Deck 1: Using the Computer in Biochemical Research
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/20
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 1: Using the Computer in Biochemical Research
1
Define each of the following terms.
(a) OSHA
(b) MSDS
(c) Flowchart
(d) Pasteur pipet
(e) Purified water
(f) Error
(g) Standard deviation
(h) Molarity
(a) OSHA
(b) MSDS
(c) Flowchart
(d) Pasteur pipet
(e) Purified water
(f) Error
(g) Standard deviation
(h) Molarity
In this problem, we are asked to define the following eight terms:
a) OSHA
b) MSDS
c) Flowchart
d) Pasteur pipet
e) Purified water
f) Error
g) Standard deviation
h) Molarity
a)OSHA is an acronym for O ccupational S afety and H ealth A dministration. They oversee US regulations for safety in the workplace.
b)MSDS is an abbreviation for M aterial S afety D ata S heet. By law, the manufacturers of chemicals must provide an MSDS for each chemical they produce and distribute detailing a variety of information about the properties, hazards, and handling of that chemical; the sheet also details proper safety equipment and steps to take in the event of a release or exposure.
c)A flowchart is used in experimental explanations to describe the experimental procedure in a visual, step-by-step manner, breaking down the work in flow paths that lead to final result.
d)A Pasteur pipet is a non-graduated pipet that can be used to transfer liquids using a rubber or latex suction bulb. When pouring is not safe or efficient, the exact volume isn't important, and a small amount of solution loss is acceptable (about 5%), then a Pasteur pipet would be useful.
e)Purified water is water that has been prepared by one of five basic processes - distillation, ion-exchange resin (DI), carbon adsorption, reverse osmosis (RO), or membrane filtration. More than one process can be used in tandem, creating ultrapure water, sometimes called Water for Injection (WFI), which is used for very sensitive operations. For most laboratory processes, DI, RO, or distilled water is used.
f)An error is a measurement taken in a experiment that deviates from the actual value; an error can be either determinate (within the control of the operator) or indeterminate (outside of experimental or equipment control).
g)Standard deviation is a term from statistics; it is a measure of the variation of data around the mean of a sample or population.
h)Molarity is a concentration of a chemical in a solution, defined as the number of moles of that chemical dissolved in one liter of the solution.
a) OSHA
b) MSDS
c) Flowchart
d) Pasteur pipet
e) Purified water
f) Error
g) Standard deviation
h) Molarity
a)OSHA is an acronym for O ccupational S afety and H ealth A dministration. They oversee US regulations for safety in the workplace.
b)MSDS is an abbreviation for M aterial S afety D ata S heet. By law, the manufacturers of chemicals must provide an MSDS for each chemical they produce and distribute detailing a variety of information about the properties, hazards, and handling of that chemical; the sheet also details proper safety equipment and steps to take in the event of a release or exposure.
c)A flowchart is used in experimental explanations to describe the experimental procedure in a visual, step-by-step manner, breaking down the work in flow paths that lead to final result.
d)A Pasteur pipet is a non-graduated pipet that can be used to transfer liquids using a rubber or latex suction bulb. When pouring is not safe or efficient, the exact volume isn't important, and a small amount of solution loss is acceptable (about 5%), then a Pasteur pipet would be useful.
e)Purified water is water that has been prepared by one of five basic processes - distillation, ion-exchange resin (DI), carbon adsorption, reverse osmosis (RO), or membrane filtration. More than one process can be used in tandem, creating ultrapure water, sometimes called Water for Injection (WFI), which is used for very sensitive operations. For most laboratory processes, DI, RO, or distilled water is used.
f)An error is a measurement taken in a experiment that deviates from the actual value; an error can be either determinate (within the control of the operator) or indeterminate (outside of experimental or equipment control).
g)Standard deviation is a term from statistics; it is a measure of the variation of data around the mean of a sample or population.
h)Molarity is a concentration of a chemical in a solution, defined as the number of moles of that chemical dissolved in one liter of the solution.
2
 What personal protection items must be worn when handling glacial acetic acid?
What personal protection items must be worn when handling glacial acetic acid?In this problem, we are asked to state what would be the correct personal protective equipment (PPE) for handling acetic acid.
Consider this chart of options for PPE: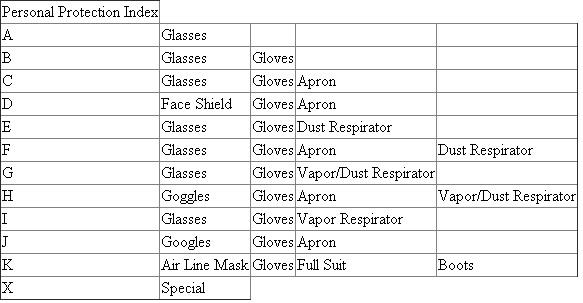 Given the hazards of acetic acid - it is flammable, damaging to skin and mucous membranes, and reacts readily with many compounds - we would place acetic acid under index H, and therefore requires splash goggles, a vapor respirator, gloves, and an apron that can withstand the acid.
Given the hazards of acetic acid - it is flammable, damaging to skin and mucous membranes, and reacts readily with many compounds - we would place acetic acid under index H, and therefore requires splash goggles, a vapor respirator, gloves, and an apron that can withstand the acid.
Consider this chart of options for PPE:
 Given the hazards of acetic acid - it is flammable, damaging to skin and mucous membranes, and reacts readily with many compounds - we would place acetic acid under index H, and therefore requires splash goggles, a vapor respirator, gloves, and an apron that can withstand the acid.
Given the hazards of acetic acid - it is flammable, damaging to skin and mucous membranes, and reacts readily with many compounds - we would place acetic acid under index H, and therefore requires splash goggles, a vapor respirator, gloves, and an apron that can withstand the acid. 3
Draw a schematic picture of your biochemistry lab and mark locations of the following safety features: eyewashes, first-aid kit, shower, fire extinguisher, chemical spill kits, and direction to nearest exit.
In this problem, we are asked to provide a schematic of our lab showing the following equipment: eyewash, first-aid kit, safety shower, fire extinguisher, chemical spill kit, and the exit.
Provided below is a schematic of a small biologics laboratory with the required equipment (along with other basic equipment).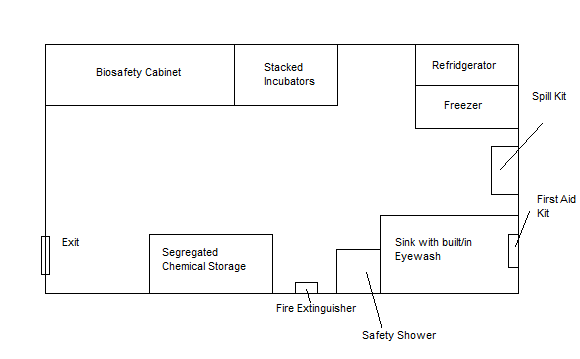
Provided below is a schematic of a small biologics laboratory with the required equipment (along with other basic equipment).

4
 Describe how you would prepare a 1-liter aqueous solution of each of the following reagents:
Describe how you would prepare a 1-liter aqueous solution of each of the following reagents:(a) 1 M glycine
(b) 0.5 M glucose
(c) 10 m M ethanol
(d) 100 n M hemoglobin

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 20 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
 Describe how you would prepare just 10 mL of each of the solutions in Problem.
Describe how you would prepare just 10 mL of each of the solutions in Problem.Describe how you would prepare a 1-liter aqueous solution of each of the following reagents:
(a) 1 M glycine
(b) 0.5 M glucose
(c) 10 m M ethanol
(d) 100 n M hemoglobin

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 20 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
 If you mix 1 mL of the 1 M glycine solution in Problem with 9 mL of water, what is the final concentration of this diluted solution in m/ M ?
If you mix 1 mL of the 1 M glycine solution in Problem with 9 mL of water, what is the final concentration of this diluted solution in m/ M ?Describe how you would prepare a 1-liter aqueous solution of each of the following reagents:
(a) 1 M glycine
(b) 0.5 M glucose
(c) 10 m M ethanol
(d) 100 n M hemoglobin

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 20 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
 Convert each of the concentrations below to m M and ? M.
Convert each of the concentrations below to m M and ? M.(a) 10 mg of glucose per 100 mL
(b) 100 mL of a solutioN2% in alanine

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 20 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
 You have just prepared a solution by weighing 20 g of sucrose, transferring it to a 1-liter volumetric flask, and adding water to the line. Calculate the concentration of the sucrose solution in terms of m M , mg/mL, and % (wt/vol).
You have just prepared a solution by weighing 20 g of sucrose, transferring it to a 1-liter volumetric flask, and adding water to the line. Calculate the concentration of the sucrose solution in terms of m M , mg/mL, and % (wt/vol).
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 20 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
 The concentrations of cholesterol, glucose, and urea in blood from a fasting individual are listed below in units of mg/100 mL (sometimes called mg%). These are standard concentration units used in the clinical chemistry lab. Convert the concentrations to m M.
The concentrations of cholesterol, glucose, and urea in blood from a fasting individual are listed below in units of mg/100 mL (sometimes called mg%). These are standard concentration units used in the clinical chemistry lab. Convert the concentrations to m M.cholesterol-200 mg%
glucose-75 mg%
urea-20 mg%

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 20 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
 The following optical rotation readings were taken by a polarimeter on a solution of an unknown carbohydrate.
The following optical rotation readings were taken by a polarimeter on a solution of an unknown carbohydrate.(a) Calculate the sample mean.
(b) Calculate the standard deviation.
(c) Calculate the 95% confidence levels for the measurement.
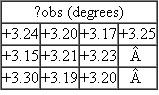

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 20 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
In Experiment 5, you will study kinetics and inhibition with the enzyme mushroom tyrosinase. Use PubMed bibliographic searches to learn the following aspects of the enzyme:
(a) What other sources of the enzyme are there besides mushrooms?
(b) What metal ion is present in the native enzyme?
(c) Find two references that study inhibition of the mushroom enzyme. What inhibitor molecules have been investigated?
(d) Find another substrate for the enzyme besides dihydroxyphenylalanine (Dopa).
(a) What other sources of the enzyme are there besides mushrooms?
(b) What metal ion is present in the native enzyme?
(c) Find two references that study inhibition of the mushroom enzyme. What inhibitor molecules have been investigated?
(d) Find another substrate for the enzyme besides dihydroxyphenylalanine (Dopa).

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 20 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Find two recent research articles published by Thomas R. Cech, who won the Nobel Prize for the discovery of ribozymes. Write brief summaries of the articles.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 20 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
The technique immobilized metal ion affinity chromatography (IMAC) is widely used to purify proteins (Experiment 4). Find two proteins that have recently been purified by this technique and briefly describe the methods for isolation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 20 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
The Western blot procedure (Experiment 7) is now used to test human serum for the presence of antibodies to the AIDS virus. Find two publications that describe procedures for this assay.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 20 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
In Experiment 9, you will study proton pumping in chloroplasts by measuring pH changes. Find an alternative experimental method to investigate proton pumping in chloroplasts.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 20 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Outline the pathway for microbial degradation of the detergent used in denaturing electrophoresis, sodium dodecyl sulfate (SDS). Hint: See the Web site on Biocatalysis/Biodegradation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 20 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Use the REBASE site to determine the specificity of the restriction enzyme Hind ll.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 20 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Use the techniques outlined in the experimental procedure to explore two enzymes you will study in later experiments. Study the two enzymes malate dehydrogenase (Experiment 10) and tyrosinase (Experiment 5). View structures and look at amino acid sequences as you did for human ? -lactalbumin.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 20 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Study the nucleotide sequence for the gene coding for human ? -lactalbumin. Hint: Begin at the NCBI home page and enter Entrez. Click on "Nucleotides" and do a search on human ? -lactalbumin. Review the GenBank report for the position of introns and exons. Obtain a FASTA report, transfer (download) the files, and complete a BLAST search for related sequences.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 20 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Use the BLAST tool to compare the amino acid sequences for human ? -lactalbumin and lysozyme. Repeat the process using BLAST to compare the nucleotide sequences for the genes coding for human ? -lactalbumin and lysozyme.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 20 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



