Deck 8: Drugs Affecting the Autonomic Ganglia
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/20
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 8: Drugs Affecting the Autonomic Ganglia
1
List the main effects of ganglionic stimulation.
The receptors present at the autonomic ganglia of both sympathetic and parasympathetic nervous systems are known as nicotinic-neural (Nn) receptors. The drugs that act to stimulate these receptors are known as ganglionic stimulants.
The ganglionic stimulation is produced by individuals who uses tobacco and thus absorbs nicotine. This stimulation ultimately increases both sympathetic and parasympathetic activity. The autonomic nervous system of human beings consists of sympathetic and parasympathetic nervous system.
The fact is that sympathetic stimulation usually dominates in the cardiovascular system and parasympathetic stimulation pre-dominates in the gastro-intestinal tract (GIT). Thus the effects found after person smokes are increase in heart rate, blood pressure and gastro-intestinal (GI) activity.
The ganglionic stimulation is produced by individuals who uses tobacco and thus absorbs nicotine. This stimulation ultimately increases both sympathetic and parasympathetic activity. The autonomic nervous system of human beings consists of sympathetic and parasympathetic nervous system.
The fact is that sympathetic stimulation usually dominates in the cardiovascular system and parasympathetic stimulation pre-dominates in the gastro-intestinal tract (GIT). Thus the effects found after person smokes are increase in heart rate, blood pressure and gastro-intestinal (GI) activity.
2
A patient has been brought by ambulance to the emergency room where you work. He's suffering from hypotension, and he's on the verge of cardiovascular collapse. The patient's wife, who accompanied him in the ambulance, says he was fine until he took some new medication for his high blood pressure. She has the bottle with her-the medication is mecamylamine. You ask her if he's taking any other medicine, and she replies that he takes propranolol for his angina. What is producing these effects in this patient
The patient is taking an adrenergic blocking drug, propranolol, which is prescribed for angina. Adrenergic blocking drugs have additive antiadrenergic effects when taken with ganglionic blocking drugs, like mecamylamine, producing hypotension and possible cardiovascular collapse.
3
Use your critical-thinking skills to answer the following questions. Select the correct answer.
The effects produced by nicotine include
A) increased heart rate
B) increased intestinal activity
C) increased blood pressure
D) CNS effects
E) all of these
The effects produced by nicotine include
A) increased heart rate
B) increased intestinal activity
C) increased blood pressure
D) CNS effects
E) all of these
Nicotine is the main ingredient in tobacco. It stimulates ganglionic receptors. It contains nitrogen made by tobacco plants and several other plants.
Consumption of nicotine in the form of cigarettes or any tobacco products can affect the human body. It shows its effect on the cardiovascular system due to sympathetic neurotransmitter stimulation. The release of norepinephrine by the sympathetic nervous system causes the nicotine which is present to induce a beta-adrenoreceptor. This causes an increase in heart rate.
Hence nicotine causes an increased heart rate. (option A)
The secretion of gastric acid increases, production of mucus differ and Gastrointestinal levels also differ because of nicotine. These lead to inflammatory diseases. Increased intestinal activity will be observed.
So, nicotine causes increased intestinal activity. ( option B)
Nicotine induces Alpha-adrenoreceptor when norepinephrine is released by the sympathetic nervous system. This causes constriction of blood vessels( called vasoconstriction). As a result, blood flow is lowered and the supply of oxygen to the heart decreases. Resistance to flow is increased and this leads to an increase in blood pressure.
Hence nicotine causes increased blood pressure. (option C).
Nicotine shows its effects on the pleasure centers of the brain. So, it can cause addiction to nicotine, mood swings, and disorders. It also affects the prefrontal cortex. It affects the nervous activity of the Central Nervous System.
So, nicotine shows the effect on the Central Nervous System. (option D)
As per the explanations mentioned above, it can be observed that all the given options are the effects produced by nicotine.
Hence option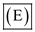 ( all of these) is correct.
( all of these) is correct.
Consumption of nicotine in the form of cigarettes or any tobacco products can affect the human body. It shows its effect on the cardiovascular system due to sympathetic neurotransmitter stimulation. The release of norepinephrine by the sympathetic nervous system causes the nicotine which is present to induce a beta-adrenoreceptor. This causes an increase in heart rate.
Hence nicotine causes an increased heart rate. (option A)
The secretion of gastric acid increases, production of mucus differ and Gastrointestinal levels also differ because of nicotine. These lead to inflammatory diseases. Increased intestinal activity will be observed.
So, nicotine causes increased intestinal activity. ( option B)
Nicotine induces Alpha-adrenoreceptor when norepinephrine is released by the sympathetic nervous system. This causes constriction of blood vessels( called vasoconstriction). As a result, blood flow is lowered and the supply of oxygen to the heart decreases. Resistance to flow is increased and this leads to an increase in blood pressure.
Hence nicotine causes increased blood pressure. (option C).
Nicotine shows its effects on the pleasure centers of the brain. So, it can cause addiction to nicotine, mood swings, and disorders. It also affects the prefrontal cortex. It affects the nervous activity of the Central Nervous System.
So, nicotine shows the effect on the Central Nervous System. (option D)
As per the explanations mentioned above, it can be observed that all the given options are the effects produced by nicotine.
Hence option
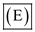 ( all of these) is correct.
( all of these) is correct. 4
What is the name of the cholinergic receptors at the ganglia

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 20 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
List the main effects of ganglionic blockade.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 20 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
A young man brought into the emergency room could hardly walk, had difficulty breathing, and had very low blood pressure. Upon questioning he said he had been chewing some type of gum to help him quit smoking. He admitted that he was still smoking a pack a day. What is going on with this patient

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 20 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Use your critical-thinking skills to answer the following questions. Select the correct answer.
Pharmacologic effects produced by mecamylamine ( Inversine ) include
A) increased urination
B) decreased blood pressure
C) diarrhea
D) increased heart rate
E) all of these
Pharmacologic effects produced by mecamylamine ( Inversine ) include
A) increased urination
B) decreased blood pressure
C) diarrhea
D) increased heart rate
E) all of these

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 20 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
What are the main therapeutic uses of the ganglionic blocking drugs

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 20 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Use your critical-thinking skills to answer the following questions. Select the correct answer.
At high or toxic doses, nicotine may cause
A) ganglionic stimulation
B) ganglionic blockade
C) skeletal muscle contraction
D) increased respiration
E) increased heart rate
At high or toxic doses, nicotine may cause
A) ganglionic stimulation
B) ganglionic blockade
C) skeletal muscle contraction
D) increased respiration
E) increased heart rate

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 20 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
List the adverse effects of the ganglionic stimulants used in nicotine replacement therapy.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 20 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Use your critical-thinking skills to answer the following questions. Select the correct answer.
The drug that blocks nicotinic receptors in the brain is
A) trimethaphan
B) atropine
C) varenicline
D) mecamylamine
E) bupropion
The drug that blocks nicotinic receptors in the brain is
A) trimethaphan
B) atropine
C) varenicline
D) mecamylamine
E) bupropion

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 20 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
List the adverse effects of the ganglionic blocking drugs.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 20 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
What neurotransmitter regulates ganglionic transmission

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 20 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Use your critical-thinking skills to answer the following questions. Select the correct answer.
Which of the following is an effect of ganglionic blockade
A) decreased blood pressure
B) reduced urination
C) bradycardia
D) impotence
E) all of these
Which of the following is an effect of ganglionic blockade
A) decreased blood pressure
B) reduced urination
C) bradycardia
D) impotence
E) all of these

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 20 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Assume that you work in a health maintenance organization (HMO), where you act as patient liaison. Patients are encouraged to talk over problems with you if they feel that the problems have not been resolved by a doctor or if they feel uncomfortable discussing the problems with a doctor. One of the patients wants to talk to you about an "embarrassing problem." He says that ever since he started taking that "strong medicine" for his high blood pressure, he hasn't been able to make love to his wife. He also has a dry mouth, and he's constipated all of the time. What drug is the patient most likely taking

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 20 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
What other drugs might interact with the ganglionic blockers

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 20 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Use your critical-thinking skills to answer the following questions. Select the correct answer.
The receptors located on the ganglia of both autonomic nerve divisions are
A) nicotinic-neural (Nn)
B) nicotinic-muscle (Nm)
C) muscarinic
D) anticholinergic
E) adrenergic
The receptors located on the ganglia of both autonomic nerve divisions are
A) nicotinic-neural (Nn)
B) nicotinic-muscle (Nm)
C) muscarinic
D) anticholinergic
E) adrenergic

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 20 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Use your critical-thinking skills to answer the following questions. Select the correct answer.
Ganglionic blocking drugs interact with which types of drugs
A) cholinergic
B) anticholinergic
C) adrenergic
D) antiadrenergic
E) all of these
Ganglionic blocking drugs interact with which types of drugs
A) cholinergic
B) anticholinergic
C) adrenergic
D) antiadrenergic
E) all of these

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 20 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Differentiate between a ganglionic stimulant and a ganglionic blocker.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 20 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Use your critical-thinking skills to answer the following questions. Select the correct answer.
The most common side effect(s) of ganglionic blockers would be
A) hypertension
B) dry mouth
C) decreased ocular pressure
D) diarrhea
E) increased heart rate
The most common side effect(s) of ganglionic blockers would be
A) hypertension
B) dry mouth
C) decreased ocular pressure
D) diarrhea
E) increased heart rate

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 20 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



