Deck 11: Retirement and Other Tax-Deferred Plans and Annuities C
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/62
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 11: Retirement and Other Tax-Deferred Plans and Annuities C
1
What are the differences between a defined-benefit pension plan and a defined-contribution pension plan?
Defined Benefit Pension Plan and Defined Contribution Plan:
"Qualified Pension Plans can be categorized as defined benefit pension plan and defined contribution plan".
The difference between these two plans is given as below:
Difference between Defined Benefit Pension Plan and Defined Contribution Plan:
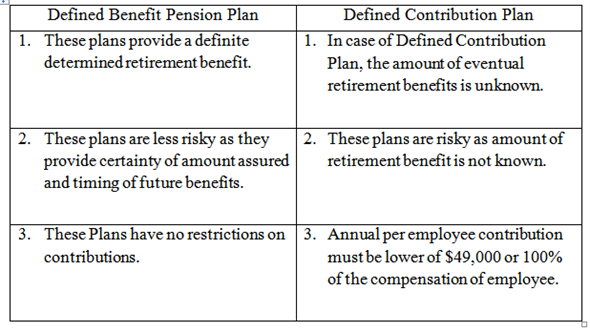
"Qualified Pension Plans can be categorized as defined benefit pension plan and defined contribution plan".
The difference between these two plans is given as below:
Difference between Defined Benefit Pension Plan and Defined Contribution Plan:

2
Tax-free distributions from a Coverdell Education Savings Account can be used for what purpose? Be specific.
Coverdell Education Savings Account:
1. An individual can opt for a Coverdell Education Savings Account when he or she wants to cover payments of elementary, secondary or higher secondary education expenses of the beneficiary.
2. As like Roth IRA, contributions made to CESA are not deductible, earnings accumulated in CESA are not taxable and distributions of CESA are not taxable if they used for only intentional purpose.Use of tax free distributions from a Coverdell Savings Account:
Distributions of CESA are not taxable if they used for only intentional purpose.It means such distributions must be used for payment of qualified elementary, secondary and higher education expenses of the beneficiary.
1. An individual can opt for a Coverdell Education Savings Account when he or she wants to cover payments of elementary, secondary or higher secondary education expenses of the beneficiary.
2. As like Roth IRA, contributions made to CESA are not deductible, earnings accumulated in CESA are not taxable and distributions of CESA are not taxable if they used for only intentional purpose.Use of tax free distributions from a Coverdell Savings Account:
Distributions of CESA are not taxable if they used for only intentional purpose.It means such distributions must be used for payment of qualified elementary, secondary and higher education expenses of the beneficiary.
3
Jack is single and age 43. He reported AGI of $115,000 in tax year 2010. He is an active participant in his employer's pension plan. What is the maximum Roth IRA contribution he can make in 2010? a. $0.
B) $1,667.
C) $3,333.
D) $5,000.
B) $1,667.
C) $3,333.
D) $5,000.
B
Rationale: ($115K - $105K) / $15K = 2/3 X $5,000 = $3,333 disallowed. So, $1,667 is his maximum contribution.
Rationale: ($115K - $105K) / $15K = 2/3 X $5,000 = $3,333 disallowed. So, $1,667 is his maximum contribution.
4
Use the same information as in Problem 52. Answer the questions indicated, assuming that Ken is considering a SIMPLE plan.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 62 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
What are the differences between a contributory and a noncontributory pension plan?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 62 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Stan has $20,000 in a traditional IRA at a bank. He decided to change trustees from a bank to a financial services firm. He requests, and receives, a check from the bank that he intends to take to the financial services firm to open a new account. He puts the check in his drawer and forgets it. Three months later, he remembers the check and takes it to the financial services firm and opens an IRA account. What are the tax implications of Stan's actions?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 62 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Without regard to AGI limitations, what is the maximum contribution permitted to a Coverdell Education Savings Account in 2010? a. $500
B) $2,000
C) $5,000
D) The lower of $5,000 or 100% of compensation
B) $2,000
C) $5,000
D) The lower of $5,000 or 100% of compensation

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 62 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Under what circumstances is it advantageous for a taxpayer to make a nondeductible contribution to a traditional IRA rather than a contribution to a Roth IRA?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 62 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
What are the similarities and differences between a pension plan and a profit-sharing plan?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 62 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
What is meant by an "expected return" on an annuity contract? How do you calculate expected return for a single person?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 62 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Vanessa and Martin file a joint return for 2010. They have one child age 12. They have combined AGI of $202,000 in 2010. What is their maximum permitted contribution to a Coverdell Education Savings Account for 2010? a. $0.
B) $800.
C) $1,200.
D) $2,000.
B) $800.
C) $1,200.
D) $2,000.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 62 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
April, who is under age 50, is considering investing in tax-free state government bonds or making a permitted tax-deductible contribution to a traditional IRA. Assume that the amounts are the same for either alternative and that she can reinvest the interest income from the government bonds indefinitely. What tax and nontax factors should she consider?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 62 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Pension plans are subject to certain vesting requirements. What does the word vesting mean? Describe the vesting rules for pension plans.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 62 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Which of the following is an individual-sponsored pension plan? a. Defined benefit plan.
B) Keogh plan.
C) Roth IRA.
D) SIMPLE plan.
B) Keogh plan.
C) Roth IRA.
D) SIMPLE plan.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 62 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Juan is single and retired on January 1, 2010 at age 62. He is entitled to receive monthly payments of $1,500 over his life from his employer's qualified pension plan. The payments began January 1, 2010. He contributed $71,500 to the plan prior to his retirement. Using the simplified method, how much of the payments will be included in his income for 2010? a. $0.
B) $3,300.
C) $14,700.
D) $18,000.
B) $3,300.
C) $14,700.
D) $18,000.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 62 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Lance is single and has a traditional IRA into which he has made deductible contributions for several years. This year he changed employers and is now an active participant in his employer's pension plan. His AGI is $80,000. He wants to make a nondeductible contribution to his IRA in the current year. What advice would you give Lance?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 62 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Briefly discuss the conditions necessary for a taxpayer to be permitted to make tax-deductible contributions to a Keogh plan.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 62 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Which of the following statements is true? a. Only employers can establish tax-deferred retirement plans.
B) Generally, plan distributions are taxable if the contributions were made with untaxed dollars.
C) The donor and the beneficiary of a retirement plan are almost never the same.
D) Retirement plan distributions can be made for any purpose and at any time.
B) Generally, plan distributions are taxable if the contributions were made with untaxed dollars.
C) The donor and the beneficiary of a retirement plan are almost never the same.
D) Retirement plan distributions can be made for any purpose and at any time.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 62 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
If a qualified pension plan is being distributed using joint life expectancy: a. The taxpayers cannot choose to refigure their life expectancy.
B) If the beneficiary dies, no adjustment of the denominator used to calculate minimum distributions is required.
C) If the beneficiary dies, the life expectancy of a different beneficiary is substituted for the original beneficiary.
D) None of the above.
B) If the beneficiary dies, no adjustment of the denominator used to calculate minimum distributions is required.
C) If the beneficiary dies, the life expectancy of a different beneficiary is substituted for the original beneficiary.
D) None of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 62 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
What are the differences between a traditional IRA and a Roth IRA regarding the deductibility of contributions, taxability of IRA earnings, and taxability of distributions?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 62 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
What is the maximum annual contribution that can be made to a Keogh plan, and how is the maximum calculated?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 62 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
A participant in a Keogh plan over the age of 50 may contribute up to what amount in 2010? a. $6,000.
B) $22,000.
C) The greater of $49,000 or 25% of earned income from self-employment.
D) The lower of $49,000 or 25% of earned income from self-employment.
B) $22,000.
C) The greater of $49,000 or 25% of earned income from self-employment.
D) The lower of $49,000 or 25% of earned income from self-employment.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 62 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Mark, who is single, must start making distributions from his pension plan beginning April 1, 2010. At the end of 2009 when Mark was 71 years old, the plan had a balance of $220,000. He will use a single life expectancy. What amount must Mark take as a distribution from the pension plan no later than April 1, 2010? a. $8,302.
B) $12,941.
C) $13,497.
D) $14,193.
B) $12,941.
C) $13,497.
D) $14,193.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 62 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Using the simplified method, determine the tax-free amount of the following distributions from a qualified pension plan. Contributions, if any, are made with previously-taxed dollars.
a. Person A, age 59, made no contributions to the pension plan and will receive a $500 monthly check for life.
b. Person B, age 66, made contributions of $23,000 to the pension plan and will receive a monthly check of $1,300 for life.
c. Person C, age 64, made contributions of $19,000 to the pension plan and will receive monthly payments of $1,200 over her life and the life of her 67-year-old husband.
d. Person D, age 55, made contributions of $32,000 to the pension plan. He will receive quarterly payments of $5,000 over his life and the life of his 58-year-old wife.
a. Person A, age 59, made no contributions to the pension plan and will receive a $500 monthly check for life.
b. Person B, age 66, made contributions of $23,000 to the pension plan and will receive a monthly check of $1,300 for life.
c. Person C, age 64, made contributions of $19,000 to the pension plan and will receive monthly payments of $1,200 over her life and the life of her 67-year-old husband.
d. Person D, age 55, made contributions of $32,000 to the pension plan. He will receive quarterly payments of $5,000 over his life and the life of his 58-year-old wife.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 62 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Briefly discuss the conditions necessary for a taxpayer to be permitted to make tax-deductible contributions to a SIMPLE plan.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 62 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
A qualified pension plan provides significant tax benefits to both employers and employees including: a. Employer contributions are not treated as compensation to the employee.
B) Earnings from the investments held in the plan are tax-deferred.
C) No tax on plan assets until the amounts are distributed.
D) All of the above.
B) Earnings from the investments held in the plan are tax-deferred.
C) No tax on plan assets until the amounts are distributed.
D) All of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 62 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Matt, age 62, retired in 2010. During the year, he received distributions of $9,000 from his IRA. He made nondeductible contributions of $20,000 to the IRA in prior years and has never received a nontaxable distribution. As of December 31, 2010, the value of his IRA was $150,000. Calculate the taxable portion of Matt's distribution. a. $1,132
B) $7,800.
C) $7,868.
D) $9,000.
B) $7,800.
C) $7,868.
D) $9,000.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 62 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Pablo and his wife Bernita are both age 45. Pablo works full-time, and Bernita works part-time. Their AGI is $90,000. Neither is a participant in an employer-sponsored retirement plan. They have been contributing to a traditional IRA for many years and have built up an IRA balance of $120,000. They are considering rolling the traditional IRA into a Roth IRA.
a. Is the couple eligible to make the conversion? Why or why not?
b. Assume that the couple does not make the conversion but, instead, establishes a separate Roth IRA in the current year and properly contributes $2,000 per year for four years at which point the balance in the Roth is $21,000. At the end of four years, they withdraw $12,000 to pay for an addition to their house. What is the tax effect, if anything, of the withdrawal?
c. Does your answer to (b) change if they withdraw $6,000? Why or why not?
d. What if the $12,000 withdrawal is used to pay qualified education expenses for their daughter who is attending college?
a. Is the couple eligible to make the conversion? Why or why not?
b. Assume that the couple does not make the conversion but, instead, establishes a separate Roth IRA in the current year and properly contributes $2,000 per year for four years at which point the balance in the Roth is $21,000. At the end of four years, they withdraw $12,000 to pay for an addition to their house. What is the tax effect, if anything, of the withdrawal?
c. Does your answer to (b) change if they withdraw $6,000? Why or why not?
d. What if the $12,000 withdrawal is used to pay qualified education expenses for their daughter who is attending college?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 62 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
What is the maximum annual contribution that can be made to a SIMPLE plan, and how is the maximum calculated?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 62 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
To obtain and retain qualified status, a pension or profit-sharing plan must not discriminate in favor of highly compensated employees, who include: a. Employees who own more than 5% of the corporation's stock.
B) Employees who received more than $100,000 compensation in the previous year.
C) Employees who were in the top 25% of employees based on compensation.
D) All of the above.
B) Employees who received more than $100,000 compensation in the previous year.
C) Employees who were in the top 25% of employees based on compensation.
D) All of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 62 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Withdrawals from a Roth IRA are: a. Subject to the required minimum distribution rules..
B) Taxable if made after the five-tax-year period beginning with the first tax year in which a Roth contribution was made.
C) Deemed to come first from contributions and then from earnings.
D) Not taxable to the extent they exceed contributions, if the five-year holding period requirement is not met.
B) Taxable if made after the five-tax-year period beginning with the first tax year in which a Roth contribution was made.
C) Deemed to come first from contributions and then from earnings.
D) Not taxable to the extent they exceed contributions, if the five-year holding period requirement is not met.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 62 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Determine the tax-free amount of the monthly payment in each of the following instances. Use the life expectancy tables.
a. Person A is age 57 and purchased an annuity for $82,000. The annuity pays $600 per month for life.
b. Person B is 73 and purchased an annuity for $80,000. The annuity pays $950 per month for life.
c. Person C is 68 and purchased an annuity for $40,000 that pays a monthly payment of $550 for 10 years.
a. Person A is age 57 and purchased an annuity for $82,000. The annuity pays $600 per month for life.
b. Person B is 73 and purchased an annuity for $80,000. The annuity pays $950 per month for life.
c. Person C is 68 and purchased an annuity for $40,000 that pays a monthly payment of $550 for 10 years.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 62 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Briefly discuss the conditions necessary for a taxpayer to be permitted to make tax-deductible contributions to a simplified employee pension (SEP).

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 62 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
A participant in a 401(k) plan under the age of 50 may contribute up to what amount in 2010? a. $5,000.
B) $14,000.
C) $16,500.
D) $49,000.
B) $14,000.
C) $16,500.
D) $49,000.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 62 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Regarding a Coverdell Education Savings Account: a. Distributions are tax-free to the beneficiary if they are used for his or her qualified education expenses.
B) Qualified education expenses include required tuition, fees, books, supplies, and equipment at an eligible education institution.
C) Qualified expenses must be reduced by scholarships or other tax-free income.
D) All of the above apply.
B) Qualified education expenses include required tuition, fees, books, supplies, and equipment at an eligible education institution.
C) Qualified expenses must be reduced by scholarships or other tax-free income.
D) All of the above apply.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 62 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Terrance is age 71 and retired. Beginning in 2010, he must start taking minimum distributions from his IRA account that had a balance of $150,000 as of December 31, 2009. Make these three assumptions: his IRA will earn 8% per year; he will withdraw the minimum distribution on the last day of each calendar year, and only one distribution will be taken in 2010. Calculate the amount of his distribution for years 2010 through 2014 and the ending balance in his IRA account on December 31, 2014.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 62 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
What is the maximum annual contribution that can be made to an SEP, and how is the maximum calculated?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 62 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Thomas is a self-employed plumber under the age of 50. His earnings from self- employment, before the Keogh deduction but after deducting half of the self-employment tax, are $80,000. What is his deductible Keogh contribution for 2010? a. $49,000.
B) $20,000.
C) $16,500.
D) $16,000.
B) $20,000.
C) $16,500.
D) $16,000.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 62 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Julio is 62 and single. He purchased a single life annuity contract that will pay him $1,000 a month for life with a minimum payout of 10 years. His expected return on the contract: a. Is $120,000.
B) Is $270,000.
C) Is $282,000.
D) Cannot be determined with the information given.
B) Is $270,000.
C) Is $282,000.
D) Cannot be determined with the information given.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 62 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Jennifer is age 50 and is seeking your advice. She has a traditional IRA with a balance of $100,000 and is considering whether to convert it (roll it over) to a Roth IRA. She has sufficient money in CDs to pay any required tax resulting from the rollover. Her current AGI is $70,000. She expects her income will be slightly higher upon retirement at age 65. What advice would you give Jennifer? Would your advice change if the fact(s) changed in each of the following independent instances? Why or why not?
a. Jennifer cannot cash the CDs and would need to pay any additional tax liability from the IRA funds.
b. She expects her income on retirement to decrease slightly.
c. Jennifer is age 30.
d. Her current AGI is $110,000.
a. Jennifer cannot cash the CDs and would need to pay any additional tax liability from the IRA funds.
b. She expects her income on retirement to decrease slightly.
c. Jennifer is age 30.
d. Her current AGI is $110,000.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 62 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
Briefly discuss the conditions necessary for a taxpayer to be permitted to make tax-deductible contributions to a traditional IRA.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 62 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Which of the following is true regarding SEPs? a. The plan cannot discriminate in favor of highly compensated employees.
B) Deductible contributions cannot exceed the lower of 15% of the employee's compensation or $49,000.
C) Self-employed individuals cannot create and contribute to an SEP.
D) The plan must cover all employees who have reached the age of 18, who have worked for the employer for at least two of the preceding five years, and who received at least $600 in compensation.
B) Deductible contributions cannot exceed the lower of 15% of the employee's compensation or $49,000.
C) Self-employed individuals cannot create and contribute to an SEP.
D) The plan must cover all employees who have reached the age of 18, who have worked for the employer for at least two of the preceding five years, and who received at least $600 in compensation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 62 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
June, age 76, and Augustus, age 78, are married. They purchased a single life annuity contract that will pay $1,500 per month for the life of June. The expected return on the contract: a. Is $190,800.
B) Is $214,200.
C) Is $405,000.
D) Cannot be determined with the information given.
B) Is $214,200.
C) Is $405,000.
D) Cannot be determined with the information given.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 62 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
What is the maximum annual contribution that can be made to a traditional IRA, and how is the maximum calculated?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 62 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Generous Corporation provides a SIMPLE plan for its employees. Under the plan, employees can contribute up to 6% of their salary and Generous Corporation will match each employee's contribution up to 3% of the employee's salary. Bob is an employee of Generous Corporation and elects to contribute 6% of his $60,000 salary to the SIMPLE plan. What is the total contribution made to his SIMPLE account? a. $11,500.
B) $5,400.
C) $3,600.
D) $1,800.
B) $5,400.
C) $3,600.
D) $1,800.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 62 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
Sanjay purchased a single life annuity contract for $200,000. The contract will pay $15,000 per year beginning in 2010 for the remainder of his life and has an expected return of $330,000. What amount of taxable income must Sanjay report in 2010? a. $5,909.
B) $9,091.
C) $15,000.
D) $130,000.
B) $9,091.
C) $15,000.
D) $130,000.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 62 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
What is the purpose of a retirement plan? Why does the government provide tax benefits to retirement plans?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 62 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
What is the deadline by which contributions must be made to a traditional IRA to obtain a tax deduction in the current year?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 62 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
Terri is single and age 32. She reported AGI of $59,000 in tax year 2010. She is an active participant in her employer's pension plan. What is the maximum deductible IRA contribution she can make in 2010? a. $0.
B) $1,500.
C) $3,500.
D) $5,000.
B) $1,500.
C) $3,500.
D) $5,000.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 62 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
Will, who is single and under age 50, is employed as a full-time tax accountant at a local manufacturing company where he earns $60,000 per year. He participates in a pension plan through his employer. Will also operates a small tax practice in his spare time during tax season and has net Schedule C income of $8,000. He is interested in establishing and contributing to other retirement plans. What options are available to Will?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 62 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
What is the "rule of thumb" noted in the text pertaining to the taxability of retirement plan distributions?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 62 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
What is the maximum annual contribution that can be made to a Roth IRA, and how is the maximum calculated?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 62 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
Ed and Cathy, both under age 50, file a joint return. Neither is covered under an employer pension plan. Ed earned compensation of $55,000 in 2010. Cathy worked part-time and earned $1,200. What is the maximum deductible IRA contribution they can make in 2010? a. $0.
B) $5,000.
C) $6,200.
D) $10,000.
B) $5,000.
C) $6,200.
D) $10,000.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 62 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
Cornell Company is considering the establishment of a pension plan. The proposed plan has the following features:
? Contributions for employees earning less than $100,000 will be based on 3% of salary, while contributions for those earning over $100,000 will be based on 4% of salary.
? To reduce employee turnover, company contributions will vest in 10 years.
? Employees with more than five years of service will be required to contribute 2% to the pension plan.
? Employee contributions will completely vest in one year.
Will the proposed pension plan be deemed a qualified pension plan? Why or why not?
? Contributions for employees earning less than $100,000 will be based on 3% of salary, while contributions for those earning over $100,000 will be based on 4% of salary.
? To reduce employee turnover, company contributions will vest in 10 years.
? Employees with more than five years of service will be required to contribute 2% to the pension plan.
? Employee contributions will completely vest in one year.
Will the proposed pension plan be deemed a qualified pension plan? Why or why not?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 62 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
Pension plans have an accumulation period and a distribution period. Explain what those terms mean.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 62 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
Anne, a single taxpayer under age 50, has wage income of $74,000 and is not covered under a retirement plan by her employer. She would like to start a retirement plan if possible. What options are available to her?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 62 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
Vickie is single and age 53. She reported AGI of $62,000 in 2010. She is an active participant in her employer's pension plan. What is the maximum deductible IRA contribution she can make in 2010? a. $2,000
B) $2,400
C) $3,600
D) $6,000
B) $2,400
C) $3,600
D) $6,000

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 62 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
Determine the maximum contribution that can be made to a Keogh plan in each of the following cases. In all instances, the individual is self-employed, and the self-employment tax reduction has already been taken.
a) Self-employment income of $46,000.
b) Self-employment income of $46,000 and wage income of $30,000.
c) Self-employment income of $125,000.
d) Self-employment income of $260,000.
a) Self-employment income of $46,000.
b) Self-employment income of $46,000 and wage income of $30,000.
c) Self-employment income of $125,000.
d) Self-employment income of $260,000.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 62 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
What are the two broad categories of retirement plans? Give some examples of each.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 62 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
What is the maximum annual contribution that can be made to a Coverdell Education Savings Account? Can an eligible beneficiary have more than one CESA?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 62 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
Patrice is single and age 26. She reported AGI of $62,000 in tax year 2010. She is an active participant in her employer's pension plan. What is the maximum deductible Roth IRA contribution she can make in 2010? a. $0.
B) $2,000.
C) $3,000.
D) $5,000.
B) $2,000.
C) $3,000.
D) $5,000.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 62 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
Ken is a self-employed architect in a small firm with four employees: himself, his office assistant, and two drafters, all of whom have worked for Ken full-time for the last four years. The office assistant earns $30,000 per year and each drafter earns $40,000. Ken's net earnings from self-employment (after deducting all expenses and one-half of self-employment taxes) are $305,000. Ken is considering whether to establish an SEP plan and has a few questions.
a) Is he eligible to establish an SEP plan?
b) Is he required to cover his employees under the plan? Why or why not?
c) If his employees must be covered, what is the maximum amount that can be contributed on their behalf?
d) If the employees are not covered, what is the maximum amount Ken can contribute for himself?
e) If Ken is required to contribute for his employees and chooses to contribute the maximum amount, what is the maximum amount Ken can contribute for himself? ( Hint: Calculate the employee amounts first.) Ignore any changes in Ken's self-employment tax.
a) Is he eligible to establish an SEP plan?
b) Is he required to cover his employees under the plan? Why or why not?
c) If his employees must be covered, what is the maximum amount that can be contributed on their behalf?
d) If the employees are not covered, what is the maximum amount Ken can contribute for himself?
e) If Ken is required to contribute for his employees and chooses to contribute the maximum amount, what is the maximum amount Ken can contribute for himself? ( Hint: Calculate the employee amounts first.) Ignore any changes in Ken's self-employment tax.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 62 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



