Deck 3: The Economic Problem
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/109
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 3: The Economic Problem
1
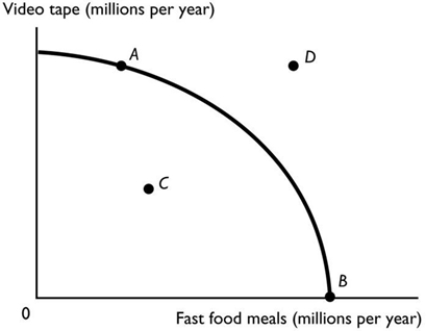 Point D in the above PPF figure is
Point D in the above PPF figure isA) an attainable production combination with unemployed resources.
B) More information is needed to determine which of the above answers is correct.
C) a production combination that can be attained once resources are fully employed.
D) an unattainable production combination.
E) a tradeoff.
an unattainable production combination.
2
. Assume that an association of young workers has lobbied the federal government to require that all workers retire once they reach the age of fifty. What impact would this law have on the nation's production possibilities frontier?
A) No impact at all.
B) The level of unemployment would decrease so the production possibilities frontier would shift outward.
C) The number of young workers would increase so the production possibilities frontier would shift outward.
D) The nation would move to a new position on its production possibilities frontier but the frontier itself would not shift.
E) The production possibilities frontier would shift inward.
A) No impact at all.
B) The level of unemployment would decrease so the production possibilities frontier would shift outward.
C) The number of young workers would increase so the production possibilities frontier would shift outward.
D) The nation would move to a new position on its production possibilities frontier but the frontier itself would not shift.
E) The production possibilities frontier would shift inward.
The production possibilities frontier would shift inward.
3
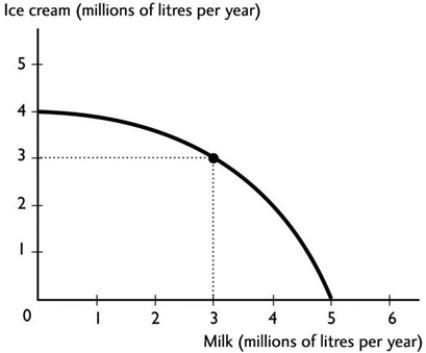 The figure above shows the production possibilities frontier for a country. A combination of 2 million litres of milk and 2 million litres of ice cream is
The figure above shows the production possibilities frontier for a country. A combination of 2 million litres of milk and 2 million litres of ice cream isA) unattainable.
B) attainable and production efficient.
C) attainable and production inefficient.
D) attainable but more than production efficient.
E) More information is needed to determine if the point is attainable or not.
attainable and production inefficient.
4
. When all of the available factors of production are being efficiently employed, the
A) economy is producing at a point beyond its PPF.
B) economy is producing at a point on its PPF.
C) PPF disappears.
D) economy is producing at a point within its PPF.
E) opportunity cost of changing production is infinite.
A) economy is producing at a point beyond its PPF.
B) economy is producing at a point on its PPF.
C) PPF disappears.
D) economy is producing at a point within its PPF.
E) opportunity cost of changing production is infinite.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Consider a production possibility frontier with jeans on the vertical axis and shoes on the horizontal axis. As the country moves along the frontier closer to the horizontal axis,
A) more jeans are produced.
B) more tradeoffs occur.
C) the country eventually chooses an unattainable point.
D) free lunches occur.
E) more shoes are produced.
A) more jeans are produced.
B) more tradeoffs occur.
C) the country eventually chooses an unattainable point.
D) free lunches occur.
E) more shoes are produced.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Which of the following is an assumption used when drawing a production possibilities frontier?
i. Human wants and desires are limited to what is available.
ii. Only two goods are considered.
iii. The level of technology is fixed and unchanging.
A) i only
B) ii only
C) i and iii
D) ii and iii
E) i, ii, and iii
i. Human wants and desires are limited to what is available.
ii. Only two goods are considered.
iii. The level of technology is fixed and unchanging.
A) i only
B) ii only
C) i and iii
D) ii and iii
E) i, ii, and iii

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
In the production possibilities frontier model, an unattainable point lies
A) only outside the production possibilities frontier.
B) both on and outside the production possibilities frontier.
C) only on the production possibilities frontier itself.
D) only inside the production possibilities frontier.
E) There are no unattainable points in the production possibilities model.
A) only outside the production possibilities frontier.
B) both on and outside the production possibilities frontier.
C) only on the production possibilities frontier itself.
D) only inside the production possibilities frontier.
E) There are no unattainable points in the production possibilities model.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
The production possibilities frontier illustrates the
A) resources the economy possesses, but not its level of technology.
B) limits to people's wants.
C) amount of each good that people want to buy.
D) maximum combinations of goods and services that can be produced.
E) goods and services people want.
A) resources the economy possesses, but not its level of technology.
B) limits to people's wants.
C) amount of each good that people want to buy.
D) maximum combinations of goods and services that can be produced.
E) goods and services people want.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
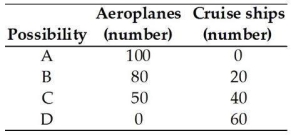 The table above gives four production possibilities for aeroplanes and cruise ships. In possibility A, how many resources are devoted to the production of cruise ships?
The table above gives four production possibilities for aeroplanes and cruise ships. In possibility A, how many resources are devoted to the production of cruise ships?A) All
B) Few
C) Most
D) None
E) It is impossible to tell without more information about the prices of airplanes and cruise ships.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Australia produced approximately ________ worth of goods and services in 20171.
A) $100 trillion
B) $100 billion
C) $10 billion
D) $10 trillion
E) $1.5 trillion
A) $100 trillion
B) $100 billion
C) $10 billion
D) $10 trillion
E) $1.5 trillion

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
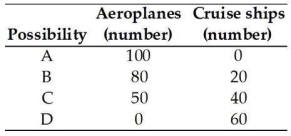 The table above gives four production possibilities for aeroplanes and cruise ships. In possibility A, how many resources are devoted to the production of aeroplanes?
The table above gives four production possibilities for aeroplanes and cruise ships. In possibility A, how many resources are devoted to the production of aeroplanes?A) None
B) Most
C) All
D) Few
E) It is impossible to tell without more information about the prices of aeroplanes and cruise ships.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
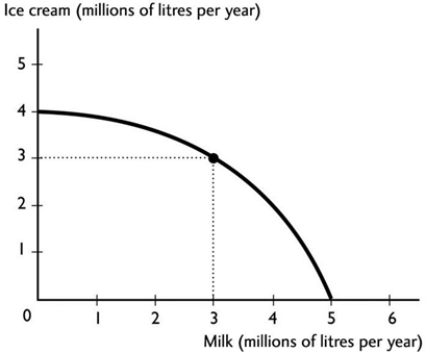 The figure above shows the production possibilities frontier for a country. A combination of 3 million litres of milk and 3 million litres of ice cream is
The figure above shows the production possibilities frontier for a country. A combination of 3 million litres of milk and 3 million litres of ice cream isA) unattainable.
B) attainable and production efficient.
C) attainable and production inefficient.
D) unattainable and production efficient.
E) More information is needed to determine if the point is attainable or not.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
 The figure above shows the production possibilities frontier for a country. In order for it to produce at point E, the
The figure above shows the production possibilities frontier for a country. In order for it to produce at point E, theA) country would need to acquire more resources and/or more advanced technology.
B) country would need to use its resources more efficiently.
C) production of SUVs would need to decrease.
D) production of station wagons would need to decrease.
E) country would need to determine that station wagons and SUVs are equally important to it.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
When production efficiency does NOT occur,
i. an economy is producing at a point within its PPF.
ii. there are unemployed resources.
iii. allocative efficiency cannot occur.
A) i only
B) i and ii
C) iii only
D) i and iii
E) i, ii and iii
i. an economy is producing at a point within its PPF.
ii. there are unemployed resources.
iii. allocative efficiency cannot occur.
A) i only
B) i and ii
C) iii only
D) i and iii
E) i, ii and iii

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
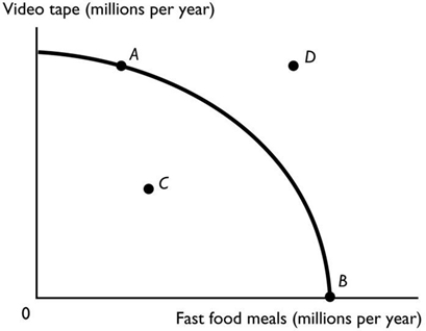
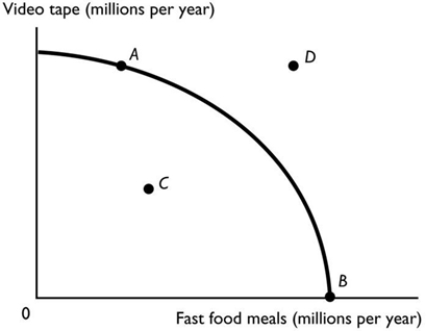 Which point in the figure above is an attainable combination that would have unemployed resources?
Which point in the figure above is an attainable combination that would have unemployed resources?A) Point A
B) Point B
C) Point C
D) Point D
E) Point A and point B

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Suppose a country operates on its production possibility frontier when it produces 1,000 books and 1,000 tables. The combination of ________ reflects ________.
A) 500 books and 500 tables; an attainable and efficient point.
B) 1,000 books and 1,000 tables; a free lunch.
C) 1,000 books and 1,500 tables; a free lunch.
D) 1,000 books and 500 tables; an efficient point.
E) 500 books and 1,000 tables; an inefficient but attainable point.
A) 500 books and 500 tables; an attainable and efficient point.
B) 1,000 books and 1,000 tables; a free lunch.
C) 1,000 books and 1,500 tables; a free lunch.
D) 1,000 books and 500 tables; an efficient point.
E) 500 books and 1,000 tables; an inefficient but attainable point.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Suppose that an economy is currently producing at a point that lies inside of its production possibilities set. Which of the following would best explain this circumstance?
A) The prevailing level of technology prevents the economy from producing at a point closer to the frontier of the production possibilities set.
B) The economy is experiencing a high level of unemployment.
C) The economy does not have enough resources to produce at a point closer to the frontier of the production possibilities set.
D) Any of the above statements could explain this situation.
E) None of the above statements could explain this situation.
A) The prevailing level of technology prevents the economy from producing at a point closer to the frontier of the production possibilities set.
B) The economy is experiencing a high level of unemployment.
C) The economy does not have enough resources to produce at a point closer to the frontier of the production possibilities set.
D) Any of the above statements could explain this situation.
E) None of the above statements could explain this situation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
If a society moves from a period of time with significant unemployment to a time with full employment, its production possibilities frontier will
A) shift leftward.
B) shift rightward.
C) not shift because the society moves from one point on the frontier to a point outside the frontier.
D) not shift because the society moves from a point inside the frontier to a point on the frontier.
E) not shift because the society moves from one point on the frontier to a point inside the frontier.
A) shift leftward.
B) shift rightward.
C) not shift because the society moves from one point on the frontier to a point outside the frontier.
D) not shift because the society moves from a point inside the frontier to a point on the frontier.
E) not shift because the society moves from one point on the frontier to a point inside the frontier.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
A production possibilities frontier shows
A) that if price of one good decreases, the price of the other has to increase.
B) how money can be allocated among two kinds of goods.
C) the limits to future growth of a nation.
D) that it is impossible to produce inefficiently.
E) the various combinations of output a nation can produce at a certain time, given its available resources and technology.
A) that if price of one good decreases, the price of the other has to increase.
B) how money can be allocated among two kinds of goods.
C) the limits to future growth of a nation.
D) that it is impossible to produce inefficiently.
E) the various combinations of output a nation can produce at a certain time, given its available resources and technology.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
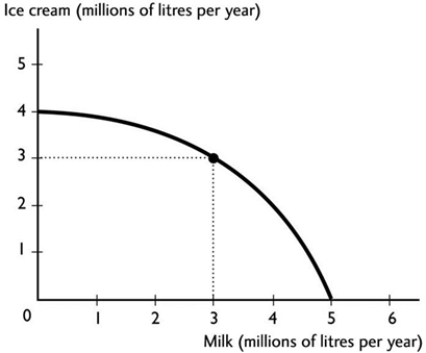 The figure above shows the production possibilities frontier for a country. A combination of 4 million litres of milk and 4 million litres of ice cream is
The figure above shows the production possibilities frontier for a country. A combination of 4 million litres of milk and 4 million litres of ice cream isA) unattainable.
B) attainable and production efficient.
C) attainable and production inefficient.
D) unattainable and production efficient.
E) More information is needed to determine if the point is attainable or not.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
During a time of high unemployment, a country can increase the production of one good or service
A) without decreasing the production of something else.
B) by using resources in the production process twice.
C) and must increase the production of something else.
D) but must decrease the production of something else.
E) but the opportunity cost is infinite.
A) without decreasing the production of something else.
B) by using resources in the production process twice.
C) and must increase the production of something else.
D) but must decrease the production of something else.
E) but the opportunity cost is infinite.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
A movement from a point inside the production possibilities frontier to a point on the production possibilities frontier represents
A) full employment of labour but not capital.
B) an infinite opportunity cost.
C) a free lunch.
D) a tradeoff.
E) unemployment of labour but not capital.
A) full employment of labour but not capital.
B) an infinite opportunity cost.
C) a free lunch.
D) a tradeoff.
E) unemployment of labour but not capital.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
A country produces only apples and bananas. Moving from point A to point B along its production possibilities frontier, 5 apples are forgone and 4 bananas are gained. What is the opportunity cost of a banana?
A) 1 banana
B) 4 apples
C) 4/5 of an apple
D) 5/4 of an apple
E) None of the above answers is correct.
A) 1 banana
B) 4 apples
C) 4/5 of an apple
D) 5/4 of an apple
E) None of the above answers is correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
On a production possibilities frontier, 500 kilograms of apples and 1200 kilograms of bananas can be produced while, at another point on the same frontier, 300 kilograms of apples and 1300 kilograms of bananas can be produced. Between these points, what is the opportunity cost of producing a kilogram of bananas?
A) 2 kilograms of bananas
B) 200 kilograms of apples
C) 0.5 a kilogram of apples
D) 2 kilograms of apples
E) 12/5 = 2.4 kilograms of apples
A) 2 kilograms of bananas
B) 200 kilograms of apples
C) 0.5 a kilogram of apples
D) 2 kilograms of apples
E) 12/5 = 2.4 kilograms of apples

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
On a production possibilities frontier, 500 kilograms of apples and 1200 kilograms of bananas can be produced while, at another point on the same frontier, 300 kilograms of apples and 1300 kilograms of bananas can be produced. Between these points, what is the opportunity cost of producing a kilogram of apples?
A) 0.5 of a kilogram of bananas
B) 5/12 of a kilogram of bananas
C) 2 kilograms of bananas
D) 2 kilograms of apples
E) 100 kilograms of bananas
A) 0.5 of a kilogram of bananas
B) 5/12 of a kilogram of bananas
C) 2 kilograms of bananas
D) 2 kilograms of apples
E) 100 kilograms of bananas

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
A country produces only apples and bananas. Moving from point A to point B along its production possibilities frontier, 5 apples are gained and 4 bananas are forgone. What is the opportunity cost of an apple?
A) 4 bananas
B) 4/5 of a banana
C) 1 apple
D) 5/4 of a banana
E) None of the above answers is correct.
A) 4 bananas
B) 4/5 of a banana
C) 1 apple
D) 5/4 of a banana
E) None of the above answers is correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
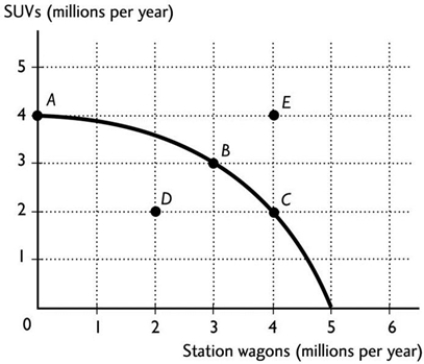 The figure above shows the production possibilities frontier for a country. If the country is producing at point D, then the
The figure above shows the production possibilities frontier for a country. If the country is producing at point D, then theA) resources are not being used efficiently and/or are unemployed.
B) technology associated with producing SUVs and station wagons is advancing.
C) resources are being used efficiently.
D) production of SUVs and station wagons is maximised.
E) None of the above answers is correct because it is not possible to produce at point D.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
When a nation is producing on its production possibilities frontier, if more resources are used to produce one good, then the production of other goods
A) must decrease.
B) must increase.
C) might increase if the nation can produce more efficiently.
D) must remain the same.
E) must change, but it might increase or decrease.
A) must decrease.
B) must increase.
C) might increase if the nation can produce more efficiently.
D) must remain the same.
E) must change, but it might increase or decrease.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
The production possibilities frontier illustrates which of the following economic ideas?
A) Opportunity cost
B) Tradeoffs
C) Efficiency
D) All of the above
E) None of the above
A) Opportunity cost
B) Tradeoffs
C) Efficiency
D) All of the above
E) None of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
The production possibilities frontier is a graph showing the
A) resources available for the economy's production use.
B) minimum combinations of goods and services that can be produced.
C) exact point of greatest efficiency for producing goods and services.
D) maximum combinations of goods and services that can be produced.
E) tradeoff between free lunches.
A) resources available for the economy's production use.
B) minimum combinations of goods and services that can be produced.
C) exact point of greatest efficiency for producing goods and services.
D) maximum combinations of goods and services that can be produced.
E) tradeoff between free lunches.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
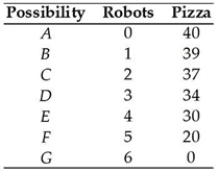 The table above shows a nation's production possibilities frontier. The opportunity cost of a robot between combination D and E is
The table above shows a nation's production possibilities frontier. The opportunity cost of a robot between combination D and E isA) 30 pizzas.
B) 1/4 of a pizza.
C) 4 pizzas.
D) 34 pizzas.
E) undefined because neither point is production efficient.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
The saying "There's no such thing as a free lunch" applies
A) to unattainable combinations of goods and services.
B) at all points inside the PPF.
C) on the production possibilities frontier.
D) when there is some unemployment.
E) when more of one good can be produced without decreasing production of another.
A) to unattainable combinations of goods and services.
B) at all points inside the PPF.
C) on the production possibilities frontier.
D) when there is some unemployment.
E) when more of one good can be produced without decreasing production of another.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
As we move along the production possibilities frontier,
A) the possibility of tradeoffs diminishes.
B) a tradeoff is not possible because nations need all goods.
C) the production of one good increases as the production of the other good decreases.
D) less of both goods can be produced.
E) more of both goods can be produced.
A) the possibility of tradeoffs diminishes.
B) a tradeoff is not possible because nations need all goods.
C) the production of one good increases as the production of the other good decreases.
D) less of both goods can be produced.
E) more of both goods can be produced.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Moving along the production possibilities frontier itself illustrates
A) the existence of unemployment of some factors of production.
B) the existence of tradeoffs.
C) the benefits of free lunches.
D) how tradeoffs need not occur if the economy is efficient.
E) how free lunches can be exploited through trade.
A) the existence of unemployment of some factors of production.
B) the existence of tradeoffs.
C) the benefits of free lunches.
D) how tradeoffs need not occur if the economy is efficient.
E) how free lunches can be exploited through trade.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
In order for Ireland to grow more potatoes, wool production must decrease. This situation is an example of
A) a tradeoff.
B) zero opportunity cost.
C) a free lunch.
D) producing at a point that lies beyond the PPF.
E) opportunity benefit.
A) a tradeoff.
B) zero opportunity cost.
C) a free lunch.
D) producing at a point that lies beyond the PPF.
E) opportunity benefit.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
The opportunity cost of producing one more unit of a good is calculated by dividing the
A) total quantity of that good by the total quantity of other good.
B) total quantity of the other good by the total quantity of the good whose opportunity cost we're calculating.
C) price of the good whose opportunity cost we are calculating by the number of units of the other good that are forgone.
D) increase in the quantity of that good by the decrease in the quantity of other good.
E) decrease in the quantity of the other good by the increase in the quantity of the good whose opportunity cost we're calculating.
A) total quantity of that good by the total quantity of other good.
B) total quantity of the other good by the total quantity of the good whose opportunity cost we're calculating.
C) price of the good whose opportunity cost we are calculating by the number of units of the other good that are forgone.
D) increase in the quantity of that good by the decrease in the quantity of other good.
E) decrease in the quantity of the other good by the increase in the quantity of the good whose opportunity cost we're calculating.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
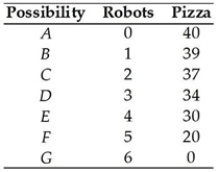 The table above shows a nation's production possibilities frontier. If the nation wants to produce 4 robots and 34 pizzas,
The table above shows a nation's production possibilities frontier. If the nation wants to produce 4 robots and 34 pizzas,A) it will shift the production possibilities frontier.
B) it will be unable to do so because the production point is unattainable.
C) the opportunity cost is 9 pizzas.
D) the nation will then be producing at a production efficient point.
E) the nation will be producing inefficiently.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
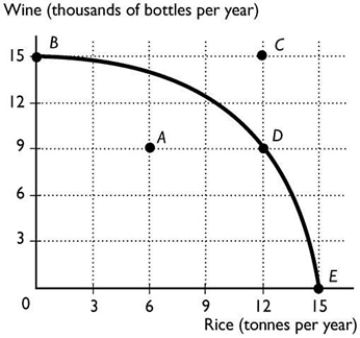 The above figure shows the production possibility frontier for a country. Suppose the country is producing at point A. What is the opportunity cost of increasing the production of rice to 12 tonnes?
The above figure shows the production possibility frontier for a country. Suppose the country is producing at point A. What is the opportunity cost of increasing the production of rice to 12 tonnes?A) 6 thousand bottles of wine
B) 9 thousand bottles of wine
C) 12 tonnes of rice
D) 15 thousand bottles of wine
E) Nothing, it is a free lunch.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
The negative slope of the production possibilities frontier represents the idea
A) of tradeoffs, that, in order to produce more of one good, the nation must produce less of another.
B) that prices rise as less is produced.
C) of unemployment.
D) of inefficient production.
E) that free lunches are possible.
A) of tradeoffs, that, in order to produce more of one good, the nation must produce less of another.
B) that prices rise as less is produced.
C) of unemployment.
D) of inefficient production.
E) that free lunches are possible.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
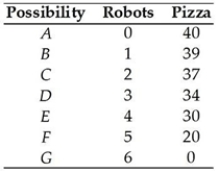 The table above shows a nation's production possibilities frontier. If the nation chooses to increase the production of robots from 2 to 3 and it is on its PPF, it will have to forgo ________ pizzas.
The table above shows a nation's production possibilities frontier. If the nation chooses to increase the production of robots from 2 to 3 and it is on its PPF, it will have to forgo ________ pizzas.A) 37
B) 3
C) 34
D) 35.5
E) None of the above answers is correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
If the production possibilities frontier between bottled water and water in a jug is a straight line, which of the following statements would be correct?
A) A large amount of unemployment must exist.
B) Producing more of one good gives the economy a free lunch.
C) There is no tradeoff between the two goods.
D) Resources are equally productive at producing either product.
E) There is no decrease in the production of one good when the production of the other is increased.
A) A large amount of unemployment must exist.
B) Producing more of one good gives the economy a free lunch.
C) There is no tradeoff between the two goods.
D) Resources are equally productive at producing either product.
E) There is no decrease in the production of one good when the production of the other is increased.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
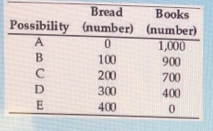
The table above shows the production possibilities for an economy. The opportunity cost of a loaf of bread is ________ when moving from possibility B to possibility C.
A) 1/2 of a book
B) 1 loaf of bread
C) 200 books
D) 100 loaves of bread
E) 2 books

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
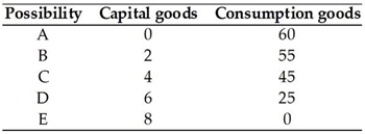 The table above presents the production possibilities frontier for a nation. Using the information in the table, when moving from possibility C to D, the cost of 1 unit of a capital good in terms of the consumption goods forgone is ________ consumption goods per capital good.
The table above presents the production possibilities frontier for a nation. Using the information in the table, when moving from possibility C to D, the cost of 1 unit of a capital good in terms of the consumption goods forgone is ________ consumption goods per capital good.A) 15
B) 20
C) 10
D) 25
E) an undefined amount of

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
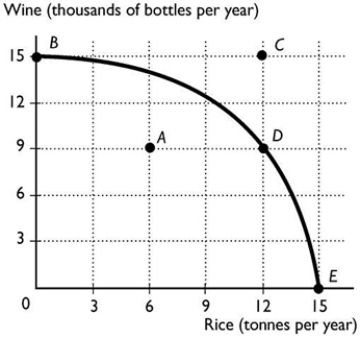
The above figure shows the production possibility frontier for a country. What is the opportunity cost per tonne of rice to move from point B to point D?
A) 1/2 of a bottle of wine
B) 500 bottles of wine
C) 2 bottles of wine
D) 1,000 bottles of wine
E) None of the above answers is correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Why does a nation experience increasing opportunity cost?
A) As the nation moves from a production point within the PPF to another point also within the PPF, opportunity costs increase.
B) Because the nation cannot produce at the unattainable production points that lie beyond the PPF.
C) As the nation moves from a production point within the PPF to one on the PPF, opportunity costs increase.
D) Resources are not equally productive in producing different kinds of goods and services.
E) When the amount of resources increases, the opportunity cost of all goods and services increases.
A) As the nation moves from a production point within the PPF to another point also within the PPF, opportunity costs increase.
B) Because the nation cannot produce at the unattainable production points that lie beyond the PPF.
C) As the nation moves from a production point within the PPF to one on the PPF, opportunity costs increase.
D) Resources are not equally productive in producing different kinds of goods and services.
E) When the amount of resources increases, the opportunity cost of all goods and services increases.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
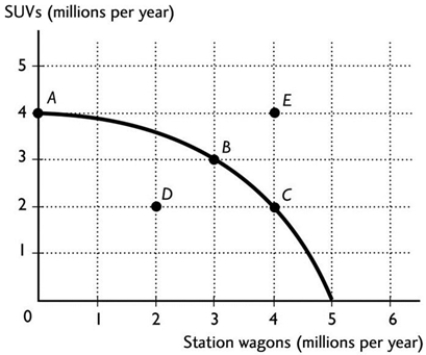 The figure above shows the production possibilities frontier for a country. In order for it to move from producing at point A to producing at point B, the country would need to
The figure above shows the production possibilities frontier for a country. In order for it to move from producing at point A to producing at point B, the country would need toA) decrease station wagon production by 3 million.
B) decrease SUV production by 1 million.
C) decrease SUV production by 3 million.
D) decrease SUV production by 4 million.
E) acquire more resources and/or more advanced technology.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
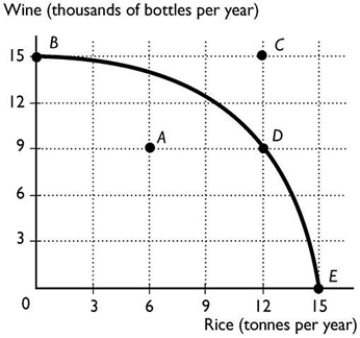 The above figure shows the production possibility frontier for a country. What is the opportunity cost to move from point D to point E?
The above figure shows the production possibility frontier for a country. What is the opportunity cost to move from point D to point E?A) 9 thousand bottles of wine
B) 6 tonnes of rice
C) 15 thousand bottles of wine
D) 6 thousand bottles of wine
E) Nothing, it is a free lunch.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
A bowed out production possibilities frontier shows
A) that resources are equally productive in all uses.
B) increasing opportunity cost.
C) that resources are not equally productive in all uses.
D) Both answers B and C are correct.
E) Both answers A and B are correct.
A) that resources are equally productive in all uses.
B) increasing opportunity cost.
C) that resources are not equally productive in all uses.
D) Both answers B and C are correct.
E) Both answers A and B are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
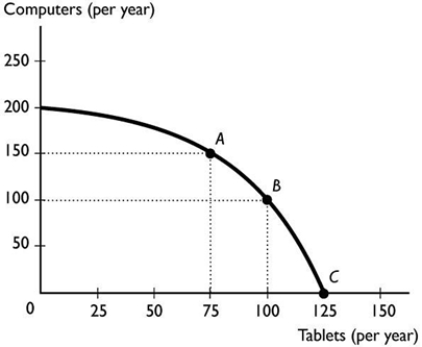 The figure above illustrates a small country's production possibilities frontier. Moving from point A to point B, the per unit opportunity cost of a tablet is ________ per tablet.
The figure above illustrates a small country's production possibilities frontier. Moving from point A to point B, the per unit opportunity cost of a tablet is ________ per tablet.A) 1 tablet
B) 4/3 of a computer
C) 2 computers
D) 1/2 of a computer
E) 100 computers

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
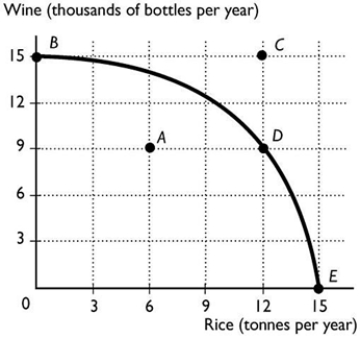 The above figure shows the production possibility frontier for a country. Suppose the country is producing at point D. What is the opportunity cost of increasing the production of rice to 15 tonnes?
The above figure shows the production possibility frontier for a country. Suppose the country is producing at point D. What is the opportunity cost of increasing the production of rice to 15 tonnes?A) 9 thousand bottles of wine
B) 12 tonnes of rice
C) 15 thousand bottles of wine
D) 6 thousand bottles of wine
E) Nothing, it is a free lunch.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51

The above figure shows the production possibility frontier for a country. What is the opportunity cost per tonne of rice to move from point D to E?
A) 333 bottles of wine
B) 3,000 bottles of wine
C) 3 bottles of wine
D) 1/3 of a bottle of wine
E) None of the above answers is correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
As an economy increasingly specialises in producing one good, the opportunity cost of that good increases. The opportunity cost increases because
A) as more of a good is produced the profit from its production must rise.
B) not all goods are equally valuable.
C) resources are not equally productive in all activities.
D) what must be paid to resources increases.
E) human wants are virtually unlimited.
A) as more of a good is produced the profit from its production must rise.
B) not all goods are equally valuable.
C) resources are not equally productive in all activities.
D) what must be paid to resources increases.
E) human wants are virtually unlimited.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53

The table above shows the production possibilities for an economy. Drawing a PPF with books on the vertical axis and bread on the horizontal axis, a movement from possibility B to possibility C to possibility D shows the opportunity cost of ________ moving down along the PPF.
A) books decreases
B) books and bread are both increasing
C) bread decreases
D) books is constant
E) bread increases

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
Suppose that, in a PPF graph, wheat is on the vertical axis and jets are on the horizontal axis. Moving down along the PPF, the
A) number of jets increases and the opportunity cost of jets increases.
B) amount of wheat increases and the opportunity cost of wheat decreases.
C) number of jets increases and the opportunity cost of jets decreases.
D) amount of wheat increases and the opportunity cost of wheat increases.
E) opportunity cost of jets and wheat both increase.
A) number of jets increases and the opportunity cost of jets increases.
B) amount of wheat increases and the opportunity cost of wheat decreases.
C) number of jets increases and the opportunity cost of jets decreases.
D) amount of wheat increases and the opportunity cost of wheat increases.
E) opportunity cost of jets and wheat both increase.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
When a production possibilities frontier is bowed outward, as more of one good is produced, its opportunity cost
A) decreases.
B) increases.
C) remains constant.
D) might increase, decrease or remain constant depending on how much people value the additional units of the good.
E) cannot be predicted.
A) decreases.
B) increases.
C) remains constant.
D) might increase, decrease or remain constant depending on how much people value the additional units of the good.
E) cannot be predicted.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
If there is increasing opportunity cost, then, when moving downward on a production possibilities frontier, the opportunity cost of the good on the horizontal axis ________ as more of the good is produced.
A) decreases and the PPF gets flatter
B) increases and the PPF gets flatter
C) increases and the PPF gets steeper
D) does not change and the PPF gets steeper
E) decreases and the PPF gets steeper
A) decreases and the PPF gets flatter
B) increases and the PPF gets flatter
C) increases and the PPF gets steeper
D) does not change and the PPF gets steeper
E) decreases and the PPF gets steeper

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
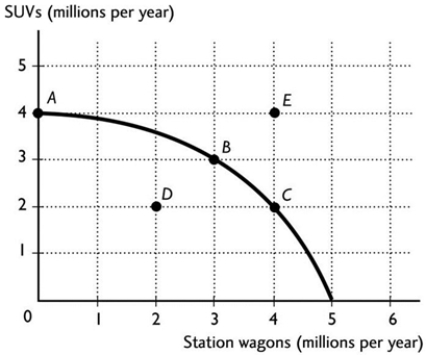 The figure above shows the production possibilities frontier for a country. In order for it to move from producing at point A to producing at point B, the country would need to incur an opportunity cost of
The figure above shows the production possibilities frontier for a country. In order for it to move from producing at point A to producing at point B, the country would need to incur an opportunity cost ofA) 1 million SUVs.
B) 3 million SUVs.
C) 3 million station wagons.
D) 4 million SUVs.
E) 0 because the gain in compact cars exceeds the loss in SUVs.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
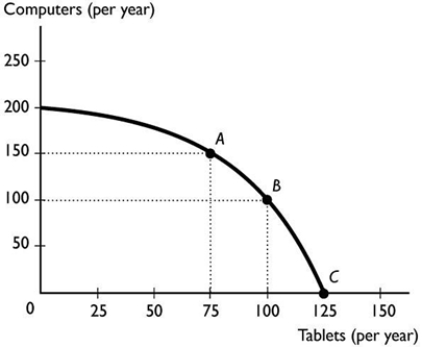 The figure above illustrates a small country's production possibilities frontier. Based on the figure, we can tell that the nation's resources are
The figure above illustrates a small country's production possibilities frontier. Based on the figure, we can tell that the nation's resources areA) equally productive in all tasks because the slope is negative.
B) unlimited because the slope is negative and the PPF is bowed out.
C) not equally productive in all tasks because the production possibilities frontier is bowed out.
D) not equally productive in all tasks because the slope is negative.
E) equally productive in all tasks because the production possibilities frontier is bowed out.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
If the production possibilities frontier between two goods were a straight line, then the opportunity cost of one good in terms of another would be
A) constant.
B) zero.
C) increasing.
D) decreasing.
E) either constant, increasing or decreasing, but more information is needed to determine which.
A) constant.
B) zero.
C) increasing.
D) decreasing.
E) either constant, increasing or decreasing, but more information is needed to determine which.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
The bowed out (concave) shape of the production possibilities curve implies that, as production of one good
A) decreases, production of other goods decreases as well.
B) increases, society must forgo decreasing amounts of another good.
C) increases, society must forgo increasing amounts of another good.
D) increases, society can obtain a free lunch.
E) increases, production of other goods increases as well.
A) decreases, production of other goods decreases as well.
B) increases, society must forgo decreasing amounts of another good.
C) increases, society must forgo increasing amounts of another good.
D) increases, society can obtain a free lunch.
E) increases, production of other goods increases as well.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
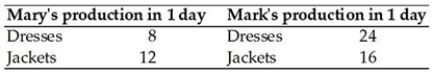 In the table above, how many jackets must Mary forgo for every dress she makes?
In the table above, how many jackets must Mary forgo for every dress she makes?A) 1 1/2 jackets
B) 2/3 of a jacket
C) 8 jackets
D) 3/4 of a jacket
E) 12 jackets

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
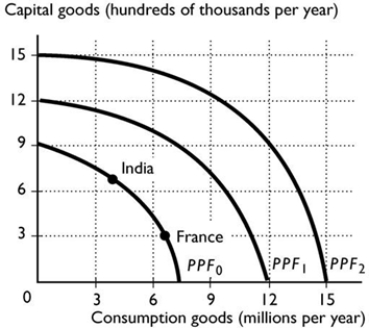 Suppose India and France have the same PPF, shown in the figure above. Based on their current production points, which is India's most likely future PPF?
Suppose India and France have the same PPF, shown in the figure above. Based on their current production points, which is India's most likely future PPF?A) PPF2
B) PPF0
C) PPF1
D) Either PPF0 or PPF1
E) None of the above because economic growth will not happen in India.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
To increase its economic growth, a nation should
A) increase current consumption.
B) encourage spending on goods and services.
C) encourage education because that increases the quality of labour.
D) limit the number of people in college because they produce nothing.
E) eliminate expenditure on capital goods.
A) increase current consumption.
B) encourage spending on goods and services.
C) encourage education because that increases the quality of labour.
D) limit the number of people in college because they produce nothing.
E) eliminate expenditure on capital goods.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
A country produces only cans of soup and ballpoint pens. If the country produces on its bowed outward PPF and increases the production of cans of soup, the opportunity cost of additional
A) cans of soup is decreasing.
B) cans of soup remains unchanged.
C) cans of soup is increasing.
D) ballpoint pens is increasing.
E) More information is needed to determine what happens to the opportunity cost.
A) cans of soup is decreasing.
B) cans of soup remains unchanged.
C) cans of soup is increasing.
D) ballpoint pens is increasing.
E) More information is needed to determine what happens to the opportunity cost.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
When Mike has an absolute advantage in the production of two goods over Tommy, Mike
A) is better off if he does not engage in specialisation and trade with Tommy.
B) is more productive in producing both goods than Tommy.
C) is less productive than Tommy.
D) cannot gain from trade with Tommy.
E) always has a comparative advantage over Tommy in the production of both goods.
A) is better off if he does not engage in specialisation and trade with Tommy.
B) is more productive in producing both goods than Tommy.
C) is less productive than Tommy.
D) cannot gain from trade with Tommy.
E) always has a comparative advantage over Tommy in the production of both goods.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
If a nation devotes a larger share of its current production to consumption goods, then
A) it must produce at a point within its PPF.
B) its PPF will shift inward.
C) its PPF will shift outward.
D) some productive factors will become unemployed.
E) its economic growth will slow down.
A) it must produce at a point within its PPF.
B) its PPF will shift inward.
C) its PPF will shift outward.
D) some productive factors will become unemployed.
E) its economic growth will slow down.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
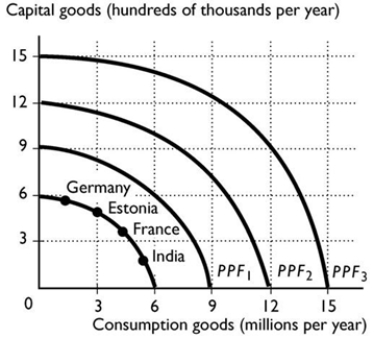 Suppose that Germany, France, Estonia and India all have the same production possibilities, illustrated in the figure above. Based on the production points in the figure, which country is most likely to expand its PPF to PPF3?
Suppose that Germany, France, Estonia and India all have the same production possibilities, illustrated in the figure above. Based on the production points in the figure, which country is most likely to expand its PPF to PPF3?A) France and Germany equally
B) Germany
C) Estonia
D) India
E) France

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
If John can produce 10 chairs or 20 lamps during a week, while Mary can produce 12 chairs or 22 lamps in the same time, who has the absolute advantage in producing each good?
A) John in producing both goods
B) John in producing chairs, Mary in producing lamps
C) Mary in producing both goods
D) Mary in producing chairs, John in producing lamps
E) Both Mary and John in both goods
A) John in producing both goods
B) John in producing chairs, Mary in producing lamps
C) Mary in producing both goods
D) Mary in producing chairs, John in producing lamps
E) Both Mary and John in both goods

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
Hank requires 1 hour to cut the grass and 3 hours to clean the house. His sister Holly requires 1 hour to cut the grass and 4 hours to clean the house. Which of the following statements is true?
A) Hank has a lower opportunity cost of cutting the grass.
B) Holly has a comparative advantage in cutting the grass.
C) Hank has a comparative advantage in both cutting the grass and cleaning the house.
D) Hank has an absolute advantage in both cutting the grass and cleaning the house.
E) Hank and Holly both have a comparative advantage in cutting the grass.
A) Hank has a lower opportunity cost of cutting the grass.
B) Holly has a comparative advantage in cutting the grass.
C) Hank has a comparative advantage in both cutting the grass and cleaning the house.
D) Hank has an absolute advantage in both cutting the grass and cleaning the house.
E) Hank and Holly both have a comparative advantage in cutting the grass.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
Increasing opportunity cost exists
A) in the real world.
B) for a country but not for an individual.
C) inside the PPF but not on the PPF.
D) only in theory but not in real life.
E) as long as there is high unemployment.
A) in the real world.
B) for a country but not for an individual.
C) inside the PPF but not on the PPF.
D) only in theory but not in real life.
E) as long as there is high unemployment.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
Moving between two points on a PPF, a country gains 6 cars and forgoes 3 trucks. The opportunity cost of 1 car is
A) 1/2 of a truck.
B) 2 trucks.
C) 3 trucks.
D) 6 cars - 3 trucks.
E) 1 car.
A) 1/2 of a truck.
B) 2 trucks.
C) 3 trucks.
D) 6 cars - 3 trucks.
E) 1 car.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
Which of the following is the best definition of economic growth?
A) The sustained expansion of production possibilities
B) The opportunity cost of consumption
C) Increased development of land and entrepreneurship
D) The opportunity cost of capital
E) The investment in capital and consumption goods by an economy
A) The sustained expansion of production possibilities
B) The opportunity cost of consumption
C) Increased development of land and entrepreneurship
D) The opportunity cost of capital
E) The investment in capital and consumption goods by an economy

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
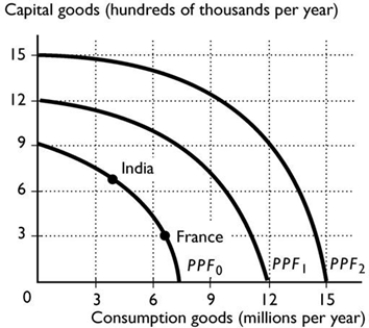 Suppose India and France have the same PPF, shown in the figure above. Based on their current production points, which is France's most likely future PPF?
Suppose India and France have the same PPF, shown in the figure above. Based on their current production points, which is France's most likely future PPF?A) PPF1
B) PPF2
C) PPF0
D) Either PPF0 or PPF1
E) None of the above because economic growth will not happen in India.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
If Wendy can produce more of all goods than Tommy in an hour, then
A) Wendy has a comparative advantage in all goods.
B) Tommy has an absolute advantage in all goods.
C) Only Tommy but not Wendy can benefit from trade between the two of them.
D) Wendy does not need to trade with Tommy in order to achieve the gains from trade.
E) Wendy has an absolute advantage in all goods.
A) Wendy has a comparative advantage in all goods.
B) Tommy has an absolute advantage in all goods.
C) Only Tommy but not Wendy can benefit from trade between the two of them.
D) Wendy does not need to trade with Tommy in order to achieve the gains from trade.
E) Wendy has an absolute advantage in all goods.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
While moving on the production possibilities frontier, if the opportunity cost of producing one good is 1/2, the opportunity cost of producing the other good (in the same range) is
A) 1/2.
B) 2.
C) 4.
D) 1/4.
E) An amount that cannot be calculated without more information.
A) 1/2.
B) 2.
C) 4.
D) 1/4.
E) An amount that cannot be calculated without more information.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
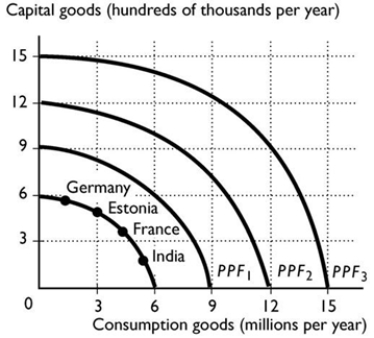 Suppose that Germany, France, Estonia and India all have the same production possibilities, illustrated in the figure above. Based on the production points in the figure, which country is most likely to expand its PPF to PPF1?
Suppose that Germany, France, Estonia and India all have the same production possibilities, illustrated in the figure above. Based on the production points in the figure, which country is most likely to expand its PPF to PPF1?A) Estonia
B) Germany
C) India
D) France
E) France and Germany equally

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
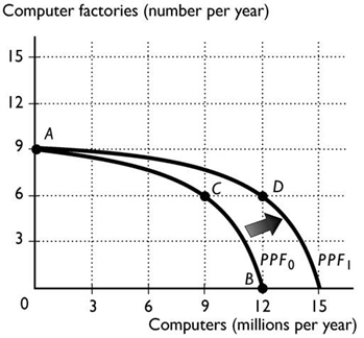 The above figure shows the PPF for a country that produces computers and computer factories. The nation's production possibilities frontier is PPF0. At which of the following production points would the economy grow most rapidly?
The above figure shows the PPF for a country that produces computers and computer factories. The nation's production possibilities frontier is PPF0. At which of the following production points would the economy grow most rapidly?A) Point A
B) Point B
C) Point C
D) It makes no difference among the three points because they are all production efficient.
E) More information is needed to answer the question.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
Economic growth depends upon which of the following?
i. Increasing the quantity of labour
ii. Lowering the prices of goods and services
iii. Advancing technology
A) i only
B) ii only
C) iii only
D) i and iii
E) i, ii and iii
i. Increasing the quantity of labour
ii. Lowering the prices of goods and services
iii. Advancing technology
A) i only
B) ii only
C) iii only
D) i and iii
E) i, ii and iii

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
The opportunity cost of economic growth is
A) a slower accumulation of human capital.
B) zero, because it means an expansion of production possibilities.
C) the decrease in the current production of productive factors.
D) the increase in the nation's capital stock and/or its technology.
E) the decrease in the current production of consumption goods.
A) a slower accumulation of human capital.
B) zero, because it means an expansion of production possibilities.
C) the decrease in the current production of productive factors.
D) the increase in the nation's capital stock and/or its technology.
E) the decrease in the current production of consumption goods.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
As an economy grows,
A) the opportunity cost of production will increase.
B) it can eliminate scarcity.
C) the opportunity cost of production will approach 0.
D) its PPF shifts outward.
E) its PPF does not shift; instead, the production point moves from inside the PPF to be closer to the PPF.
A) the opportunity cost of production will increase.
B) it can eliminate scarcity.
C) the opportunity cost of production will approach 0.
D) its PPF shifts outward.
E) its PPF does not shift; instead, the production point moves from inside the PPF to be closer to the PPF.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



