Deck 9: Meiosis and the Genetic Basis of Sexual Reproduction
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/50
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 9: Meiosis and the Genetic Basis of Sexual Reproduction
1
During prophase I, a diploid organism contains how many copies of each gene?
A) 1
B) 2
C) 3
D) 4
E) 8
A) 1
B) 2
C) 3
D) 4
E) 8
D
2
During the G 1 stage of interphase, a diploid organism contains how many copies of each gene?
A) 1
B) 2
C) 4
D) 8
E) 16
A) 1
B) 2
C) 4
D) 8
E) 16
B
3
Which statement best describes how homologous chromosomes are separated during meiosis I?
A) The two homologous chromosomes separate into two different daughter cells.
B) The sister chromatids of each chromosome separate into different daughter cells.
C) The nonsister chromatids of each homologous pairs separate into different daughter cells.
D) The two homologous chromosomes travel together into one new daughter cell.
E) The two homologous chromosomes are not separated during meiosis I.
A) The two homologous chromosomes separate into two different daughter cells.
B) The sister chromatids of each chromosome separate into different daughter cells.
C) The nonsister chromatids of each homologous pairs separate into different daughter cells.
D) The two homologous chromosomes travel together into one new daughter cell.
E) The two homologous chromosomes are not separated during meiosis I.
A
4
Armadillos have a diploid chromosome number of 64. At prophase I, an armadillo's cell would have how many homologous pairs?
A) 16
B) 32
C) 64
D) 80
E) 128
A) 16
B) 32
C) 64
D) 80
E) 128

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
A homologous pair is composed of
A) two chromosomes with two sister chromatids each.
B) two sister chromatids with separate centromeres.
C) four chromosomes with two sister chromatids each.
D) four sister chromatids, each with its owncentromere.
E) four sister chromatids attached at a common centromere.
A) two chromosomes with two sister chromatids each.
B) two sister chromatids with separate centromeres.
C) four chromosomes with two sister chromatids each.
D) four sister chromatids, each with its owncentromere.
E) four sister chromatids attached at a common centromere.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
The chances of a woman over 40 years old having a baby with Down Syndrome is
A) 1 in 800.
B) 1 in 400.
C) 1 in 40.
D) 1 in 80.
E) 1 in 21.
A) 1 in 800.
B) 1 in 400.
C) 1 in 40.
D) 1 in 80.
E) 1 in 21.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
During metaphase I, the homologous chromosomes align at the spindle equator with each homologue
A) facing the same spindle pole.
B) facing both spindle poles.
C) facing opposite spindle poles.
D) not facing either spindle pole.
E) being separated into two sister chromatids.
A) facing the same spindle pole.
B) facing both spindle poles.
C) facing opposite spindle poles.
D) not facing either spindle pole.
E) being separated into two sister chromatids.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
A tetrad consists of
A) two homologous chromosomes each comprised of two sister chromatids.
B) two homologous chromosomes each comprised of two nonsister chromatids.
C) one duplicated chromosome consisting of two nonsister chromatids.
D) one duplicated chromosome consisting of two sister chromatids.
E) two homologous chromosomes consisting of a single DNA strand each.
A) two homologous chromosomes each comprised of two sister chromatids.
B) two homologous chromosomes each comprised of two nonsister chromatids.
C) one duplicated chromosome consisting of two nonsister chromatids.
D) one duplicated chromosome consisting of two sister chromatids.
E) two homologous chromosomes consisting of a single DNA strand each.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
During crossing-over,
A) genetic material is exchanged between sister chromatids, resulting in new combinations of alleles.
B) genetic material is exchanged between nonsister chromatids, resulting in new combinations of alleles.
C) sister chromatids from each homologous chromosome of a tetrad are exchanged, resulting in new combinations of alleles.
D) nonsister chromatids from each homologous chromosome of a tetrad are exchanged, resulting in new combinations of alleles.
E) one homologous chromosome of a tetrad is exchanged with another tetrad, resulting in new combinations of alleles.
A) genetic material is exchanged between sister chromatids, resulting in new combinations of alleles.
B) genetic material is exchanged between nonsister chromatids, resulting in new combinations of alleles.
C) sister chromatids from each homologous chromosome of a tetrad are exchanged, resulting in new combinations of alleles.
D) nonsister chromatids from each homologous chromosome of a tetrad are exchanged, resulting in new combinations of alleles.
E) one homologous chromosome of a tetrad is exchanged with another tetrad, resulting in new combinations of alleles.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
One major difference between meiosis I and meiosis II is that
A) sister chromatids are separated during meiosis I, while homologous chromosomes are separated during meiosis II.
B) crossing-over occurs in prophase of meiosis I but not in prophase of meiosis II.
C) the resulting cells at the end of meiosis I are diploid, while the cells at the end of meiosis II are haploid.
D) in telophase of meiosis I, four gametes form from the parent cell, and in telophase of meiosis II, each parent cell gives rise to two identical daughter cells.
E) in meiosis I there is no pairing of chromosomes while homologues pair in meiosis II.
A) sister chromatids are separated during meiosis I, while homologous chromosomes are separated during meiosis II.
B) crossing-over occurs in prophase of meiosis I but not in prophase of meiosis II.
C) the resulting cells at the end of meiosis I are diploid, while the cells at the end of meiosis II are haploid.
D) in telophase of meiosis I, four gametes form from the parent cell, and in telophase of meiosis II, each parent cell gives rise to two identical daughter cells.
E) in meiosis I there is no pairing of chromosomes while homologues pair in meiosis II.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
The failure of sister chromatids to separate during meiosis is called
A) synapsis.
B) crossing-over.
C) tetrad formation.
D) disjunction.
E) nondisjunction.
A) synapsis.
B) crossing-over.
C) tetrad formation.
D) disjunction.
E) nondisjunction.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
During prophase II, a cell contains how many copies of each gene?
A) 1
B) 2
C) 3
D) 4
E) 8
A) 1
B) 2
C) 3
D) 4
E) 8

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
For the figure shown here, indicate the correct stage of meiosis and the whether the cell is haploid (n) or diploid (2n). 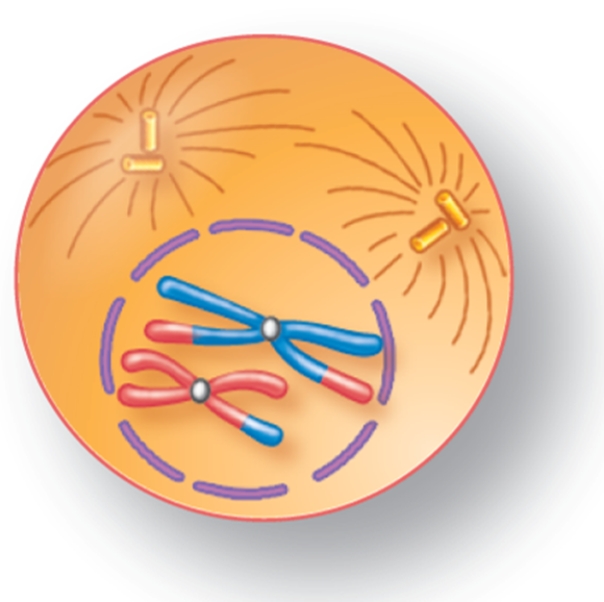
A) prophase I, n
B) prophase II, 2n
C) metaphase I, n
D) metaphase II, 2n
E) prophase II, n

A) prophase I, n
B) prophase II, 2n
C) metaphase I, n
D) metaphase II, 2n
E) prophase II, n

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Which of the following is a correct match?
A) separation of tetrads - anaphase II
B) synapsis - metaphase I
C) separation of sister chromatids - anaphase I
D) synapsis - prophase II
E) separation of sister chromatids - anaphase II
A) separation of tetrads - anaphase II
B) synapsis - metaphase I
C) separation of sister chromatids - anaphase I
D) synapsis - prophase II
E) separation of sister chromatids - anaphase II

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Which of the following processes contributes to creating genetic variability in the offspring?
A) crossing-over
B) independent assortment of chromosomes
C) pairing of homologous chromosomes
D) having different alleles of the same gene
E) All of the answers describe processes that contribute to genetic variability.
A) crossing-over
B) independent assortment of chromosomes
C) pairing of homologous chromosomes
D) having different alleles of the same gene
E) All of the answers describe processes that contribute to genetic variability.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
In each gamete following telophase II, how many copies of each gene is/are present?
A) 1
B) 2
C) 3
D) 4
E) 8
A) 1
B) 2
C) 3
D) 4
E) 8

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
In the human life cycle,
A) meiosis produces haploid gametes, and fertilization creates a diploid cell that divides by mitosis to produce a new individual.
B) mitosis produces haploid gametes, and fertilization creates a diploid cell that divides by meiosis to produce a new individual.
C) diploid gametes are produced by meiosis, and fertilization produces haploid daughter cells that divide by mitosis to produce a new individual.
D) diploid gametes are produced by mitosis, and fertilization results in tetrapolid daughter cells that divide by meiosis to produce a new individual.
E) a haploid zygote is produced by meiosis and fertilization results in a diploid daughter cells that divide by mitosis to produce a new individual.
A) meiosis produces haploid gametes, and fertilization creates a diploid cell that divides by mitosis to produce a new individual.
B) mitosis produces haploid gametes, and fertilization creates a diploid cell that divides by meiosis to produce a new individual.
C) diploid gametes are produced by meiosis, and fertilization produces haploid daughter cells that divide by mitosis to produce a new individual.
D) diploid gametes are produced by mitosis, and fertilization results in tetrapolid daughter cells that divide by meiosis to produce a new individual.
E) a haploid zygote is produced by meiosis and fertilization results in a diploid daughter cells that divide by mitosis to produce a new individual.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Which of the following statements is correct?
A) Meiosis involves two divisions and produces four nonidentical gametes.
B) Meiosis involves one division and produces two nonidentical gametes.
C) Mitosis involves one division and produces two nonidentical gametes.
D) Mitosis involves two divisions and produces four identical gametes.
E) Meiosis involves two divisions and produces four identical gametes.
A) Meiosis involves two divisions and produces four nonidentical gametes.
B) Meiosis involves one division and produces two nonidentical gametes.
C) Mitosis involves one division and produces two nonidentical gametes.
D) Mitosis involves two divisions and produces four identical gametes.
E) Meiosis involves two divisions and produces four identical gametes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Which of the following processes and products are paired correctly?
A) spermatogenesis - 2n zygote
B) oogenesis - 2n zygote
C) oogenesis - 1n gamete
D) meiosis - 2n zygote
E) mitosis - 1n gamete
A) spermatogenesis - 2n zygote
B) oogenesis - 2n zygote
C) oogenesis - 1n gamete
D) meiosis - 2n zygote
E) mitosis - 1n gamete

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Which of the following only occurs once during meiosis?
A) cytokinesis
B) spindle formation
C) pairing of homologous chromosomes
D) separation of genetic material
E) alignment of chromosomes at the spindle equator
A) cytokinesis
B) spindle formation
C) pairing of homologous chromosomes
D) separation of genetic material
E) alignment of chromosomes at the spindle equator

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Turner syndrome is associated with which of the following karyotypes?
A) 47, XXY
B) 47, XXX
C) 46, XY
D) 47, XY, trisomy 21
E) 45, XO
A) 47, XXY
B) 47, XXX
C) 46, XY
D) 47, XY, trisomy 21
E) 45, XO

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Which of the following human syndromes is a monosomy?
A) Turner syndrome
B) Klinefelter syndrome
C) Down syndrome
D) Swyer syndrome
E) Barr body syndrome
A) Turner syndrome
B) Klinefelter syndrome
C) Down syndrome
D) Swyer syndrome
E) Barr body syndrome

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Following meiosis I, the daughter cells are ________; following meiosis II, the daughter cells are ________; and following fertilization and mitosis, the daughter cells are ________.
A) diploid; haploid; diploid
B) diploid; diploid; haploid
C) haploid; haploid; diploid
D) haploid; haploid; haploid
E) diploid; diploid; diploid
A) diploid; haploid; diploid
B) diploid; diploid; haploid
C) haploid; haploid; diploid
D) haploid; haploid; haploid
E) diploid; diploid; diploid

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
An individual with Swyer syndrome (46, XY) differs from an individual with Klinefelter syndrome (47, XXY) because
A) an individual with Swyer syndrome has a Barr body, while an individual with Klinefelter syndrome does not.
B) an individual with Klinefelter syndrome has a functional SRY gene on his Y chromosome, whereas an individual with Swyer syndrome does not.
C) both individuals have a functional SRY gene, but the extra X chromosome makes the individual with Klinefelter syndrome appear female.
D) neither individual has a functional SRY gene, but the X chromosome of the individual with Swyer syndrome has a functional SRY and appears male.
E) an individual with Swyer syndrome lacks a functional SRY gene, but appears male because it has moved to the X chromosome as in an individual with Klinefelter syndrome.
A) an individual with Swyer syndrome has a Barr body, while an individual with Klinefelter syndrome does not.
B) an individual with Klinefelter syndrome has a functional SRY gene on his Y chromosome, whereas an individual with Swyer syndrome does not.
C) both individuals have a functional SRY gene, but the extra X chromosome makes the individual with Klinefelter syndrome appear female.
D) neither individual has a functional SRY gene, but the X chromosome of the individual with Swyer syndrome has a functional SRY and appears male.
E) an individual with Swyer syndrome lacks a functional SRY gene, but appears male because it has moved to the X chromosome as in an individual with Klinefelter syndrome.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Which of the following phases results in separation of sister chromatids into daughter chromosomes?
A) anaphase of mitosis only
B) anaphase I, anaphase II, and anaphase of mitosis
C) anaphase I and anaphase II
D) anaphase I and anaphase of mitosis
E) anaphase II and anaphase of mitosis
A) anaphase of mitosis only
B) anaphase I, anaphase II, and anaphase of mitosis
C) anaphase I and anaphase II
D) anaphase I and anaphase of mitosis
E) anaphase II and anaphase of mitosis

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Klinefelter syndrome can result fromnondisjunction during
A) meiosis I in the female parent.
B) meiosis I in the male parent.
C) meiosis I in either female parent.
D) meiosis I or II in the male parent.
E) meiosis I or II in either parent.
A) meiosis I in the female parent.
B) meiosis I in the male parent.
C) meiosis I in either female parent.
D) meiosis I or II in the male parent.
E) meiosis I or II in either parent.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Metaphase II is more similar to metaphase of mitosis than to metaphase I because
A) in metaphase I, tetrads align together at the spindle equator.
B) in metaphase II, tetrads align separately at the spindle equator.
C) in metaphase of mitosis, tetrads align separately at the spindle equator.
D) in metaphase II, chromosomes align separately at the spindle equator.
E) in metaphase I, chromosomes align separately at the spindle equator.
A) in metaphase I, tetrads align together at the spindle equator.
B) in metaphase II, tetrads align separately at the spindle equator.
C) in metaphase of mitosis, tetrads align separately at the spindle equator.
D) in metaphase II, chromosomes align separately at the spindle equator.
E) in metaphase I, chromosomes align separately at the spindle equator.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
The failure of sister chromatids to separate in one of the cells during meiosis II would result in how many normal gametes?
A) 0
B) 1
C) 2
D) 3
E) 4
A) 0
B) 1
C) 2
D) 3
E) 4

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
An individual with the karyotype 48, XYYY would have how many Barr bodies?
A) 0
B) 1
C) 2
D) 3
E) 4
A) 0
B) 1
C) 2
D) 3
E) 4

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Which of the following is a function only of mitosis?
A) organismal growth
B) creating genetic variability
C) reducing the chromosome number in gametes
D) keeping the chromosome number constant from one generation to the next
E) producing gametes
A) organismal growth
B) creating genetic variability
C) reducing the chromosome number in gametes
D) keeping the chromosome number constant from one generation to the next
E) producing gametes

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
During meiosis II,
A) homologous chromosomes line up separately, with sister chromatids facing the same spindle pole.
B) chromosomes line up separately, with sister chromatids facing opposite spindle poles.
C) chromosomes line up separately, with sister chromatids facing the same spindle pole.
D) homologous chromosomes line up separately, with sister chromatids facing opposite spindle poles.
E) homologous chromosomes line up together, with sister chromatids facing opposite spindle poles.
A) homologous chromosomes line up separately, with sister chromatids facing the same spindle pole.
B) chromosomes line up separately, with sister chromatids facing opposite spindle poles.
C) chromosomes line up separately, with sister chromatids facing the same spindle pole.
D) homologous chromosomes line up separately, with sister chromatids facing opposite spindle poles.
E) homologous chromosomes line up together, with sister chromatids facing opposite spindle poles.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Interphase differs from interkinesis because
A) DNA is duplicated during interphase, but not during interkinesis.
B) DNA is duplicated during interkinesis, but not during interphase.
C) homologous chromosomes separate during interkinesis, but not during interphase.
D) homologous chromosomes separate during interphase, but not during interkinesis.
E) interkinesis only occurs during mitosis, while interphase occurs during both meiosis and mitosis.
A) DNA is duplicated during interphase, but not during interkinesis.
B) DNA is duplicated during interkinesis, but not during interphase.
C) homologous chromosomes separate during interkinesis, but not during interphase.
D) homologous chromosomes separate during interphase, but not during interkinesis.
E) interkinesis only occurs during mitosis, while interphase occurs during both meiosis and mitosis.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Swyer syndrome (46, XY, female appearance), would most likely result from
A) nondisjunction during meiosis I in the female parent.
B) nondisjunction during meiosis I in the male parent.
C) nondisjunction during meiosis II in the female parent.
D) nondisjunction during meiosis II in the male parent.
E) normal disjunction during meiosis, but deletion of a portion of the Y chromosome in the male parent.
A) nondisjunction during meiosis I in the female parent.
B) nondisjunction during meiosis I in the male parent.
C) nondisjunction during meiosis II in the female parent.
D) nondisjunction during meiosis II in the male parent.
E) normal disjunction during meiosis, but deletion of a portion of the Y chromosome in the male parent.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
For the figure shown here, indicate the correct stage of meiosis and whether the cell is haploid (n) or diploid (2n). 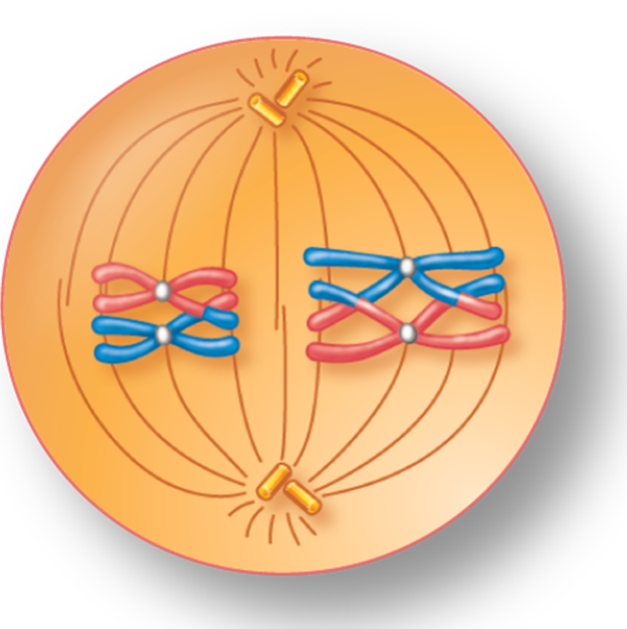
A) metaphase II, 2n
B) metaphase II, n
C) metaphase I, 2n
D) metaphase I, n
E) anaphase I, 2n

A) metaphase II, 2n
B) metaphase II, n
C) metaphase I, 2n
D) metaphase I, n
E) anaphase I, 2n

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Camels have a diploid chromosome number of 70. At prophase II, each cell would contain how many tetrads?
A) 0
B) 35
C) 70
D) 140
E) 280
A) 0
B) 35
C) 70
D) 140
E) 280

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Goats have a diploid chromosome number of 60. At prophase I, each cell would have ________ tetrads present, for a total of ________chromatids.
A) 30; 120
B) 30; 60
C) 60; 120
D) 60; 240
E) 30; 240
A) 30; 120
B) 30; 60
C) 60; 120
D) 60; 240
E) 30; 240

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
For the figure shown here, indicate the correct stage of meiosis and whether the cell is haploid (n) or diploid (2n). 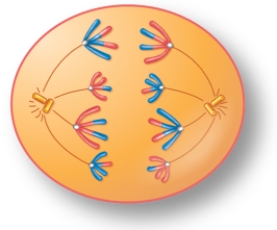
A) anaphase I, 2n
B) anaphase II, n
C) anaphase I, n
D) anaphase II, 2n
E) neither anaphase I or anaphase II.

A) anaphase I, 2n
B) anaphase II, n
C) anaphase I, n
D) anaphase II, 2n
E) neither anaphase I or anaphase II.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
A human egg with 22 chromosomes that is fertilized by a normal sperm will result in
A) a zygote with trisomy.
B) a zygote with disomy.
C) a zygote with monosomy.
D) a zygote with a normal chromosome number.
E) a fertilized egg with 44 chromosomes.
A) a zygote with trisomy.
B) a zygote with disomy.
C) a zygote with monosomy.
D) a zygote with a normal chromosome number.
E) a fertilized egg with 44 chromosomes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
The first 22 pairs of chromosomes are called ________ while the 23rd pair are known as the __________ chromosomes, which code for gender.
A) homologous; autosomes
B) autosomes; homologous
C) diploid; haploid
D) autosomes: sex
E) sex; autosomes
A) homologous; autosomes
B) autosomes; homologous
C) diploid; haploid
D) autosomes: sex
E) sex; autosomes

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Camels have a diploid chromosome number of 70. At prophase II, each cell would contain how many chromatids?
A) 0
B) 35
C) 70
D) 140
E) 280
A) 0
B) 35
C) 70
D) 140
E) 280

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
Which pair of chromosomes on a karyotype would show you the sex of a baby?
A) 21st pair
B) 18th pair
C) 23rd pair
D) 6th pair
E) 1st pair
A) 21st pair
B) 18th pair
C) 23rd pair
D) 6th pair
E) 1st pair

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Crossing-over between sister chromatids does not result in recombination of genetic material, while crossing-over between nonsister chromatids does because
A) sister chromatids have the same alleles, while nonsister chromatids have different ones.
B) sister chromatids have the same genes, while nonsister chromatids have different ones.
C) sister chromatids have the same alleles but different genes, while nonsister chromatids have different alleles but the same genes.
D) nonsister chromatids have the same alleles, while sister chromatids have different ones.
E) nonsister chromatids have the same genes, while sister chromatids have different ones.
A) sister chromatids have the same alleles, while nonsister chromatids have different ones.
B) sister chromatids have the same genes, while nonsister chromatids have different ones.
C) sister chromatids have the same alleles but different genes, while nonsister chromatids have different alleles but the same genes.
D) nonsister chromatids have the same alleles, while sister chromatids have different ones.
E) nonsister chromatids have the same genes, while sister chromatids have different ones.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
Which of the following statements is true?
A) Chromosomes are classified into two categories:the sex chromosomes that determine gender and autosomes that determine non-gender related traits.
B) Homologous chromosomes differ in banding patterns, the traits they code for, and size.
C) While sex chromosomes determine different genders, they look the same until they are stained.
D) In humans all 46 chromosomes have an identical match called the homologue.
E) Chromosomes are classified into two categories:autosomes that determine gender and the sex chromosomes that determine non-gender related traits.
A) Chromosomes are classified into two categories:the sex chromosomes that determine gender and autosomes that determine non-gender related traits.
B) Homologous chromosomes differ in banding patterns, the traits they code for, and size.
C) While sex chromosomes determine different genders, they look the same until they are stained.
D) In humans all 46 chromosomes have an identical match called the homologue.
E) Chromosomes are classified into two categories:autosomes that determine gender and the sex chromosomes that determine non-gender related traits.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
The human life cycle consists of
A) adults who are haploid and produce diploid gametes; these gametes fuse to produce a haploid zygote which grows into an adult.
B) zygotes who are haploid fuse to produce a diploid gamete which grows into an adult.
C) gametes that are diploid and produce haploid zygotes; these grow into haploid adults.
D) adults who are diploid and produce haploid gametes; these gametes fuse to produce a diploid zygote which grows into an adult.
E) adults that are diploid who produce zygotes that are also diploid.
A) adults who are haploid and produce diploid gametes; these gametes fuse to produce a haploid zygote which grows into an adult.
B) zygotes who are haploid fuse to produce a diploid gamete which grows into an adult.
C) gametes that are diploid and produce haploid zygotes; these grow into haploid adults.
D) adults who are diploid and produce haploid gametes; these gametes fuse to produce a diploid zygote which grows into an adult.
E) adults that are diploid who produce zygotes that are also diploid.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
All but which one of the following results from nondisjunction?
A) trisomy
B) diploidy
C) monosomy
D) polyploidy
E) Down syndrome
A) trisomy
B) diploidy
C) monosomy
D) polyploidy
E) Down syndrome

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
Which of the following is an inaccurate statement about crossing-over?
A) Crossing-over is preceded by a process known as synapsis, where homologous chromosomes attach to each other.
B) Crossing-over results in greater genetic variability in offspring.
C) Crossing-over occurs between sister chromatids.
D) Crossing-over occurs during prophase I when homologous chromosomes line up prior to separation.
E) In humans, crossing-over results in genetic recombination.
A) Crossing-over is preceded by a process known as synapsis, where homologous chromosomes attach to each other.
B) Crossing-over results in greater genetic variability in offspring.
C) Crossing-over occurs between sister chromatids.
D) Crossing-over occurs during prophase I when homologous chromosomes line up prior to separation.
E) In humans, crossing-over results in genetic recombination.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
Which of the following is a characteristic of someone with Down syndrome?
A) short stature
B) eyelid fold
C) stubby fingers
D) fissured tongue
E) All of the above answers describe characteristics of someone with Down syndrome.
A) short stature
B) eyelid fold
C) stubby fingers
D) fissured tongue
E) All of the above answers describe characteristics of someone with Down syndrome.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
You are looking at a cell under a microscope and see what appears to be several "X" structures being pulled to each side of the cell. What stage of meiosis are you looking at?
A) anaphase I
B) prophase I
C) prophase II
D) metaphase I
E) anaphase II
A) anaphase I
B) prophase I
C) prophase II
D) metaphase I
E) anaphase II

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
One of the main goals of meiosis is
A) create cells that are genetically identical to their parent cell.
B) to create a fertilized egg that has half the genetic material of the parents.
C) to reduce the number of chromosomes by half in gametes.
D) to prevent genetic disorders.
E) to reduce genetic diversity.
A) create cells that are genetically identical to their parent cell.
B) to create a fertilized egg that has half the genetic material of the parents.
C) to reduce the number of chromosomes by half in gametes.
D) to prevent genetic disorders.
E) to reduce genetic diversity.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
During which stage of meiosis will the pairs of homologous chromosomes line up?
A) metaphase I
B) metaphase II
C) metaphase
D) anaphase I
E) prophase II
A) metaphase I
B) metaphase II
C) metaphase
D) anaphase I
E) prophase II

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



