Deck 16: Theory and Reality
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/16
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 16: Theory and Reality
1
The 2008 fiscal policy package included roughly $100 billion in tax rebates that were mailed to taxpayers. By how much would aggregate demand shift ( a ) initially and ( b ) ultimately as a result of these rebates? Assume the MPC is 0.95.
It has been provided that as part of 2008 fiscal policy package roughly $100 billion in tax rebates had been mailed to tax payers.
These tax rebates will increase the disposable income of tax payers.
Thus, disposable income in economy is increased by $100 billion.
(a) Disposable income in economy has increased by $100 billion.
This increase in disposable income will result in increase in consumption.
Calculate increase in consumption -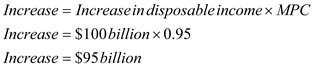 This increase in disposable income due to tax rebates will initially increase the consumption in the economy by $95 billion.
This increase in disposable income due to tax rebates will initially increase the consumption in the economy by $95 billion.
Consumption expenditure is a component of aggregate demand.
So, this initial increase in consumption in economy by $95 billion will, initially, shift (rightwards) the aggregate demand by $95 billion as well.
(b) Calculate the value of multiplier - The value of multiplier is 20.
The value of multiplier is 20.
Calculate ultimate (final) increase in aggregate demand -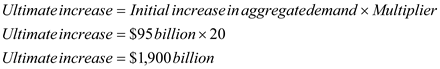 Thus, aggregate demand will ultimately shift (rightwards) by $1,900 billion as a result of these tax rebates.
Thus, aggregate demand will ultimately shift (rightwards) by $1,900 billion as a result of these tax rebates.
These tax rebates will increase the disposable income of tax payers.
Thus, disposable income in economy is increased by $100 billion.
(a) Disposable income in economy has increased by $100 billion.
This increase in disposable income will result in increase in consumption.
Calculate increase in consumption -
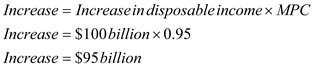 This increase in disposable income due to tax rebates will initially increase the consumption in the economy by $95 billion.
This increase in disposable income due to tax rebates will initially increase the consumption in the economy by $95 billion.Consumption expenditure is a component of aggregate demand.
So, this initial increase in consumption in economy by $95 billion will, initially, shift (rightwards) the aggregate demand by $95 billion as well.
(b) Calculate the value of multiplier -
 The value of multiplier is 20.
The value of multiplier is 20.Calculate ultimate (final) increase in aggregate demand -
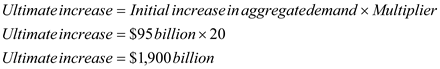 Thus, aggregate demand will ultimately shift (rightwards) by $1,900 billion as a result of these tax rebates.
Thus, aggregate demand will ultimately shift (rightwards) by $1,900 billion as a result of these tax rebates. 2
What policies would Keynesians, monetarists, and supply- siders advocate for
( a ) Restraining inflation?
( b ) Reducing unemployment?
( a ) Restraining inflation?
( b ) Reducing unemployment?
Keynesian theory:
It is an economic theory of total economy spending and it effect on the inflation and output in other words it is also called Keynesian demand-side theory. Keynesian theory was formed to understand the great depression. The founder raised the government expenses and reduced the tax to stimulate the demand and help the economy to move out of depression.
Monetarism:
Monetarism is refers to the study of the economics school of thoughts. The monetarism deals with the money supply in the economy, influences by the output and price levels. It is regulated and controlled by the central bank and the government. Government controls the circulation of the money in the economy and central bank control supply and demand for the money and price stability.
Supply Siders theory:
Supply siders theory advocates to cutting marginal tax in order increase investment by the firm and create more jobs. As investment increases, there is an increase in supply and decrease in unemployment.
a) Restraining inflation:
According Keynesian theory, government should reduce government spending and increased tax, which causes decrease the aggregate demand and restrain the inflation.
According monetarist, government should use restrictive monetary policy to tame inflation.
And Supply-sider's theorist suggest to reduce marginal tax and reduce government intervention in order increase output and contain the inflation.
b) Reducing unemployment
According Keynesian theory, government should increase government spending and decreased marginal tax. This cause to increase the aggregate demand and reduce unemployment.
According monetarist, government should use expansive monetary policy to increase output and reduce the unemployment rate.
And Supply-sider's theorist suggest to reduce marginal tax and reduce government intervention in order increase output and contain the inflation and unemployment.
It is an economic theory of total economy spending and it effect on the inflation and output in other words it is also called Keynesian demand-side theory. Keynesian theory was formed to understand the great depression. The founder raised the government expenses and reduced the tax to stimulate the demand and help the economy to move out of depression.
Monetarism:
Monetarism is refers to the study of the economics school of thoughts. The monetarism deals with the money supply in the economy, influences by the output and price levels. It is regulated and controlled by the central bank and the government. Government controls the circulation of the money in the economy and central bank control supply and demand for the money and price stability.
Supply Siders theory:
Supply siders theory advocates to cutting marginal tax in order increase investment by the firm and create more jobs. As investment increases, there is an increase in supply and decrease in unemployment.
a) Restraining inflation:
According Keynesian theory, government should reduce government spending and increased tax, which causes decrease the aggregate demand and restrain the inflation.
According monetarist, government should use restrictive monetary policy to tame inflation.
And Supply-sider's theorist suggest to reduce marginal tax and reduce government intervention in order increase output and contain the inflation.
b) Reducing unemployment
According Keynesian theory, government should increase government spending and decreased marginal tax. This cause to increase the aggregate demand and reduce unemployment.
According monetarist, government should use expansive monetary policy to increase output and reduce the unemployment rate.
And Supply-sider's theorist suggest to reduce marginal tax and reduce government intervention in order increase output and contain the inflation and unemployment.
3
The expiration of the FICA payroll tax cut of January 1, 2013 raised taxes by $110 billion per year. If the marginal propensity to save was 0.20, ( a ) by how much did consumer spending decrease initially? ( b ) What was the ultimate decline in aggregate demand?
It has been provided that expiration of payroll tax cuts will raise taxes by $110 billion per year.
This increase in taxes will decrease the disposable income of tax payers.
Thus, disposable income in economy will decrease by $110 billion.
(a) Disposable income in economy has decreased by $110 billion.
This decrease in disposable income will result in decrease in consumption.
Calculate MPC -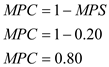 Calculate decrease in consumption -
Calculate decrease in consumption - 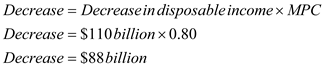 This decrease in disposable income due to tax rebates will initially decrease the consumption in the economy by $88 billion.
This decrease in disposable income due to tax rebates will initially decrease the consumption in the economy by $88 billion.
Consumption expenditure is a component of aggregate demand. So, this initial decrease in consumption expenditure will initially decrease the aggregate demand in economy by $88 billion as well.
So, initially, consumer spending in economy will decrease by $88 billion.
(b) Calculate the value of multiplier - The value of multiplier is 5.
The value of multiplier is 5.
Calculate ultimate (final) decrease in aggregate demand -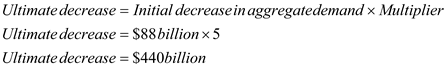 Thus, aggregate demand will ultimately decline by $440 billion.
Thus, aggregate demand will ultimately decline by $440 billion.
This increase in taxes will decrease the disposable income of tax payers.
Thus, disposable income in economy will decrease by $110 billion.
(a) Disposable income in economy has decreased by $110 billion.
This decrease in disposable income will result in decrease in consumption.
Calculate MPC -
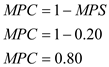 Calculate decrease in consumption -
Calculate decrease in consumption - 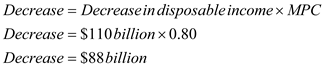 This decrease in disposable income due to tax rebates will initially decrease the consumption in the economy by $88 billion.
This decrease in disposable income due to tax rebates will initially decrease the consumption in the economy by $88 billion.Consumption expenditure is a component of aggregate demand. So, this initial decrease in consumption expenditure will initially decrease the aggregate demand in economy by $88 billion as well.
So, initially, consumer spending in economy will decrease by $88 billion.
(b) Calculate the value of multiplier -
 The value of multiplier is 5.
The value of multiplier is 5.Calculate ultimate (final) decrease in aggregate demand -
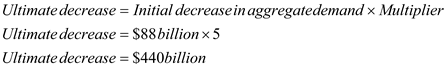 Thus, aggregate demand will ultimately decline by $440 billion.
Thus, aggregate demand will ultimately decline by $440 billion. 4
Suppose it is an election year and aggregate demand is growing so fast that it threatens to set off an inflationary movement. Why might Congress and the president hesitate to cut back on government spending or raise taxes, as economic theory suggests is appropriate?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 16 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Suppose that for every 1 percentage point increase ( decrease) in GDP growth, automatic stabilizers
(i) increase (decrease) tax revenues revenues by $90 billion and
(ii) decrease (increase) transfer payments by $30 billion.
Using this information, complete the table.

(i) increase (decrease) tax revenues revenues by $90 billion and
(ii) decrease (increase) transfer payments by $30 billion.
Using this information, complete the table.


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 16 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Should military spending be subject to macroeconomic constraints? What programs should be expanded or contracted to bring about needed changes in the budget?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 16 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
If automatic stabilizers increase the federal budget balance by $60 billion for every 1 percent increase in real GDP growth, what will happen to the federal budget balance if the economy falls into a recession of ?3 percent from a growth path of +2 percent?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 16 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Why does it take so long to recognize that a recession has begun (see the News Wire "Macro Models")?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 16 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
The following table presents hypothetical data on inflation, unemployment, and pollution associated with various levels of government expenditure and taxation. A government decision maker is trying to determine the optimal level of government expenditures and taxation with each of the three columns being a possible option (policy options A, B, or C).
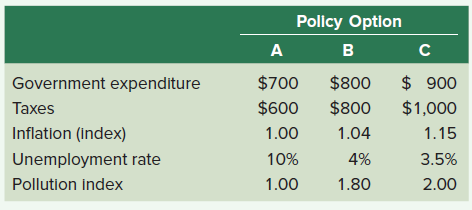
( a ) Compute the federal budget balance for each policy option.
( b ) What policy option would best accomplish each of the following goals?
I. Lowest taxes
II. Lowest pollution
III. Lowest inflation rate
IV. Lowest unemployment rate
V. A balanced federal budget

( a ) Compute the federal budget balance for each policy option.
( b ) What policy option would best accomplish each of the following goals?
I. Lowest taxes
II. Lowest pollution
III. Lowest inflation rate
IV. Lowest unemployment rate
V. A balanced federal budget

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 16 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Republicans asserted that many of President Obama's fiscal spending projects were "wasteful and ineffective." Does the content of fiscal stimulus spending matter?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 16 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
POLICY PERSPECTIVES Monetary stimulus in the form of lower interest rates is an alternative to fiscal stimulus. If a 0.1 percentage point change in interest rates has the stimulus impact of $10 billion in spending, what is the monetary equivalent (in terms of a change in the interest rate) of a $600 billion fiscal stimulus?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 16 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Outline a macro policy package for attaining full employment and price stability in the next 12 months. What obstacles, if any, will impede attainment of these goals?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 16 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Which nation had the best macro performance in 2004-2014 (see the News Wire "Comparative Performance")?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 16 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
According to the News Wire "Comparative Performance," which country had ( a ) the fastest growth and highest inflation? ( b ) The slowest growth and the lowest inflation? ( c ) Why might these performance measures be correlated?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 16 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Compare and contrast the performance of three countries in terms of real growth, inflation, and unemployment (see the News Wire "Comparative Performance").

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 16 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
POLICY PERSPECTIVES Should economic policies respond immediately to any changes in reported unemployment or inflation rates? When should a response be undertaken?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 16 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



