Deck 32: International Corporate Finance
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/54
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 32: International Corporate Finance
1
Triangular arbitrage would take place if the _____ rate between two currencies was not _____ to the ratio of the two direct rates.
A) cross; equal.
B) spot; equal.
C) cross; less than.
D) spot; less than.
E) cross; greater than.
A) cross; equal.
B) spot; equal.
C) cross; less than.
D) spot; less than.
E) cross; greater than.
cross; equal.
2
When the German mark is quoted as 1.923 marks this quote is a(n):
A) indirect rate.
B) direct rate.
C) cross rate.
D) triangular rate.
A) indirect rate.
B) direct rate.
C) cross rate.
D) triangular rate.
direct rate.
3
Swiss franc denominated bonds issued in Switzerland by a French company are called:
A) Eurobonds.
B) Foreign bonds.
C) European Original Issue (EOI) bonds.
D) American Depository Bonds (ADBs).
A) Eurobonds.
B) Foreign bonds.
C) European Original Issue (EOI) bonds.
D) American Depository Bonds (ADBs).
Foreign bonds.
4
You want to import $45,000 worth of rugs from India. How many rupees will you need to pay for this purchase if one rupee is worth $.0218?
A) 1,843,010Rs
B) 2,032,018Rs
C) 2,064,220Rs
D) 2,075,002Rs
E) 2,076,289Rs
A) 1,843,010Rs
B) 2,032,018Rs
C) 2,064,220Rs
D) 2,075,002Rs
E) 2,076,289Rs

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
The cross rate is the:
A) exchange rate between the US dollar and other currency.
B) exchange rate between two currencies generally other than the US dollar.
C) rate converting the direct rate into the indirect rate.
D) the attitude of the agent at the exchange kiosk.
A) exchange rate between the US dollar and other currency.
B) exchange rate between two currencies generally other than the US dollar.
C) rate converting the direct rate into the indirect rate.
D) the attitude of the agent at the exchange kiosk.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
How many euros can you get for $2,500 given the following exchange rates? 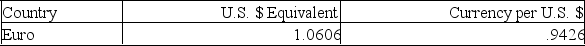
A) €2,306
B) €2,357
C) €2,451
D) €2,652
E) €2,675
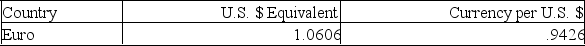
A) €2,306
B) €2,357
C) €2,451
D) €2,652
E) €2,675

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
If the direct rate for French francs (FF) is $.143 and the direct rate for Australian dollars (A$) is $0.44, what must the cross rate between A$ and FF be to prevent triangular arbitrage?
A) FF3.08
B) FF0.063
C) FF15.89
D) FF0.325
A) FF3.08
B) FF0.063
C) FF15.89
D) FF0.325

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
When the German mark is quoted as $.52 this quote is a(n):
A) triangular rate.
B) indirect rate.
C) direct rate.
D) cross rate.
A) triangular rate.
B) indirect rate.
C) direct rate.
D) cross rate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
In foreign exchange markets the swap rate is:
A) the volume of currency traded in a day.
B) the rate of profit made on any transaction.
C) the nightlife of the stereotypical Frenchman.
D) the difference in the foreign exchange rates on a roundtrip agreement to buy and sell a currency.
A) the volume of currency traded in a day.
B) the rate of profit made on any transaction.
C) the nightlife of the stereotypical Frenchman.
D) the difference in the foreign exchange rates on a roundtrip agreement to buy and sell a currency.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
The forward rate market is dependent upon:
A) current forward rates exceeding current spot rates.
B) current spot rates exceeding current forward rates over time.
C) current spot rates equaling current forward rates on average over time.
D) forward rates equaling the actual future spot rates on average over time.
A) current forward rates exceeding current spot rates.
B) current spot rates exceeding current forward rates over time.
C) current spot rates equaling current forward rates on average over time.
D) forward rates equaling the actual future spot rates on average over time.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
What kind of trade involves agreeing today on an exchange rate for settlement in future?
A) Spot trade.
B) Futures trade.
C) Forward trade.
D) Triangle trade.
A) Spot trade.
B) Futures trade.
C) Forward trade.
D) Triangle trade.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Which one of the following statements is correct assuming that exchange rates are quoted as units of foreign currency per dollar?
A) The exchange rate moves opposite to the value of the dollar.
B) The exchange rate rises when the U.S. inflation rate is higher than the foreign country's.
C) When a foreign currency appreciates in value it strengthens relative to the dollar.
D) The exchange rate falls as the dollar strengthens.
A) The exchange rate moves opposite to the value of the dollar.
B) The exchange rate rises when the U.S. inflation rate is higher than the foreign country's.
C) When a foreign currency appreciates in value it strengthens relative to the dollar.
D) The exchange rate falls as the dollar strengthens.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Assume that the Euro is selling in the spot market for $1.10. Simultaneously, in the 3-month forward market the Euro is selling for $1.12. Which one of the following statements correctly describes this situation?
A) The spot market is out of equilibrium.
B) The forward market is out of equilibrium.
C) The dollar is selling at a premium relative to the euro.
D) The Euro is selling at a premium relative to the dollar.
A) The spot market is out of equilibrium.
B) The forward market is out of equilibrium.
C) The dollar is selling at a premium relative to the euro.
D) The Euro is selling at a premium relative to the dollar.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Currently, $1 will buy C$1.36 while $1.10 will buy €1. What is the exchange rate between the Canadian dollar and the euro?
A) C$1 = €1.10
B) C$1 = €.9091
C) C$1 = €1.2364
D) C$1.36 = €1.10
E) C$1.36 = €.9091
A) C$1 = €1.10
B) C$1 = €.9091
C) C$1 = €1.2364
D) C$1.36 = €1.10
E) C$1.36 = €.9091

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
The acronym LIBOR stands for:
A) London Interbank Offered Rate.
B) Lending Institution Bank Receipt.
C) Leading Indicator Borrowing Rate.
D) Loan Interest Bank Order Receipt.
A) London Interbank Offered Rate.
B) Lending Institution Bank Receipt.
C) Leading Indicator Borrowing Rate.
D) Loan Interest Bank Order Receipt.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
The European Currency Unit (ECU) is (a):
A) measure of how well the European Community keeps up with the times.
B) basket of 30 European currencies.
C) money on deposit in financial centers outside the country whose currency is involved.
D) the nickname for NATO troops from Europe.
A) measure of how well the European Community keeps up with the times.
B) basket of 30 European currencies.
C) money on deposit in financial centers outside the country whose currency is involved.
D) the nickname for NATO troops from Europe.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
What kind of trade would involve settling a foreign exchange transaction in two days?
A) Spot trade.
B) Futures trade.
C) Forward trade.
D) Triangle trade.
A) Spot trade.
B) Futures trade.
C) Forward trade.
D) Triangle trade.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
A Yankee bond is a:
A) dollar-denominated Eurobond issued by a non-U.S. company.
B) a foreign bond issued in the U.S. by a foreign entity.
C) Eurobond issued by a U.S. company.
D) ECU-denominated bond issued by a non-U.S. company.
A) dollar-denominated Eurobond issued by a non-U.S. company.
B) a foreign bond issued in the U.S. by a foreign entity.
C) Eurobond issued by a U.S. company.
D) ECU-denominated bond issued by a non-U.S. company.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
The Deutschemark is currently selling for .72 U.S. dollars and also for .87 Canadian dollars. If you determined the rate of exchange between U.S. and Canadian dollars from this information you would have calculated:
A) the ECU value.
B) interest rate parity.
C) the cross rate.
D) the indirect rate.
A) the ECU value.
B) interest rate parity.
C) the cross rate.
D) the indirect rate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Dollar-denominated bonds issued in several European countries by a U.S. company are called:
A) Eurobonds.
B) American Depository Bonds (ADBs).
C) Foreign bonds.
D) European Original Issue (EOI) bonds.
A) Eurobonds.
B) American Depository Bonds (ADBs).
C) Foreign bonds.
D) European Original Issue (EOI) bonds.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
The idea that the exchange rate adjusts to keep buying power constant among currencies is called:
A) the unbiased forward rates condition.
B) uncovered interest rate parity.
C) the international Fisher effect.
D) purchasing power parity.
E) interest rate parity.
A) the unbiased forward rates condition.
B) uncovered interest rate parity.
C) the international Fisher effect.
D) purchasing power parity.
E) interest rate parity.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
The NPV of a foreign investment will be lower if:
A) not all cash flows are remitted to the parent and unremitted cash flows are reinvested at a rate equal to the domestic cost of capital.
B) not all cash flows are remitted to the parent and unremitted cash flows are reinvested at a rate less than the domestic cost of capital.
C) all cash flows are remitted to the parent and are reinvested at a rate equal to the domestic cost of capital.
D) Remittance rates nor foreign reinvestment rates do not affect the NPV.
A) not all cash flows are remitted to the parent and unremitted cash flows are reinvested at a rate equal to the domestic cost of capital.
B) not all cash flows are remitted to the parent and unremitted cash flows are reinvested at a rate less than the domestic cost of capital.
C) all cash flows are remitted to the parent and are reinvested at a rate equal to the domestic cost of capital.
D) Remittance rates nor foreign reinvestment rates do not affect the NPV.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Suppose that the Greer Company knows that it must pay £7 million for goods that it will receive in England. The current exchange rate is $1.75£. The risk that the corporate Treasurer faces is that:
A) the pound exchange rate falls in a month's time to $1.50£.
B) the pound exchange rate rises in a month's time to $2.00£.
C) the pound exchange rate does not change from its current position.
D) the pound exchange rate falls in a month's time to $1.25£.
A) the pound exchange rate falls in a month's time to $1.50£.
B) the pound exchange rate rises in a month's time to $2.00£.
C) the pound exchange rate does not change from its current position.
D) the pound exchange rate falls in a month's time to $1.25£.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
If a country is experiencing higher inflation than another country, in general, the currency of the first country will _______ with respect to the currency of the second country.
A) do nothing
B) appreciate
C) depreciate
D) impossible to tell without values
E) stabilize.
A) do nothing
B) appreciate
C) depreciate
D) impossible to tell without values
E) stabilize.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
The direct rate exchange for D-marks is.56. The indirect exchange rate for pounds is.61. If there is no triangle arbitrage, how many pounds does it take to buy a D-mark?
A) 0.340.
B) 3.400.
C) 0.920.
D) 1.090.
A) 0.340.
B) 3.400.
C) 0.920.
D) 1.090.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
The Peruvian economy is predicted to average double digit inflation over the next three years of 40% per annum. The forecast for the U.S. is 3% per annum. If the current exchange rate is $.2777/Sol, how much will a Sol cost you in three years?
A) $.1986
B) $.1421
C) $.1016.
D) $.1928
E) $.2334
A) $.1986
B) $.1421
C) $.1016.
D) $.1928
E) $.2334

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
The direct spot exchange rate for British pounds is 1.4329. The 180 day risk-free rates in the U.S. and Britain are 4.5% and 5.2%, respectively. What is the direct forward exchange rate?
A) 1.4281
B) 1.4234
C) 1.4425
D) 1.4368
A) 1.4281
B) 1.4234
C) 1.4425
D) 1.4368

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
"A commodity costs the same regardless of what currency is used to purchase it." This is a statement of:
A) the law of one price (LOP).
B) relative purchasing power parity (RPPP).
C) the first principle of international finance.
D) the conservation of currency value.
A) the law of one price (LOP).
B) relative purchasing power parity (RPPP).
C) the first principle of international finance.
D) the conservation of currency value.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Remitting cash flows is a term used to describe:
A) cash flows earned in a foreign country.
B) moving cash flows from the foreign subsidiary to the parent firm.
C) forecasting the value of foreign currency one-year hence.
D) forecasting the value of U.S. currency one-year hence.
A) cash flows earned in a foreign country.
B) moving cash flows from the foreign subsidiary to the parent firm.
C) forecasting the value of foreign currency one-year hence.
D) forecasting the value of U.S. currency one-year hence.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Suppose that the one-year forward rate on pounds is $1.75£. Given no arbitrage opportunities, this implies that traders expect:
A) the spot rate to be $1.75£ in one year.
B) the spot rate to be greater than $1.75£ in one year.
C) the spot rate to be less than $1.75£ in one year.
D) the spot rate to be greater than or equal to $1.75£ in one year.
E) the spot rate to be less than or equal to $1.75£ in one year.
A) the spot rate to be $1.75£ in one year.
B) the spot rate to be greater than $1.75£ in one year.
C) the spot rate to be less than $1.75£ in one year.
D) the spot rate to be greater than or equal to $1.75£ in one year.
E) the spot rate to be less than or equal to $1.75£ in one year.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
A bottle of Dom Perignon is selling for 550FF in Paris and the exchange rate is $0.167/FF. The champagne is selling for $95 on average in the U.S. exclusive of transportation cost. The price in the U.S. is:
A) priced just right.
B) is $3.15 undervalued.
C) is $3.15 overvalued.
D) the Law of One Price does not hold for special commodities like champagne.
A) priced just right.
B) is $3.15 undervalued.
C) is $3.15 overvalued.
D) the Law of One Price does not hold for special commodities like champagne.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Relative purchasing power parity (RPPP) is different than purchasing power parity (PPP) because:
A) PPP is based on the idea that LOP does not hold while it does for RPPP.
B) under PPP exchange rates adjust so that the market basket of goods cost the same regardless of country while for RPPP the LOP does not hold.
C) PPP is based on the idea that LOP does not hold while for RPPP the rate of change in the price level in one country relative the rate of change in the price level of another country determines the change in the exchange rate.
D) for RPPP the rate of change in the price level in one country relative the rate of change in the price level of another country determines the change in the exchange rate while under PPP exchange rates adjust so that the market basket of goods cost the same regardless of country.
A) PPP is based on the idea that LOP does not hold while it does for RPPP.
B) under PPP exchange rates adjust so that the market basket of goods cost the same regardless of country while for RPPP the LOP does not hold.
C) PPP is based on the idea that LOP does not hold while for RPPP the rate of change in the price level in one country relative the rate of change in the price level of another country determines the change in the exchange rate.
D) for RPPP the rate of change in the price level in one country relative the rate of change in the price level of another country determines the change in the exchange rate while under PPP exchange rates adjust so that the market basket of goods cost the same regardless of country.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Suppose the spot exchange rate is 2 U.S. dollars per British pound. The forward exchange rate is 1.9 dollars per pound. Which of the following is true?
A) The U.S. inflation rate is higher.
B) The pound is selling at a premium.
C) The pound is selling at a discount.
D) U.S. interest rates are lower.
A) The U.S. inflation rate is higher.
B) The pound is selling at a premium.
C) The pound is selling at a discount.
D) U.S. interest rates are lower.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
The Brazilian inflation rate is expected to be 30% per year for the next 4 years. The U.S. inflation rate is expected to be 3% per year over the same period. A Brazilian real currently costs 87.36 cents. Assuming RPPP holds, how many reals will you need to buy a dollar in four years?
A) 11.447.
B) 2.905.
C) 2.862.
D) 1.676.
A) 11.447.
B) 2.905.
C) 2.862.
D) 1.676.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Interest rate parity:
A) eliminates covered interest arbitrage opportunities.
B) exists when spot rates are equal for multiple countries.
C) means that the nominal risk-free rate of return must be the same across countries.
D) exists when the spot rate is equal to the futures rate.
A) eliminates covered interest arbitrage opportunities.
B) exists when spot rates are equal for multiple countries.
C) means that the nominal risk-free rate of return must be the same across countries.
D) exists when the spot rate is equal to the futures rate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Suppose it takes 3.2 DM francs to buy 1 U.S. dollar. The direct exchange rate on dollar is:
A) .3125.
B) .4550.
C) 2.20.
D) 3.20.
A) .3125.
B) .4550.
C) 2.20.
D) 3.20.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
International corporations that borrow capital in the foreign country for investment face:
A) exchange rate risk on the investment.
B) exchange rate risk on the residual financing.
C) cross rate risk on exports.
D) exchange rate risk on the borrowing.
E) swap rate risk on the repurchase.
A) exchange rate risk on the investment.
B) exchange rate risk on the residual financing.
C) cross rate risk on exports.
D) exchange rate risk on the borrowing.
E) swap rate risk on the repurchase.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
_____ holds because of the possibility of covered interest arbitrage.
A) Uncovered interest parity
B) Interest rate parity
C) The international Fisher effect
D) Unbiased forward rates
E) Purchasing power parity
A) Uncovered interest parity
B) Interest rate parity
C) The international Fisher effect
D) Unbiased forward rates
E) Purchasing power parity

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
"The rate of change in commodity price levels between two countries determines the rate of change in exchange rates between the two countries." This is a statement of:
A) absolute purchasing power parity (APPP).
B) relative purchase power parity (RPPP).
C) international fisher effect (IFE).
D) interest rate parity (IRP).
E) unbiased forward exchange rates (UFER).
A) absolute purchasing power parity (APPP).
B) relative purchase power parity (RPPP).
C) international fisher effect (IFE).
D) interest rate parity (IRP).
E) unbiased forward exchange rates (UFER).

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
If financial markets are segmented, and if firms in the U.S. are not subject to the same barriers of international investment, then this could lead to _____ risk premiums on international projects.
A) higher
B) zero
C) negative
D) lower
E) infinite
A) higher
B) zero
C) negative
D) lower
E) infinite

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
Financial Accounting Standard Statement Number 52 requires that most assets and liabilities be translated at the current exchange rate. Gains and losses are recorded:
A) against shareholder's equity.
B) as a normal part of income.
C) as an extraordinary item against income.
D) as a footnote to the statements.
E) only on the income tax statements.
A) against shareholder's equity.
B) as a normal part of income.
C) as an extraordinary item against income.
D) as a footnote to the statements.
E) only on the income tax statements.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Underwriters of Eurobonds sell the bonds on a:
A) best-efforts basis.
B) best-efforts, all or none basis.
C) firm-commitment basis.
D) regular basis to governments.
A) best-efforts basis.
B) best-efforts, all or none basis.
C) firm-commitment basis.
D) regular basis to governments.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
The inflation rates in the U.S. and Canada are predicted to be 3 and 5%, respectively, in the coming year. The exchange rate is currently 1.44 Canadian dollars for 1 U.S. dollars. Assuming RPPP holds, how many U.S. dollars will it take to buy 1 Canadian dollar at the end of the year? What will it cost to buy a U.S. dollar?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
The U.S. inflation rate for the coming year is 2%. The German inflation rate for the coming year is 42%. You can buy 1.7 D-marks with 1 U.S. dollar today. Based on relative purchase power parity, how many D-marks will you be able to buy with 1 dollar in 1 year?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
The two terms Purchasing Power Parity (PPP) and Relative Purchasing Power Parity (RPPP) are similar but not synonymous. Explain these two, their differences and why differences in exchange rates in the market may vary from the values implied by PPP or RPPP.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
You want to invest in a riskless project in Sweden. The project has an initial cost of SKr2.1 million and is expected to produce cash inflows of SKr810,000 a year for 3 years. The project will be worthless after the first 3 years. The expected inflation rate in Sweden is 2 percent while it is 5 percent in the U.S. A risk-free security is paying 6 percent in the U.S. The current spot rate is $1 = SKr7.55. What is the net present value of this project in Swedish krona using the foreign currency approach? Assume that the international Fisher effect applies.
A) SKr185,607
B) SKr192,434
C) SKr196,910
D) SKr197,867
E) SKr202,818
A) SKr185,607
B) SKr192,434
C) SKr196,910
D) SKr197,867
E) SKr202,818

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
The 90-day risk-free rate in the U.S. is 3%. The spot exchange rate between the U.S. and Japan is 1 dollar for 133 yen. The 90-day forward exchange rate is 1 dollar for 135 yen. What is the Japanese 90-day risk-free rate?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
Describe the foreign currency and home currency approaches to capital budgeting. Which is better? Which approach would you recommend a U.S. firm use? Justify your answer.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
When a multinational consolidates the financial statements, the foreign business values must be converted to domestic values. If the exchange rate of the domestic currency has appreciated relative to the foreign currency, there will be a resultant:
A) accounting gain in translation.
B) real income gain in translation.
C) accounting loss in translation.
D) real income loss in translation.
A) accounting gain in translation.
B) real income gain in translation.
C) accounting loss in translation.
D) real income loss in translation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
A Eurobond investor prefers this market to the Yankee bond market because:
A) these bonds are registered.
B) the bonds are in bearer form.
C) an agent is used to transfer ownership.
D) income is taxed directly.
A) these bonds are registered.
B) the bonds are in bearer form.
C) an agent is used to transfer ownership.
D) income is taxed directly.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
Suppose that Walkman stereos sell in the U.S. for $40, but sell in Germany for DM 87.5. Under the law of one price, what must be the number of dollars needed to purchase a D mark?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
Newsat Telco is planning on investing $40 billion in Europe this year for a satellite communications systems. The expected cash flow over the next three years is 20.6 billion Euros per year growing at the rate of inflation. After three year they will abandon the system as worthless. The European current and expected inflation rate is 5.2% per annum over this period and the U.S. inflation rate is expected to be 2.8% per annum. The current exchange rate is $.9/Euro. Newsat has a U.S. cost of capital of 15%. Should Newsat invest?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
You are considering a project in Poland which has an initial cost of 250,000PLN. The project is expected to return a one-time payment of 400,000PLN 5 years from now. The risk-free rate of return is 3 percent in the U.S. and 4 percent in Poland. The inflation rate is 2 percent in the U.S. and 5 percent in Poland. Currently, you can buy 375PLN for 100USD. How much will the payment 5 years from now be worth in U.S. dollars?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
Eurocurrency loans are made to:
A) individuals as any retail bank does.
B) corporations and governments as any retail bank does.
C) stock market investors only as brokers do.
D) corporations and governments solely, unlike a retail bank.
A) individuals as any retail bank does.
B) corporations and governments as any retail bank does.
C) stock market investors only as brokers do.
D) corporations and governments solely, unlike a retail bank.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



