Deck 2: An Introduction to Genes and Genomes
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/14
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 2: An Introduction to Genes and Genomes
1
Compare and contrast genes and chromosomes and describe their roles in the cell.
GENES:
The genes are the sequences of DNA nucleotides and are generally 1000 to around 4000 nucleotides long. The sequence of the DNA nucleotides provides the instructions or code for the synthesis of the RNA (ribonucleic acid). Most of the genes produce messenger ribonucleic acid (mRNA) molecules that encode protein, but some genes produce RNAs that do not code for proteins. The genes control the proteins produced by a cell and influence how cells, tissues, and organs seem, both through the naked eye and a microscope. These inherited appearances are called traits. The genes influence the cell metabolism, and cognitive and behavioral abilities such as intelligence. The genes affect our susceptibility to certain types of the genetic disorder. Some traits are controlled by a single gene, and some are determined by multiple protein-producing genes.
CHROMOSOMES:
The genes are contained in chromosomes. The chromosomes are the tightly packed coils of the DNA and protein. During the cell division process, the chromosomes enable cells to separate the DNA content evenly in daughter cells. Multiple numbers of genes are contained in chromosomes, and the number of genes contained in a chromosome can vary depending on the size of the chromosome.
The genes are the sequences of DNA nucleotides and are generally 1000 to around 4000 nucleotides long. The sequence of the DNA nucleotides provides the instructions or code for the synthesis of the RNA (ribonucleic acid). Most of the genes produce messenger ribonucleic acid (mRNA) molecules that encode protein, but some genes produce RNAs that do not code for proteins. The genes control the proteins produced by a cell and influence how cells, tissues, and organs seem, both through the naked eye and a microscope. These inherited appearances are called traits. The genes influence the cell metabolism, and cognitive and behavioral abilities such as intelligence. The genes affect our susceptibility to certain types of the genetic disorder. Some traits are controlled by a single gene, and some are determined by multiple protein-producing genes.
CHROMOSOMES:
The genes are contained in chromosomes. The chromosomes are the tightly packed coils of the DNA and protein. During the cell division process, the chromosomes enable cells to separate the DNA content evenly in daughter cells. Multiple numbers of genes are contained in chromosomes, and the number of genes contained in a chromosome can vary depending on the size of the chromosome.
2
If the sequence of one strand of a DNA molecule is 5'-AGCCCCGACTCTATTC-3', what is the sequence of the complementary strand
The cDNA or complementary DNA is DNA produced from a messenger RNA (mRNA) template in a reaction, which is catalyzed by the enzymes DNA polymerase and reverse transcriptase. To make clones of prokaryotes, the cDNA is regularly used.
The sequence of the one strand of DNA molecule is:
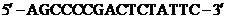 .
.
The complementary strand will be an antiparallel strand to the strand of DNA. The sequence of the antiparallel strand would be:
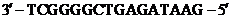 .
.
The sequence of the one strand of DNA molecule is:
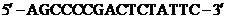 .
.The complementary strand will be an antiparallel strand to the strand of DNA. The sequence of the antiparallel strand would be:
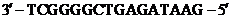 .
. 3
What does the phrase "gene expression" mean
The method by which the information stored in genes is utilized to construct a functional gene product is known as gene expression. The functional gene products are generally proteins, but in genes which are non-protein coding, such as rRNA genes or tRNA genes, the functional RNA is the gene product. The procedure of gene expression is used by eukaryotes, viruses, and prokaryotes to produce the macromolecular machinery such as DNA for life.
The steps involved in the procedure of gene expression can be modified, including the transcription, translation, post-translational modification, and RNA splicing of a protein. Gene regulation offers the cell control over function and structure, and is the source for cellular morphogenesis, differentiation, and the flexibility and versatility of any organism. Gene regulation may also support as a substrate for evolutionary change, since control of the timing, location, and amount of gene expression can have a superficial effect on the actions of the gene in a cell or in a multicellular organism.
The steps involved in the procedure of gene expression can be modified, including the transcription, translation, post-translational modification, and RNA splicing of a protein. Gene regulation offers the cell control over function and structure, and is the source for cellular morphogenesis, differentiation, and the flexibility and versatility of any organism. Gene regulation may also support as a substrate for evolutionary change, since control of the timing, location, and amount of gene expression can have a superficial effect on the actions of the gene in a cell or in a multicellular organism.
4
Suppose you identified a new strain of bacteria. If the DNA content of this organism's cells is 13% adenine, approximately what percentage of this organism's genome consists of guanine Explain your answer.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 14 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Provide at least three important differences between DNA and RNA.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 14 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Consider the following sequence of mRNA: 5'-AGCACCAUGCCCCGAACCUCAAAGUGAAA-CAAAAA-3'. How many codons are included in this mRNA How many amino acids are coded for by this sequence Use Table 2.3 to determine the amino acid sequence encoded by this mRNA. Note: Remember that mRNA molecules are actually much larger than the very short sequence shown here.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 14 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Consider the following sequence of DNA: 5'-TTTATGGG TTGGCCCGGGTCATGATT- 3' 3'-AAATCCCAACCGGGCCCAGT ACTAA- 5'
a. Transcribe each of these sequences into mRNA. Which DNA sequence (top or bottom strand) produces a functional mRNA containing a start codon What is the amino acid sequence of the polypeptide produced from this mRNA
b. For the DNA strand producing a functional mRNA, number each base from left to right with the first base numbered "1." Insert a "T" between bases 10 and 11, representing a base insertion mutation. Transcribe an mRNA from this new strand and translate it into a protein. Compare the amino acid sequence of this protein to the one translated in (a). What happened Explain.
a. Transcribe each of these sequences into mRNA. Which DNA sequence (top or bottom strand) produces a functional mRNA containing a start codon What is the amino acid sequence of the polypeptide produced from this mRNA
b. For the DNA strand producing a functional mRNA, number each base from left to right with the first base numbered "1." Insert a "T" between bases 10 and 11, representing a base insertion mutation. Transcribe an mRNA from this new strand and translate it into a protein. Compare the amino acid sequence of this protein to the one translated in (a). What happened Explain.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 14 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Name the three types of RNA involved in protein synthesis and describe the function of each.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 14 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
What is an operon How do bacteria use operons to regulate gene expression

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 14 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
What is gene expression regulation Why is it important Describe examples of ways in which gene expression can be regulated.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 14 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Diagram the process of semiconservative replication of DNA by drawing a replication fork and indicating important enzymes, proteins, and other components involved in this process. Provide a one-sentence description of the function of each component.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 14 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Why do some mutations affect changes in protein structure and function that can result in disease whereas other mutations have no significant effects on protein structure and function

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 14 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
In a nucleotide of DNA, which carbon in the deoxyribose sugar is bonded to the nitrogenous base

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 14 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
What is the epigenome and why are biotechnology and pharmaceutical companies interested in the epigenome

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 14 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



