Deck 12: Us Inflation, Unemployment, and Business Cycle
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/24
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 12: Us Inflation, Unemployment, and Business Cycle
1
Debate on Causes of Joblessness Grows
What is the cause of the high unemployment rate One side says there is not enough government spending. The other says it's a structural problem-people who can't move to take new jobs because they are tied down to burdensome mortgages or firms that can't find workers with the requisite skills to fill job openings. Source: The Wall Street Journal, September 4, 2010 Which business cycle theory would say that most of the unemployment is cyclical Which would say it is an increase in the natural rate Why
What is the cause of the high unemployment rate One side says there is not enough government spending. The other says it's a structural problem-people who can't move to take new jobs because they are tied down to burdensome mortgages or firms that can't find workers with the requisite skills to fill job openings. Source: The Wall Street Journal, September 4, 2010 Which business cycle theory would say that most of the unemployment is cyclical Which would say it is an increase in the natural rate Why
Mainstream Business Cycle Theory and Real Business Cycle Theory are the two major economic growth theories that tend to predict the behavior of real GDP. While the Mainstream Business Cycle Theory assumes potential GDP as growing at a steady rate and a fluctuating real GDP, Real Business Cycle Theory assumes a fluctuating potential GDP.
Accordingly, Real Business Cycle Theory attributes the presence of unemployment as a consequence of structural changes in the economy on the account of technical changes. When a technology of production changes, it either ousts labor with capital or a labor with old skills with labor having new and advance skills compatible with the technology. In this way, potential GDP of the economy can change and with that, the natural rate of unemployment. Hence, unemployment increases due to increase in its natural rate.
In contrast, most of the unemployment is cyclical as explained by the Mainstream Business Cycle Theory. This is so because usually, the unemployment is at its natural rate (NAIRU) when output gap is zero or real and potential GDP are same. But due to business cycle fluctuations, Aggregate Demand is fluctuating, thereby keeping the real GDP floating around its potential. In this way, unemployment increases due to business cycle.
Accordingly, Real Business Cycle Theory attributes the presence of unemployment as a consequence of structural changes in the economy on the account of technical changes. When a technology of production changes, it either ousts labor with capital or a labor with old skills with labor having new and advance skills compatible with the technology. In this way, potential GDP of the economy can change and with that, the natural rate of unemployment. Hence, unemployment increases due to increase in its natural rate.
In contrast, most of the unemployment is cyclical as explained by the Mainstream Business Cycle Theory. This is so because usually, the unemployment is at its natural rate (NAIRU) when output gap is zero or real and potential GDP are same. But due to business cycle fluctuations, Aggregate Demand is fluctuating, thereby keeping the real GDP floating around its potential. In this way, unemployment increases due to business cycle.
2
High Food and Energy Prices Here to Stay
On top of rising energy prices, a severe drought, bad harvests, and a poor monsoon season in Asia have sent grain prices soaring. Globally, this is the third major food price shock in five years. Source: The Telegraph, August 29, 2012 Explain what type of inflation the news clip is describing and provide a graphical analysis of it.
On top of rising energy prices, a severe drought, bad harvests, and a poor monsoon season in Asia have sent grain prices soaring. Globally, this is the third major food price shock in five years. Source: The Telegraph, August 29, 2012 Explain what type of inflation the news clip is describing and provide a graphical analysis of it.
An increase in the overall or general price level in the country over a period of time is known as inflation. Accordingly, there can be an inflation due to demand side factors (demand-pull) or there can be an inflation due to changes in the cost of production (supply-side). Asian countries have seen severe monsoon floods in past few years and there has been a sharp reduction in agricultural production. This has an immediate effect on the prices of staple grains.
It can be expected that the inflation on the account of bad harvest is a supply side inflation, perhaps a cost-push inflation. Although there is no direct increase in the cost of procuring raw material or money wages, a bad harvest implies little production. This causes the Aggregate Supply curve to shift to the left in the short run and there shortage of grains at the current price. This induces the producers to increase the price as competition among the buyers and this bids up the general price level.
It can be expected that the inflation on the account of bad harvest is a supply side inflation, perhaps a cost-push inflation. Although there is no direct increase in the cost of procuring raw material or money wages, a bad harvest implies little production. This causes the Aggregate Supply curve to shift to the left in the short run and there shortage of grains at the current price. This induces the producers to increase the price as competition among the buyers and this bids up the general price level.
3
Some events occur and the economy experiences a demand-pull inflation. What might those events have been Describe their initial effects and explain how a demand-pull inflation spiral results. Use the following figure to work Problem. The economy starts out on the curves labeled AD₀ and SAS₀.
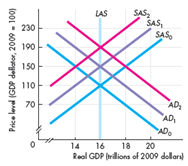

The economy begins with its long run equilibrium position. At this position, the level of real GDP is equal to its full employment potential of 16 trillion. Price level, as measured by an index value, is currently at 110. This situation is the result of intersection of Long run Aggregate Supply curve (LAS), Short Run Aggregate Supply Curve (SAS) and Aggregate Demand Curve (AD).
A Demand-Pull inflation is the result of a positive Aggregate Demand shock (that causes AD to shift rightwards). The likely cause of such increases in the AD include favourable changes in the factors affecting AD. A cut in the tax rate, lowering down of the real interest rate, increase in government spending, trade surplus, or increased investment opportunities on the account of favourable business environment.
For demand-pull inflation to cause a spiral of AD shifts, there needs to be an active monetary policy. The initial phase shifts the AD to the right (perhaps due to a monetary expansion that lowers the interest rate). This causes the real GDP to rise above its potential level at a new level of $16.5 trillion and results in short run inflation (price level rises to 121). This is matched by a long run response by the firms that observe their cost of production rising due to inflation so they produce and supply less. This act shifts the short run Aggregate Supply Curve SAS to the left, increasing the inflation further.
The spiral of AD-AS shifts begins when the Fed starts curbing the price level from increasing by increasing money supply. This event shifts the Aggregate Demand AD to the right once again, and the price index rises once again. Real GDP one again rises above its potential level at a new level of $16.5 trillion and this again results in a short run inflation. If the Fed continues to conduct monetary expansion, this spiral of demand-pull inflation will continue to occur. This results in a persistently rising price level.
A Demand-Pull inflation is the result of a positive Aggregate Demand shock (that causes AD to shift rightwards). The likely cause of such increases in the AD include favourable changes in the factors affecting AD. A cut in the tax rate, lowering down of the real interest rate, increase in government spending, trade surplus, or increased investment opportunities on the account of favourable business environment.
For demand-pull inflation to cause a spiral of AD shifts, there needs to be an active monetary policy. The initial phase shifts the AD to the right (perhaps due to a monetary expansion that lowers the interest rate). This causes the real GDP to rise above its potential level at a new level of $16.5 trillion and results in short run inflation (price level rises to 121). This is matched by a long run response by the firms that observe their cost of production rising due to inflation so they produce and supply less. This act shifts the short run Aggregate Supply Curve SAS to the left, increasing the inflation further.
The spiral of AD-AS shifts begins when the Fed starts curbing the price level from increasing by increasing money supply. This event shifts the Aggregate Demand AD to the right once again, and the price index rises once again. Real GDP one again rises above its potential level at a new level of $16.5 trillion and this again results in a short run inflation. If the Fed continues to conduct monetary expansion, this spiral of demand-pull inflation will continue to occur. This results in a persistently rising price level.
4
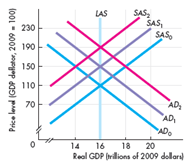
Some events occur and the economy experiences a cost-push inflation. What might those events have been Describe their initial effects and explain how a cost-push inflation spiral develops. Use the following figure to work Problem. The economy starts out on the curves labeled AD₀ and SAS₀.


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 24 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
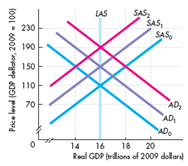
Some events occur and the economy is expected to experience inflation. What might those events have been Describe their initial effects and what happens as an expected inflation proceeds. Use the following figure to work Problem. The economy starts out on the curves labeled AD₀ and SAS₀.


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 24 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Suppose that the velocity of circulation of money is constant and real GDP is growing at 3 percent a year.
a. To achieve an inflation target of 2 percent a year, at what rate would the central bank grow the quantity of money
b. At what growth rate of the quantity of money would deflation be created
a. To achieve an inflation target of 2 percent a year, at what rate would the central bank grow the quantity of money
b. At what growth rate of the quantity of money would deflation be created

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 24 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Eurozone Unemployment Hits Record High As Inflation Rises Unexpectedly Eurozone unemployment rose to 10.7 percent. At the same time, eurozone inflation unexpectedly rose to 2.7 percent a year, up from the previous month's 2.6 percent a year. Source: Huffngton Post, March 1, 2012
a. How does the Phillips curve model account for a very high unemployment rate
b. Explain the change in unemployment and inflation in the eurozone in terms of what is happening to the short-run and long-run Phillips curves.
a. How does the Phillips curve model account for a very high unemployment rate
b. Explain the change in unemployment and inflation in the eurozone in terms of what is happening to the short-run and long-run Phillips curves.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 24 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
From the Fed's Minutes
Members expected real GDP growth to be moderate over coming quarters and then to pick up very gradually, with the unemployment rate declining only slowly. With longer-term inflation expectations stable, members anticipated that inflation over the medium run would be at or below 2 percent a year.
Are FOMC members predicting that the U.S. economy will move rightward or leftward along a short-run Phillips curve or that the short-run Phillips curve will shift up or down through 2012 and 2013
Members expected real GDP growth to be moderate over coming quarters and then to pick up very gradually, with the unemployment rate declining only slowly. With longer-term inflation expectations stable, members anticipated that inflation over the medium run would be at or below 2 percent a year.
Are FOMC members predicting that the U.S. economy will move rightward or leftward along a short-run Phillips curve or that the short-run Phillips curve will shift up or down through 2012 and 2013

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 24 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
The Business Cycle
Use the following information to work Problem.
Suppose that the business cycle in the United States is best described by RBC theory and that a new technology increases productivity.
Draw a graph to show the effect of the new technology in the market for loanable funds.
Use the following information to work Problem.
Suppose that the business cycle in the United States is best described by RBC theory and that a new technology increases productivity.
Draw a graph to show the effect of the new technology in the market for loanable funds.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 24 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
The Business Cycle
Use the following information to work Problem.
Suppose that the business cycle in the United States is best described by RBC theory and that a new technology increases productivity.
Draw a graph to show the effect of the new technology in the labor market.
Use the following information to work Problem.
Suppose that the business cycle in the United States is best described by RBC theory and that a new technology increases productivity.
Draw a graph to show the effect of the new technology in the labor market.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 24 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
The Business Cycle
Use the following information to work Problem.
Suppose that the business cycle in the United States is best described by RBC theory and that a new technology increases productivity.
Explain the when-to-work decision when technology advances.
Use the following information to work Problem.
Suppose that the business cycle in the United States is best described by RBC theory and that a new technology increases productivity.
Explain the when-to-work decision when technology advances.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 24 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
The Business Cycle
The Business Cycle
Real Wages Fail to Match a Rise in Productivity
For most of the last century, wages and productivity-the key measure of the economy's efficiency-have risen together, increasing rapidly through the 1950s and '60s and far more slowly in the 1970s and '80s. But in recent years, the productivity gains have continued while the pay increases have not kept up.
Explain the relationship between wages and productivity in this news clip in terms of real business cycle theory.
The Business Cycle
Real Wages Fail to Match a Rise in Productivity
For most of the last century, wages and productivity-the key measure of the economy's efficiency-have risen together, increasing rapidly through the 1950s and '60s and far more slowly in the 1970s and '80s. But in recent years, the productivity gains have continued while the pay increases have not kept up.
Explain the relationship between wages and productivity in this news clip in terms of real business cycle theory.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 24 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Inflation Cycles
Use the following news clip to work Problem.
Inflation Should Be Feared
The Fed is trying as hard as it can to spur growth, and to create some inflation. But the Fed must be careful. Inflation remains a danger because U.S. debt is skyrocketing, with no visible plan to pay it back. For the moment, foreigners are buying that debt. But they are buying out of fear that their governments are worse. They are short-term investors, waiting out the storm, not long-term investors confident that the United States will pay back its debts. If their fear passes, or they decide some other haven is safer, watch out. Inflation will come with a vengeance. It's not happening yet: Interest rates are low now. But so were mortgage-backed security rates and Greek government debt rates just a few years ago. But if it happens, it will happen with little warning, the Fed will be powerless to stop it, and it will bring stagnation rather than prosperity.
What type of inflation process does John Cochrane warn could happen Explain the role that inflation expectations would play if the outbreak of inflation were to "happen with little warning."
Use the following news clip to work Problem.
Inflation Should Be Feared
The Fed is trying as hard as it can to spur growth, and to create some inflation. But the Fed must be careful. Inflation remains a danger because U.S. debt is skyrocketing, with no visible plan to pay it back. For the moment, foreigners are buying that debt. But they are buying out of fear that their governments are worse. They are short-term investors, waiting out the storm, not long-term investors confident that the United States will pay back its debts. If their fear passes, or they decide some other haven is safer, watch out. Inflation will come with a vengeance. It's not happening yet: Interest rates are low now. But so were mortgage-backed security rates and Greek government debt rates just a few years ago. But if it happens, it will happen with little warning, the Fed will be powerless to stop it, and it will bring stagnation rather than prosperity.
What type of inflation process does John Cochrane warn could happen Explain the role that inflation expectations would play if the outbreak of inflation were to "happen with little warning."

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 24 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Inflation Cycles
Use the following news clip to work Problem.
Inflation Should Be Feared
The Fed is trying as hard as it can to spur growth, and to create some inflation. But the Fed must be careful. Inflation remains a danger because U.S. debt is skyrocketing, with no visible plan to pay it back. For the moment, foreigners are buying that debt. But they are buying out of fear that their governments are worse. They are short-term investors, waiting out the storm, not long-term investors confident that the United States will pay back its debts. If their fear passes, or they decide some other haven is safer, watch out. Inflation will come with a vengeance. It's not happening yet: Interest rates are low now. But so were mortgage-backed security rates and Greek government debt rates just a few years ago. But if it happens, it will happen with little warning, the Fed will be powerless to stop it, and it will bring stagnation rather than prosperity.
Explain why the inflation that John Cochrane fears would "bring stagnation rather than prosperity."
Use the following news clip to work Problem.
Inflation Should Be Feared
The Fed is trying as hard as it can to spur growth, and to create some inflation. But the Fed must be careful. Inflation remains a danger because U.S. debt is skyrocketing, with no visible plan to pay it back. For the moment, foreigners are buying that debt. But they are buying out of fear that their governments are worse. They are short-term investors, waiting out the storm, not long-term investors confident that the United States will pay back its debts. If their fear passes, or they decide some other haven is safer, watch out. Inflation will come with a vengeance. It's not happening yet: Interest rates are low now. But so were mortgage-backed security rates and Greek government debt rates just a few years ago. But if it happens, it will happen with little warning, the Fed will be powerless to stop it, and it will bring stagnation rather than prosperity.
Explain why the inflation that John Cochrane fears would "bring stagnation rather than prosperity."

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 24 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Europe's Deflation Risk
The United States is planning to push Europe toward new and more aggressive efforts to boost aggregate demand given a renewed risk of deflation in the euro zone.
Source: Reuters , September 12, 2014
a. Explain the process by which deflation occurs.
b. How might Europe boost its aggregate demand Might the boost to aggregate demand create demand-pull inflation
The United States is planning to push Europe toward new and more aggressive efforts to boost aggregate demand given a renewed risk of deflation in the euro zone.
Source: Reuters , September 12, 2014
a. Explain the process by which deflation occurs.
b. How might Europe boost its aggregate demand Might the boost to aggregate demand create demand-pull inflation

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 24 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Inflation and Unemployment: The Phillips Curve
Use the following information to work Problem.
An economy has an unemployment rate of 4 percent and an inflation rate of 5 percent a year at point A in the figure.
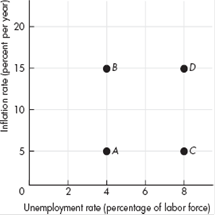
Some events occur that move the economy in a clockwise loop from A to B to D to C and back to A.
Describe the events that could create this sequence. Has the economy experienced demand-pull inflation, cost-push inflation, expected inflation, or none of these
Use the following information to work Problem.
An economy has an unemployment rate of 4 percent and an inflation rate of 5 percent a year at point A in the figure.

Some events occur that move the economy in a clockwise loop from A to B to D to C and back to A.
Describe the events that could create this sequence. Has the economy experienced demand-pull inflation, cost-push inflation, expected inflation, or none of these

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 24 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Inflation and Unemployment: The Phillips Curve
Use the following information to work Problem.
An economy has an unemployment rate of 4 percent and an inflation rate of 5 percent a year at point A in the figure.
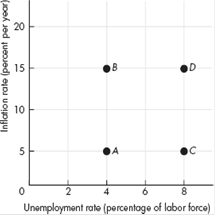
Some events occur that move the economy in a clockwise loop from A to B to D to C and back to A.
Draw in the figure the sequence of the economy's short-run and long-run Phillips curves.
Use the following information to work Problem.
An economy has an unemployment rate of 4 percent and an inflation rate of 5 percent a year at point A in the figure.

Some events occur that move the economy in a clockwise loop from A to B to D to C and back to A.
Draw in the figure the sequence of the economy's short-run and long-run Phillips curves.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 24 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Inflation and Unemployment: The Phillips Curve
Use the following information to work Problem.
The Reserve Bank of New Zealand signed an agreement with the New Zealand government in which the Bank agreed to maintain inflation inside a low target range. Failure to achieve the target would result in the governor of the Bank (the equivalent of the chairman of the Fed) losing his job.
Explain how this arrangement might have influenced New Zealand's short-run Phillips curve.
Use the following information to work Problem.
The Reserve Bank of New Zealand signed an agreement with the New Zealand government in which the Bank agreed to maintain inflation inside a low target range. Failure to achieve the target would result in the governor of the Bank (the equivalent of the chairman of the Fed) losing his job.
Explain how this arrangement might have influenced New Zealand's short-run Phillips curve.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 24 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Inflation and Unemployment: The Phillips Curve
Use the following information to work Problem.
The Reserve Bank of New Zealand signed an agreement with the New Zealand government in which the Bank agreed to maintain inflation inside a low target range. Failure to achieve the target would result in the governor of the Bank (the equivalent of the chairman of the Fed) losing his job.
Explain how this arrangement might have influenced New Zealand's long-run Phillips curve.
Use the following information to work Problem.
The Reserve Bank of New Zealand signed an agreement with the New Zealand government in which the Bank agreed to maintain inflation inside a low target range. Failure to achieve the target would result in the governor of the Bank (the equivalent of the chairman of the Fed) losing his job.
Explain how this arrangement might have influenced New Zealand's long-run Phillips curve.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 24 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Fed Pause Promises Financial Disaster
The indication is that inflationary expectations have become entrenched and strongly rooted in world markets. As a result, the risk of global stagflation has become significant. A drawn-out inflationary process always precedes stagflation. Following the attritional effect of inflation, the economy starts to grow below its potential. It experiences a persistent output gap, rising unemployment, and increasingly entrenched inflationary expectations.
Source: Asia Times Online , May 20, 2008
Evaluate the claim that if "inflationary expectations" become strongly "entrenched" an economy will experience "a persistent output gap."
The indication is that inflationary expectations have become entrenched and strongly rooted in world markets. As a result, the risk of global stagflation has become significant. A drawn-out inflationary process always precedes stagflation. Following the attritional effect of inflation, the economy starts to grow below its potential. It experiences a persistent output gap, rising unemployment, and increasingly entrenched inflationary expectations.
Source: Asia Times Online , May 20, 2008
Evaluate the claim that if "inflationary expectations" become strongly "entrenched" an economy will experience "a persistent output gap."

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 24 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Inflation and Unemployment: The Phillips Curve
Use the following information to work Problem.
Because the Fed doubled the monetary base in 2008 and the government spent billions of dollars bailing out troubled banks, insurance companies, and auto producers, some people are concerned that a serious upturn in the inflation rate will occur, not immediately but in a few years' time. At the same time, massive changes in the global economy might bring the need for structural change in the United States.
Explain how the Fed's doubling of the monetary base and government bailouts might influence the short-run and long-run unemployment-inflation tradeoffs. Will the influence come from changes in the expected inflation rate, the natural unemployment rate, or both
Use the following information to work Problem.
Because the Fed doubled the monetary base in 2008 and the government spent billions of dollars bailing out troubled banks, insurance companies, and auto producers, some people are concerned that a serious upturn in the inflation rate will occur, not immediately but in a few years' time. At the same time, massive changes in the global economy might bring the need for structural change in the United States.
Explain how the Fed's doubling of the monetary base and government bailouts might influence the short-run and long-run unemployment-inflation tradeoffs. Will the influence come from changes in the expected inflation rate, the natural unemployment rate, or both

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 24 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Inflation and Unemployment: The Phillips Curve
Use the following information to work Problem.
Because the Fed doubled the monetary base in 2008 and the government spent billions of dollars bailing out troubled banks, insurance companies, and auto producers, some people are concerned that a serious upturn in the inflation rate will occur, not immediately but in a few years' time. At the same time, massive changes in the global economy might bring the need for structural change in the United States.
Explain how large-scale structural change might influence the short-run and long-run unemployment-inflation tradeoffs. Will the influence come from changes in the expected inflation rate, the natural unemployment rate, or both
Use the following information to work Problem.
Because the Fed doubled the monetary base in 2008 and the government spent billions of dollars bailing out troubled banks, insurance companies, and auto producers, some people are concerned that a serious upturn in the inflation rate will occur, not immediately but in a few years' time. At the same time, massive changes in the global economy might bring the need for structural change in the United States.
Explain how large-scale structural change might influence the short-run and long-run unemployment-inflation tradeoffs. Will the influence come from changes in the expected inflation rate, the natural unemployment rate, or both

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 24 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
After you have studied Economics in the News on pp. 312-313, answer the following questions.
a. What are the macroeconomic problems in the Eurozone economy that the ECB is seeking to address
b. Is the European unemployment problem structural, cyclical, or both and how can we determine its type
c. Explain which type of unemployment the ECB can help with.
d. Use the AS-AD model to show the changes in aggregate demand and/or aggregate supply that created the Eurozone's macroeconomic problems.
e. Use the AS-AD model to show the changes in aggregate demand and/or aggregate supply that the ECB must bring about to achieve its goal.
a. What are the macroeconomic problems in the Eurozone economy that the ECB is seeking to address
b. Is the European unemployment problem structural, cyclical, or both and how can we determine its type
c. Explain which type of unemployment the ECB can help with.
d. Use the AS-AD model to show the changes in aggregate demand and/or aggregate supply that created the Eurozone's macroeconomic problems.
e. Use the AS-AD model to show the changes in aggregate demand and/or aggregate supply that the ECB must bring about to achieve its goal.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 24 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Economics in the News
Germany Leads Slowdown in Eurozone
The pace of German economic growth has weakened "markedly," but the reason is the weaker global prospects. Although German policymakers worry about the country's exposure to a fall in demand for its export goods, evidence is growing that the recovery is broadening with real wage rates rising and unemployment falling, which will lead into stronger consumer spending.
a. How does "exposure to a fall in demand for its export goods" influence Germany's aggregate demand, aggregate supply, unemployment, and inflation
b. Use the AS-AD model to illustrate your answer to part (a).
c. Use the Phillips curve model to illustrate your answer to part (a).
d. What do you think the news clip means by "the recovery is broadening with real wage rates rising and unemployment falling, which will lead into stronger consumer spending"
e. Use the AS-AD model to illustrate your answer to part (d).
f. Use the Phillips curve model to illustrate your answer to part (d).
Germany Leads Slowdown in Eurozone
The pace of German economic growth has weakened "markedly," but the reason is the weaker global prospects. Although German policymakers worry about the country's exposure to a fall in demand for its export goods, evidence is growing that the recovery is broadening with real wage rates rising and unemployment falling, which will lead into stronger consumer spending.
a. How does "exposure to a fall in demand for its export goods" influence Germany's aggregate demand, aggregate supply, unemployment, and inflation
b. Use the AS-AD model to illustrate your answer to part (a).
c. Use the Phillips curve model to illustrate your answer to part (a).
d. What do you think the news clip means by "the recovery is broadening with real wage rates rising and unemployment falling, which will lead into stronger consumer spending"
e. Use the AS-AD model to illustrate your answer to part (d).
f. Use the Phillips curve model to illustrate your answer to part (d).

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 24 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



