Deck 21: Productivity and Growth
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/19
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 21: Productivity and Growth
1
INFLATION Why do people dislike inflation?
People dislike Inflation
To attain rapid growth and sustainable development, inflation is a cost that an economy should pay for. Thus, inflation and growth of an economy go hand in hand.If the actual inflation rate equals the anticipated inflation rate, then the impact of inflation on the economy is at a minimum and at this level, real growth is high. But, inflation can be evil when unanticipated inflation is high and profound.A prevailing inflation rate is greater than the anticipated inflation rate, which may lead to increase in nominal money income, but it would cause the real money income to fall, and thus, results in a fall in purchasing power of households. Higher the unanticipated inflation, the lower will be the purchasing power and vice-versa.Inflation is totally not an evil from the point of view of increase in nominal money income. But, the negative impact of inflation is more profound in that it masks the increase in the nominal money income.Prevailing higher level of inflation in an economy might result in skewed distribution of money income, and it may also create winners and losers among the economic agents. Lenders and sellers tend to lose real purchasing power of the money when the rate of inflation increases due to an unanticipated inflation.
To attain rapid growth and sustainable development, inflation is a cost that an economy should pay for. Thus, inflation and growth of an economy go hand in hand.If the actual inflation rate equals the anticipated inflation rate, then the impact of inflation on the economy is at a minimum and at this level, real growth is high. But, inflation can be evil when unanticipated inflation is high and profound.A prevailing inflation rate is greater than the anticipated inflation rate, which may lead to increase in nominal money income, but it would cause the real money income to fall, and thus, results in a fall in purchasing power of households. Higher the unanticipated inflation, the lower will be the purchasing power and vice-versa.Inflation is totally not an evil from the point of view of increase in nominal money income. But, the negative impact of inflation is more profound in that it masks the increase in the nominal money income.Prevailing higher level of inflation in an economy might result in skewed distribution of money income, and it may also create winners and losers among the economic agents. Lenders and sellers tend to lose real purchasing power of the money when the rate of inflation increases due to an unanticipated inflation.
2
MEASURING UNEMPLOYMENT Determine the impact on each of the following if 2 million formerly unemployed workers decide to return to school full time and stop looking for work:
a. The labor force participation rate
b. The size of the labor force
c. The unemployment rate
a. The labor force participation rate
b. The size of the labor force
c. The unemployment rate
a. The labor force participation rate and fall in unemployed workers
The labor force participation rate will fall due to drop in the size of the labor force by 2 million.
b.The size of the labor force and fall in unemployed workers
The size of labor force will fall exactly by 2 million because 2 million formerly unemployed workers decided to return to the school full-time and stop looking for work. Thus, these 2 million workers will be left out of the labor force.
c.The unemployment rate and fall in unemployed workers
Unemployment rate will fall because the fall in the number of unemployed is greater than the percentage fall in the labor force.The fall in unemployed laborers would cause a fall in the ratio of unemployed laborers to total labor force.Thus, the unemployment rate will fall.
The labor force participation rate will fall due to drop in the size of the labor force by 2 million.
b.The size of the labor force and fall in unemployed workers
The size of labor force will fall exactly by 2 million because 2 million formerly unemployed workers decided to return to the school full-time and stop looking for work. Thus, these 2 million workers will be left out of the labor force.
c.The unemployment rate and fall in unemployed workers
Unemployment rate will fall because the fall in the number of unemployed is greater than the percentage fall in the labor force.The fall in unemployed laborers would cause a fall in the ratio of unemployed laborers to total labor force.Thus, the unemployment rate will fall.
3
MEASURING UNEMPLOYMENT Suppose that the U.S. noninstitutional adult population is 230 million and the labor force participation rate is 67 percent.
a. What would be the size of the U.S. labor force?
b. If 85 million adults are not working, what is the unemployment rate?
a. What would be the size of the U.S. labor force?
b. If 85 million adults are not working, what is the unemployment rate?
Given information:
• U.S non-institutional adult population is 230 million.
• Labor force participation rate is 67 percent.
• Non- working adult population is 85 million.
a. Size of labor force
The size of labor force can be calculated as follows: The size of U.S labor force is
The size of U.S labor force is 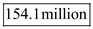 .
.
b.People outside the labor force
The number of people outside the labor force is calculated as follows: The number of people outside the labor force is
The number of people outside the labor force is  .
.
Unemployed people in the labor force
The number of unemployed people in the labor force is calculated as follows: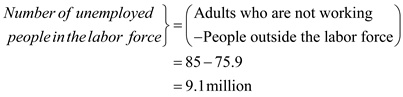 The number of unemployed people in the total labor force is
The number of unemployed people in the total labor force is  .
.
Unemployment rate
Unemployment rate is calculated as follows: The unemployment rate is
The unemployment rate is 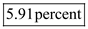 .
.
• U.S non-institutional adult population is 230 million.
• Labor force participation rate is 67 percent.
• Non- working adult population is 85 million.
a. Size of labor force
The size of labor force can be calculated as follows:
 The size of U.S labor force is
The size of U.S labor force is 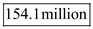 .
.b.People outside the labor force
The number of people outside the labor force is calculated as follows:
 The number of people outside the labor force is
The number of people outside the labor force is  .
.Unemployed people in the labor force
The number of unemployed people in the labor force is calculated as follows:
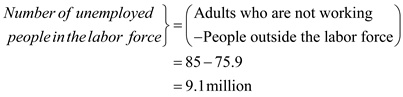 The number of unemployed people in the total labor force is
The number of unemployed people in the total labor force is  .
.Unemployment rate
Unemployment rate is calculated as follows:
 The unemployment rate is
The unemployment rate is 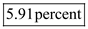 .
. 4
TYPES OF UNEMPLOYMENT Determine whether each of the following would be considered frictional, structural, seasonal, or cyclical unemployment:
a. A UPS employee who was hired for the Christmas season is laid off after Christmas.
b. A worker is laid off due to reduced aggregate demand in the economy.
c. A worker in a DVD rental store becomes unemployed as video-on-demand service becomes more popular.
d. A new college graduate is looking for employment.
a. A UPS employee who was hired for the Christmas season is laid off after Christmas.
b. A worker is laid off due to reduced aggregate demand in the economy.
c. A worker in a DVD rental store becomes unemployed as video-on-demand service becomes more popular.
d. A new college graduate is looking for employment.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 19 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
LABOR FORCE Refer to Exhibit 1 in the chapter to determine whether each of the following statements is true or false.
a. Some people who are officially unemployed are not in the labor force.
b. Some people in the labor force are not working.
c. Everyone who is not unemployed is in the labor force.
d. Some people who are not working are not unemployed.
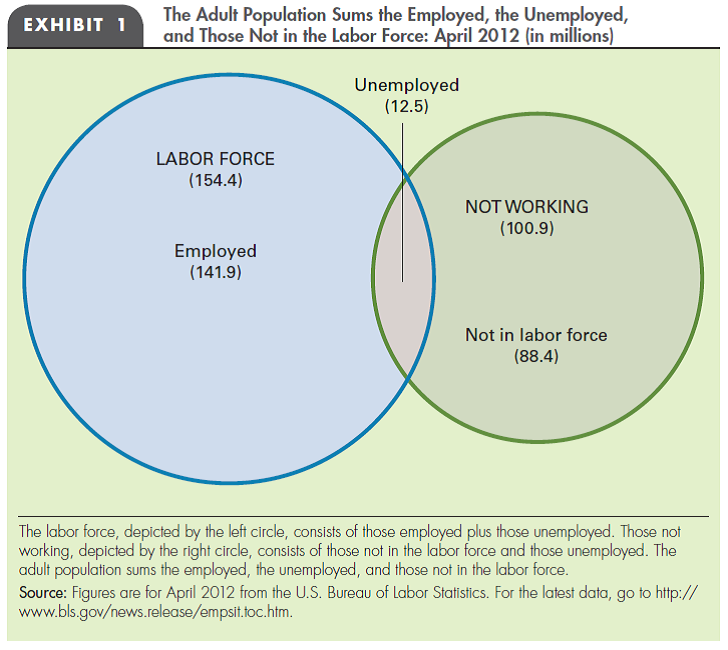
a. Some people who are officially unemployed are not in the labor force.
b. Some people in the labor force are not working.
c. Everyone who is not unemployed is in the labor force.
d. Some people who are not working are not unemployed.


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 19 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
INFLATION Here are some recent data on the U.S. consumer price index:
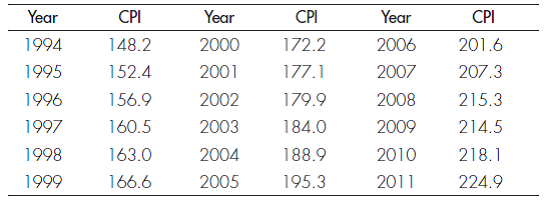
Compute the inflation rate for each year 1995-2011 and determine which years were years of inflation. In which years did deflation occur? In which years did disinflation occur? Was there hyperinflation in any year?

Compute the inflation rate for each year 1995-2011 and determine which years were years of inflation. In which years did deflation occur? In which years did disinflation occur? Was there hyperinflation in any year?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 19 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
UNEMPLOYMENT IN VARIOUS GROUPS Does the overall unemployment rate offer an accurate picture of the impact of unemployment on each U.S. population group?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 19 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
SOURCES OF INFLATION Using the concepts of aggregate supply and aggregate demand, explain why inflation usually increases during wartime.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 19 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
UNEMPLOYMENT RATE If people dropped out of the labor force because they could not find work, what would this do to the unemployment rate? Why?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 19 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
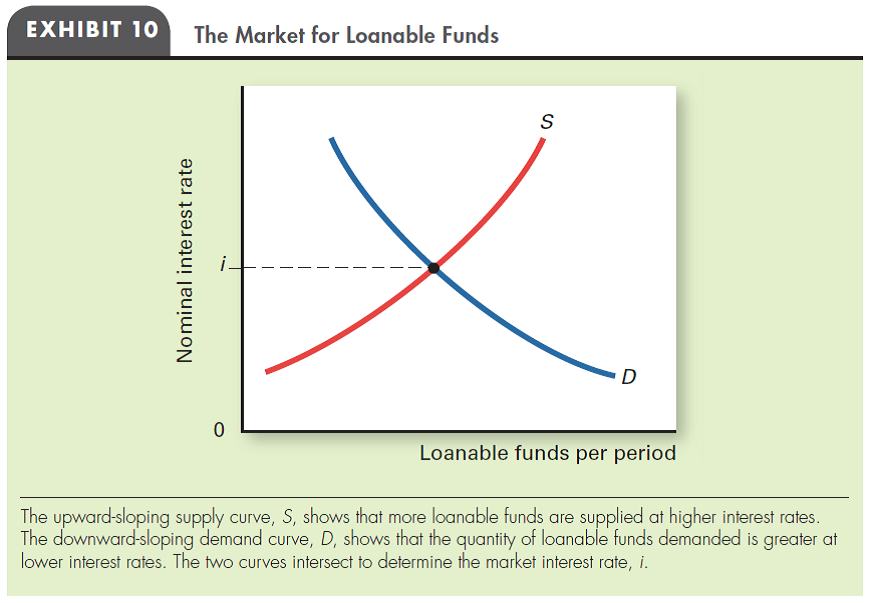
INFLATION AND INTEREST RATES Using a demand-supply diagram for loanable funds (like Exhibit 10), show what happens to the nominal interest rate and the equilibrium quantity of loans when both borrowers and lenders increase their estimates of the expected inflation rate from 5 percent to 10 percent.


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 19 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
THE MEANING OF FULL EMPLOYMENT When the economy is at full employment, is the unemployment rate at zero percent? Why or why not? How would a more generous unemployment insurance system affect the full employment figure?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 19 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
INTERNATIONAL COMPARISONS OF UNEMPLOYMENT How has the U.S. unemployment rate compared with rates in other major economies? Can you offer any reasons why rates on average have differed across major economies during the last three decades?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 19 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
OFFICIAL UNEMPLOYMENT FIGURES Explain why most experts believe that official U.S. data underestimate the actual rate of unemployment. What factors could make the official rate overstate the actual unemployment rate?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 19 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Case Study: Hyperinflation in Zimbabwe
In countries such as Zimbabwe, which had problems with high inflation, the increased use of another country's currency (such as the U.S. dollar) became common. Why do you suppose this occurred?
In countries such as Zimbabwe, which had problems with high inflation, the increased use of another country's currency (such as the U.S. dollar) became common. Why do you suppose this occurred?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 19 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
SOURCES OF INFLATION What are the two sources of inflation? Illustrate them graphically.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 19 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
ANTICIPATED VERSUS UNANTICIPATED INFLATION If actual inflation exceeds anticipated inflation, who will lose purchasing power and who will gain?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 19 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
INFLATION AND RELATIVE PRICE CHANGES What does the consumer price index measure? Does the index measure changes in relative prices? Why, or why not?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 19 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
INFLATION AND INTEREST RATES Explain as carefully as you can why borrowers would be willing to pay a higher interest rate if they expected the inflation rate to increase in the future.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 19 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
INFLATION Why is a relatively constant and predictable inflation rate less harmful to an economy than a rate that fluctuates unpredictably?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 19 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



