Deck 12: Investing in Stocks and Bonds
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/6
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 12: Investing in Stocks and Bonds
1
The price of Garden Designs, Inc. is now $85. The company pays no dividends. Sean Perth expects the price four years from now to be $125 a share. Should Sean buy Garden Designs if he wants a 15 percent rate of return? Explain.
The following formula is used for calculating yield on investment which is as follows:
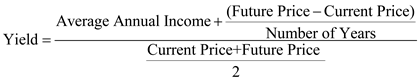 Substitute $0 for ' Average Annual income ', $125 for ' Future price ', $85 for ' Current price ', and 4years for ' Number of years '
Substitute $0 for ' Average Annual income ', $125 for ' Future price ', $85 for ' Current price ', and 4years for ' Number of years '
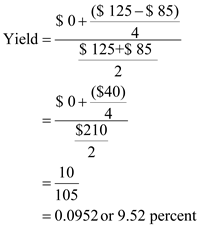 Therefore, from the above calculations it can be concluded that, the yield on stock is
Therefore, from the above calculations it can be concluded that, the yield on stock is
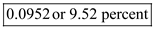 which is significantly lower than the expectation of Mr. S hence, he should not invest.
which is significantly lower than the expectation of Mr. S hence, he should not invest.
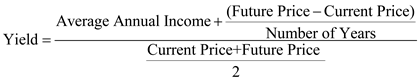 Substitute $0 for ' Average Annual income ', $125 for ' Future price ', $85 for ' Current price ', and 4years for ' Number of years '
Substitute $0 for ' Average Annual income ', $125 for ' Future price ', $85 for ' Current price ', and 4years for ' Number of years '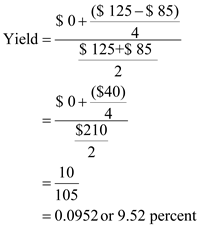 Therefore, from the above calculations it can be concluded that, the yield on stock is
Therefore, from the above calculations it can be concluded that, the yield on stock is 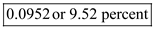 which is significantly lower than the expectation of Mr. S hence, he should not invest.
which is significantly lower than the expectation of Mr. S hence, he should not invest. 2
The Clarkson Company recently reported net profits after taxes of $15.8 million. It has 2.5 million shares of common stock outstanding and pays preferred dividends of $1 million a year. The company's stock currently trades at $60 per share.
a. Compute the stock's earnings per share (EPS).
b. What is the stock's P/E ratio?
c. Determine what the stock's dividend yield would be if it paid $1.75 per share to common stockholders.
a. Compute the stock's earnings per share (EPS).
b. What is the stock's P/E ratio?
c. Determine what the stock's dividend yield would be if it paid $1.75 per share to common stockholders.
a)
The following formula for EPS is used to calculate, which is as follows:
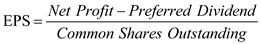 Substitute $15.8 million for ' Net profit ', $1 million for ' Preferred Dividend ', and 2.5 million for ' Common shares Outstanding '
Substitute $15.8 million for ' Net profit ', $1 million for ' Preferred Dividend ', and 2.5 million for ' Common shares Outstanding '
 Therefore, from the above calculations it can be concluded that, the EPS of the stock is
Therefore, from the above calculations it can be concluded that, the EPS of the stock is
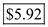 b)
b)
The following formula is used to calculate P/E ratio , which is as follows:
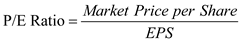 Substitute $60 for ' Market price per share ', and $5.92 for ' EPS '
Substitute $60 for ' Market price per share ', and $5.92 for ' EPS '
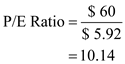 Therefore, form the above calculations it can be concluded that, the P/E ratio of the stocks is
Therefore, form the above calculations it can be concluded that, the P/E ratio of the stocks is
 c)
c)
The following formula is used to calculate dividend yield , which is as follows:
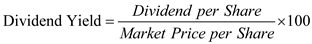 Substitute $1.75 for ' Dividend per share ', and $60 for ' Market price per share '
Substitute $1.75 for ' Dividend per share ', and $60 for ' Market price per share '
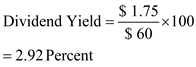 Therefore, from the above calculations it can be concluded that, the dividend yield of the common stock is
Therefore, from the above calculations it can be concluded that, the dividend yield of the common stock is
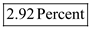
The following formula for EPS is used to calculate, which is as follows:
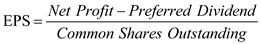 Substitute $15.8 million for ' Net profit ', $1 million for ' Preferred Dividend ', and 2.5 million for ' Common shares Outstanding '
Substitute $15.8 million for ' Net profit ', $1 million for ' Preferred Dividend ', and 2.5 million for ' Common shares Outstanding ' Therefore, from the above calculations it can be concluded that, the EPS of the stock is
Therefore, from the above calculations it can be concluded that, the EPS of the stock is 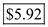 b)
b) The following formula is used to calculate P/E ratio , which is as follows:
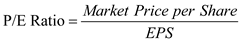 Substitute $60 for ' Market price per share ', and $5.92 for ' EPS '
Substitute $60 for ' Market price per share ', and $5.92 for ' EPS '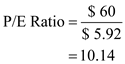 Therefore, form the above calculations it can be concluded that, the P/E ratio of the stocks is
Therefore, form the above calculations it can be concluded that, the P/E ratio of the stocks is  c)
c) The following formula is used to calculate dividend yield , which is as follows:
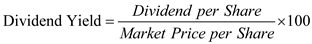 Substitute $1.75 for ' Dividend per share ', and $60 for ' Market price per share '
Substitute $1.75 for ' Dividend per share ', and $60 for ' Market price per share '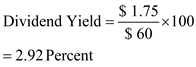 Therefore, from the above calculations it can be concluded that, the dividend yield of the common stock is
Therefore, from the above calculations it can be concluded that, the dividend yield of the common stock is 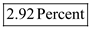
3
An investor in the 28 percent tax bracket is trying to decide which of two bonds to select: one is a 5.5 percent U.S. Treasury bond selling at par; the other is a municipal bond with a 4.25 percent coupon, which is also selling at par. Which of these two bonds should the investor select? Why?
Return of government bond is calculated by the using following formula:
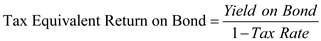 The tax equivalent return on municipal bond which is tax exempted is calculated as follows:
The tax equivalent return on municipal bond which is tax exempted is calculated as follows:
Substitute 4.25 percent for ' Yield on bond ', and 0.28 for ' Tax rate '
 Therefore, from the above calculations it can be concluded that, the investor should select municipal bond as the return on the bond after adjusting the tax exemption is
Therefore, from the above calculations it can be concluded that, the investor should select municipal bond as the return on the bond after adjusting the tax exemption is
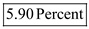 as against the return of 5.5 percent on Treasury bond.
as against the return of 5.5 percent on Treasury bond.
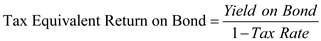 The tax equivalent return on municipal bond which is tax exempted is calculated as follows:
The tax equivalent return on municipal bond which is tax exempted is calculated as follows:Substitute 4.25 percent for ' Yield on bond ', and 0.28 for ' Tax rate '
 Therefore, from the above calculations it can be concluded that, the investor should select municipal bond as the return on the bond after adjusting the tax exemption is
Therefore, from the above calculations it can be concluded that, the investor should select municipal bond as the return on the bond after adjusting the tax exemption is 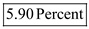 as against the return of 5.5 percent on Treasury bond.
as against the return of 5.5 percent on Treasury bond. 4
Describe and differentiate between a bond's (a) current yield and (b) yield to maturity. Why are these yield measures important to the bond investor? Find the yield to maturity of a 20-year, 9 percent, $1,000 par value bond trading at a price of $850. What's the current yield on this bond?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 6 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
What makes for a good investment? Use the approximate yield formula or a financial calculator to rank the following investments according to their expected returns.
a. Buy a stock for $30 a share, hold it for three years, and then sell it for $60 a share (the stock pays annual dividends of $2 a share).
b. Buy a security for $40, hold it for two years, and then sell it for $100 (current income on this security is zero).
c. Buy a one-year, 5 percent note for $1,000 (assume that the note has a $1,000 par value and that it will be held to maturity).
a. Buy a stock for $30 a share, hold it for three years, and then sell it for $60 a share (the stock pays annual dividends of $2 a share).
b. Buy a security for $40, hold it for two years, and then sell it for $100 (current income on this security is zero).
c. Buy a one-year, 5 percent note for $1,000 (assume that the note has a $1,000 par value and that it will be held to maturity).

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 6 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
An investor is thinking about buying some shares of Razortronics, Inc., at $75 a share. She expects the price of the stock to rise to $115 a share over the next three years. During that time, she also expects to receive annual dividends of $4 per share. Assuming that the investor's expectations (about the future price of the stock and the dividends that it pays) hold up, what rate of return can the investor expect to earn on this investment? ( Hint: Use either the approximate yield formula or a financial calculator to solve this problem.)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 6 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



