Deck 30: Growth and the Less-Developed Countries
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/43
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 30: Growth and the Less-Developed Countries
1
What is the difference between industrially advanced countries (IACs) and less-developed countries (LDCs)? List five IACs and five LDCs.
Difference between industrially advanced countries (IACs) and less-developed countries (LDCs):
Advanced countries (IACs):
Countries with high GDP per capita and outputs produced by technologically advanced capital. Countries that have high incomes without widespread industrial development, such as the oil-rich Arab countries, are not included in the IAC list
Example:
• Luxembourg
• Norway
• Ireland
• Denmark
• Switzerland
Less-developed countries (LDCs):
Nations without large stocks of technologically advanced capital and well-educated labor. LDCs are economies based on agriculture, such as most countries of Africa, Asia, and Latin America
Example:
• Russia
• Mexico
• Chile
• Romania
• Brazil
Differences:
Difference is based on GDP per capita
Classification is some what Arbitrary
Countries with high GDP per capita and narrow industrial development based on oil, such as united Arab Emirates, is excluded from the IACs list
Advanced countries (IACs):
Countries with high GDP per capita and outputs produced by technologically advanced capital. Countries that have high incomes without widespread industrial development, such as the oil-rich Arab countries, are not included in the IAC list
Example:
• Luxembourg
• Norway
• Ireland
• Denmark
• Switzerland
Less-developed countries (LDCs):
Nations without large stocks of technologically advanced capital and well-educated labor. LDCs are economies based on agriculture, such as most countries of Africa, Asia, and Latin America
Example:
• Russia
• Mexico
• Chile
• Romania
• Brazil
Differences:
Difference is based on GDP per capita
Classification is some what Arbitrary
Countries with high GDP per capita and narrow industrial development based on oil, such as united Arab Emirates, is excluded from the IACs list
2
According to the definition given in the text, which of the following is not an LDC?
A) India.
B) Egypt.
C) China.
D) Ireland.
A) India.
B) Egypt.
C) China.
D) Ireland.
According to the definition given in the chapter, which of the following is not an LDC?
Answer: (D) Ireland
Explanation:
Ireland is an Industrially Advanced countries (IUACs) and it's GDP per Capita ($) is 61,900, hence it's not an LDC
Answer: (D) Ireland
Explanation:
Ireland is an Industrially Advanced countries (IUACs) and it's GDP per Capita ($) is 61,900, hence it's not an LDC
3
Which of the following problems do LDCs face?
A) Low per capita income and high GDP growth rate.
B) Low population growth and low per capita income.
C) Rapid population growth and low human capital.
D) Low per capita income and high saving rate.
A) Low per capita income and high GDP growth rate.
B) Low population growth and low per capita income.
C) Rapid population growth and low human capital.
D) Low per capita income and high saving rate.
Which of the following problems do LDCs face?
Answer: (C) Rapid population growth and low human capital
Explanation:
Rapid population growth combined with low human capital investment explains why many countries are LCDs.hence these two factors LDCs need to overcome on a consistent basis
Answer: (C) Rapid population growth and low human capital
Explanation:
Rapid population growth combined with low human capital investment explains why many countries are LCDs.hence these two factors LDCs need to overcome on a consistent basis
4
THE INTERNATIONAL ECONOMY
This road map feature helps you tie together material in the part as you travel the Economic Way of Thinking Highway. The following are review questions listed by chapters from the previous part. The key concept in each question is given for emphasis, and each question or set of questions concludes with an interactive game to reinforce the concepts. Visit cengagebrain.com to purchase the MindTap product where you can select a chapter and play the visual causation chain game designed to make learning fun. The correct answers to the multiple choice questions are given in Appendix C on the instructor'sresourcesite.
Key Concept: Exchange rate changes
Which of the following would cause the supply of dollars curve in the United States to shift to the right?
A) Japanese imports become less popular.
B) The value of the dollar falls.
C) The supply of dollars decreases.
D) Japanese imports become more popular.
Causation Chain Game
Changes in the Supply and Demand Curves for Dollars-Exhibit 10
This road map feature helps you tie together material in the part as you travel the Economic Way of Thinking Highway. The following are review questions listed by chapters from the previous part. The key concept in each question is given for emphasis, and each question or set of questions concludes with an interactive game to reinforce the concepts. Visit cengagebrain.com to purchase the MindTap product where you can select a chapter and play the visual causation chain game designed to make learning fun. The correct answers to the multiple choice questions are given in Appendix C on the instructor'sresourcesite.
Key Concept: Exchange rate changes
Which of the following would cause the supply of dollars curve in the United States to shift to the right?
A) Japanese imports become less popular.
B) The value of the dollar falls.
C) The supply of dollars decreases.
D) Japanese imports become more popular.

Causation Chain Game
Changes in the Supply and Demand Curves for Dollars-Exhibit 10

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 43 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Why is the quest for economic growth and development complicated?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 43 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Which of the following best defines the vicious circle of poverty?
A) The GDP per capita must rise before people can save and invest.
B) People cannot save while capital accumulates.
C) Increased GDP per capita relates to lower population growth.
D) Poverty, saving, and investment are related like a circle.
A) The GDP per capita must rise before people can save and invest.
B) People cannot save while capital accumulates.
C) Increased GDP per capita relates to lower population growth.
D) Poverty, saving, and investment are related like a circle.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 43 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
There is a significant positive relationship between ______ and ______.
A) natural resource commodity exports; high levels of per capita GDP
B) investment in capital; high levels of per capita GDP
C) high levels of illiteracy; high levels of per capita GDP
D) limited government recognition of land tenure and property ownership; high levels of per capita GDP
A) natural resource commodity exports; high levels of per capita GDP
B) investment in capital; high levels of per capita GDP
C) high levels of illiteracy; high levels of per capita GDP
D) limited government recognition of land tenure and property ownership; high levels of per capita GDP

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 43 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Explain why GDP per capita comparisons among nations are not a perfect measure of differences in economic well-being.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 43 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
THE INTERNATIONAL ECONOMY
This road map feature helps you tie together material in the part as you travel the Economic Way of Thinking Highway. The following are review questions listed by chapters from the previous part. The key concept in each question is given for emphasis, and each question or set of questions concludes with an interactive game to reinforce the concepts. Visit cengagebrain.com to purchase the MindTap product where you can select a chapter and play the visual causation chain game designed to make learning fun. The correct answers to the multiple choice questions are given in Appendix C on the instructor'sresourcesite.
Key Concept: Economic growth
Which of the following statements is correct ?
A) Economic development is more quantitative than economic growth.
B) A country cannot achieve economic growth with a limited base of natural resources.
C) Infrastructure is capital provided by the private sector.
D) All of the answers above are correct.
E) All of the answers above are incorrect.
Causation Chain Game
Economic Growth-Exhibit 4
This road map feature helps you tie together material in the part as you travel the Economic Way of Thinking Highway. The following are review questions listed by chapters from the previous part. The key concept in each question is given for emphasis, and each question or set of questions concludes with an interactive game to reinforce the concepts. Visit cengagebrain.com to purchase the MindTap product where you can select a chapter and play the visual causation chain game designed to make learning fun. The correct answers to the multiple choice questions are given in Appendix C on the instructor'sresourcesite.
Key Concept: Economic growth
Which of the following statements is correct ?
A) Economic development is more quantitative than economic growth.
B) A country cannot achieve economic growth with a limited base of natural resources.
C) Infrastructure is capital provided by the private sector.
D) All of the answers above are correct.
E) All of the answers above are incorrect.

Causation Chain Game
Economic Growth-Exhibit 4

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 43 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Which of the following is infrastructure?
A) International Harvester tractor plant.
B) Waste and water system provided by government.
C) Airplane.
D) Service of postal workers.
A) International Harvester tractor plant.
B) Waste and water system provided by government.
C) Airplane.
D) Service of postal workers.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 43 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
THE INTERNATIONAL ECONOMY
This road map feature helps you tie together material in the part as you travel the Economic Way of Thinking Highway. The following are review questions listed by chapters from the previous part. The key concept in each question is given for emphasis, and each question or set of questions concludes with an interactive game to reinforce the concepts. Visit cengagebrain.com to purchase the MindTap product where you can select a chapter and play the visual causation chain game designed to make learning fun. The correct answers to the multiple choice questions are given in Appendix C on the instructor'sresourcesite.
Key Concept: Impact of relative price level changes
An increase in inflation in the United States relative to the rate in France would make
A) U.S. goods relatively less expensive in the United States and in France.
B) French goods relatively less expensive in the United States, and U.S. goods relatively more expensive in France.
C) French goods relatively more expensive in the United States and in France.
D) French goods relatively more expensive in the United States, and U.S. goods relatively less expensive in France.
This road map feature helps you tie together material in the part as you travel the Economic Way of Thinking Highway. The following are review questions listed by chapters from the previous part. The key concept in each question is given for emphasis, and each question or set of questions concludes with an interactive game to reinforce the concepts. Visit cengagebrain.com to purchase the MindTap product where you can select a chapter and play the visual causation chain game designed to make learning fun. The correct answers to the multiple choice questions are given in Appendix C on the instructor'sresourcesite.
Key Concept: Impact of relative price level changes
An increase in inflation in the United States relative to the rate in France would make
A) U.S. goods relatively less expensive in the United States and in France.
B) French goods relatively less expensive in the United States, and U.S. goods relatively more expensive in France.
C) French goods relatively more expensive in the United States and in France.
D) French goods relatively more expensive in the United States, and U.S. goods relatively less expensive in France.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 43 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Which of the following is true when making GDPs per capita comparisons between nations?
A) The GDP per capita is subject to greater measurement errors for LDCs compared to IACs.
B) The GDP per capita does not measure income distribution.
C) The GDP per capita is subject to fluctuations from changes in exchange rates.
D) All of the answers above are correct.
A) The GDP per capita is subject to greater measurement errors for LDCs compared to IACs.
B) The GDP per capita does not measure income distribution.
C) The GDP per capita is subject to fluctuations from changes in exchange rates.
D) All of the answers above are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 43 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Economic growth and development in LDCs are low because many of them lack
A) capital investment.
B) technological progress.
C) a favorable political environment.
D) All of the answers above are correct.
E) None of the answers above are correct.
A) capital investment.
B) technological progress.
C) a favorable political environment.
D) All of the answers above are correct.
E) None of the answers above are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 43 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
______ generally results in increases in per-capita GDP.
A) Civil war
B) High levels of inequality in the distribution of land ownership
C) Investment in human capital
D) A stock of natural resources
A) Civil war
B) High levels of inequality in the distribution of land ownership
C) Investment in human capital
D) A stock of natural resources

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 43 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
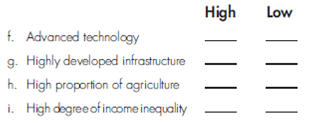
Indicate whether each of the following is associated with a high or low level of economic growth and development: 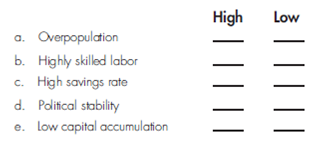



Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 43 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Which of the following makes short-term conditional low-interest loans to developing countries?
A) Agency for International Development (AID).
B) World Bank.
C) International Monetary Fund (IMF).
D) New International Economic Order (NIEO).
A) Agency for International Development (AID).
B) World Bank.
C) International Monetary Fund (IMF).
D) New International Economic Order (NIEO).

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 43 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Assume you are given the following data for country Alpha and country Beta: 
a. Based on the GDP per capita data given above, in which country would you prefer to live?
b. Now assume you are given the following additional quality-of-life data. In which country would you prefer to reside?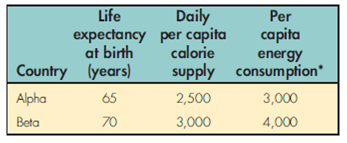
*Kilograms of oil equivalent.

a. Based on the GDP per capita data given above, in which country would you prefer to live?
b. Now assume you are given the following additional quality-of-life data. In which country would you prefer to reside?

*Kilograms of oil equivalent.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 43 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
THE INTERNATIONAL ECONOMY
This road map feature helps you tie together material in the part as you travel the Economic Way of Thinking Highway. The following are review questions listed by chapters from the previous part. The key concept in each question is given for emphasis, and each question or set of questions concludes with an interactive game to reinforce the concepts. Visit cengagebrain.com to purchase the MindTap product where you can select a chapter and play the visual causation chain game designed to make learning fun. The correct answers to the multiple choice questions are given in Appendix C on the instructor'sresourcesite.
Key Concept: Achieving economic growth
Which of the following can be a barrier to an LDC's economic growth and development?
A) Low population growth
B) A low level of human capital
C) Faster capital accumulation
D) More infrastructure
This road map feature helps you tie together material in the part as you travel the Economic Way of Thinking Highway. The following are review questions listed by chapters from the previous part. The key concept in each question is given for emphasis, and each question or set of questions concludes with an interactive game to reinforce the concepts. Visit cengagebrain.com to purchase the MindTap product where you can select a chapter and play the visual causation chain game designed to make learning fun. The correct answers to the multiple choice questions are given in Appendix C on the instructor'sresourcesite.
Key Concept: Achieving economic growth
Which of the following can be a barrier to an LDC's economic growth and development?
A) Low population growth
B) A low level of human capital
C) Faster capital accumulation
D) More infrastructure

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 43 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Which of the following makes long-term low-interest loans to less-developed countries (LDCs)?
A) The Agency for International Development (AID).
B) New International Economic Order (NIEO).
C) International Monetary Fund (IMF).
D) The World Bank.
A) The Agency for International Development (AID).
B) New International Economic Order (NIEO).
C) International Monetary Fund (IMF).
D) The World Bank.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 43 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
THE INTERNATIONAL ECONOMY
This road map feature helps you tie together material in the part as you travel the Economic Way of Thinking Highway. The following are review questions listed by chapters from the previous part. The key concept in each question is given for emphasis, and each question or set of questions concludes with an interactive game to reinforce the concepts. Visit cengagebrain.com to purchase the MindTap product where you can select a chapter and play the visual causation chain game designed to make learning fun. The correct answers to the multiple choice questions are given in Appendix C on the instructor'sresourcesite.
Key Concept: Impact of relative price level changes
If the Japanese price level falls relative to the price level in the United States, then
A) Japanese buy U.S. exports.
B) the demand for dollars decreases.
C) the supply of dollars increases.
D) the value of the dollar falls.
E) All of the answers above are correct.
Causation Chain Game
The Impact of Relative Price Level Changes on Exchange Rates-Exhibit 11
This road map feature helps you tie together material in the part as you travel the Economic Way of Thinking Highway. The following are review questions listed by chapters from the previous part. The key concept in each question is given for emphasis, and each question or set of questions concludes with an interactive game to reinforce the concepts. Visit cengagebrain.com to purchase the MindTap product where you can select a chapter and play the visual causation chain game designed to make learning fun. The correct answers to the multiple choice questions are given in Appendix C on the instructor'sresourcesite.
Key Concept: Impact of relative price level changes
If the Japanese price level falls relative to the price level in the United States, then
A) Japanese buy U.S. exports.
B) the demand for dollars decreases.
C) the supply of dollars increases.
D) the value of the dollar falls.
E) All of the answers above are correct.

Causation Chain Game
The Impact of Relative Price Level Changes on Exchange Rates-Exhibit 11

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 43 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
LDCs are characterized by
A) high life expectancy.
B) high adult literacy.
C) high infant mortality.
D) All of the answers above are correct.
E) None of the answers above are correct.
A) high life expectancy.
B) high adult literacy.
C) high infant mortality.
D) All of the answers above are correct.
E) None of the answers above are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 43 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
In order for Ethiopia to increase its future economic growth, it must choose a point that is
A) below its production possibilities curve.
B) further along on its production possibilities curve toward the capital goods axis.
C) further along on its production possibilities curve toward the consumption goods axis.
D) further along on its production possibilities curve away from the population axis.
E) above its production possibilities curve.
A) below its production possibilities curve.
B) further along on its production possibilities curve toward the capital goods axis.
C) further along on its production possibilities curve toward the consumption goods axis.
D) further along on its production possibilities curve away from the population axis.
E) above its production possibilities curve.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 43 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Which of the following represents a problem with using per capita GDP to compare standard of living between less-developed and industrially advanced countries?
A) GDP per capita does not take into account differences in population between countries.
B) GDP is particularly difficult to measure in industrially advanced countries because a much larger percentage of economic activity occurs outside of officially measured market activity than in less-developed countries.
C) GDP per capita will overstate the prevailing standard of living for the average person in countries with extreme levels of income inequality.
D) None of the answers above are correct.
A) GDP per capita does not take into account differences in population between countries.
B) GDP is particularly difficult to measure in industrially advanced countries because a much larger percentage of economic activity occurs outside of officially measured market activity than in less-developed countries.
C) GDP per capita will overstate the prevailing standard of living for the average person in countries with extreme levels of income inequality.
D) None of the answers above are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 43 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Without external financing from foreign private investment, foreign aid, and foreign loans, poor countries are caught in the vicious circle of poverty. Explain. How does external financing help poor countries achieve economic growth and development?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 43 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
HONG KONG: A CROUCHING PACIFIC RIM TIGER
Applicable Concept: recently industrialized economies
As the map shows, the Pacific Rim economies are located along an are extending from Japan and South Korea in the north to New Zealand in the south. The Four Tigers of East Asia are Hong Kong, Singapore, South Korea, and Taiwan. These "miracle economies" have often experienced higher economic growth rates, lower inflation rates, and lower unemployment rates than many long-established advanced countries.
Hong Kong is a great success story. When Adam Smith published his famous book, The Wealth of Nations, in 1776, Hong Kong was little more than a small, barren rock island void of natural resources except fish. Today, Hong Kong is a bustling model of free enterprise in spite of the fact that 7 million inhabitants are crowded into only about 400 square miles-one of the highest population densities in the world.
What is the reason for Hong Kong's success? Following the doctrine of Adam Smith, this economy is a paragon of laissez-faire. Hong Kong has among the lowest individual and corporate income tax rates in the world and almost no legal restrictions on business. It has no capital gains tax, no interest tax, no sales tax, and no withholding tax. Hong Kong has become the largest banking center in the Pacific region after Tokyo. International trade is also largely unrestricted, and Hong Kong depends to a large extent on trade through its magnificent harbor for its economic success. Tariffs on imported goods are low, and Hong Kong is known as a safe-haven warehouse and trading center, with little or no interference from the government.
Hong Kong has proved that industrious people and entrepreneurs working hard on a crowded island with minimum regulations and open trade can improve their living standard without natural resources. Nevertheless, Hong Kong faces economic and political uncertainty. Undera99-yearlease signed in 1898, the United Kingdom transferred Hong Kong to the People's Republic of China in 1997. Will China allow Hong Kong to continue to follow Adam Smith's laissez-faire philosophy, resulting in high growth rates, or will Hong Kong change direction? It is any-one'sguess. So far, China has not tampered with Hong Kong's laissez-faire economy, and its economic freedom ranking is higher than any country in the world.
Recessions in the United States affect the global economy, and Hong Kong is no exception. Hong Kong's GDP growth depends heavily on its exports. If, for example, U.S. consumers cut back on purchasing electronic devices, then Hong Kong's growth rate declines. After an 8 percent growth rate in 2000, the falloff in global demand triggered by the 2001 recession in the United States slowed Hong Kong's real GDP growth rate to only 0.5 percent in 2001. Between 2004 and 2007, Hong Kong's growth rate recovered to an average of 7.3 percent, and this East Asian tiger was leaping forward and roaring again. However, as a result of the U.S. Great Recession of 2007-2009, Hong Kong slipped into recession in 2009 with a growth rate of ?2.5 percent, which rose to 2.3 percent in 2014. Hong Kong is therefore a "crouching tiger" waiting to leap forward again. The following map compares 2011 data for the Four Tigers of East Asia.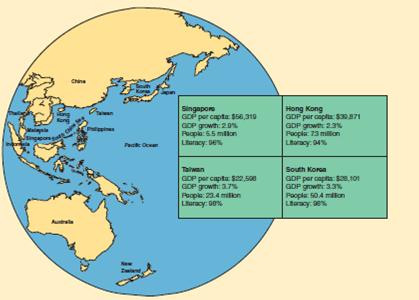
One of the keys to Hong Kong's success is its free trade policy. Why is this so important for a developing country? What would be the effect of Hong Kong attempting to protect its domestic industries by raising tariffs and following other protectionist trade policies?
Applicable Concept: recently industrialized economies
As the map shows, the Pacific Rim economies are located along an are extending from Japan and South Korea in the north to New Zealand in the south. The Four Tigers of East Asia are Hong Kong, Singapore, South Korea, and Taiwan. These "miracle economies" have often experienced higher economic growth rates, lower inflation rates, and lower unemployment rates than many long-established advanced countries.
Hong Kong is a great success story. When Adam Smith published his famous book, The Wealth of Nations, in 1776, Hong Kong was little more than a small, barren rock island void of natural resources except fish. Today, Hong Kong is a bustling model of free enterprise in spite of the fact that 7 million inhabitants are crowded into only about 400 square miles-one of the highest population densities in the world.
What is the reason for Hong Kong's success? Following the doctrine of Adam Smith, this economy is a paragon of laissez-faire. Hong Kong has among the lowest individual and corporate income tax rates in the world and almost no legal restrictions on business. It has no capital gains tax, no interest tax, no sales tax, and no withholding tax. Hong Kong has become the largest banking center in the Pacific region after Tokyo. International trade is also largely unrestricted, and Hong Kong depends to a large extent on trade through its magnificent harbor for its economic success. Tariffs on imported goods are low, and Hong Kong is known as a safe-haven warehouse and trading center, with little or no interference from the government.

Hong Kong has proved that industrious people and entrepreneurs working hard on a crowded island with minimum regulations and open trade can improve their living standard without natural resources. Nevertheless, Hong Kong faces economic and political uncertainty. Undera99-yearlease signed in 1898, the United Kingdom transferred Hong Kong to the People's Republic of China in 1997. Will China allow Hong Kong to continue to follow Adam Smith's laissez-faire philosophy, resulting in high growth rates, or will Hong Kong change direction? It is any-one'sguess. So far, China has not tampered with Hong Kong's laissez-faire economy, and its economic freedom ranking is higher than any country in the world.
Recessions in the United States affect the global economy, and Hong Kong is no exception. Hong Kong's GDP growth depends heavily on its exports. If, for example, U.S. consumers cut back on purchasing electronic devices, then Hong Kong's growth rate declines. After an 8 percent growth rate in 2000, the falloff in global demand triggered by the 2001 recession in the United States slowed Hong Kong's real GDP growth rate to only 0.5 percent in 2001. Between 2004 and 2007, Hong Kong's growth rate recovered to an average of 7.3 percent, and this East Asian tiger was leaping forward and roaring again. However, as a result of the U.S. Great Recession of 2007-2009, Hong Kong slipped into recession in 2009 with a growth rate of ?2.5 percent, which rose to 2.3 percent in 2014. Hong Kong is therefore a "crouching tiger" waiting to leap forward again. The following map compares 2011 data for the Four Tigers of East Asia.

One of the keys to Hong Kong's success is its free trade policy. Why is this so important for a developing country? What would be the effect of Hong Kong attempting to protect its domestic industries by raising tariffs and following other protectionist trade policies?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 43 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
What is the difference between economic development and economic growth? Give examples of how each of these concepts can be measured.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 43 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
THE INTERNATIONAL ECONOMY
This road map feature helps you tie together material in the part as you travel the Economic Way of Thinking Highway. The following are review questions listed by chapters from the previous part. The key concept in each question is given for emphasis, and each question or set of questions concludes with an interactive game to reinforce the concepts. Visit cengagebrain.com to purchase the MindTap product where you can select a chapter and play the visual causation chain game designed to make learning fun. The correct answers to the multiple choice questions are given in Appendix C on the instructor'sresourcesite.
Key Concept: Economic growth and development
To grow and prosper, less-developed countries must not
A) invest in human capital.
B) build a strong infrastructure.
C) shift resources out of the production of consumer goods and into the production of capital goods.
D) shift resources out of the production of capital goods and into the production of consumer goods.
E) improve the quality of the water supply.
Causation Chain Game
The Effect of External Financing on an LDC's Production Possibilities Curve-Exhibit 7
This road map feature helps you tie together material in the part as you travel the Economic Way of Thinking Highway. The following are review questions listed by chapters from the previous part. The key concept in each question is given for emphasis, and each question or set of questions concludes with an interactive game to reinforce the concepts. Visit cengagebrain.com to purchase the MindTap product where you can select a chapter and play the visual causation chain game designed to make learning fun. The correct answers to the multiple choice questions are given in Appendix C on the instructor'sresourcesite.
Key Concept: Economic growth and development
To grow and prosper, less-developed countries must not
A) invest in human capital.
B) build a strong infrastructure.
C) shift resources out of the production of consumer goods and into the production of capital goods.
D) shift resources out of the production of capital goods and into the production of consumer goods.
E) improve the quality of the water supply.

Causation Chain Game
The Effect of External Financing on an LDC's Production Possibilities Curve-Exhibit 7

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 43 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
THE INTERNATIONAL ECONOMY
This road map feature helps you tie together material in the part as you travel the Economic Way of Thinking Highway. The following are review questions listed by chapters from the previous part. The key concept in each question is given for emphasis, and each question or set of questions concludes with an interactive game to reinforce the concepts. Visit cengagebrain.com to purchase the MindTap product where you can select a chapter and play the visual causation chain game designed to make learning fun. The correct answers to the multiple choice questions are given in Appendix C on the instructor'sresourcesite.
Key Concept: Command economy
Which of the following statements is true about a command economy?
A) Shortages occur because of complexities in the planning process.
B) Planners determine what, how many, and for whom goods and services are to be produced.
C) Planners often allocate goods and services using a rationing system.
D) The quality of produced goods and services tends to be inferior.
E) All of the answers above are correct.
This road map feature helps you tie together material in the part as you travel the Economic Way of Thinking Highway. The following are review questions listed by chapters from the previous part. The key concept in each question is given for emphasis, and each question or set of questions concludes with an interactive game to reinforce the concepts. Visit cengagebrain.com to purchase the MindTap product where you can select a chapter and play the visual causation chain game designed to make learning fun. The correct answers to the multiple choice questions are given in Appendix C on the instructor'sresourcesite.
Key Concept: Command economy
Which of the following statements is true about a command economy?
A) Shortages occur because of complexities in the planning process.
B) Planners determine what, how many, and for whom goods and services are to be produced.
C) Planners often allocate goods and services using a rationing system.
D) The quality of produced goods and services tends to be inferior.
E) All of the answers above are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 43 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
According to the classification in the text, which of the following is not an IAC?
A) United Arab Emirates
B) Israel.
C) Hong Kong.
D) Greece.
A) United Arab Emirates
B) Israel.
C) Hong Kong.
D) Greece.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 43 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Which of the following is an example of foreign private investment?
A) Elite government leaders in a less-developed country develop a domestic logging monopoly that proceeds to deforest lands recently cleared of residents by the military.
B) The U.S. government provides $10 million in financial assistance to a less-developed country that provides space for U.S. military bases.
C) A multinational corporation builds shoe-manufacturing facility in a less-developed country.
D) None of the answers above are correct.
A) Elite government leaders in a less-developed country develop a domestic logging monopoly that proceeds to deforest lands recently cleared of residents by the military.
B) The U.S. government provides $10 million in financial assistance to a less-developed country that provides space for U.S. military bases.
C) A multinational corporation builds shoe-manufacturing facility in a less-developed country.
D) None of the answers above are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 43 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
What are some of the problems for LDCs of accepting foreign aid?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 43 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Do you agree with the argument that the rich nations are getting richer and the poor nations are getting poorer? Is this an oversimplification? Explain.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 43 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
When the government fixes the exchange rate above market exchange rates,
A) international trade falls.
B) the infrastructure improves.
C) real GDP per capita rises.
D) the vicious circle of poverty is broken.
A) international trade falls.
B) the infrastructure improves.
C) real GDP per capita rises.
D) the vicious circle of poverty is broken.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 43 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
THE INTERNATIONAL ECONOMY
This road map feature helps you tie together material in the part as you travel the Economic Way of Thinking Highway. The following are review questions listed by chapters from the previous part. The key concept in each question is given for emphasis, and each question or set of questions concludes with an interactive game to reinforce the concepts. Visit cengagebrain.com to purchase the MindTap product where you can select a chapter and play the visual causation chain game designed to make learning fun. The correct answers to the multiple choice questions are given in Appendix C on the instructor'sresourcesite.
Key Concept: Command economy
Which of the following statements best describes the role played by prices in a command economy such as the former Soviet Union?
A) Prices were used to allocate resources.
B) Prices played the same role as in a market economy.
C) Prices were used to ration final goods and services but not to allocate resources.
D) None of the above statements are true.
Causation Chain Game
Central Planners Fixing Prices-Exhibit 2
This road map feature helps you tie together material in the part as you travel the Economic Way of Thinking Highway. The following are review questions listed by chapters from the previous part. The key concept in each question is given for emphasis, and each question or set of questions concludes with an interactive game to reinforce the concepts. Visit cengagebrain.com to purchase the MindTap product where you can select a chapter and play the visual causation chain game designed to make learning fun. The correct answers to the multiple choice questions are given in Appendix C on the instructor'sresourcesite.
Key Concept: Command economy
Which of the following statements best describes the role played by prices in a command economy such as the former Soviet Union?
A) Prices were used to allocate resources.
B) Prices played the same role as in a market economy.
C) Prices were used to ration final goods and services but not to allocate resources.
D) None of the above statements are true.

Causation Chain Game
Central Planners Fixing Prices-Exhibit 2

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 43 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Why would an LDC argue for "trade, not aid"?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 43 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
An LDC is defined as a country
A) without large stocks of advanced capital.
B) without well-educated labor.
C) with a low GDP per capita.
D) that is described by all of the above.
A) without large stocks of advanced capital.
B) without well-educated labor.
C) with a low GDP per capita.
D) that is described by all of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 43 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Which of the following statements is true ?
A) An LDC is a country with a low GDP per capita, low levels of capital, and uneducated workers.
B) The vicious circle of poverty exists because GDP must rise before people can save and invest.
C) LDCs are characterized by rapid population growth and low levels of investment in human capital.
D) All of the answers above are correct.
A) An LDC is a country with a low GDP per capita, low levels of capital, and uneducated workers.
B) The vicious circle of poverty exists because GDP must rise before people can save and invest.
C) LDCs are characterized by rapid population growth and low levels of investment in human capital.
D) All of the answers above are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 43 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
THE INTERNATIONAL ECONOMY
This road map feature helps you tie together material in the part as you travel the Economic Way of Thinking Highway. The following are review questions listed by chapters from the previous part. The key concept in each question is given for emphasis, and each question or set of questions concludes with an interactive game to reinforce the concepts. Visit cengagebrain.com to purchase the MindTap product where you can select a chapter and play the visual causation chain game designed to make learning fun. The correct answers to the multiple choice questions are given in Appendix C on the instructor'sresourcesite.
Key Concept: Exchange rate changes
Which of the following would cause the U.S. demand curve for Japanese yen to shift to the right?
A) An increase in the U.S. inflation rate compared to the rate in Japan
B) A higher real rate of interest on investments in Japan than on investments in the United States
C) The popularity of Japanese products increases in the United States
D) All of the answers above are correct.
This road map feature helps you tie together material in the part as you travel the Economic Way of Thinking Highway. The following are review questions listed by chapters from the previous part. The key concept in each question is given for emphasis, and each question or set of questions concludes with an interactive game to reinforce the concepts. Visit cengagebrain.com to purchase the MindTap product where you can select a chapter and play the visual causation chain game designed to make learning fun. The correct answers to the multiple choice questions are given in Appendix C on the instructor'sresourcesite.
Key Concept: Exchange rate changes
Which of the following would cause the U.S. demand curve for Japanese yen to shift to the right?
A) An increase in the U.S. inflation rate compared to the rate in Japan
B) A higher real rate of interest on investments in Japan than on investments in the United States
C) The popularity of Japanese products increases in the United States
D) All of the answers above are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 43 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Explain why it is so difficult for poor LDCs to generate investment in capital in order to increase productivity and growth and therefore improve their standard of living.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 43 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Explain the differences among the Agency for International Development (AID), the World Bank, and the International Monetary Fund (IMF).

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 43 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
Which of the following distinguishes industrially advanced countries from less-developed countries?
A) GDP per capita.
B) Educational attainment of the workforce.
C) Extent to which capital is technologically advanced.
D) All of the answers above are correct.
A) GDP per capita.
B) Educational attainment of the workforce.
C) Extent to which capital is technologically advanced.
D) All of the answers above are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 43 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
THE INTERNATIONAL ECONOMY
This road map feature helps you tie together material in the part as you travel the Economic Way of Thinking Highway. The following are review questions listed by chapters from the previous part. The key concept in each question is given for emphasis, and each question or set of questions concludes with an interactive game to reinforce the concepts. Visit cengagebrain.com to purchase the MindTap product where you can select a chapter and play the visual causation chain game designed to make learning fun. The correct answers to the multiple choice questions are given in Appendix C on the instructor'sresourcesite.
Key Concept: Economic growth
An outward shift of an economy's production possibilities curve is caused by an
A) increase in capital.
B) increase in labor.
C) advance in technology.
D) All of the answers above are correct.
This road map feature helps you tie together material in the part as you travel the Economic Way of Thinking Highway. The following are review questions listed by chapters from the previous part. The key concept in each question is given for emphasis, and each question or set of questions concludes with an interactive game to reinforce the concepts. Visit cengagebrain.com to purchase the MindTap product where you can select a chapter and play the visual causation chain game designed to make learning fun. The correct answers to the multiple choice questions are given in Appendix C on the instructor'sresourcesite.
Key Concept: Economic growth
An outward shift of an economy's production possibilities curve is caused by an
A) increase in capital.
B) increase in labor.
C) advance in technology.
D) All of the answers above are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 43 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
An outward shift of the production possibilities curve represents
A) economic growth.
B) a decline in economic development.
C) a decrease in human capital.
D) a decrease in resources.
A) economic growth.
B) a decline in economic development.
C) a decrease in human capital.
D) a decrease in resources.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 43 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



