Deck 21: The Twenties
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/55
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 21: The Twenties
1
Who launched the government crusade to rid the country of political radicals like Emma Goldman, an anarchist and feminist, during the Red Scare of 1919?
A) Oliver Wendell Holmes
B) A. Mitchell Palmer
C) Calvin Coolidge
D) Woodrow Wilson
A) Oliver Wendell Holmes
B) A. Mitchell Palmer
C) Calvin Coolidge
D) Woodrow Wilson
A. Mitchell Palmer
2
Which of the following consumer goods had a transformative impact on day-to-day life in the United States during the 1920s?
A) Vacuum cleaners
B) Washing machines
C) Automobiles
D) Toasters
A) Vacuum cleaners
B) Washing machines
C) Automobiles
D) Toasters
Automobiles
3
What was the movement of thousands of African Americans from the South to the North and West in search of better jobs and better treatment during World War I called?
A) The Mass Exodus
B) The Great Migration
C) Black Tuesday
D) The Harlem Renaissance
A) The Mass Exodus
B) The Great Migration
C) Black Tuesday
D) The Harlem Renaissance
The Great Migration
4
The fact that, by 1929, Americans bought 60 percent of their cars and 80 percent of radios on the installment plan was evidence that
A) wages and incomes were declining.
B) only the wealthy could enjoy the new technologies.
C) corporate profits had peaked.
D) the nation's economic growth was dependent on mass consumption.
A) wages and incomes were declining.
B) only the wealthy could enjoy the new technologies.
C) corporate profits had peaked.
D) the nation's economic growth was dependent on mass consumption.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
The corruption scandal that rocked President Warren G. Harding's administration was known as
A) the Red Scare.
B) Black Tuesday.
C) Teapot Dome.
D) American Mercury.
A) the Red Scare.
B) Black Tuesday.
C) Teapot Dome.
D) American Mercury.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
J. Edgar Hoover was the first director of the
A) U.S. Department of Justice.
B) Federal Bureau of Investigation.
C) American Civil Liberties Union.
D) National Association for the Advancement of Colored People.
A) U.S. Department of Justice.
B) Federal Bureau of Investigation.
C) American Civil Liberties Union.
D) National Association for the Advancement of Colored People.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Treasury Secretary Andrew Mellon's belief in "trickle down" economics was a result of his
A) commitment to laissez-faire economics.
B) concern for the well-being of the working class.
C) faith in government regulatory agencies.
D) experience as a corporate titan.
A) commitment to laissez-faire economics.
B) concern for the well-being of the working class.
C) faith in government regulatory agencies.
D) experience as a corporate titan.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
As a consequence of the influenza epidemic,
A) many Americans refused to interact with friends and neighbors.
B) 400,000 African Americans migrated from the South to the North.
C) agricultural products and other foodstuffs were rationed.
D) hundreds of foreigners were arrested and deported by the federal government.
A) many Americans refused to interact with friends and neighbors.
B) 400,000 African Americans migrated from the South to the North.
C) agricultural products and other foodstuffs were rationed.
D) hundreds of foreigners were arrested and deported by the federal government.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
The establishment of the American Civil Liberties Union was inspired by
A) the end of World War I.
B) the "Red Summer" of 1919.
C) the Bolshevik Revolution.
D) the Palmer raids.
A) the end of World War I.
B) the "Red Summer" of 1919.
C) the Bolshevik Revolution.
D) the Palmer raids.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Charles Schenck was convicted of espionage in 1919 because he
A) protested American intervention in the Russian Revolution.
B) was a member of the Industrial Workers of the World.
C) urged Americans to oppose the military draft during World War I.
D) sent a mail bomb to the home of the attorney general of the United States.
A) protested American intervention in the Russian Revolution.
B) was a member of the Industrial Workers of the World.
C) urged Americans to oppose the military draft during World War I.
D) sent a mail bomb to the home of the attorney general of the United States.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
In the 1920s, advertisers increasingly focused their attention on the
A) unique qualities of their product.
B) reputation of the manufacturer.
C) low price of mass consumer goods.
D) personal psychology of the consumer.
A) unique qualities of their product.
B) reputation of the manufacturer.
C) low price of mass consumer goods.
D) personal psychology of the consumer.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Which of the following reflected American anxiety about the spread of communism in the wake of the Russian Revolution?
A) The use of the National Guard to end a strike by Boston's police officers
B) The outbreak of race riots during Chicago's "Red Summer"
C) The perfection of the assembly line to speed up the production of automobiles
D) The extension of credit to American consumers so they could "buy now, pay later"
A) The use of the National Guard to end a strike by Boston's police officers
B) The outbreak of race riots during Chicago's "Red Summer"
C) The perfection of the assembly line to speed up the production of automobiles
D) The extension of credit to American consumers so they could "buy now, pay later"

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
The incident that sparked the Chicago race riots of 1919 demonstrated that
A) racial segregation was practiced in the North as well as the South.
B) World War I veterans were not being reintegrated into American society.
C) the Great Migration had little impact on life in northern cities.
D) many African Americans were radicals and anti-capitalists.
A) racial segregation was practiced in the North as well as the South.
B) World War I veterans were not being reintegrated into American society.
C) the Great Migration had little impact on life in northern cities.
D) many African Americans were radicals and anti-capitalists.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
What kind of obstacles did African Americans encounter in northern cities?
A) An aggressive Ku Klux Klan
B) Hostility from white Northerners
C) Legal segregation in all public spaces
D) Voting restrictions
A) An aggressive Ku Klux Klan
B) Hostility from white Northerners
C) Legal segregation in all public spaces
D) Voting restrictions

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
What was the impact of the assembly line on American manufacturing?
A) It lowered the cost of producing consumer goods.
B) It made workers' jobs easier.
C) It increased workers' camaraderie.
D) It made it possible to uphold quality standards.
A) It lowered the cost of producing consumer goods.
B) It made workers' jobs easier.
C) It increased workers' camaraderie.
D) It made it possible to uphold quality standards.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
How did the automobile shape American housing?
A) Garages became standard features even for city apartments.
B) Americans eagerly bought homes close to interstate freeways for easy commutes.
C) Americans grew obsessed with trailer parks.
D) Americans moved into suburbs in growing numbers.
A) Garages became standard features even for city apartments.
B) Americans eagerly bought homes close to interstate freeways for easy commutes.
C) Americans grew obsessed with trailer parks.
D) Americans moved into suburbs in growing numbers.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
In 1920, according to the U.S. Census, the majority of Americans lived
A) on farms.
B) in suburbs.
C) in towns with populations of less than 1,000.
D) in cities with populations of more than 2,500.
A) on farms.
B) in suburbs.
C) in towns with populations of less than 1,000.
D) in cities with populations of more than 2,500.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
What was the reason for widespread labor unrest after World War I?
A) The influence of Communists on the labor movement
B) Salaries being outpaced by inflation
C) Opposition to U.S. intervention in the Russian Revolution
D) Workers' frustration with growing income inequality
A) The influence of Communists on the labor movement
B) Salaries being outpaced by inflation
C) Opposition to U.S. intervention in the Russian Revolution
D) Workers' frustration with growing income inequality

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
The "American Plan," proposed by Secretary of Commerce Herbert Hoover, sought to undermine labor unions by encouraging business leaders to
A) fire union members.
B) provide workers with health insurance.
C) ban the distribution of leaflets.
D) export jobs to other countries.
A) fire union members.
B) provide workers with health insurance.
C) ban the distribution of leaflets.
D) export jobs to other countries.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Roughly how many Americans worked in industries related to automobile production in 1929?
A) One in four
B) One in eight
C) Three in eight
D) One in sixteen
A) One in four
B) One in eight
C) Three in eight
D) One in sixteen

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
The writers and artists who saw the spread of mass culture and growth of consumerism as assaults on individualism, creativity, and intellectual exploration were known as the
A) Lost Generation.
B) Talented Tenth.
C) star system.
D) New Negroes.
A) Lost Generation.
B) Talented Tenth.
C) star system.
D) New Negroes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
The National Origins Act was designed to
A) limit the number of Northern European immigrants.
B) increase the number of immigrants from Asia.
C) increase the number of immigrants from Mexico.
D) limit the number of Southern and Eastern European immigrants.
A) limit the number of Northern European immigrants.
B) increase the number of immigrants from Asia.
C) increase the number of immigrants from Mexico.
D) limit the number of Southern and Eastern European immigrants.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Who promoted the "Back to Africa" movement, which sought to move black Americans to their ancestral homelands?
A) W. E. B. Du Bois and the National Association for the Advancement of Colored People
B) D. C. Stephenson and the Ku Klux Klan
C) A. Philip Randolph and the African American labor movement
D) Marcus Garvey and the Universal Negro Improvement Association
A) W. E. B. Du Bois and the National Association for the Advancement of Colored People
B) D. C. Stephenson and the Ku Klux Klan
C) A. Philip Randolph and the African American labor movement
D) Marcus Garvey and the Universal Negro Improvement Association

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Despite their differences, Langston Hughes and Marcus Garvey agreed that
A) to be truly free, black Americans needed to return to Africa.
B) African American success did not depend on white approval.
C) economic self-sufficiency was essential to developing racial pride.
D) artistic expression was crucial to the development of a positive African American identity.
A) to be truly free, black Americans needed to return to Africa.
B) African American success did not depend on white approval.
C) economic self-sufficiency was essential to developing racial pride.
D) artistic expression was crucial to the development of a positive African American identity.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
How did the marketing of Listerine during the 1920s reflect the role of advertising in a consumer-oriented economy?
A) It compared the product's quality to other similar items.
B) It convinced consumers they had a need they weren't previously aware of.
C) It identified the wealthy as the product's target audience.
D) It suggested that use of the product would improve the consumer's economic prospects.
A) It compared the product's quality to other similar items.
B) It convinced consumers they had a need they weren't previously aware of.
C) It identified the wealthy as the product's target audience.
D) It suggested that use of the product would improve the consumer's economic prospects.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Due to economic conditions during the 1920s, the majority of Americans
A) lived below the poverty line.
B) were considered wealthy.
C) were able to save part of their income.
D) invested in the stock market.
A) lived below the poverty line.
B) were considered wealthy.
C) were able to save part of their income.
D) invested in the stock market.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
The research findings of Franz Boas and Ruth Benedict on race and culture supported the beliefs of
A) Henry Ford.
B) W. J. Simmons.
C) W. E. B. Du Bois.
D) E. P. Cubberly.
A) Henry Ford.
B) W. J. Simmons.
C) W. E. B. Du Bois.
D) E. P. Cubberly.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
According to the educator E. P. Cubbery, the work of assimilation included
A) breaking up ethnic communities.
B) restoring ethnic pride in immigrant communities.
C) teaching immigrant children in their native language.
D) requiring immigrants to pass literacy tests before they were allowed to vote.
A) breaking up ethnic communities.
B) restoring ethnic pride in immigrant communities.
C) teaching immigrant children in their native language.
D) requiring immigrants to pass literacy tests before they were allowed to vote.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
During the 1920s, women who wore short skirts and makeup and enjoyed smoking, drinking, and dancing were called
A) New Negroes.
B) matinee idols.
C) suffragettes.
D) flappers.
A) New Negroes.
B) matinee idols.
C) suffragettes.
D) flappers.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Why did Marcus Garvey acquire the Black Star Line Steamship Company?
A) He wanted to create a black-owned business engaged in the import of African raw materials.
B) He wanted to ship coffee and other colonial goods from Latin America to the United States.
C) He wanted to aid in the migration of African Americans back to Africa and the West Indies.
D) He wanted white tourists to travel to the West Indies and Africa.
A) He wanted to create a black-owned business engaged in the import of African raw materials.
B) He wanted to ship coffee and other colonial goods from Latin America to the United States.
C) He wanted to aid in the migration of African Americans back to Africa and the West Indies.
D) He wanted white tourists to travel to the West Indies and Africa.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
African American culture in the 1920s, from poetry to the blues, was notable for
A) its expression of middle-class black values.
B) pandering to white audiences.
C) authentically reflecting the black experience.
D) reinforcing racist stereotypes.
A) its expression of middle-class black values.
B) pandering to white audiences.
C) authentically reflecting the black experience.
D) reinforcing racist stereotypes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Movie stars during the 1920s strongly promoted new
A) politics.
B) views on immigration.
C) fashions and hairstyles.
D) arts.
A) politics.
B) views on immigration.
C) fashions and hairstyles.
D) arts.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
What ended the wild speculation in Florida real estate during the late 1920s?
A) Lack of amenities for tourists
B) Rising gasoline prices
C) Bad weather
D) Rising land prices
A) Lack of amenities for tourists
B) Rising gasoline prices
C) Bad weather
D) Rising land prices

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
The Harlem Renaissance would not have occurred were it not for the
A) Great Migration.
B) National Association for the Advancement of Colored People.
C) Universal Negro Improvement Association.
D) Chicago Defender.
A) Great Migration.
B) National Association for the Advancement of Colored People.
C) Universal Negro Improvement Association.
D) Chicago Defender.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
What made it possible for income inequality to grow during the 1920s, a period of apparent prosperity?
A) Government corruption scandals like Teapot Dome benefited the wealthy and hurt the poor.
B) Increased mechanization of factory work led to massive unemployment among unskilled laborers.
C) Corporate and governmental efforts to destroy labor unions resulted in lower wages among the working class.
D) Corporate profits grew much faster than wages did, so more wealth was accumulated by the already rich.
A) Government corruption scandals like Teapot Dome benefited the wealthy and hurt the poor.
B) Increased mechanization of factory work led to massive unemployment among unskilled laborers.
C) Corporate and governmental efforts to destroy labor unions resulted in lower wages among the working class.
D) Corporate profits grew much faster than wages did, so more wealth was accumulated by the already rich.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Which of the following challenged the homogeneity of mass consumer culture?
A) Motion pictures
B) Advertising
C) Radio
D) Fashion
A) Motion pictures
B) Advertising
C) Radio
D) Fashion

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
The impact of the new field of psychology on the American public was visible in the
A) motion picture industry's depiction of romance.
B) advertising industry's manipulation of consumers' fears and insecurities.
C) depiction of family life on popular radio programs.
D) disillusionment expressed in the writings of the Lost Generation.
A) motion picture industry's depiction of romance.
B) advertising industry's manipulation of consumers' fears and insecurities.
C) depiction of family life on popular radio programs.
D) disillusionment expressed in the writings of the Lost Generation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Who promoted a campaign of anti-Semitic hysteria based on the belief that Jews were attempting to undermine American society and values?
A) E. P. Cubberly
B) Henry Ford
C) Felix Frankfurter
D) Nicola Sacco
A) E. P. Cubberly
B) Henry Ford
C) Felix Frankfurter
D) Nicola Sacco

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
The Sacco and Vanzetti case, like the cases of Charles Schenck and Jacob Abrams, demonstrated a predisposition among native-born Americans to see immigrants as
A) a threat to the safety and security of the American people.
B) proponents of free speech and civil liberties.
C) responsible for spreading the influenza epidemic.
D) to blame for America's moral decline.
A) a threat to the safety and security of the American people.
B) proponents of free speech and civil liberties.
C) responsible for spreading the influenza epidemic.
D) to blame for America's moral decline.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Which of the following characterized the U.S. relationship with Western Europe in the wake of World War I?
A) The U.S. economy was strengthened because the European states had become indebted to it.
B) The destructions caused by the war made the European nations an ideal market for American manufacturers.
C) The U.S. economy was weakened by the European nations' inability to repay their war debts or purchase American goods.
D) The growth of the American consumer market meant that the U.S. economy could function independently of Europe's.
A) The U.S. economy was strengthened because the European states had become indebted to it.
B) The destructions caused by the war made the European nations an ideal market for American manufacturers.
C) The U.S. economy was weakened by the European nations' inability to repay their war debts or purchase American goods.
D) The growth of the American consumer market meant that the U.S. economy could function independently of Europe's.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
Why is "Black Tuesday" considered the starting point of the Great Depression?
A) The Federal Reserve Board lowered interest rates.
B) Stock market prices fell dramatically.
C) Labor unions called a general strike.
D) Europe stopped importing American goods.
A) The Federal Reserve Board lowered interest rates.
B) Stock market prices fell dramatically.
C) Labor unions called a general strike.
D) Europe stopped importing American goods.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
In his article "The Case against the Reds" in Forum magazine in 1920 (Document 21.1), Attorney General A. Mitchell Palmer declared that "[r]obbery, not war, is the ideal of communism. This has been demonstrated in Russia, Germany, and in America." What was Palmer comparing communism to?
A) Criminality
B) Jingoism
C) Nationalism
D) Internationalism
A) Criminality
B) Jingoism
C) Nationalism
D) Internationalism

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
The results of the 1928 presidential election reflected
A) a rural-urban divide over basic values.
B) the grassroots popularity of Herbert Hoover.
C) the political influence of the Ku Klux Klan.
D) the demise of the Progressive Party.
A) a rural-urban divide over basic values.
B) the grassroots popularity of Herbert Hoover.
C) the political influence of the Ku Klux Klan.
D) the demise of the Progressive Party.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
The passage of the National Origins Act in 1924 inspired nativist reformers to
A) declare victory and withdraw from politics.
B) organize English language and citizenship classes for immigrants.
C) encourage Mexican Americans to return to their native land.
D) oppose the execution of the Italian anarchists Sacco and Vanzetti.
A) declare victory and withdraw from politics.
B) organize English language and citizenship classes for immigrants.
C) encourage Mexican Americans to return to their native land.
D) oppose the execution of the Italian anarchists Sacco and Vanzetti.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Republican victory in the 1924 presidential election can be attributed to the split within the Democratic Party over
A) social welfare policy.
B) Darwin's theory of evolution.
C) farm relief.
D) prohibition.
A) social welfare policy.
B) Darwin's theory of evolution.
C) farm relief.
D) prohibition.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
What does the image of the Ku Klux Klan wedding from 1925 (Document 21.2) reveal about the organization? 
A) It remained a southern organization.
B) It remained predominantly rural.
C) It had given up on white supremacist terrorism.
D) It had become a socially acceptable public organization.

A) It remained a southern organization.
B) It remained predominantly rural.
C) It had given up on white supremacist terrorism.
D) It had become a socially acceptable public organization.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
What can we conclude from the map of the election of 1924 (Map 21.2)? 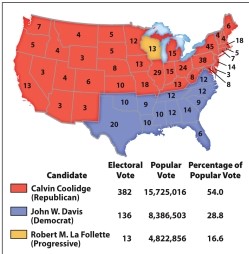
A) The Democrats' support for prohibition hurt their campaign in the Northeast.
B) Wisconsin embraced socialist politics during the 1920s.
C) Warren G. Harding won reelection despite the Teapot Dome Scandal.
D) Nothing had changed in national politics since the 1860 split.

A) The Democrats' support for prohibition hurt their campaign in the Northeast.
B) Wisconsin embraced socialist politics during the 1920s.
C) Warren G. Harding won reelection despite the Teapot Dome Scandal.
D) Nothing had changed in national politics since the 1860 split.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
The Ku Klux Klan showed significant strength in which of the following cities?
A) Indianapolis, Indiana
B) Charleston, South Carolina
C) Memphis, Tennessee
D) Jackson, Mississippi
A) Indianapolis, Indiana
B) Charleston, South Carolina
C) Memphis, Tennessee
D) Jackson, Mississippi

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
The presidential candidacy of Al Smith was possible because of
A) the demise of the Klan.
B) the groundwork laid by John W. Davis.
C) the support of Franklin D. Roosevelt.
D) his support for prohibition.
A) the demise of the Klan.
B) the groundwork laid by John W. Davis.
C) the support of Franklin D. Roosevelt.
D) his support for prohibition.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
In his acceptance of the Republican presidential nomination in 1928, Hoover declared confidence that
A) the United States would rebuild its international prestige.
B) his administration would tackle the Great Depression effectively.
C) racial discrimination would soon be a thing of the past.
D) the United States would be able to eradicate poverty permanently.
A) the United States would rebuild its international prestige.
B) his administration would tackle the Great Depression effectively.
C) racial discrimination would soon be a thing of the past.
D) the United States would be able to eradicate poverty permanently.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
Ohio high school teacher John Scopes was put on trial for giving a lecture on the theories of
A) Charles Darwin.
B) Henry Ford.
C) Gertrude Stein.
D) Franz Boas.
A) Charles Darwin.
B) Henry Ford.
C) Gertrude Stein.
D) Franz Boas.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
The Scopes trial was a perfect reflection of the culture wars of the 1920s because it
A) focused on the negative impact of immigrants on American society.
B) addressed the hot button issue of prohibition.
C) explored the impact of popular culture on social mores.
D) resulted in a guilty verdict and its subsequent overturning left both sides feeling vindicated.
A) focused on the negative impact of immigrants on American society.
B) addressed the hot button issue of prohibition.
C) explored the impact of popular culture on social mores.
D) resulted in a guilty verdict and its subsequent overturning left both sides feeling vindicated.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
What did Clifford K. Berryman's cartoon "Juggernaut" of the Teapot Dome scandal in the Washington Evening Star imply? 
A) Harding's cabinet was making a mockery of his presidency.
B) The scandal was bound to implicate the White House itself.
C) Secretary of the Interior Albert Fall was maneuvering the crisis deftly.
D) Secretary of the Navy Edward Denby was innocent of the charges.

A) Harding's cabinet was making a mockery of his presidency.
B) The scandal was bound to implicate the White House itself.
C) Secretary of the Interior Albert Fall was maneuvering the crisis deftly.
D) Secretary of the Navy Edward Denby was innocent of the charges.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
What conclusion does Figure 21.2, Income Inequality, 1923-1929, permit? 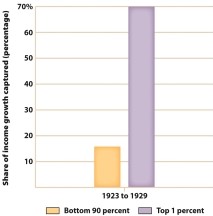
A) The bottom 90 percent held only 15 percent of the nation's wealth.
B) The top 1 percent held 15 percent of the nation's wealth.
C) The middle class was earning only 15 percent of the nation's income.
D) The richest 1 percent reaped most of the growth in income during the 1920s.

A) The bottom 90 percent held only 15 percent of the nation's wealth.
B) The top 1 percent held 15 percent of the nation's wealth.
C) The middle class was earning only 15 percent of the nation's income.
D) The richest 1 percent reaped most of the growth in income during the 1920s.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
The growth of the Ku Klux Klan outside the South during the 1920s can be attributed to the
A) spread of white supremacist ideology.
B) passage of the National Origins Act.
C) organization's adoption of nativist and traditionalist views.
D) popularity of Garveyism among African Americans.
A) spread of white supremacist ideology.
B) passage of the National Origins Act.
C) organization's adoption of nativist and traditionalist views.
D) popularity of Garveyism among African Americans.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



