) the government sets a limit on the quantity of a product that a farmer is allowed to bring to market, which is intended to cause farmers to cut back on the number of acres they cultivate.
B) farmers are paid to take part of their land out of cultivation.
C) farmers are given limits as to the number of acres that can be farmed.
D) farmers are paid the difference between the market price of their product and a governmentally determined price that would maintain an established price parity.
E) the government establishes a minimum price that farmers will be paid for their product, which causes the farmers to cut back on the number of acres planted.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 149 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Exhibit 39-1

Refer to Exhibit 39-1.Given the target price of PT,the deficiency payment per unit is
A) PT - P2.
B) PT + P1.
C) PT - P2.
D) PT - P1.

Refer to Exhibit 39-1.Given the target price of PT,the deficiency payment per unit is
A) PT - P2.
B) PT + P1.
C) PT - P2.
D) PT - P1.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 149 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Which of the following combinations of factors comes closest to describing the situation in agriculture?
A) elastic demand for agricultural products and large swings in supply
B) elastic demand for agricultural products and small swings in supply
C) inelastic demand for agricultural products and constant supply
D) inelastic demand for agricultural products and large swings in supply
E) none of the above
A) elastic demand for agricultural products and large swings in supply
B) elastic demand for agricultural products and small swings in supply
C) inelastic demand for agricultural products and constant supply
D) inelastic demand for agricultural products and large swings in supply
E) none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 149 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Exhibit 39-1

Refer to Exhibit 39-1.Given the target price of PT,farmers will receive a total income equal to
A) 0PTBQ2.
B) 0P1CQ2.
C) 0PTAQ3.
D) 0P2EQ1.

Refer to Exhibit 39-1.Given the target price of PT,farmers will receive a total income equal to
A) 0PTBQ2.
B) 0P1CQ2.
C) 0PTAQ3.
D) 0P2EQ1.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 149 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Which combination of factors would lead to large price and total revenue changes?
A) inelastic demand for a product and large swings in supply
B) elastic demand for a product and small swings in supply
C) inelastic demand for a product and constant supply
D) a and c
E) none of the above
A) inelastic demand for a product and large swings in supply
B) elastic demand for a product and small swings in supply
C) inelastic demand for a product and constant supply
D) a and c
E) none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 149 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
If the government establishes a price floor for agricultural products,then
A) consumers will pay a lower price for the products.
B) consumers will increase the quantity that they are willing to consume.
C) farmers will want to decrease their production.
D) the government will need to purchase the resulting surplus.
E) all of the above
A) consumers will pay a lower price for the products.
B) consumers will increase the quantity that they are willing to consume.
C) farmers will want to decrease their production.
D) the government will need to purchase the resulting surplus.
E) all of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 149 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Why is bad weather sometimes good news for farmers?
A) Bad weather shifts the supply curve of agricultural products leftward, driving up price and total revenue (assuming demand is inelastic).
B) Bad weather shifts the supply curve of agricultural products leftward, driving down price, and raising total revenue (assuming demand is elastic).
C) Bad weather increases the demand for and price of agricultural products.
D) Bad weather increases both the demand for and supply of agricultural products.
A) Bad weather shifts the supply curve of agricultural products leftward, driving up price and total revenue (assuming demand is inelastic).
B) Bad weather shifts the supply curve of agricultural products leftward, driving down price, and raising total revenue (assuming demand is elastic).
C) Bad weather increases the demand for and price of agricultural products.
D) Bad weather increases both the demand for and supply of agricultural products.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 149 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
In agriculture during much of the 20th century,supply grew more than demand.Which two farm problems are these?
A) the high-productivity problem and the income elasticity problem
B) the low-productivity problem and the income inelasticity problem
C) the high-productivity problem and the income inelasticity problem
D) the low-productivity problem and the income elasticity problem
E) none of the above
A) the high-productivity problem and the income elasticity problem
B) the low-productivity problem and the income inelasticity problem
C) the high-productivity problem and the income inelasticity problem
D) the low-productivity problem and the income elasticity problem
E) none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 149 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Which of the following increases the quantity supplied of agricultural goods?
A) acreage allotments
B) assigning market quotas
C) agricultural price supports
D) a, b, and c
A) acreage allotments
B) assigning market quotas
C) agricultural price supports
D) a, b, and c

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 149 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Which of the following government agricultural policies is not aimed at restricting supply?
A) price supports
B) acreage allotments
C) market quotas
D) paying farmers not to produce
A) price supports
B) acreage allotments
C) market quotas
D) paying farmers not to produce

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 149 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
One unintended consequence of the various attempts to restrict farm acreage was that
A) output generally decreased, price increased, and farmers earned higher incomes.
B) individual farmers intensified their efforts to harvest crops from the land still under cultivation.
C) farmers' incomes remained constant in real terms.
D) the land that was set aside became less productive.
A) output generally decreased, price increased, and farmers earned higher incomes.
B) individual farmers intensified their efforts to harvest crops from the land still under cultivation.
C) farmers' incomes remained constant in real terms.
D) the land that was set aside became less productive.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 149 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Under a marketing quota system,
A) the government sets a limit on the quantity of a product that a farmer is allowed to bring to market.
B) farmers are paid to take part of their land out of cultivation.
C) farmers are given limits as to the number of acres that can be used to produce a particular product.
D) farmers are paid the difference between the market price of their product and a governmentally determined price that would maintain an established price parity.
E) the government establishes a minimum price that farmers will be paid for their product, which causes the farmers to cut back on the number of acres planted.
A) the government sets a limit on the quantity of a product that a farmer is allowed to bring to market.
B) farmers are paid to take part of their land out of cultivation.
C) farmers are given limits as to the number of acres that can be used to produce a particular product.
D) farmers are paid the difference between the market price of their product and a governmentally determined price that would maintain an established price parity.
E) the government establishes a minimum price that farmers will be paid for their product, which causes the farmers to cut back on the number of acres planted.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 149 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
If the demand for a particular agricultural product is highly elastic and bad weather causes the supply to decrease,then we would expect the price of agricultural products to
A) decrease and farmers' revenues to decrease.
B) increase and the demand to decrease.
C) increase while farmers' revenues decrease significantly.
D) increase by a large percentage while farmers' revenues decrease only slightly.
A) decrease and farmers' revenues to decrease.
B) increase and the demand to decrease.
C) increase while farmers' revenues decrease significantly.
D) increase by a large percentage while farmers' revenues decrease only slightly.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 149 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Under the target price program,
A) the government ends up buying the surplus product that results.
B) taxpayers pay the difference between the price consumers pay and the target price.
C) deficiency payments are made to both rich and poor farmers.
D) the surplus that results is sometimes dumped or otherwise wasted.
E) b and c
A) the government ends up buying the surplus product that results.
B) taxpayers pay the difference between the price consumers pay and the target price.
C) deficiency payments are made to both rich and poor farmers.
D) the surplus that results is sometimes dumped or otherwise wasted.
E) b and c

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 149 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
If the government establishes a target price for particular agricultural products,then
A) the government sets a limit on the quantity of a product that a farmer is allowed to bring to market.
B) farmers are paid to take part of their land out of cultivation, the intent being to reduce supply and raise price to the target level.
C) farmers are given limits as to the number of acres that can be used to produce a particular product, the intent being to reduce supply and raise price to the target level.
D) farmers are paid the difference between the market price of their product and a government-determined price.
E) the government establishes a minimum price that farmers will be paid for their product, which causes the farmers to cut back on the number of acres planted in certain products, which, in turn, causes the price to rise to the target level.
A) the government sets a limit on the quantity of a product that a farmer is allowed to bring to market.
B) farmers are paid to take part of their land out of cultivation, the intent being to reduce supply and raise price to the target level.
C) farmers are given limits as to the number of acres that can be used to produce a particular product, the intent being to reduce supply and raise price to the target level.
D) farmers are paid the difference between the market price of their product and a government-determined price.
E) the government establishes a minimum price that farmers will be paid for their product, which causes the farmers to cut back on the number of acres planted in certain products, which, in turn, causes the price to rise to the target level.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 149 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Suppose the government decides that milk producers are not earning a high enough price for their milk to maintain an adequate standard of living and that the solution to the problem is to guarantee the milk producers a minimum price.We would expect that
A) consumers will have to pay a higher price per gallon of milk and will not be able to consume as much as they did before.
B) the government will have to purchase the surplus milk on the market and then find a means of storing this milk.
C) the dairy farmers will enjoy a higher standard of living at the expense of taxpayers and consumers.
D) all of the above
A) consumers will have to pay a higher price per gallon of milk and will not be able to consume as much as they did before.
B) the government will have to purchase the surplus milk on the market and then find a means of storing this milk.
C) the dairy farmers will enjoy a higher standard of living at the expense of taxpayers and consumers.
D) all of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 149 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
In general,agricultural price supports
A) raise food prices.
B) have no impact on food prices.
C) are designed to lower food prices.
D) c and d
A) raise food prices.
B) have no impact on food prices.
C) are designed to lower food prices.
D) c and d

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 149 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
A shift of the supply curve for farm products to the right in a price inelastic region of the demand curve for farm products
A) reduces price and total revenue.
B) increases price and reduces total revenue.
C) reduces price and increases total revenue.
D) increases prices and total revenue.
A) reduces price and total revenue.
B) increases price and reduces total revenue.
C) reduces price and increases total revenue.
D) increases prices and total revenue.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 149 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
Exhibit 39-2
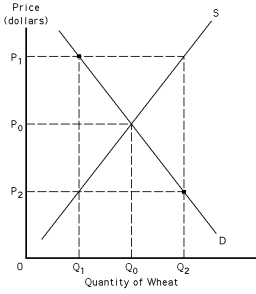
Refer to Exhibit 39-2.If P? is a price support,the quantity of wheat purchased by the market would be equal to
A) Q2.
B) Q0.
C) Q1.
D) Q2 - Q1.
E) Q1 - Q0.

Refer to Exhibit 39-2.If P? is a price support,the quantity of wheat purchased by the market would be equal to
A) Q2.
B) Q0.
C) Q1.
D) Q2 - Q1.
E) Q1 - Q0.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 149 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
Supply-restricting policies are intended to shift the
A) supply curve to the left.
B) supply curve to the right.
C) demand curve to the left.
D) demand curve to the right.
E) b and d
A) supply curve to the left.
B) supply curve to the right.
C) demand curve to the left.
D) demand curve to the right.
E) b and d

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 149 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Agricultural price supports refer to
A) minimum prices set by the government on certain farm products.
B) maximum prices set by the government on certain farm products.
C) supply-restricting policies imposed by the government on certain farm products.
D) b and c
E) none of the above
A) minimum prices set by the government on certain farm products.
B) maximum prices set by the government on certain farm products.
C) supply-restricting policies imposed by the government on certain farm products.
D) b and c
E) none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 149 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
The acreage allotment program involves
A) no direct payments to farmers.
B) direct payments to farmers.
C) the government leasing land to farmers that is to be cultivated by the farmers.
D) the government leasing land from farmers that is to be cultivated by the government.
E) none of the above
A) no direct payments to farmers.
B) direct payments to farmers.
C) the government leasing land to farmers that is to be cultivated by the farmers.
D) the government leasing land from farmers that is to be cultivated by the government.
E) none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 149 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
Increased productivity in the agricultural sector has __________ the output and __________ the prices of agricultural goods.
A) increased; reduced
B) increased; increased
C) decreased; reduced
D) decreased; increased
E) had no impact on; had no impact on
A) increased; reduced
B) increased; increased
C) decreased; reduced
D) decreased; increased
E) had no impact on; had no impact on

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 149 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
Exhibit 39-2

Refer to Exhibit 39-2.If P? is a price support,the cost of the price support program to the government is
A) P1 x Q2.
B) P1 x (Q2 - Q0).
C) P1 x (Q0 - Q1).
D) P1 x (Q2 - Q1).
E) none of the above

Refer to Exhibit 39-2.If P? is a price support,the cost of the price support program to the government is
A) P1 x Q2.
B) P1 x (Q2 - Q0).
C) P1 x (Q0 - Q1).
D) P1 x (Q2 - Q1).
E) none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 149 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
The effect of a drought on the price of an agricultural product will be greater the more __________ the demand for the agricultural product.
A) price inelastic
B) price elastic
C) income elastic
D) a and c
E) b and c
A) price inelastic
B) price elastic
C) income elastic
D) a and c
E) b and c

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 149 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
Exhibit 39-2

Refer to Exhibit 39-2.If P? is a price support,the quantity of wheat purchased by the government would be equal to
A) Q0 - Q1.
B) Q2 - Q1.
C) Q2 - Q0.
D) Q2.
E) Q1.

Refer to Exhibit 39-2.If P? is a price support,the quantity of wheat purchased by the government would be equal to
A) Q0 - Q1.
B) Q2 - Q1.
C) Q2 - Q0.
D) Q2.
E) Q1.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 149 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
Under the target price system,
A) supply is restricted.
B) consumers must pay the target price.
C) payments are made to the government when the price paid by consumers rises above the target price.
D) farmers are paid a deficiency payment if the market price for their goods is below the target price.
E) a and c
A) supply is restricted.
B) consumers must pay the target price.
C) payments are made to the government when the price paid by consumers rises above the target price.
D) farmers are paid a deficiency payment if the market price for their goods is below the target price.
E) a and c

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 149 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
Supply-restricting policies are intended to __________ prices and __________ farmers' revenues.
A) lower; increase
B) lower; reduce
C) raise; increase
D) raise; reduce
A) lower; increase
B) lower; reduce
C) raise; increase
D) raise; reduce

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 149 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
Exhibit 39-1

Refer to Exhibit 39-1.At a support price of PT,private sector spending on this good equals
A) PT x Q3.
B) PT x Q2.
C) P1 x Q3.
D) P1 x Q2.

Refer to Exhibit 39-1.At a support price of PT,private sector spending on this good equals
A) PT x Q3.
B) PT x Q2.
C) P1 x Q3.
D) P1 x Q2.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 149 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
Exhibit 39-1

Refer to Exhibit 39-1.Given the target price PT,the total deficiency payment made by the government is the area of
A) 0P1CQ2.
B) 0PTBQ2.
C) PTBCP1.
D) PTBEP2.

Refer to Exhibit 39-1.Given the target price PT,the total deficiency payment made by the government is the area of
A) 0P1CQ2.
B) 0PTBQ2.
C) PTBCP1.
D) PTBEP2.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 149 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
An increase in productivity in the agricultural sector when the demand curve is inelastic results in __________ prices for consumers and __________ revenues for farmers
A) higher; lower
B) higher; higher
C) lower; lower
D) lower; higher
E) no change in; no change in
A) higher; lower
B) higher; higher
C) lower; lower
D) lower; higher
E) no change in; no change in

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 149 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
Exhibit 39-2

Refer to Exhibit 39-2.Given a target price of P?,what is the total deficiency payment made by the government?
A) (P1 - P2) x Q2
B) (P1 - P0) x Q2
C) P1 x Q1
D) P0 x Q0

Refer to Exhibit 39-2.Given a target price of P?,what is the total deficiency payment made by the government?
A) (P1 - P2) x Q2
B) (P1 - P0) x Q2
C) P1 x Q1
D) P0 x Q0

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 149 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
Exhibit 39-1

Refer to Exhibit 39-1.At the support price of PT,how many units of the good must the government buy and store?
A) Q1
B) Q3
C) Q1 - Q3
D) Q2 - Q3

Refer to Exhibit 39-1.At the support price of PT,how many units of the good must the government buy and store?
A) Q1
B) Q3
C) Q1 - Q3
D) Q2 - Q3

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 149 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
Increased productivity in the agricultural sector in conjunction with an inelastic demand curve for agricultural goods has caused a(n)__________ in output,a(n)__________ in price,and __________ revenues for farmers.
A) increase; decrease; higher
B) increase; decrease; lower
C) decrease; increase; higher
D) decrease; increase; lower
E) increase; increase; higher
A) increase; decrease; higher
B) increase; decrease; lower
C) decrease; increase; higher
D) decrease; increase; lower
E) increase; increase; higher

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 149 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
Exhibit 39-2

Refer to Exhibit 39-2.Given a target price of P?,what price does the consumer pay?
A) P1.
B) P0.
C) P2.
D) a price not shown on the diagram.

Refer to Exhibit 39-2.Given a target price of P?,what price does the consumer pay?
A) P1.
B) P0.
C) P2.
D) a price not shown on the diagram.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 149 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
A decrease in the supply of an agricultural product will increase the total revenue of farmers if the demand for the agricultural product is
A) income elastic.
B) income inelastic.
C) price elastic.
D) price inelastic.
E) none of the above
A) income elastic.
B) income inelastic.
C) price elastic.
D) price inelastic.
E) none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 149 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
Exhibit 39-4
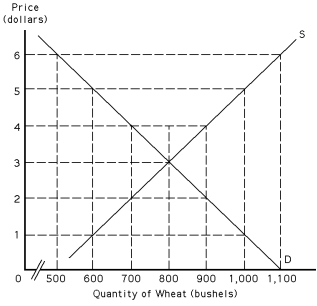
Refer to Exhibit 39-4.If the government sets a target price at $5 per bushel,the quantity of wheat produced will be
A) 600 bushels.
B) 700 bushels.
C) 800 bushels.
D) 900 bushels.
E) 1,000 bushels.

Refer to Exhibit 39-4.If the government sets a target price at $5 per bushel,the quantity of wheat produced will be
A) 600 bushels.
B) 700 bushels.
C) 800 bushels.
D) 900 bushels.
E) 1,000 bushels.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 149 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
An increase in productivity in the agricultural sector in conjunction with an income inelastic demand for farm products
A) causes prices to fall.
B) causes prices to rise.
C) causes prices to remain constant.
D) may cause prices to rise, fall, or remain the same, depending upon the relative shifts in the supply and demand curves.
A) causes prices to fall.
B) causes prices to rise.
C) causes prices to remain constant.
D) may cause prices to rise, fall, or remain the same, depending upon the relative shifts in the supply and demand curves.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 149 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
Exhibit 39-4

Refer to Exhibit 39-4.The government feels that the present level of farmers' total revenues is insufficient to support a reasonable standard of living and wants to raise it to exactly $3,000.This can be achieved by
A) restricting supply so that price increases to $4.
B) a price support of $5.
C) restricting supply so that price increases to $5.
D) any of the above
E) none of the above

Refer to Exhibit 39-4.The government feels that the present level of farmers' total revenues is insufficient to support a reasonable standard of living and wants to raise it to exactly $3,000.This can be achieved by
A) restricting supply so that price increases to $4.
B) a price support of $5.
C) restricting supply so that price increases to $5.
D) any of the above
E) none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 149 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
Exhibit 39-3
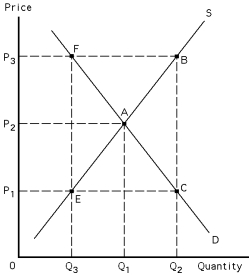
Refer to Exhibit 39-3.If P? is a target price,the deficiency payment per unit is
A) P1.
B) P2.
C) P3.
D) P3 - P1.
E) P3 - P2.

Refer to Exhibit 39-3.If P? is a target price,the deficiency payment per unit is
A) P1.
B) P2.
C) P3.
D) P3 - P1.
E) P3 - P2.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 149 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
Exhibit 39-4

Refer to Exhibit 39-4.At the competitive equilibrium price and quantity,the total revenue of wheat farmers will be
A) $1,400.
B) $1,800.
C) $2,400.
D) $2,800.
E) $5,000.

Refer to Exhibit 39-4.At the competitive equilibrium price and quantity,the total revenue of wheat farmers will be
A) $1,400.
B) $1,800.
C) $2,400.
D) $2,800.
E) $5,000.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 149 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
Exhibit 39-4

Refer to Exhibit 39-4.The price support of $6 per bushel would cost the government
A) $600.
B) $3,000.
C) $3,600.
D) $4,800.
E) $6,600.

Refer to Exhibit 39-4.The price support of $6 per bushel would cost the government
A) $600.
B) $3,000.
C) $3,600.
D) $4,800.
E) $6,600.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 149 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
Exhibit 39-3

Refer to Exhibit 39-3.If P? is a target price,the quantity supplied is
A) Q1.
B) Q2.
C) Q3.
D) Q2 - Q3.
E) Q1 - Q3.

Refer to Exhibit 39-3.If P? is a target price,the quantity supplied is
A) Q1.
B) Q2.
C) Q3.
D) Q2 - Q3.
E) Q1 - Q3.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 149 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
A government agricultural policy in which a guaranteed price is set and no surplus is created is the
A) marketing quota system.
B) acreage allotment program.
C) price support program.
D) target price system.
A) marketing quota system.
B) acreage allotment program.
C) price support program.
D) target price system.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 149 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
The demand for farm goods is income inelastic if the percentage change in quantity demanded is __________ the percentage change in __________.
A) greater than; income
B) equal to; income
C) less than; income
D) greater than; revenue
E) less than; revenue
A) greater than; income
B) equal to; income
C) less than; income
D) greater than; revenue
E) less than; revenue

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 149 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
Exhibit 39-4

Refer to Exhibit 39-4.The price elasticity of demand for wheat between the prices of $3 and $4 is
A) equal to 1.
B) less than 1.
C) greater than 1.
D) equal to 100.
E) c and d

Refer to Exhibit 39-4.The price elasticity of demand for wheat between the prices of $3 and $4 is
A) equal to 1.
B) less than 1.
C) greater than 1.
D) equal to 100.
E) c and d

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 149 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
A government agricultural policy in which a mandated minimum price is set is the
A) marketing quota system.
B) acreage allotment program.
C) price support program.
D) target price system.
E) paying farmers not to produce system.
A) marketing quota system.
B) acreage allotment program.
C) price support program.
D) target price system.
E) paying farmers not to produce system.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 149 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
Suppose that both the demand for and supply of agricultural products increases. If the increase in the supply of agricultural products is greater than the increase in demand,prices of agricultural products
A) increase.
B) decrease.
C) remain the same.
D) may increase, decrease, or remain the same.
A) increase.
B) decrease.
C) remain the same.
D) may increase, decrease, or remain the same.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 149 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
A government agricultural policy that restricts output by limiting the number of farm acres that can be used to produce a particular crop is the
A) marketing quota system.
B) acreage allotment program.
C) price support program.
D) target price system.
E) paying farmers not to produce system.
A) marketing quota system.
B) acreage allotment program.
C) price support program.
D) target price system.
E) paying farmers not to produce system.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 149 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
Exhibit 39-3

Refer to Exhibit 39-3.If P? is a target price,the total deficiency payment that government makes to farmers is
A) P2 x Q3.
B) P3 x Q3.
C) (P3 - P1) x Q1.
D) (P3 - P1) x Q2.
E) (P3 - P2) x Q3.

Refer to Exhibit 39-3.If P? is a target price,the total deficiency payment that government makes to farmers is
A) P2 x Q3.
B) P3 x Q3.
C) (P3 - P1) x Q1.
D) (P3 - P1) x Q2.
E) (P3 - P2) x Q3.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 149 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
When the government institutes a target price,
A) a surplus is created.
B) consumers must pay the target price.
C) the farmer receives a deficiency payment if the market price is below the target price.
D) the farmer receives a deficiency payment if the market price is above the target price.
E) all of the above
A) a surplus is created.
B) consumers must pay the target price.
C) the farmer receives a deficiency payment if the market price is below the target price.
D) the farmer receives a deficiency payment if the market price is above the target price.
E) all of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 149 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
A government agricultural policy that sets a limit on the quantity of a product that a farmer is allowed to bring to market is the
A) marketing quota system.
B) acreage allotment program.
C) price support program.
D) target price system.
E) paying farmers not to produce system.
A) marketing quota system.
B) acreage allotment program.
C) price support program.
D) target price system.
E) paying farmers not to produce system.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 149 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
Exhibit 39-3

Refer to Exhibit 39-3.If P? is a target price,the price at which output will be purchased is
A) P1.
B) P2.
C) P3.
D) P3 - P2.
E) P1 - P2.

Refer to Exhibit 39-3.If P? is a target price,the price at which output will be purchased is
A) P1.
B) P2.
C) P3.
D) P3 - P2.
E) P1 - P2.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 149 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
If the demand for agricultural products is price inelastic and the supply is dependent upon weather conditions,then
A) price changes are likely to be small, and farm revenues are likely to be highly volatile.
B) price changes are likely to be large, and farm revenues are likely to be highly volatile.
C) prices are likely to be constant, and farm revenues are likely to be constant.
D) prices are likely to be constant, and farm revenues are likely to be highly volatile.
E) price changes are likely to be small, and farm revenues are likely to be constant.
A) price changes are likely to be small, and farm revenues are likely to be highly volatile.
B) price changes are likely to be large, and farm revenues are likely to be highly volatile.
C) prices are likely to be constant, and farm revenues are likely to be constant.
D) prices are likely to be constant, and farm revenues are likely to be highly volatile.
E) price changes are likely to be small, and farm revenues are likely to be constant.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 149 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
Exhibit 39-3

Refer to Exhibit 39-3.If P? is a price support,the amount sold on private markets is
A) Q1.
B) Q2.
C) Q3.
D) Q2 - Q3.
E) Q1 - Q3.

Refer to Exhibit 39-3.If P? is a price support,the amount sold on private markets is
A) Q1.
B) Q2.
C) Q3.
D) Q2 - Q3.
E) Q1 - Q3.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 149 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
Exhibit 39-4

Refer to Exhibit 39-4.The price support of $6 per bushel results in private citizens spending __________ on wheat.
A) $600
B) $3,000
C) $3,600
D) $4,800
E) $6,600

Refer to Exhibit 39-4.The price support of $6 per bushel results in private citizens spending __________ on wheat.
A) $600
B) $3,000
C) $3,600
D) $4,800
E) $6,600

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 149 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



