Deck 11: Managing Aggregate Demand: Fiscal Policy
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/19
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 11: Managing Aggregate Demand: Fiscal Policy
1
Suppose you are put in charge of fiscal policy for the economy described in Test Yourself Question 1. There is an inflationary gap, and you want to reduce income by $120. What specific actions can you take to achieve this goal
Government purchases need to be reduced by $30
A one-dollar change in government purchases changes the income level by $4. Thus, a reduction of $30 in government purchases will reduce the income by $120.
Hence, to eliminate the inflationary gap through fiscal policy adjustment, government purchases should be reduced by $30
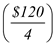 so that income will be reduced by $120.
so that income will be reduced by $120.
A one-dollar change in government purchases changes the income level by $4. Thus, a reduction of $30 in government purchases will reduce the income by $120.
Hence, to eliminate the inflationary gap through fiscal policy adjustment, government purchases should be reduced by $30
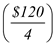 so that income will be reduced by $120.
so that income will be reduced by $120. 2
(More difficult) Advocates of lower taxes on capital gains argue that this type of tax cut will raise aggregate supply by spurring business investment. Compare the effects on investment, aggregate supply, and tax revenues of three different ways to cut the capital gains tax:
a. Reduce capital gains taxes on all investments, including those that were made before tax rates were cut.
b. Reduce capital gains taxes only on investments made after tax rates are cut.
c. Reduce capital gains taxes only on certain types of investments, such as corporate stocks and bonds. Which of the three options seems most desirable to you Why
a. Reduce capital gains taxes on all investments, including those that were made before tax rates were cut.
b. Reduce capital gains taxes only on investments made after tax rates are cut.
c. Reduce capital gains taxes only on certain types of investments, such as corporate stocks and bonds. Which of the three options seems most desirable to you Why
a. Reduction in capital gain tax on all investments
When there is a reduction in the capital gain tax on both old and new investments, it increases the profit. This encourages investors to invest more, which in turn increases new investments. Here, when the new investment increases, it increases the production; consequently, it increases the aggregate supply.
Since increase in output will generate more income, tax revenue will increase.
b. Reduction in capital gain tax on new investment
When there is a reduction in capital gain tax on new investments, this encourages investors to invest more, which in turn increases the new investments.
Here, when the new investment increases, it increases the production; consequently, it increases the aggregate supply.
Since increase in output will generate more income, tax revenue will increase.
c. Reduction in capital gain tax on certain investments
When there is a reduction in capital gain tax on certain investments such as corporate stocks and bonds, it increases the new investment only in particular sectors.
Here, only some particular sectors are concentrated with new investments; perhaps, the investment diverts from other sectors to this particular sector to enjoy the privilege of tax cut.
As a result, the aggregate supply will reduce since the investment flows only to particular sectors and others are neglected. The reduction in output will generate less tax revenue to the government.
Desirable option is (b)
Option (c) will divert the investment and in turn supply will fall. Option (a) will make government more expensive by offering tax cut to both old and new investments. On the other hand, offering tax cut on new investment will increase the aggregate supply with less government expenditure. Hence, option (b) seems good.
When there is a reduction in the capital gain tax on both old and new investments, it increases the profit. This encourages investors to invest more, which in turn increases new investments. Here, when the new investment increases, it increases the production; consequently, it increases the aggregate supply.
Since increase in output will generate more income, tax revenue will increase.
b. Reduction in capital gain tax on new investment
When there is a reduction in capital gain tax on new investments, this encourages investors to invest more, which in turn increases the new investments.
Here, when the new investment increases, it increases the production; consequently, it increases the aggregate supply.
Since increase in output will generate more income, tax revenue will increase.
c. Reduction in capital gain tax on certain investments
When there is a reduction in capital gain tax on certain investments such as corporate stocks and bonds, it increases the new investment only in particular sectors.
Here, only some particular sectors are concentrated with new investments; perhaps, the investment diverts from other sectors to this particular sector to enjoy the privilege of tax cut.
As a result, the aggregate supply will reduce since the investment flows only to particular sectors and others are neglected. The reduction in output will generate less tax revenue to the government.
Desirable option is (b)
Option (c) will divert the investment and in turn supply will fall. Option (a) will make government more expensive by offering tax cut to both old and new investments. On the other hand, offering tax cut on new investment will increase the aggregate supply with less government expenditure. Hence, option (b) seems good.
3
Now put yourself in charge of the economy in Test Yourself Question 2, and suppose that full employment comes at a GDP of $1,840. How can you push income up to that level
Fiscal policy adjustment to obtain full employment level of GDP
The equilibrium level of GDP is $1,720, and multiplier effect of government purchases is 2.
To achieve full employment level of GDP, that is, $1,840, we need to stimulate consumption expenditure by regulating the fiscal policy.
The government purchases multiplier is 2, whereas the output gap is $120
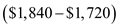 .
.
Hence, the required amount of GDP, that is, $120, can be obtained by increasing government purchases by $60
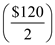 .
.
The equilibrium level of GDP is $1,720, and multiplier effect of government purchases is 2.
To achieve full employment level of GDP, that is, $1,840, we need to stimulate consumption expenditure by regulating the fiscal policy.
The government purchases multiplier is 2, whereas the output gap is $120
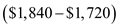 .
.Hence, the required amount of GDP, that is, $120, can be obtained by increasing government purchases by $60
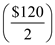 .
. 4
When the income-tax rate declines, as it did in the United States in the early 2000s, does the multiplier go up or down Explain why.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 19 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Which of the following is considered a fixed tax and which a variable tax
a. The gasoline tax
b. The corporate income tax
c. The estate tax
d. The payroll tax
a. The gasoline tax
b. The corporate income tax
c. The estate tax
d. The payroll tax

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 19 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Discuss the pros and cons of having a higher or lower multiplier.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 19 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
In a certain economy, the multiplier for government purchases is 2 and the multiplier for changes in fixed taxes is 1.5. The government then proposes to raise both spending and taxes by $100 billion. What should happen to equilibrium GDP on the demand side

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 19 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
( More difficult ) Suppose real GDP is $10,000 billion and the basic expenditure multiplier is two. If two tax changes are made at the same time:
a. fixed taxes are raised by $100 billion,
b. the income-tax rate is reduced from 20 percent to 18 percent, will equilibrium GDP on the demand side rise or fall
a. fixed taxes are raised by $100 billion,
b. the income-tax rate is reduced from 20 percent to 18 percent, will equilibrium GDP on the demand side rise or fall

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 19 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Consider an economy described by the following set of equations:
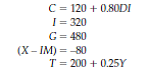
Find the equilibrium level of GDP. Next, find the multipliers for government purchases and for fixed taxes. If full employment comes at Y = 1,800, what are some policies that would move GDP to that level
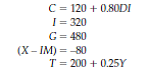
Find the equilibrium level of GDP. Next, find the multipliers for government purchases and for fixed taxes. If full employment comes at Y = 1,800, what are some policies that would move GDP to that level

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 19 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
The federal government spending (relative to the size of the economy) was cut back in several dimensions after the gigantic budget deficits of 2009 and 2010. How would GDP in the United States have been affected if this lower spending led to
a. smaller budget deficits
b. more spending elsewhere in the budget, so that total government purchases remained the same
a. smaller budget deficits
b. more spending elsewhere in the budget, so that total government purchases remained the same

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 19 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
This question is a variant of the previous problem that approaches things in the way that a fiscal policy planner might. In an economy whose consumption function and tax function are as given in Test Yourself Question 1, with investment fixed at 320 and net exports fixed at -80, find the value of G that would make GDP equal to 1,800
Reference Test Yourself Question 1,
Consider an economy described by the following set of equations:
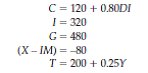
Find the equilibrium level of GDP. Next, find the multipliers for government purchases and for fixed taxes. If full employment comes at Y = 1,800, what are some policies that would move GDP to that level
Reference Test Yourself Question 1,
Consider an economy described by the following set of equations:
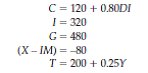
Find the equilibrium level of GDP. Next, find the multipliers for government purchases and for fixed taxes. If full employment comes at Y = 1,800, what are some policies that would move GDP to that level

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 19 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Consider an economy in which tax collections are always $400 and in which the four components of aggregate demand are as follows:
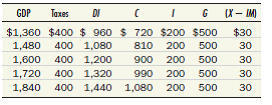
Find the equilibrium of this economy graphically. What is the marginal propensity to consume What is the multiplier What would happen to equilibrium GDP if government purchases were reduced by $60 and the price level remained unchanged

Find the equilibrium of this economy graphically. What is the marginal propensity to consume What is the multiplier What would happen to equilibrium GDP if government purchases were reduced by $60 and the price level remained unchanged

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 19 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
You are given the following information about an economy:
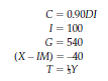
a. Find equilibrium GDP and the budget deficit.
b. Suppose the government, unhappy with the budget deficit, decides to cut government spending by precisely the amount of the deficit you just found. What actually happens to GDP and the budget deficit, and why
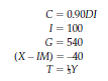
a. Find equilibrium GDP and the budget deficit.
b. Suppose the government, unhappy with the budget deficit, decides to cut government spending by precisely the amount of the deficit you just found. What actually happens to GDP and the budget deficit, and why

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 19 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Explain why G has the same multiplier as I , but taxes have a different multiplier.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 19 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
(More difficult) In the economy considered in Test Yourself Question 3, suppose the government, seeing that it has not wiped out the deficit, keeps cutting G until it succeeds in balancing the budget. What level of GDP will then prevail
Reference Test Yourself Question 3,
You are given the following information about an economy:
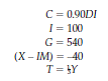
a. Find equilibrium GDP and the budget deficit.
b. Suppose the government, unhappy with the budget deficit, decides to cut government spending by precisely the amount of the deficit you just found. What actually happens to GDP and the budget deficit, and why
Reference Test Yourself Question 3,
You are given the following information about an economy:
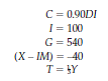
a. Find equilibrium GDP and the budget deficit.
b. Suppose the government, unhappy with the budget deficit, decides to cut government spending by precisely the amount of the deficit you just found. What actually happens to GDP and the budget deficit, and why

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 19 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Consider an economy similar to that in the preceding question in which investment is also $200, government purchases are also $500, net exports are also $30, and the price level is also fixed. But taxes now vary with income, and as a result, the consumption schedule looks like the following:
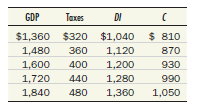
Find the equilibrium graphically. What is the marginal propensity to consume What is the tax rate Use your diagram to show the effect of a decrease of $60 in government purchases. What is the multiplier Compare this answer to your answer to Test Yourself Question 1. What do you conclude

Find the equilibrium graphically. What is the marginal propensity to consume What is the tax rate Use your diagram to show the effect of a decrease of $60 in government purchases. What is the multiplier Compare this answer to your answer to Test Yourself Question 1. What do you conclude

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 19 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
If the government decides that aggregate demand is excessive and is causing inflation, what options are open to it What if the government decides that aggregate demand is too weak instead

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 19 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Return to the hypothetical economy in Test Yourself Question 1, and now suppose that both taxes and government purchases are increased by $120. Find the new equilibrium under the assumption that consumer spending continues to be exactly three-quarters of disposable income (as it is in Test Yourself Question 1).
Reference Test Yourself Question 1
Consider an economy in which tax collections are always $400 and in which the four components of aggregate demand are as follows:
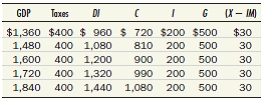
Find the equilibrium of this economy graphically. What is the marginal propensity to consume What is the multiplier What would happen to equilibrium GDP if government purchases were reduced by $60 and the price level remained unchanged
Reference Test Yourself Question 1
Consider an economy in which tax collections are always $400 and in which the four components of aggregate demand are as follows:

Find the equilibrium of this economy graphically. What is the marginal propensity to consume What is the multiplier What would happen to equilibrium GDP if government purchases were reduced by $60 and the price level remained unchanged

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 19 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Which of the proposed supply-side tax cuts appeals to you most Draw up a list of arguments for and against enacting such a cut right now.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 19 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



