Deck 10: Public Goods and the Role of Government
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/36
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 10: Public Goods and the Role of Government
1
A pure public good is both _____ and _____
Public goods:
Public good refers to the product that cannot reduce the consumption of one person due to the consumption of other people. This is known as non-rivalries good. And the provision of public good is available for all the people (Non excludability).
Therefore, the answer is non-rival and non-excludable.
Public good refers to the product that cannot reduce the consumption of one person due to the consumption of other people. This is known as non-rivalries good. And the provision of public good is available for all the people (Non excludability).
Therefore, the answer is non-rival and non-excludable.
2
[Related to Application 10.1 on page 201] Read Application 10.1 carefully. Many Cubs games are broadcast for free on television. Why, men, do you suppose the Cubs were so concerned about people watching their games for free from nearby apartment vbuildings? Would tl1e Cubs's strategy have been as successful if the neighboring buildings were 10 stories taller?
Concerned for Cubs games:
The Cubs were much concerned because the fans who were watching the game from the street were willing to pay to see the game. Since there were limited seats in the Cubs' small park, many of them couldn't find seats to watch the cub's game. The manager of the cub's decided they didn't want to prevent people in apartments from watching the game. Instead, they wanted to generate a piece of the revenue.
Strategy of generating revenue:
The Cubs wanted to knock into that revenue through the cub's game. The Cubs might have had a harder time excluding the fans if the buildings were 10 stories tall; if they built the barrier more to stop watching the game from outside, then it will cost more and the barriers would have been much more difficult to erect which increases further cost.
Thus, the main concern of cub's form manager was to add some more revenue into account and allow people to watch games from apartments nearby stadium.
The Cubs were much concerned because the fans who were watching the game from the street were willing to pay to see the game. Since there were limited seats in the Cubs' small park, many of them couldn't find seats to watch the cub's game. The manager of the cub's decided they didn't want to prevent people in apartments from watching the game. Instead, they wanted to generate a piece of the revenue.
Strategy of generating revenue:
The Cubs wanted to knock into that revenue through the cub's game. The Cubs might have had a harder time excluding the fans if the buildings were 10 stories tall; if they built the barrier more to stop watching the game from outside, then it will cost more and the barriers would have been much more difficult to erect which increases further cost.
Thus, the main concern of cub's form manager was to add some more revenue into account and allow people to watch games from apartments nearby stadium.
3
Consider this copy of your textbook: It is difficult for more than one person at a time to read it. This means that your textbook is a(n) _____ good.
A) Rival
B) Nonrival
C) Excludable
D) Nonexcludable
A) Rival
B) Nonrival
C) Excludable
D) Nonexcludable
Non-rival good:
Non rival goods refer to those goods that do not reduce the consumption of one person due to the consumption of other people. Therefore, option "b" is incorrect.
Excludable:
Excludable goods refer to those goods that are possible to exclude people from the consumption or benefit of the good. The consumer has to pay the price in order to avail the goods. Therefore, option "c" is incorrect.
Non-excludable good:
Non excludable goods refer to those goods that are impossible to exclude people from the consumption or benefit of the good. People who are not paying for the good will enjoy the benefit. Therefore, option "d" is incorrect.
Rival good:
Rival goods refer to those goods that reduce the consumption of one person due to the consumption of other people.
Therefore, option " a " is the correct answer.
Non rival goods refer to those goods that do not reduce the consumption of one person due to the consumption of other people. Therefore, option "b" is incorrect.
Excludable:
Excludable goods refer to those goods that are possible to exclude people from the consumption or benefit of the good. The consumer has to pay the price in order to avail the goods. Therefore, option "c" is incorrect.
Non-excludable good:
Non excludable goods refer to those goods that are impossible to exclude people from the consumption or benefit of the good. People who are not paying for the good will enjoy the benefit. Therefore, option "d" is incorrect.
Rival good:
Rival goods refer to those goods that reduce the consumption of one person due to the consumption of other people.
Therefore, option " a " is the correct answer.
4
Four people want to commission a beautiful statue to grace their neighborhood. The difficulties they experience in getting one another to commit to paying for the statue are best described as ______.
A) Property rights
B) Transactions costs
C) Incongruent incentives
D) Eminent domain
A) Property rights
B) Transactions costs
C) Incongruent incentives
D) Eminent domain

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 36 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Consider this copy of your textbook: If your annoying roommate, who didn't buy the book, keeps trying to read your copy, you can prevent it by hiding it or locking it away. This means your textbook is a(n) ____ good.
A) Rival
B) Nonrival
C) Excludable
D) Nonexcludable
A) Rival
B) Nonrival
C) Excludable
D) Nonexcludable

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 36 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
In the case of public goods, the ability to free ride on the efforts of others is an example of _______.
A) low transactions costs
B) insecure property rights
C) the taxing power of government
D) poor cost-benefit analysis
A) low transactions costs
B) insecure property rights
C) the taxing power of government
D) poor cost-benefit analysis

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 36 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Based on your answers to problems 1 and 2, it is likely that your textbook is a _____
A) Pure private good
B) Pure public good
C) Common pool resource
D) Club good
Problem 1:
Consider this copy of your textbook: It is difficult for more than one person at a time to read it. This means that your textbook is a(n) _____ good.
A) Rival
B) Nonrival
C) Excludable
D) Nonexcludable
Problem 2:
Consider this copy of your textbook: If your annoying roommate, who didn't buy the book, keeps trying to read your copy, you can prevent it by hiding it or locking it away. This means your textbook is a(n) ____ good.
A) Rival
B) Nonrival
C) Excludable
D) Nonexcludable
A) Pure private good
B) Pure public good
C) Common pool resource
D) Club good
Problem 1:
Consider this copy of your textbook: It is difficult for more than one person at a time to read it. This means that your textbook is a(n) _____ good.
A) Rival
B) Nonrival
C) Excludable
D) Nonexcludable
Problem 2:
Consider this copy of your textbook: If your annoying roommate, who didn't buy the book, keeps trying to read your copy, you can prevent it by hiding it or locking it away. This means your textbook is a(n) ____ good.
A) Rival
B) Nonrival
C) Excludable
D) Nonexcludable

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 36 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Explain the role that transactions costs play in public goods problems.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 36 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
If you wish, you can subscribe to the Netflix streaming service. Netflix streaming can be characterized as ______.
A) Rival and excludable
B) Nonrival and nonexcludable
C) Rival and nonexcludable
D) Nonrival and excludable
A) Rival and excludable
B) Nonrival and nonexcludable
C) Rival and nonexcludable
D) Nonrival and excludable

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 36 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Which characteristic of a pure public good is linked to poorly defined property rights? Which is not? Explain both of your answers.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 36 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Based on your answer to problem, Netflix streaming can best be categorized as a _______.
A) Pure private good
B) Pure public good
C) Common pool resource
D) Club good
Problem:
If you wish, you can subscribe to the Netflix streaming service. Netflix streaming can be characterized as ______.
A) Rival and excludable
B) Nonrival and nonexcludable
C) Rival and nonexcludable
D) Nonrival and excludable
A) Pure private good
B) Pure public good
C) Common pool resource
D) Club good
Problem:
If you wish, you can subscribe to the Netflix streaming service. Netflix streaming can be characterized as ______.
A) Rival and excludable
B) Nonrival and nonexcludable
C) Rival and nonexcludable
D) Nonrival and excludable

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 36 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Explain, referring to poorly defined property rights, the parallels between pollution problems and the public goods problem.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 36 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Which of the following best meets the criteria for being a pure public good?
A) A city swimming pool
B) A fireworks show
C) A theatre performance of Rent
D) An iPod
A) A city swimming pool
B) A fireworks show
C) A theatre performance of Rent
D) An iPod

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 36 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
A pure public good ______.
A) Is any good that is provided by government
B) Will never be provided by individuals acting on their own initiative
C) Both (a) and (b) are true.
D) Neither (a) nor (b) is true.
A) Is any good that is provided by government
B) Will never be provided by individuals acting on their own initiative
C) Both (a) and (b) are true.
D) Neither (a) nor (b) is true.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 36 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Explain, using the terminology developed in this section, why the aurora borealis (the Northern Lights) is different from a city swimming pool. Which best meets the criteria of a pure public good? What type of good is the other good?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 36 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Government typically solves the free rider issue by using its ______.
A) Power of eminent domain
B) Ability to print money
C) Power of taxation
D) Ability to borrow money without paying interest
A) Power of eminent domain
B) Ability to print money
C) Power of taxation
D) Ability to borrow money without paying interest

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 36 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Come up with one fresh example of each of the four types of goods discussed in this section: pure private goods, pure public goods, club goods, and common pool resources. Explain your reasoning, being sure to discuss for each good the criteria of rivalry and excludability.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 36 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
To maximize the economic pie, government _______.
A) Should provide all possible pure public goods
B) Should provide only public goods whose benefits outweigh their costs
C) Should provide only public goods whose costs outweigh their benefits
D) Should not provide any public goods
A) Should provide all possible pure public goods
B) Should provide only public goods whose benefits outweigh their costs
C) Should provide only public goods whose costs outweigh their benefits
D) Should not provide any public goods

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 36 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
A person who receives me benefits of a public good without bearing a proportional share of the costs is known as a(n) ______.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 36 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Club goods and common pool resources are neither purely private goods nor purely public goods. Explain why the government may have a more compelling economic interest in intervening in the market for common pool resources than in the market for club goods.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 36 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
If private individuals are the only producers of a pure public good, those individuals are likely to produce less of it than is socially desirable. This outcome is known as ______.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 36 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
The federal government created the interstate highway system. That road network is largely nonrival, and the government has chosen to make it available to all. Suppose the government has the choice of paying for the maintenance and upkeep of the highway system with a tax on gasoline or, alternatively, with income tax. Which source would you recommend? Why?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 36 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
The free-rider problem arises because pure public goods are ______.
A) Rival
B) Nonrival
C) Excludable
D) Nonexcludable
A) Rival
B) Nonrival
C) Excludable
D) Nonexcludable

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 36 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Stephanie was shocked to discover that the federal government charges an entry fee to view the Grand Canyon. "It's everyone's property. I ought to be able to view it for free. The government should pay for it like it pays for everything else-with tax dollars!" Argue in favor of using an entry fee to pay for the upkeep and personnel needed to maintain the Grand Canyon.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 36 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
A good that is rival and excludable is known as a(n) ______.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 36 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Because of the opportunity for free ridership mat pure public goods present, private individuals probably _______.
A) Provide the right amount of pure public goods
B) Provide fewer public goods than the benevolent social planner would like to see
C) Provide more public goods than me benevolent social planner would like to see
A) Provide the right amount of pure public goods
B) Provide fewer public goods than the benevolent social planner would like to see
C) Provide more public goods than me benevolent social planner would like to see

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 36 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
[Related to Application 10.2 on page 206] The current farm bill includes a number of different subsidies for producers of mohair, a yarn made from the wool of the Angora goat, amounting to some $20 million each year. Taxpayers fund those subsidies. Economists know that the mohair subsidy makes Americans poorer on the whole. Apply Mancur Olson's explanation of the power of organized interests to explain why it is so difficult for U.S. taxpayers to end the mohair subsidy. Your explanation should incorporate the term transactions costs.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 36 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
If it's hard to prevent people from enjoying the benefits of a particular good, that good is said to be ________.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 36 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Mai and Rafe are considering contributing to a project. Their payoffs are shown in the following payoff matrix:
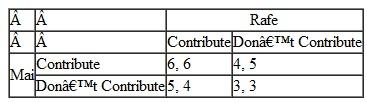 Will the public goods problem prevent this project from being completed? Explain why or why not.
Will the public goods problem prevent this project from being completed? Explain why or why not.
 Will the public goods problem prevent this project from being completed? Explain why or why not.
Will the public goods problem prevent this project from being completed? Explain why or why not.
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 36 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
[Related to Application 10.2 on page 206] Read Application 10.2 carefully. Then describe a bargain between consumers/taxpayers and sugar producers that would (a) end the quota and (b) be mutually beneficial to both parties. The bargain you describe should incorporate numbers from the application. Why is such a bargain unlikely to be reached in real life?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 36 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Because the enjoyment you get from watching a lunar eclipse doesn't diminish when others watch, too, the lunar eclipse is said to be _____

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 36 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Do you agree or disagree with the following statement: "The real problem with pure public goods is that they're nonrival." Explain your reasoning.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 36 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
[Related to Application 10.3 on page 209] Read Application 10.3 carefully. Can you come up with an example of a pure private good that your government provides? Or perhaps a club good? Hypothesize a likely rationale for the government provision of the good you list.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 36 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
A club good is a good that is nonrival and _____

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 36 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Homeowners in many rural areas obtain fire protection by voluntarily enrolling in, and paying a fee for, a rural fire service. In 2010, Gene Cranick's rural Tennessee home caught fire. The fire service sent its trucks to Cranick's neighborhood, but because Cranick had not paid his $7 5 annual fee, firefighters simply watched his home burn to the ground. When the desperate Cranick offered to enroll in the fire service on the spot, he was turned away. Would the benevolent social planner have approved of the fire service's decision to let Cranick's home burn? Was the fire department's refusal to extinguish the fire and accept Cranick's enrollment a good decision for society? Does your answer depend on whether you consider the short run or the long run? Explain.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 36 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Consider the case of fire protection discussed in problem. To what extent is fire protection a public good? To what extent is it a private good? Can you make a case for the public provision of fire protection? Can you make a case for private fire protection? Does your answer depend on whether the people being served are rural or urban? Explain.
Problem:
Homeowners in many rural areas obtain fire protection by voluntarily enrolling in, and paying a fee for, a rural fire service. In 2010, Gene Cranick's rural Tennessee home caught fire. The fire service sent its trucks to Cranick's neighborhood, but because Cranick had not paid his $7 5 annual fee, firefighters simply watched his home burn to the ground. When the desperate Cranick offered to enroll in the fire service on the spot, he was turned away. Would the benevolent social planner have approved of the fire service's decision to let Cranick's home burn? Was the fire department's refusal to extinguish the fire and accept Cranick's enrollment a good decision for society? Does your answer depend on whether you consider the short run or the long run? Explain.
Problem:
Homeowners in many rural areas obtain fire protection by voluntarily enrolling in, and paying a fee for, a rural fire service. In 2010, Gene Cranick's rural Tennessee home caught fire. The fire service sent its trucks to Cranick's neighborhood, but because Cranick had not paid his $7 5 annual fee, firefighters simply watched his home burn to the ground. When the desperate Cranick offered to enroll in the fire service on the spot, he was turned away. Would the benevolent social planner have approved of the fire service's decision to let Cranick's home burn? Was the fire department's refusal to extinguish the fire and accept Cranick's enrollment a good decision for society? Does your answer depend on whether you consider the short run or the long run? Explain.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 36 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



