Deck 12: Of Masses and Visions of the Modern 1910-1939
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/86
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 12: Of Masses and Visions of the Modern 1910-1939
1
Questions refer to the passage below.
"Eight to ten million soldiers will swallow each other up and in so doing eat all Europe more bare than any swarm of locusts. The devastation of the Thirty Years War compressed into the space of three or four years and extending over a whole continent; famine, sickness, want, brutalizing the army and the mass of the population; irrevocable confusion of our artificial structure of trade, industry and credit, ending in general bankruptcy; collapse of the old states and their traditional states craft, so that crowns will roll by dozens in the gutter and no one will be found to pick them up; it is absolutely impossible to predict where it will all end and who will emerge from the struggle as victor. Only one result is absolutely certain: a general exhaustion and the establishment of the conditions for the final victory of the working class."
Friederich Engels, German Socialist, 1887 from James Joll, The Origins of the
First World War, New York: Addison Wesley Longman, 1992
Engels's writing and prediction is best understood in the context of:
A) the application of Enlightenment ideals that originated in the eighteenth century.
B) increasing and crushing inequalities that emerged during the Industrial Revolution.
C) global objections to the oppression that European Imperialism in Africa caused.
D) new technologies that were emerging during the Second Industrial Revolution.
"Eight to ten million soldiers will swallow each other up and in so doing eat all Europe more bare than any swarm of locusts. The devastation of the Thirty Years War compressed into the space of three or four years and extending over a whole continent; famine, sickness, want, brutalizing the army and the mass of the population; irrevocable confusion of our artificial structure of trade, industry and credit, ending in general bankruptcy; collapse of the old states and their traditional states craft, so that crowns will roll by dozens in the gutter and no one will be found to pick them up; it is absolutely impossible to predict where it will all end and who will emerge from the struggle as victor. Only one result is absolutely certain: a general exhaustion and the establishment of the conditions for the final victory of the working class."
Friederich Engels, German Socialist, 1887 from James Joll, The Origins of the
First World War, New York: Addison Wesley Longman, 1992
Engels's writing and prediction is best understood in the context of:
A) the application of Enlightenment ideals that originated in the eighteenth century.
B) increasing and crushing inequalities that emerged during the Industrial Revolution.
C) global objections to the oppression that European Imperialism in Africa caused.
D) new technologies that were emerging during the Second Industrial Revolution.
increasing and crushing inequalities that emerged during the Industrial Revolution.
2
Questions refer to the documents below.
Document A. Trench Warfare, World War I Document B. Dulce et decorum est* (Excerpt), Wilfred Owen (1918)
Document B. Dulce et decorum est* (Excerpt), Wilfred Owen (1918)
Bent double, like old beggars under sacks,
Knock-kneed, coughing like hags, we cursed through sludge,
Till on the haunting flares we turned our backs
And towards our distant rest began to trudge.
Men marched asleep. Many had lost their boots
But limped on, blood-shod. All went lame; all blind;
Drunk with fatigue; deaf even to the hoots
Of gas-shells dropping softly behind.
*translation: From the Latin phrase "Dulce et decorum est, pro patria mori"
"It is sweet and fitting to die for one's country."
What was one of the consequences of World War I outside of Europe?
A) A resurgence of independence and nationalist movements in British colonies
B) The elimination of international communist movements
C) The permanent decline of the welfare state
D) A more positive view of Western traditions and institutions
Document A. Trench Warfare, World War I
 Document B. Dulce et decorum est* (Excerpt), Wilfred Owen (1918)
Document B. Dulce et decorum est* (Excerpt), Wilfred Owen (1918)Bent double, like old beggars under sacks,
Knock-kneed, coughing like hags, we cursed through sludge,
Till on the haunting flares we turned our backs
And towards our distant rest began to trudge.
Men marched asleep. Many had lost their boots
But limped on, blood-shod. All went lame; all blind;
Drunk with fatigue; deaf even to the hoots
Of gas-shells dropping softly behind.
*translation: From the Latin phrase "Dulce et decorum est, pro patria mori"
"It is sweet and fitting to die for one's country."
What was one of the consequences of World War I outside of Europe?
A) A resurgence of independence and nationalist movements in British colonies
B) The elimination of international communist movements
C) The permanent decline of the welfare state
D) A more positive view of Western traditions and institutions
A resurgence of independence and nationalist movements in British colonies
3
Questions refer to the documents below.
Document A. Trench Warfare, World War I Document B. Dulce et decorum est* (Excerpt), Wilfred Owen (1918)
Document B. Dulce et decorum est* (Excerpt), Wilfred Owen (1918)
Bent double, like old beggars under sacks,
Knock-kneed, coughing like hags, we cursed through sludge,
Till on the haunting flares we turned our backs
And towards our distant rest began to trudge.
Men marched asleep. Many had lost their boots
But limped on, blood-shod. All went lame; all blind;
Drunk with fatigue; deaf even to the hoots
Of gas-shells dropping softly behind.
*translation: From the Latin phrase "Dulce et decorum est, pro patria mori"
"It is sweet and fitting to die for one's country."
The scenes described in Documents A and B resulted in:
A) political censorship, to prevent soldiers from sharing their experiences following the war.
B) widespread isolationist movements as nations sought to avoid being dragged into future wars.
C) the formations of new international organizations dedicated to maintaining world peace.
D) a permanent and effective ban on trench warfare.
Document A. Trench Warfare, World War I
 Document B. Dulce et decorum est* (Excerpt), Wilfred Owen (1918)
Document B. Dulce et decorum est* (Excerpt), Wilfred Owen (1918)Bent double, like old beggars under sacks,
Knock-kneed, coughing like hags, we cursed through sludge,
Till on the haunting flares we turned our backs
And towards our distant rest began to trudge.
Men marched asleep. Many had lost their boots
But limped on, blood-shod. All went lame; all blind;
Drunk with fatigue; deaf even to the hoots
Of gas-shells dropping softly behind.
*translation: From the Latin phrase "Dulce et decorum est, pro patria mori"
"It is sweet and fitting to die for one's country."
The scenes described in Documents A and B resulted in:
A) political censorship, to prevent soldiers from sharing their experiences following the war.
B) widespread isolationist movements as nations sought to avoid being dragged into future wars.
C) the formations of new international organizations dedicated to maintaining world peace.
D) a permanent and effective ban on trench warfare.
the formations of new international organizations dedicated to maintaining world peace.
4
Which of the following is the reason that Tsar Nicholas II abdicated in February 1917?
A) His generals believed that protests against the tsar in the capital threatened the war effort along the Eastern Front.
B) His generals believed that the troops along the Eastern Front were needed to fight the Ottomans, but the Tsar did not agree.
C) The Tsar abdicated because his son was desperately ill and needed his father's care.
D) The Tsar abdicated in protest over the failures of the Russian military against the German army.
A) His generals believed that protests against the tsar in the capital threatened the war effort along the Eastern Front.
B) His generals believed that the troops along the Eastern Front were needed to fight the Ottomans, but the Tsar did not agree.
C) The Tsar abdicated because his son was desperately ill and needed his father's care.
D) The Tsar abdicated in protest over the failures of the Russian military against the German army.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 86 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Questions refer to the passage below.
"The Eastern Question, which is primarily involved in any discussion regarding the future of the Turks, may be called the ghost that stalks . . . the hall at Paris in which the representatives of the great nations are at present assembled for deliberation as a crisis in the world's history . . .
[At] the close of the eighteenth century the definite decline of Turkey brought the Eastern Question to an acute stage, the European Powers alternately supported the "Sick Man of Europe" or . . . hasten[ed] his demise. [Take the] famous remark of Lord Salisbury after the Crimean War, in which he apologized . . . for England's taking what turned out to be the wrong side, by declaring that she had unfortunately backed the wrong horse, is characteristic of the policy that was pursued in regard to Turkey by all the Powers. It was a question not of the right side, but of the winning side."
The Decline of the Ottoman Empire (1919) Morris Jastrow, Jr., scholar
Jastrow's description of the Eastern question as the "ghost that stalks . . . the halls at Paris" is a direct reference to:
A) the rise of Islamic fundamentalism.
B) the dismantling of the Ottoman Empire after World War I.
C) the Ottoman genocide against its Armenian population.
D) Britain's desire to dominate the Middle East following the war.
"The Eastern Question, which is primarily involved in any discussion regarding the future of the Turks, may be called the ghost that stalks . . . the hall at Paris in which the representatives of the great nations are at present assembled for deliberation as a crisis in the world's history . . .
[At] the close of the eighteenth century the definite decline of Turkey brought the Eastern Question to an acute stage, the European Powers alternately supported the "Sick Man of Europe" or . . . hasten[ed] his demise. [Take the] famous remark of Lord Salisbury after the Crimean War, in which he apologized . . . for England's taking what turned out to be the wrong side, by declaring that she had unfortunately backed the wrong horse, is characteristic of the policy that was pursued in regard to Turkey by all the Powers. It was a question not of the right side, but of the winning side."
The Decline of the Ottoman Empire (1919) Morris Jastrow, Jr., scholar
Jastrow's description of the Eastern question as the "ghost that stalks . . . the halls at Paris" is a direct reference to:
A) the rise of Islamic fundamentalism.
B) the dismantling of the Ottoman Empire after World War I.
C) the Ottoman genocide against its Armenian population.
D) Britain's desire to dominate the Middle East following the war.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 86 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Questions refer to the passage below.
"Eight to ten million soldiers will swallow each other up and in so doing eat all Europe more bare than any swarm of locusts. The devastation of the Thirty Years War compressed into the space of three or four years and extending over a whole continent; famine, sickness, want, brutalizing the army and the mass of the population; irrevocable confusion of our artificial structure of trade, industry and credit, ending in general bankruptcy; collapse of the old states and their traditional states craft, so that crowns will roll by dozens in the gutter and no one will be found to pick them up; it is absolutely impossible to predict where it will all end and who will emerge from the struggle as victor. Only one result is absolutely certain: a general exhaustion and the establishment of the conditions for the final victory of the working class."
Friederich Engels, German Socialist, 1887 from James Joll, The Origins of the
First World War, New York: Addison Wesley Longman, 1992
Engels accurately predicted the devastation brought by World War I. What would he have observed that could have led him to such a conclusion?
A) The Enlightenment
B) The Industrial Revolution
C) Imperialism
D) The Russian Revolution
"Eight to ten million soldiers will swallow each other up and in so doing eat all Europe more bare than any swarm of locusts. The devastation of the Thirty Years War compressed into the space of three or four years and extending over a whole continent; famine, sickness, want, brutalizing the army and the mass of the population; irrevocable confusion of our artificial structure of trade, industry and credit, ending in general bankruptcy; collapse of the old states and their traditional states craft, so that crowns will roll by dozens in the gutter and no one will be found to pick them up; it is absolutely impossible to predict where it will all end and who will emerge from the struggle as victor. Only one result is absolutely certain: a general exhaustion and the establishment of the conditions for the final victory of the working class."
Friederich Engels, German Socialist, 1887 from James Joll, The Origins of the
First World War, New York: Addison Wesley Longman, 1992
Engels accurately predicted the devastation brought by World War I. What would he have observed that could have led him to such a conclusion?
A) The Enlightenment
B) The Industrial Revolution
C) Imperialism
D) The Russian Revolution

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 86 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Questions refer to the passage below.
Military Participation and Military Losses in World War I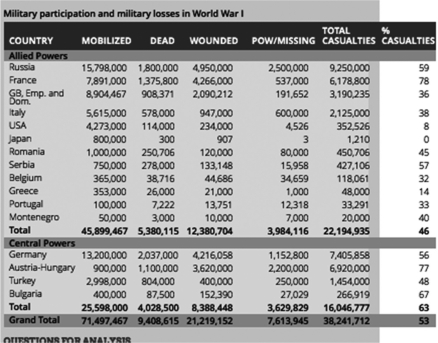
What was one consequence of the relatively low percentage (8 percent) of American casualties?
A) The American public was more willing to become involved in future European wars.
B) There were more job opportunities for women following the war.
C) It was harder to convince Britain and France to take a more lenient stance toward Germany in the Treaty of Versailles.
D) Other nations did not think American troops were very good fighters.
Military Participation and Military Losses in World War I

What was one consequence of the relatively low percentage (8 percent) of American casualties?
A) The American public was more willing to become involved in future European wars.
B) There were more job opportunities for women following the war.
C) It was harder to convince Britain and France to take a more lenient stance toward Germany in the Treaty of Versailles.
D) Other nations did not think American troops were very good fighters.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 86 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
During the 1920s and 1930s, most ideas about "being modern" acknowledged that modernity implied:
A) stylistic innovation.
B) realism in art.
C) mass production and consumption.
D) strong, authoritarian leadership.
A) stylistic innovation.
B) realism in art.
C) mass production and consumption.
D) strong, authoritarian leadership.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 86 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Questions refer to the passage below.
"Eight to ten million soldiers will swallow each other up and in so doing eat all Europe more bare than any swarm of locusts. The devastation of the Thirty Years War compressed into the space of three or four years and extending over a whole continent; famine, sickness, want, brutalizing the army and the mass of the population; irrevocable confusion of our artificial structure of trade, industry and credit, ending in general bankruptcy; collapse of the old states and their traditional states craft, so that crowns will roll by dozens in the gutter and no one will be found to pick them up; it is absolutely impossible to predict where it will all end and who will emerge from the struggle as victor. Only one result is absolutely certain: a general exhaustion and the establishment of the conditions for the final victory of the working class."
Friederich Engels, German Socialist, 1887 from James Joll, The Origins of the
First World War, New York: Addison Wesley Longman, 1992
Of the following events, which one MOST closely resembles what Engels believed to be "absolutely certain"?
A) The Russian Revolution
B) The rise of fascism in Italy and Germany
C) The Great Depression
D) The rise of anticolonial movements
"Eight to ten million soldiers will swallow each other up and in so doing eat all Europe more bare than any swarm of locusts. The devastation of the Thirty Years War compressed into the space of three or four years and extending over a whole continent; famine, sickness, want, brutalizing the army and the mass of the population; irrevocable confusion of our artificial structure of trade, industry and credit, ending in general bankruptcy; collapse of the old states and their traditional states craft, so that crowns will roll by dozens in the gutter and no one will be found to pick them up; it is absolutely impossible to predict where it will all end and who will emerge from the struggle as victor. Only one result is absolutely certain: a general exhaustion and the establishment of the conditions for the final victory of the working class."
Friederich Engels, German Socialist, 1887 from James Joll, The Origins of the
First World War, New York: Addison Wesley Longman, 1992
Of the following events, which one MOST closely resembles what Engels believed to be "absolutely certain"?
A) The Russian Revolution
B) The rise of fascism in Italy and Germany
C) The Great Depression
D) The rise of anticolonial movements

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 86 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Questions refer to the passage below.
"The Eastern Question, which is primarily involved in any discussion regarding the future of the Turks, may be called the ghost that stalks . . . the hall at Paris in which the representatives of the great nations are at present assembled for deliberation as a crisis in the world's history . . .
[At] the close of the eighteenth century the definite decline of Turkey brought the Eastern Question to an acute stage, the European Powers alternately supported the "Sick Man of Europe" or . . . hasten[ed] his demise. [Take the] famous remark of Lord Salisbury after the Crimean War, in which he apologized . . . for England's taking what turned out to be the wrong side, by declaring that she had unfortunately backed the wrong horse, is characteristic of the policy that was pursued in regard to Turkey by all the Powers. It was a question not of the right side, but of the winning side."
The Decline of the Ottoman Empire (1919) Morris Jastrow, Jr., scholar
Based on your knowledge of world history, which of the following is a long-term consequence of the decisions made at Versailles to dismantle the Ottoman Empire?
A) The ongoing conflict between the Israeli state and displaced Palestinians
B) The rise of a theocratic Islamic Shi'a state in Iran
C) The creation of Saudi Arabia and control over a significant portion of the world's oil reserves
D) The creation of democratic governments throughout the Middle East
"The Eastern Question, which is primarily involved in any discussion regarding the future of the Turks, may be called the ghost that stalks . . . the hall at Paris in which the representatives of the great nations are at present assembled for deliberation as a crisis in the world's history . . .
[At] the close of the eighteenth century the definite decline of Turkey brought the Eastern Question to an acute stage, the European Powers alternately supported the "Sick Man of Europe" or . . . hasten[ed] his demise. [Take the] famous remark of Lord Salisbury after the Crimean War, in which he apologized . . . for England's taking what turned out to be the wrong side, by declaring that she had unfortunately backed the wrong horse, is characteristic of the policy that was pursued in regard to Turkey by all the Powers. It was a question not of the right side, but of the winning side."
The Decline of the Ottoman Empire (1919) Morris Jastrow, Jr., scholar
Based on your knowledge of world history, which of the following is a long-term consequence of the decisions made at Versailles to dismantle the Ottoman Empire?
A) The ongoing conflict between the Israeli state and displaced Palestinians
B) The rise of a theocratic Islamic Shi'a state in Iran
C) The creation of Saudi Arabia and control over a significant portion of the world's oil reserves
D) The creation of democratic governments throughout the Middle East

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 86 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Questions refer to the passage below.
"Eight to ten million soldiers will swallow each other up and in so doing eat all Europe more bare than any swarm of locusts. The devastation of the Thirty Years War compressed into the space of three or four years and extending over a whole continent; famine, sickness, want, brutalizing the army and the mass of the population; irrevocable confusion of our artificial structure of trade, industry and credit, ending in general bankruptcy; collapse of the old states and their traditional states craft, so that crowns will roll by dozens in the gutter and no one will be found to pick them up; it is absolutely impossible to predict where it will all end and who will emerge from the struggle as victor. Only one result is absolutely certain: a general exhaustion and the establishment of the conditions for the final victory of the working class."
Friederich Engels, German Socialist, 1887 from James Joll, The Origins of the
First World War, New York: Addison Wesley Longman, 1992
Which of the following empires fell as a result of World War I?
A) The British Empire
B) The Ming dynasty
C) The Ottoman Empire
D) The Portuguese Empire
"Eight to ten million soldiers will swallow each other up and in so doing eat all Europe more bare than any swarm of locusts. The devastation of the Thirty Years War compressed into the space of three or four years and extending over a whole continent; famine, sickness, want, brutalizing the army and the mass of the population; irrevocable confusion of our artificial structure of trade, industry and credit, ending in general bankruptcy; collapse of the old states and their traditional states craft, so that crowns will roll by dozens in the gutter and no one will be found to pick them up; it is absolutely impossible to predict where it will all end and who will emerge from the struggle as victor. Only one result is absolutely certain: a general exhaustion and the establishment of the conditions for the final victory of the working class."
Friederich Engels, German Socialist, 1887 from James Joll, The Origins of the
First World War, New York: Addison Wesley Longman, 1992
Which of the following empires fell as a result of World War I?
A) The British Empire
B) The Ming dynasty
C) The Ottoman Empire
D) The Portuguese Empire

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 86 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Which of the following was a major consequence of World War I?
A) European claims of a superior level of culture were supported by military victories.
B) The interdependence of global trade networks intensified in the 1920s and 1930s.
C) Social hierarchies in European societies were shaken up or overthrown.
D) States were free to act without the support of their citizens or subjects.
A) European claims of a superior level of culture were supported by military victories.
B) The interdependence of global trade networks intensified in the 1920s and 1930s.
C) Social hierarchies in European societies were shaken up or overthrown.
D) States were free to act without the support of their citizens or subjects.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 86 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Questions refer to the passage below.
Military Participation and Military Losses in World War I
A historian studying the table above would find it most useful in determining:
A) the relative size of each military.
B) who had the strongest military.
C) the manpower contributions of colonies.
D) who had the best technology.
Military Participation and Military Losses in World War I

A historian studying the table above would find it most useful in determining:
A) the relative size of each military.
B) who had the strongest military.
C) the manpower contributions of colonies.
D) who had the best technology.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 86 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Which of the following was a consequence of the mass mobilizations required by World War I?
A) Fewer colonial soldiers were required since a high number of European men were called up.
B) European food production to supply the military rapidly increased.
C) Traditional gender boundaries were undermined.
D) Unionized labor movements demanded higher wages.
A) Fewer colonial soldiers were required since a high number of European men were called up.
B) European food production to supply the military rapidly increased.
C) Traditional gender boundaries were undermined.
D) Unionized labor movements demanded higher wages.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 86 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Questions refer to the documents below.
Document A. Trench Warfare, World War I Document B. Dulce et decorum est* (Excerpt), Wilfred Owen (1918)
Document B. Dulce et decorum est* (Excerpt), Wilfred Owen (1918)
Bent double, like old beggars under sacks,
Knock-kneed, coughing like hags, we cursed through sludge,
Till on the haunting flares we turned our backs
And towards our distant rest began to trudge.
Men marched asleep. Many had lost their boots
But limped on, blood-shod. All went lame; all blind;
Drunk with fatigue; deaf even to the hoots
Of gas-shells dropping softly behind.
*translation: From the Latin phrase "Dulce et decorum est, pro patria mori"
"It is sweet and fitting to die for one's country."
Document B describes the effects of:
A) an attack by the new weapon, tanks.
B) forced marches to cover the long distances to the front.
C) chemical warfare and poison gas.
D) sleep deprivation from long periods at the front.
Document A. Trench Warfare, World War I
 Document B. Dulce et decorum est* (Excerpt), Wilfred Owen (1918)
Document B. Dulce et decorum est* (Excerpt), Wilfred Owen (1918)Bent double, like old beggars under sacks,
Knock-kneed, coughing like hags, we cursed through sludge,
Till on the haunting flares we turned our backs
And towards our distant rest began to trudge.
Men marched asleep. Many had lost their boots
But limped on, blood-shod. All went lame; all blind;
Drunk with fatigue; deaf even to the hoots
Of gas-shells dropping softly behind.
*translation: From the Latin phrase "Dulce et decorum est, pro patria mori"
"It is sweet and fitting to die for one's country."
Document B describes the effects of:
A) an attack by the new weapon, tanks.
B) forced marches to cover the long distances to the front.
C) chemical warfare and poison gas.
D) sleep deprivation from long periods at the front.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 86 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
The tension in Europe that led to World War I was partly caused by a growing nationalist rivalry between which two states?
A) Great Britain and Germany
B) Great Britain and France
C) France and Russia
D) Russia and Great Britain
A) Great Britain and Germany
B) Great Britain and France
C) France and Russia
D) Russia and Great Britain

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 86 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Questions refer to the passage below.
Military Participation and Military Losses in World War I
The relatively high casualty rates (compared to future wars) can best be explained by:
A) the creation of new, more powerful weapons.
B) superior military leadership.
C) the fluid nature of the war on the Western Front.
D) the deliberate bombing of cities by bombers and zeppelins.
Military Participation and Military Losses in World War I

The relatively high casualty rates (compared to future wars) can best be explained by:
A) the creation of new, more powerful weapons.
B) superior military leadership.
C) the fluid nature of the war on the Western Front.
D) the deliberate bombing of cities by bombers and zeppelins.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 86 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Questions refer to the passage below.
"The Eastern Question, which is primarily involved in any discussion regarding the future of the Turks, may be called the ghost that stalks . . . the hall at Paris in which the representatives of the great nations are at present assembled for deliberation as a crisis in the world's history . . .
[At] the close of the eighteenth century the definite decline of Turkey brought the Eastern Question to an acute stage, the European Powers alternately supported the "Sick Man of Europe" or . . . hasten[ed] his demise. [Take the] famous remark of Lord Salisbury after the Crimean War, in which he apologized . . . for England's taking what turned out to be the wrong side, by declaring that she had unfortunately backed the wrong horse, is characteristic of the policy that was pursued in regard to Turkey by all the Powers. It was a question not of the right side, but of the winning side."
The Decline of the Ottoman Empire (1919) Morris Jastrow, Jr., scholar
Based on the passage above, which statement best supports the author's assertion that European powers took care to pursue the "winning side" rather than the "right side" when it came to foreign policy regarding the Ottoman Empire?
A) European nations supported the "Sick Man of Europe" to maintain the status quo.
B) Britain was inclined to "back the wrong horse" in international affairs.
C) Depending on the situation, European nations either supported or weakened the Ottomans.
D) Turkey's decline brought about a new European foreign policy to support the new states.
"The Eastern Question, which is primarily involved in any discussion regarding the future of the Turks, may be called the ghost that stalks . . . the hall at Paris in which the representatives of the great nations are at present assembled for deliberation as a crisis in the world's history . . .
[At] the close of the eighteenth century the definite decline of Turkey brought the Eastern Question to an acute stage, the European Powers alternately supported the "Sick Man of Europe" or . . . hasten[ed] his demise. [Take the] famous remark of Lord Salisbury after the Crimean War, in which he apologized . . . for England's taking what turned out to be the wrong side, by declaring that she had unfortunately backed the wrong horse, is characteristic of the policy that was pursued in regard to Turkey by all the Powers. It was a question not of the right side, but of the winning side."
The Decline of the Ottoman Empire (1919) Morris Jastrow, Jr., scholar
Based on the passage above, which statement best supports the author's assertion that European powers took care to pursue the "winning side" rather than the "right side" when it came to foreign policy regarding the Ottoman Empire?
A) European nations supported the "Sick Man of Europe" to maintain the status quo.
B) Britain was inclined to "back the wrong horse" in international affairs.
C) Depending on the situation, European nations either supported or weakened the Ottomans.
D) Turkey's decline brought about a new European foreign policy to support the new states.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 86 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Questions refer to the passage below.
"The Eastern Question, which is primarily involved in any discussion regarding the future of the Turks, may be called the ghost that stalks . . . the hall at Paris in which the representatives of the great nations are at present assembled for deliberation as a crisis in the world's history . . .
[At] the close of the eighteenth century the definite decline of Turkey brought the Eastern Question to an acute stage, the European Powers alternately supported the "Sick Man of Europe" or . . . hasten[ed] his demise. [Take the] famous remark of Lord Salisbury after the Crimean War, in which he apologized . . . for England's taking what turned out to be the wrong side, by declaring that she had unfortunately backed the wrong horse, is characteristic of the policy that was pursued in regard to Turkey by all the Powers. It was a question not of the right side, but of the winning side."
The Decline of the Ottoman Empire (1919) Morris Jastrow, Jr., scholar
Which of the following was a key factor in the weakening of the Ottoman Empire through the latter half of the nineteenth century?
A) Continued conflict with Spain for control of the Mediterranean Sea
B) Failure to modernize industry and the economy, and to reform government
C) Failure to defeat Russia during the Crimean War, opening the door for Russian expansion around the Black Sea
D) Failure to capture the city of Vienna from the Hapsburg Empire.
"The Eastern Question, which is primarily involved in any discussion regarding the future of the Turks, may be called the ghost that stalks . . . the hall at Paris in which the representatives of the great nations are at present assembled for deliberation as a crisis in the world's history . . .
[At] the close of the eighteenth century the definite decline of Turkey brought the Eastern Question to an acute stage, the European Powers alternately supported the "Sick Man of Europe" or . . . hasten[ed] his demise. [Take the] famous remark of Lord Salisbury after the Crimean War, in which he apologized . . . for England's taking what turned out to be the wrong side, by declaring that she had unfortunately backed the wrong horse, is characteristic of the policy that was pursued in regard to Turkey by all the Powers. It was a question not of the right side, but of the winning side."
The Decline of the Ottoman Empire (1919) Morris Jastrow, Jr., scholar
Which of the following was a key factor in the weakening of the Ottoman Empire through the latter half of the nineteenth century?
A) Continued conflict with Spain for control of the Mediterranean Sea
B) Failure to modernize industry and the economy, and to reform government
C) Failure to defeat Russia during the Crimean War, opening the door for Russian expansion around the Black Sea
D) Failure to capture the city of Vienna from the Hapsburg Empire.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 86 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Questions refer to the documents below.
Document A. Trench Warfare, World War I Document B. Dulce et decorum est* (Excerpt), Wilfred Owen (1918)
Document B. Dulce et decorum est* (Excerpt), Wilfred Owen (1918)
Bent double, like old beggars under sacks,
Knock-kneed, coughing like hags, we cursed through sludge,
Till on the haunting flares we turned our backs
And towards our distant rest began to trudge.
Men marched asleep. Many had lost their boots
But limped on, blood-shod. All went lame; all blind;
Drunk with fatigue; deaf even to the hoots
Of gas-shells dropping softly behind.
*translation: From the Latin phrase "Dulce et decorum est, pro patria mori"
"It is sweet and fitting to die for one's country."
Trench warfare, as depicted in Documents A and B, led to:
A) an increase in wartime casualties.
B) rapid progress in major battles.
C) major breakthroughs on the Eastern Front with Russia.
D) improved morale among soldiers.
Document A. Trench Warfare, World War I
 Document B. Dulce et decorum est* (Excerpt), Wilfred Owen (1918)
Document B. Dulce et decorum est* (Excerpt), Wilfred Owen (1918)Bent double, like old beggars under sacks,
Knock-kneed, coughing like hags, we cursed through sludge,
Till on the haunting flares we turned our backs
And towards our distant rest began to trudge.
Men marched asleep. Many had lost their boots
But limped on, blood-shod. All went lame; all blind;
Drunk with fatigue; deaf even to the hoots
Of gas-shells dropping softly behind.
*translation: From the Latin phrase "Dulce et decorum est, pro patria mori"
"It is sweet and fitting to die for one's country."
Trench warfare, as depicted in Documents A and B, led to:
A) an increase in wartime casualties.
B) rapid progress in major battles.
C) major breakthroughs on the Eastern Front with Russia.
D) improved morale among soldiers.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 86 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Why did Lenin accept the defeat of the Russian army and a peace treaty with Germany in 1917 that ceded a huge amount of land?
A) He envisioned a German-Russian counter-offensive against the Entente powers.
B) He felt his priority was to defend the socialist revolution in Russia.
C) He became sympathetic to the German monarchy's war aims.
D) He anticipated an imminent socialist revolution in Germany.
A) He envisioned a German-Russian counter-offensive against the Entente powers.
B) He felt his priority was to defend the socialist revolution in Russia.
C) He became sympathetic to the German monarchy's war aims.
D) He anticipated an imminent socialist revolution in Germany.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 86 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
By the end of the 1930s, how did most people perceive the liberal democratic model of governance?
A) Revolutionary and exciting
B) Established and successful
C) Weak and vulnerable
D) Incompetent and disastrous
A) Revolutionary and exciting
B) Established and successful
C) Weak and vulnerable
D) Incompetent and disastrous

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 86 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
How did World War I change the role of states?
A) It made them afraid of overstepping and causing another war.
B) It led to an increase in the size and scope of their role in society.
C) It encouraged them to cooperate more closely with one another after the war.
D) It led to more autonomy for individual citizens and subjects.
A) It made them afraid of overstepping and causing another war.
B) It led to an increase in the size and scope of their role in society.
C) It encouraged them to cooperate more closely with one another after the war.
D) It led to more autonomy for individual citizens and subjects.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 86 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
How did Joseph Stalin plan to replace capitalist agriculture with socialist agriculture in the Soviet Union?
A) By replacing the market for agricultural products with a subsistence economy where everyone was responsible for growing their own food
B) By requiring all farmers to sell their produce to state-run marketing cooperatives that would guarantee farmers a significant profit
C) By forcing peasant farmers to join state-run agricultural collectives
D) By making it illegal for anyone to profit from the sale of farm machinery or animals
A) By replacing the market for agricultural products with a subsistence economy where everyone was responsible for growing their own food
B) By requiring all farmers to sell their produce to state-run marketing cooperatives that would guarantee farmers a significant profit
C) By forcing peasant farmers to join state-run agricultural collectives
D) By making it illegal for anyone to profit from the sale of farm machinery or animals

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 86 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
What did the authoritarian political systems of Germany, Japan, and Italy have in common?
A) All were defeated in World War I.
B) All of them lost their colonies after the Versailles Treaty was signed.
C) All were excluded from the League of Nations.
D) All disliked the left-wing government that emerged in the Soviet Union.
A) All were defeated in World War I.
B) All of them lost their colonies after the Versailles Treaty was signed.
C) All were excluded from the League of Nations.
D) All disliked the left-wing government that emerged in the Soviet Union.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 86 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Which of the following was a consequence of countries imposing protective tariffs?
A) Manufacturers cut back on production and laid off millions of workers.
B) Local industries and products were able to drive out foreign imports.
C) The flow of trade was made easier within a hemisphere.
D) The production of raw materials soared.
A) Manufacturers cut back on production and laid off millions of workers.
B) Local industries and products were able to drive out foreign imports.
C) The flow of trade was made easier within a hemisphere.
D) The production of raw materials soared.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 86 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Which of the following was implied by the economic theories promoted by John Maynard Keynes?
A) The role of business and economic production was to serve the interests of the state.
B) Human nature was best served by an economy made up of many small producers in competition with one another.
C) The ideal human society was one in which everyone contributed what they could and took what they needed.
D) At times states needed to compensate for failures in the market by stimulating the economy with job creation and increasing the supply of currency.
A) The role of business and economic production was to serve the interests of the state.
B) Human nature was best served by an economy made up of many small producers in competition with one another.
C) The ideal human society was one in which everyone contributed what they could and took what they needed.
D) At times states needed to compensate for failures in the market by stimulating the economy with job creation and increasing the supply of currency.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 86 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
How did World War I contribute to the rise of mass production?
A) The state took greater control of economic decision making.
B) Large amounts of standardized war materiel had to be produced as quickly and cheaply as possible.
C) The development of economic nationalism was encouraged by the combatant states.
D) Campaigns encouraged people to buy more goods in order to show their patriotism.
A) The state took greater control of economic decision making.
B) Large amounts of standardized war materiel had to be produced as quickly and cheaply as possible.
C) The development of economic nationalism was encouraged by the combatant states.
D) Campaigns encouraged people to buy more goods in order to show their patriotism.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 86 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
In the immediate aftermath of World War I, how did European powers respond to claims for self-determination in their colonies?
A) They organized an international congress to discuss the rights of colonial subjects.
B) They granted greater local autonomy and authored a roadmap to full independence.
C) They violently suppressed nationalist movements in their colonies.
D) They instituted a renewed policy of salutary neglect.
A) They organized an international congress to discuss the rights of colonial subjects.
B) They granted greater local autonomy and authored a roadmap to full independence.
C) They violently suppressed nationalist movements in their colonies.
D) They instituted a renewed policy of salutary neglect.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 86 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Why did Henry Ford pay his automobile factory workers more than double the usual industrial wage?
A) High pay was the only way to entice workers to become cogs in a depersonalized labor process.
B) Ford employed primarily veterans of World War I and saw high wages as his patriotic duty.
C) Ford was influenced by modern socialist ideals.
D) Ford understood that consumers drove production and wanted his workers to be able to consume.
A) High pay was the only way to entice workers to become cogs in a depersonalized labor process.
B) Ford employed primarily veterans of World War I and saw high wages as his patriotic duty.
C) Ford was influenced by modern socialist ideals.
D) Ford understood that consumers drove production and wanted his workers to be able to consume.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 86 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Which of the following describes the overall impact of the New Deal?
A) It offered a quick end to the Great Depression in the United States.
B) It preserved the American system of capitalism.
C) It caused the emergence of authoritarian rule in the United States.
D) It generated an extensive redistribution of wealth in American society.
A) It offered a quick end to the Great Depression in the United States.
B) It preserved the American system of capitalism.
C) It caused the emergence of authoritarian rule in the United States.
D) It generated an extensive redistribution of wealth in American society.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 86 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Which of the following describes the first response of the U.S. government to the Great Depression?
A) It created a jobs program to help the unemployed return to productivity.
B) It expanded the role of the state to meet the economic crisis.
C) It promoted more active participation in the League of Nations.
D) It insisted on individual thrift and self-reliance, not government handouts.
A) It created a jobs program to help the unemployed return to productivity.
B) It expanded the role of the state to meet the economic crisis.
C) It promoted more active participation in the League of Nations.
D) It insisted on individual thrift and self-reliance, not government handouts.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 86 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Which of the following demonstrated authoritarian governments' inability to exercise total control over mass culture?
A) Germany was unable to suppress Triumph of the Will.
B) Powerful radio transmitters permitted stations to reach larger national audiences.
C) Jazz recordings were available in Germany and the Soviet Union.
D) Josephine Baker was very popular after the war.
A) Germany was unable to suppress Triumph of the Will.
B) Powerful radio transmitters permitted stations to reach larger national audiences.
C) Jazz recordings were available in Germany and the Soviet Union.
D) Josephine Baker was very popular after the war.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 86 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
On what did Soviet governance under Stalin rely to ensure citizen compliance with its policies?
A) Terror
B) Tacit support from church hierarchies
C) Cooperation
D) Bribery and corruption
A) Terror
B) Tacit support from church hierarchies
C) Cooperation
D) Bribery and corruption

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 86 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Which of the following was a cause of the Great Depression?
A) Abandoning the gold standard
B) The rise of protectionism and decline of free trade
C) The Soviet Union's isolation from the League of Nations
D) Low interest rates in the United States
A) Abandoning the gold standard
B) The rise of protectionism and decline of free trade
C) The Soviet Union's isolation from the League of Nations
D) Low interest rates in the United States

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 86 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Which of the following is a similarity among European states' response to World War I?
A) All states, even democracies, suspended many democratic rights and intervened in both production and consumption.
B) Democratic states, such as Britain and France, held fast to liberal policies despite the war.
C) The war and economic crises that followed led all states to reduce the scope of their control.
D) In Russia, France, and Britain, liberal capitalism prevailed following the war.
A) All states, even democracies, suspended many democratic rights and intervened in both production and consumption.
B) Democratic states, such as Britain and France, held fast to liberal policies despite the war.
C) The war and economic crises that followed led all states to reduce the scope of their control.
D) In Russia, France, and Britain, liberal capitalism prevailed following the war.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 86 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Which of the following accurately characterizes the October 1917 Bolshevik Revolution?
A) The Bolshevik Revolution was an overthrow of the Russian monarchy.
B) The Bolshevik Revolution was an attempt by military and political elites to restore order.
C) The Bolshevik Revolution was proclaimed by socialists in order to overtake the earlier "bourgeois" revolution.
D) The Bolshevik Revolution was initiated by the Ottomans in order to pull Russia out of World War I.
A) The Bolshevik Revolution was an overthrow of the Russian monarchy.
B) The Bolshevik Revolution was an attempt by military and political elites to restore order.
C) The Bolshevik Revolution was proclaimed by socialists in order to overtake the earlier "bourgeois" revolution.
D) The Bolshevik Revolution was initiated by the Ottomans in order to pull Russia out of World War I.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 86 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Which of the following industries best represents the development of mass culture in the United States after World War I?
A) The steel industry
B) The railroad industry
C) The shipping industry
D) The advertising industry
A) The steel industry
B) The railroad industry
C) The shipping industry
D) The advertising industry

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 86 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
How did the French Popular Front government respond to threats of a rightist coup in the 1930s?
A) It instituted a forty-hour workweek, the right to collective bargaining, and a minimum wage.
B) It called up the military in Paris to suppress riots.
C) It ejected the French Communist Party from its national coalition.
D) It made the fascist party illegal in France and reaffirmed its adherence to liberal capitalism.
A) It instituted a forty-hour workweek, the right to collective bargaining, and a minimum wage.
B) It called up the military in Paris to suppress riots.
C) It ejected the French Communist Party from its national coalition.
D) It made the fascist party illegal in France and reaffirmed its adherence to liberal capitalism.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 86 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Woodrow Wilson's Fourteen Points most directly influenced which provision of the Treaty of Versailles?
A) The organization of a League of Nations
B) The requirement that Germany pay reparations to the victorious Allied nations
C) The assignment of blame for World War I to Germany
D) The transfer of Germany's concessions in China to Japan
A) The organization of a League of Nations
B) The requirement that Germany pay reparations to the victorious Allied nations
C) The assignment of blame for World War I to Germany
D) The transfer of Germany's concessions in China to Japan

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 86 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
Which of the following was Mustafa Kemal's first action to create a European-style secular state in Turkey?
A) Replacing the sultanate with a republic
B) Reinforcing the role of Islam in law and politics
C) Putting a Swiss legal code into place
D) Instituting Western-style dress codes for Turkish public life
A) Replacing the sultanate with a republic
B) Reinforcing the role of Islam in law and politics
C) Putting a Swiss legal code into place
D) Instituting Western-style dress codes for Turkish public life

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 86 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Under what circumstances did Benito Mussolini initially gain control of the Italian government?
A) The Fascist Party achieved a large majority of the vote in national elections.
B) The Fascist Party overthrew the Italian government in a violent coup d'état.
C) Mussolini was appointed prime minister by the Italian king.
D) He used intimidation tactics to force the prime minister to do his bidding.
A) The Fascist Party achieved a large majority of the vote in national elections.
B) The Fascist Party overthrew the Italian government in a violent coup d'état.
C) Mussolini was appointed prime minister by the Italian king.
D) He used intimidation tactics to force the prime minister to do his bidding.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 86 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
What prevented the republic established in China in 1911 from gaining legitimacy?
A) Opposition from the Guomindang
B) Opposition from Chiang Kai-shek
C) Factional and regional conflicts
D) Lack of support from the military or rural elites
A) Opposition from the Guomindang
B) Opposition from Chiang Kai-shek
C) Factional and regional conflicts
D) Lack of support from the military or rural elites

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 86 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
In general, anticolonial nationalist movements wanted to:
A) use their indigenous cultural and religious traditions as sources for mobilization.
B) use violent means to gain their independence from colonial rule.
C) use local religions as a template that could lead to a better form of government.
D) rely on indigenous prophetic movements to oppose colonial control.
A) use their indigenous cultural and religious traditions as sources for mobilization.
B) use violent means to gain their independence from colonial rule.
C) use local religions as a template that could lead to a better form of government.
D) rely on indigenous prophetic movements to oppose colonial control.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 86 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Which individual was most responsible for mobilizing a mass anticolonial movement in British-controlled India?
A) Jawaharlal Nehru
B) Mohandas K. Gandhi
C) Mohammad Ali Jinnah
D) Mustafa Kemal Ataturk
A) Jawaharlal Nehru
B) Mohandas K. Gandhi
C) Mohammad Ali Jinnah
D) Mustafa Kemal Ataturk

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 86 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
What was Satyagraha?
A) A philosophy of nonviolent resistance
B) A philosophy of self-reliance
C) An Indian epic poem
D) A dance with martial overtones that upset authorities
A) A philosophy of nonviolent resistance
B) A philosophy of self-reliance
C) An Indian epic poem
D) A dance with martial overtones that upset authorities

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 86 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
In what ways did Getulio Vargas seek support from Brazilian blacks?
A) He supported public schools and paved roads.
B) He legalized candomblé dances and samba schools.
C) He enfranchised literate women voters.
D) He built steel mills and factories.
A) He supported public schools and paved roads.
B) He legalized candomblé dances and samba schools.
C) He enfranchised literate women voters.
D) He built steel mills and factories.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 86 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
Which African leader invoked precolonial traditions as a basis for resisting British colonialism in Kenya?
A) Blaise Diagne
B) Mohandas K. Gandhi
C) Jomo Kenyatta
D) Bambatha Zondi
A) Blaise Diagne
B) Mohandas K. Gandhi
C) Jomo Kenyatta
D) Bambatha Zondi

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 86 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
Italian Fascists considered themselves to be the defenders of which of the following?
A) Large corporations and the capitalist system in which they participated
B) The Italian monarchy and aristocracy
C) Peasants, nonsocialist workers, veterans, students, and white-collar professionals
D) Unionized factory workers and miners
A) Large corporations and the capitalist system in which they participated
B) The Italian monarchy and aristocracy
C) Peasants, nonsocialist workers, veterans, students, and white-collar professionals
D) Unionized factory workers and miners

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 86 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
Following World War I, Indian nationalists embraced which of the following methods of combating colonial control?
A) Indians joined forces with other colonized peoples in Africa and Asia to wage war against all Western domination.
B) Indians cooperated with British rule to prove that they were ready for self-government.
C) Indians supported the actions of educated elite lawyers and merchants in the Indian
National Congress.
D) Indians boycotted British goods, refused to pay taxes, and refused to send their children to British schools.
A) Indians joined forces with other colonized peoples in Africa and Asia to wage war against all Western domination.
B) Indians cooperated with British rule to prove that they were ready for self-government.
C) Indians supported the actions of educated elite lawyers and merchants in the Indian
National Congress.
D) Indians boycotted British goods, refused to pay taxes, and refused to send their children to British schools.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 86 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
Which of the following was a reason why Adolf Hitler and the Nazis were popular with the German electorate?
A) They refused to resort to force or public disturbances.
B) They supported the Weimar Republic.
C) They claimed success in restoring order and improving the economy.
D) They nationalized agriculture and industry.
A) They refused to resort to force or public disturbances.
B) They supported the Weimar Republic.
C) They claimed success in restoring order and improving the economy.
D) They nationalized agriculture and industry.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 86 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
Which of the following initiated Japan's turn toward authoritarian rule?
A) The Korean rebellion against Japanese rule
B) World War I ending
C) Emperor Hirohito's coming to power
D) An uprising of naval officers and army cadets
A) The Korean rebellion against Japanese rule
B) World War I ending
C) Emperor Hirohito's coming to power
D) An uprising of naval officers and army cadets

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 86 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
Which of the following best describes a corporatist political system?
A) A system in which the state limits itself to performing functions that private interests are unwilling or unable to carry out
B) A system in which the state assumes complete control of economic activity and sets goals for the society as a whole
C) A system in which large corporations control such a high percentage of national wealth that they are able to influence government policies and functions
D) A system in which the state establishes political parties and encourages interest groups such as chambers of commerce and trade unions to associate with those parties
A) A system in which the state limits itself to performing functions that private interests are unwilling or unable to carry out
B) A system in which the state assumes complete control of economic activity and sets goals for the society as a whole
C) A system in which large corporations control such a high percentage of national wealth that they are able to influence government policies and functions
D) A system in which the state establishes political parties and encourages interest groups such as chambers of commerce and trade unions to associate with those parties

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 86 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
Which of the following is an element common to all the authoritarian systems of the mid-twentieth century?
A) State-supported anti-Semitism
B) A willingness to use violence and terror against their own citizens
C) A willingness to allow private enterprises to manage themselves without state interference
D) A refusal to allow public roles for women
A) State-supported anti-Semitism
B) A willingness to use violence and terror against their own citizens
C) A willingness to allow private enterprises to manage themselves without state interference
D) A refusal to allow public roles for women

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 86 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
How did fascist parties in Italy and Germany enhance their legitimacy?
A) The fascist parties claimed that they represented a glorious historical legacy.
B) The fascists incorporated socialist and communist leaders into their ranks.
C) The fascist parties supplanted the existing powerful institutions in favor of their own weaker ones.
D) The fascist parties promised an end to all foreign wars.
A) The fascist parties claimed that they represented a glorious historical legacy.
B) The fascists incorporated socialist and communist leaders into their ranks.
C) The fascist parties supplanted the existing powerful institutions in favor of their own weaker ones.
D) The fascist parties promised an end to all foreign wars.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 86 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
Which of the following is accurate for both Hitler and Mussolini?
A) Both began their political careers as socialists.
B) Neither won an electoral majority before being appointed to power.
C) Both were appointed chancellor by their respective kings.
D) Neither had actual military experience in World War I.
A) Both began their political careers as socialists.
B) Neither won an electoral majority before being appointed to power.
C) Both were appointed chancellor by their respective kings.
D) Neither had actual military experience in World War I.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 86 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
How did Latin American governments respond to the decline of their export economies and access to foreign capital during the 1920s and 1930s?
A) They created their own alternative international banking system.
B) They worked to make domestic industry and consumption their main engine of economic growth.
C) They withdrew from the world economy and became entirely self-sufficient.
D) They convinced their citizens to accept a lower standard of living through an austerity program.
A) They created their own alternative international banking system.
B) They worked to make domestic industry and consumption their main engine of economic growth.
C) They withdrew from the world economy and became entirely self-sufficient.
D) They convinced their citizens to accept a lower standard of living through an austerity program.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 86 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
What role did African people play in governing Europe's African colonies in the post-World War I period?
A) Africans had a significant voice in colonial administration and governance.
B) People of African descent were often elected to the legislative bodies of their colonizer.
C) African traditions provided the templates that Europeans used to rule their colonies.
D) Africans had little voice in colonial governance and made their opinions known through protest.
A) Africans had a significant voice in colonial administration and governance.
B) People of African descent were often elected to the legislative bodies of their colonizer.
C) African traditions provided the templates that Europeans used to rule their colonies.
D) Africans had little voice in colonial governance and made their opinions known through protest.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 86 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
Why did Gandhi choose salt as the testing ground for his principles of civil disobedience?
A) Salt, a government monopoly, symbolized Indians' subjugation to British rule.
B) Salt was easy to make in India and so it would not be difficult to replace British sources.
C) The British were not as heavily invested in the salt trade as they were in tea and opium production.
D) The British would likely react more leniently to civil disobedience if its purpose was to collect salt for personal use.
A) Salt, a government monopoly, symbolized Indians' subjugation to British rule.
B) Salt was easy to make in India and so it would not be difficult to replace British sources.
C) The British were not as heavily invested in the salt trade as they were in tea and opium production.
D) The British would likely react more leniently to civil disobedience if its purpose was to collect salt for personal use.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 86 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
Jawaharlal Nehru disagreed with Gandhi in which of the following ways?
A) Nehru advocated for the creation of a separate Muslim state.
B) Nehru believed that India needed to embrace science and technology to develop as a modern nation.
C) Nehru wanted a revolution, not peaceful protests.
D) Nehru backed the industrial proletariat and class consciousness as the motivation for resistance.
A) Nehru advocated for the creation of a separate Muslim state.
B) Nehru believed that India needed to embrace science and technology to develop as a modern nation.
C) Nehru wanted a revolution, not peaceful protests.
D) Nehru backed the industrial proletariat and class consciousness as the motivation for resistance.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 86 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
Peasants in the Soviet Union eagerly relinquished their small plots of land in order to work in large state collectives.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 86 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
Which of the following best describes the purpose of the White Wolf movement in China?
A) A communist party initiative to radicalize peasants
B) A peasant uprising meant to rid the countryside of Christian missionaries
C) A peasant-supported band of armed men who robbed the rich to give to the poor to restore justice
D) Chiang Kai-shek's plan to instill moral purpose and discipline in the Chinese public
A) A communist party initiative to radicalize peasants
B) A peasant uprising meant to rid the countryside of Christian missionaries
C) A peasant-supported band of armed men who robbed the rich to give to the poor to restore justice
D) Chiang Kai-shek's plan to instill moral purpose and discipline in the Chinese public

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 86 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
The Ottoman massacre and deportation of over a million Armenians during World War I is generally considered to have been the world's first genocide.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 86 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
Use the passage below to answer all parts of the question that follows.
"The discovery of the Americas resulted in a vast movement of peoples across the Atlantic Ocean from Europe and Africa into the Western Hemisphere. These population movements, among the largest in world history up to that point, pale when measured against the long-distance migrations that occurred in the hundred years between 1840-1940. During these years, 150 million individuals of European and Asian descent filled up the less populous parts of the world moving from Europe, South Asia, and China into the Americas, Southeast Asia, northern Asia and even Africa, spreading a capitalist mode of production wherever they moved. A great many of the migrants went as laborers and worked in factories and on railroads, and on the rubber, sugar, tea, and coffee plantations springing up in tropical zones.
Although the new watchword in economic relations was free labor, not all men and women who moved were in fact free workers. Indentured servitude-that is, agreeing to work for a certain number of years, (usually between three and seven) in return for transportation, food, housing, clothing and small wages-was widely used with Chinese and Indian workers."
Adapted from Population Movements: Filling Up the Empty Spaces and Spreading Capitalism, pp. 912-913, WTWA Concise 2E, 2019
(A) Identify ONE continuity in global migration in the periods before and after 1840.
(B) Explain ONE change in global migration in the periods before and after 1840.
(C) Explain ONE global process after 1840 that contributed to the use of non-free labor systems.
"The discovery of the Americas resulted in a vast movement of peoples across the Atlantic Ocean from Europe and Africa into the Western Hemisphere. These population movements, among the largest in world history up to that point, pale when measured against the long-distance migrations that occurred in the hundred years between 1840-1940. During these years, 150 million individuals of European and Asian descent filled up the less populous parts of the world moving from Europe, South Asia, and China into the Americas, Southeast Asia, northern Asia and even Africa, spreading a capitalist mode of production wherever they moved. A great many of the migrants went as laborers and worked in factories and on railroads, and on the rubber, sugar, tea, and coffee plantations springing up in tropical zones.
Although the new watchword in economic relations was free labor, not all men and women who moved were in fact free workers. Indentured servitude-that is, agreeing to work for a certain number of years, (usually between three and seven) in return for transportation, food, housing, clothing and small wages-was widely used with Chinese and Indian workers."
Adapted from Population Movements: Filling Up the Empty Spaces and Spreading Capitalism, pp. 912-913, WTWA Concise 2E, 2019
(A) Identify ONE continuity in global migration in the periods before and after 1840.
(B) Explain ONE change in global migration in the periods before and after 1840.
(C) Explain ONE global process after 1840 that contributed to the use of non-free labor systems.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 86 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
European and Middle Eastern leaders collaborated in shaping the geopolitics of the post-World War I Middle East.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 86 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
Nationalist intellectuals in Europe's African and Asian colonies disagreed about which political system would best replace colonial rule.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 86 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
Introducing new types of weapons broke the stalemate on the Western Front in World War I.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 86 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
A variety of factors contributed to the outbreak of World War I, and events of its aftermath.
Develop an argument that evaluates one or more cause(s) and consequence(s) of World War I.
In your response you should do the following:
Respond to the prompt with a historically defensible thesis or claim that establishes a line of reasoning.
Describe a broader historical context relevant to the prompt.
Support an argument in response to the prompt using specific and relevant examples of evidence.
Use historical reasoning (e.g., comparison, causation, continuity or change) to frame or structure an argument that addresses the prompt.
Use evidence to corroborate, qualify, or modify an argument that addresses the prompt.
Develop an argument that evaluates one or more cause(s) and consequence(s) of World War I.
In your response you should do the following:
Respond to the prompt with a historically defensible thesis or claim that establishes a line of reasoning.
Describe a broader historical context relevant to the prompt.
Support an argument in response to the prompt using specific and relevant examples of evidence.
Use historical reasoning (e.g., comparison, causation, continuity or change) to frame or structure an argument that addresses the prompt.
Use evidence to corroborate, qualify, or modify an argument that addresses the prompt.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 86 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
Like other authoritarian movements, the Bolsheviks first acquired power through legal, electoral means.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 86 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
Use the two maps below to answer all parts of the question that follows. 
 (A) Explain ONE significant reason for changes in the recognition of self-determination from 1914-1923, as illustrated by the two maps.
(A) Explain ONE significant reason for changes in the recognition of self-determination from 1914-1923, as illustrated by the two maps.
(B) Explain ONE significant reason for continuities in the recognition of self-determination 1914-1923, as illustrated by the two maps.
(C) Explain ONE limitation of using the maps to measure the recognition of the concept of self-determination in the first half of the twentieth century.

 (A) Explain ONE significant reason for changes in the recognition of self-determination from 1914-1923, as illustrated by the two maps.
(A) Explain ONE significant reason for changes in the recognition of self-determination from 1914-1923, as illustrated by the two maps.(B) Explain ONE significant reason for continuities in the recognition of self-determination 1914-1923, as illustrated by the two maps.
(C) Explain ONE limitation of using the maps to measure the recognition of the concept of self-determination in the first half of the twentieth century.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 86 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
Answer all parts of the questions.
(A) Identify ONE challenge faced by liberal democracies between 1919 and 1939.
(B) Explain ONE reason some states adopted authoritarian forms of government between 1919 and 1939.
(C) Describe ONE response to global economic conditions in Latin America between 1919 and 1939.
(A) Identify ONE challenge faced by liberal democracies between 1919 and 1939.
(B) Explain ONE reason some states adopted authoritarian forms of government between 1919 and 1939.
(C) Describe ONE response to global economic conditions in Latin America between 1919 and 1939.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 86 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
How did the goals of the Muslim Brotherhood in Egypt differ from those of the Wafd?
A) The Muslim Brotherhood wanted to use the nation-state as a means of returning to a pure form of Islam, while the Wafd was primarily a secular nationalist group.
B) The Muslim Brotherhood advocated using Western weapons as they undertook a traditional Islamic holy war, while the Wafd wanted to use civil disobedience to achieve their goals.
C) The Wafd was a peasant group, while the Muslim Brotherhood was composed of merchants and military leaders.
D) The Wafd argued that Egypt should embrace liberal capitalism, while the Muslim Brotherhood supported socialism.
A) The Muslim Brotherhood wanted to use the nation-state as a means of returning to a pure form of Islam, while the Wafd was primarily a secular nationalist group.
B) The Muslim Brotherhood advocated using Western weapons as they undertook a traditional Islamic holy war, while the Wafd wanted to use civil disobedience to achieve their goals.
C) The Wafd was a peasant group, while the Muslim Brotherhood was composed of merchants and military leaders.
D) The Wafd argued that Egypt should embrace liberal capitalism, while the Muslim Brotherhood supported socialism.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 86 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
For Gandhi, the most effective route to accomplishing Indian independence was for all Indians to embrace self-reliance and nonviolent resistance to colonial rule.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 86 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
The introduction of the assembly line by American automobile manufacturer Henry Ford allowed his company to increase production sharply while dramatically reducing costs.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 86 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
Excerpts from Victor Klemperer's diary and Anna Kovaleva's "Letter to Marfa Gudzia" demonstrate that people in Nazi Germany and the Soviet Union often ignored what their respective states said.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 86 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
Which of the following models of political modernity was accepted most often in Western Europe and the Americas by the 1930s?
A) The anticolonial model
B) The authoritarian model
C) The hybrid corporatist model
D) The liberal democratic model
A) The anticolonial model
B) The authoritarian model
C) The hybrid corporatist model
D) The liberal democratic model

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 86 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
World War I was the first total war. Governments used a variety of strategies to mobilize populations for the purpose of waging war.
Develop an argument that evaluates how one or more governments conducted the war.
In your response you should do the following:
Respond to the prompt with a historically defensible thesis or claim that establishes a line of reasoning.
Describe a broader historical context relevant to the prompt.
Support an argument in response to the prompt using specific and relevant examples of evidence.
Use historical reasoning (e.g., comparison, causation, continuity or change) to frame or structure an argument that addresses the prompt.
Use evidence to corroborate, qualify, or modify an argument that addresses the prompt.
Develop an argument that evaluates how one or more governments conducted the war.
In your response you should do the following:
Respond to the prompt with a historically defensible thesis or claim that establishes a line of reasoning.
Describe a broader historical context relevant to the prompt.
Support an argument in response to the prompt using specific and relevant examples of evidence.
Use historical reasoning (e.g., comparison, causation, continuity or change) to frame or structure an argument that addresses the prompt.
Use evidence to corroborate, qualify, or modify an argument that addresses the prompt.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 86 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
Which social phenomenon is "pretotalitarian" according to political philosopher Hannah Arendt?
A) Stigmatization of an "other"
B) Conformity of belief
C) Isolation of the individual
D) Widespread terror
A) Stigmatization of an "other"
B) Conformity of belief
C) Isolation of the individual
D) Widespread terror

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 86 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
The German government's unwillingness to tax its citizens at a rate similar to that of other European countries following World War I helped lead to hyperinflation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 86 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
Diego Rivera's 1923 mural of the Detroit Motor Company does which of the following?
A) It celebrates the gender inclusiveness of the assembly line.
B) It celebrates the ethnic diversity of the assembly line.
C) It laments the spread of bourgeois values among the workers.
D) It laments the alienation of the workers' labor.
A) It celebrates the gender inclusiveness of the assembly line.
B) It celebrates the ethnic diversity of the assembly line.
C) It laments the spread of bourgeois values among the workers.
D) It laments the alienation of the workers' labor.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 86 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



