Deck 23: Aggregate Demand and Aggregate Supply
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/13
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 23: Aggregate Demand and Aggregate Supply
1
In 1939, with the U.S. economy not yet fully recovered from the Great Depression, President Roosevelt proclaimed that Thanksgiving would fall a week earlier than usual so that the shopping period before Christmas would be longer. Explain what President Roosevelt might have been trying to achieve, using the model of aggregate demand and aggregate supply.
The idea of President-RO proclaiming that the thanksgiving would fall a week earlier than usual so that the shopping period before Christmas would be longer. This augmentation of the shopping period between Thanksgiving and Christmas was to increase aggregate demand. From the aggregate demand and supply diagram, we could observe that this could increase output back to its long-run equilibrium level, and shows Price level and Quantity of output.
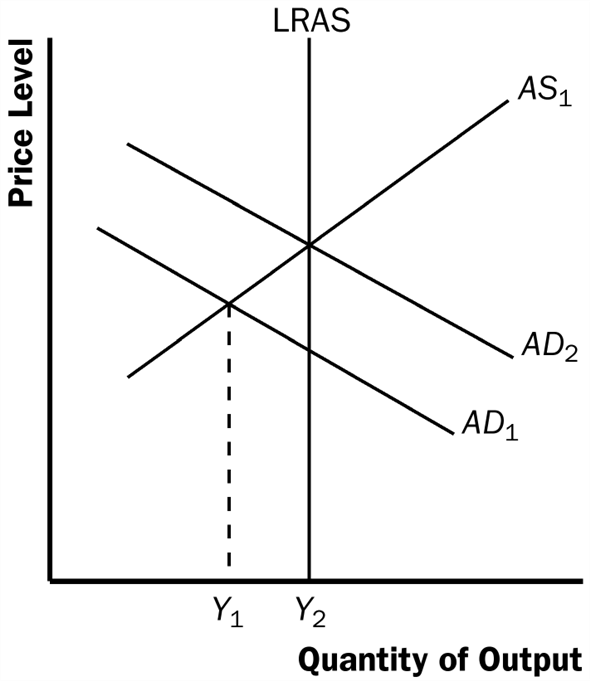 Initially the economy is at short run equilibrium at output level Y 1. The reaction of thanksgiving earlier will lead to rightward shift in the aggregate demand curve, so that the economy moves back to the long run equilibrium with higher level of output with higher prices. The reason is to start the process of spending and earning. To spend, one has to earn and earning starts when one spends on consumption.
Initially the economy is at short run equilibrium at output level Y 1. The reaction of thanksgiving earlier will lead to rightward shift in the aggregate demand curve, so that the economy moves back to the long run equilibrium with higher level of output with higher prices. The reason is to start the process of spending and earning. To spend, one has to earn and earning starts when one spends on consumption.
 Initially the economy is at short run equilibrium at output level Y 1. The reaction of thanksgiving earlier will lead to rightward shift in the aggregate demand curve, so that the economy moves back to the long run equilibrium with higher level of output with higher prices. The reason is to start the process of spending and earning. To spend, one has to earn and earning starts when one spends on consumption.
Initially the economy is at short run equilibrium at output level Y 1. The reaction of thanksgiving earlier will lead to rightward shift in the aggregate demand curve, so that the economy moves back to the long run equilibrium with higher level of output with higher prices. The reason is to start the process of spending and earning. To spend, one has to earn and earning starts when one spends on consumption. 2
Explain why the long-run aggregate-supply curve is vertical.
The long-run aggregate supply curve is vertical because in the long run because the quantity of goods and services supplied depends on the economy's labor, capital , natural resources, aggregate supply and technology but not on the overall level of prices.
Technology is the existing production technology used to turn these resources into goods and services.
The overall level of price does not have an effect on these long-run determinants of real GDP.
Technology is the existing production technology used to turn these resources into goods and services.
The overall level of price does not have an effect on these long-run determinants of real GDP.
3
Stagflation is caused by
A) a leftward shift in the aggregate-demand curve.
B) a rightward shift in the aggregate-demand curve.
C) a leftward shift in the aggregate-supply curve.
D) a rightward shift in the aggregate-supply curve.
A) a leftward shift in the aggregate-demand curve.
B) a rightward shift in the aggregate-demand curve.
C) a leftward shift in the aggregate-supply curve.
D) a rightward shift in the aggregate-supply curve.
Stagflation:
Stagflation occurs when there is a leftward shift in the short run aggregate-supply curve. The effect of this shift makes the output to fall and price level to raise that in turn leads to high inflation and unemployment rate.
Hence, option 'c' is correct.
Stagflation occurs when there is a leftward shift in the short run aggregate-supply curve. The effect of this shift makes the output to fall and price level to raise that in turn leads to high inflation and unemployment rate.
Hence, option 'c' is correct.
4
Explain why the following statements are false.
a. "The aggregate-demand curve slopes downward because it is the horizontal sum of the demand curves for individual goods."
b. "The long-run aggregate-supply curve is vertical because economic forces do not affect long-run aggregate supply."
c. "If firms adjusted their prices every day, then the short-run aggregate-supply curve would be horizontal."
d. "Whenever the economy enters a recession, its long-run aggregate-supply curve shifts to the left."
a. "The aggregate-demand curve slopes downward because it is the horizontal sum of the demand curves for individual goods."
b. "The long-run aggregate-supply curve is vertical because economic forces do not affect long-run aggregate supply."
c. "If firms adjusted their prices every day, then the short-run aggregate-supply curve would be horizontal."
d. "Whenever the economy enters a recession, its long-run aggregate-supply curve shifts to the left."

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 13 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
List and explain the three theories for why the short-run aggregate-supply curve slopes upward.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 13 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
The idea that economic downturns result from an inadequate aggregate demand for goods and services is derived from the work of which economist?
A) Adam Smith
B) David Hume
C) David Ricardo
D) John Maynard Keynes
A) Adam Smith
B) David Hume
C) David Ricardo
D) John Maynard Keynes

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 13 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
For each of the three theories for the upward slope of the short-run aggregate-supply curve, carefully explain the following:
a. how the economy recovers from a recession and returns to its long-run equilibrium without any policy intervention
b. what determines the speed of that recovery
a. how the economy recovers from a recession and returns to its long-run equilibrium without any policy intervention
b. what determines the speed of that recovery

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 13 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
What might shift the aggregate-demand curve to the left? Use the model of aggregate demand and aggregate supply to trace through the short-run and long-run effects of such a shift on output and the price level.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 13 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
The economy begins in long-run equilibrium. Then one day, the president appoints a new chairman of the Fed. This new chairman is well known for her view that inflation is not a major problem for an economy.
a. How would this news affect the price level that people would expect to prevail?
b. How would this change in the expected price level affect the nominal wage that workers and firms agree to in their new labor contracts?
c. How would this change in the nominal wage affect the profitability of producing goods and services at any given price level?
d. How does this change in profitability affect the short-run aggregate-supply curve?
e. If aggregate demand is held constant, how does this shift in the aggregate-supply curve affect the price level and the quantity of output produced?
f. Do you think this Fed chairman was a good appointment?
a. How would this news affect the price level that people would expect to prevail?
b. How would this change in the expected price level affect the nominal wage that workers and firms agree to in their new labor contracts?
c. How would this change in the nominal wage affect the profitability of producing goods and services at any given price level?
d. How does this change in profitability affect the short-run aggregate-supply curve?
e. If aggregate demand is held constant, how does this shift in the aggregate-supply curve affect the price level and the quantity of output produced?
f. Do you think this Fed chairman was a good appointment?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 13 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
What might shift the aggregate-supply curve to the left? Use the model of aggregate demand and aggregate supply to trace through the short-run and long-run effects of such a shift on output and the price level.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 13 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Explain whether each of the following events shifts the short-run aggregate-supply curve, the aggregate-demand curve, both, or neither. For each event that does shift a curve, draw a diagram to illustrate the effect on the economy.
a. Households decide to save a larger share of their income.
b. Florida orange groves suffer a prolonged period of below-freezing temperatures.
c. Increased job opportunities overseas cause many people to leave the country.
a. Households decide to save a larger share of their income.
b. Florida orange groves suffer a prolonged period of below-freezing temperatures.
c. Increased job opportunities overseas cause many people to leave the country.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 13 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
For each of the following events, explain the short-run and long-run effects on output and the price level, assuming policymakers take no action.
a. The stock market declines sharply, reducing consumers' wealth.
b. The federal government increases spending on national defense.
c. A technological improvement raises productivity.
d. A recession overseas causes foreigners to buy fewer U.S. goods.
a. The stock market declines sharply, reducing consumers' wealth.
b. The federal government increases spending on national defense.
c. A technological improvement raises productivity.
d. A recession overseas causes foreigners to buy fewer U.S. goods.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 13 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Suppose firms become very optimistic about future business conditions and invest heavily in new capital equipment.
a. Draw an aggregate-demand/aggregate-supply diagram to show the short-run effect of this optimism on the economy. Label the new levels of prices and real output. Explain in words why the aggregate quantity of output supplied changes.
b. Now use the diagram from part (a) to show the new long-run equilibrium of the economy. (For now, assume there is no change in the long-run aggregate-supply curve.) Explain in words why the aggregate quantity of output demanded changes between the short run and the long run.
c. How might the investment boom affect the long-run aggregate-supply curve? Explain.
a. Draw an aggregate-demand/aggregate-supply diagram to show the short-run effect of this optimism on the economy. Label the new levels of prices and real output. Explain in words why the aggregate quantity of output supplied changes.
b. Now use the diagram from part (a) to show the new long-run equilibrium of the economy. (For now, assume there is no change in the long-run aggregate-supply curve.) Explain in words why the aggregate quantity of output demanded changes between the short run and the long run.
c. How might the investment boom affect the long-run aggregate-supply curve? Explain.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 13 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



