Deck 6: The Economics of Interest-Rate Spreads and Yield Curves
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/70
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 6: The Economics of Interest-Rate Spreads and Yield Curves
1
No government agency has ever defaulted on its bonds in the United States.
True
2
The liquidity premium is included in calculations of the yield curve to account for interest rate risk.
True
3
A change in the relative return of a bond affects the bond's risk premium.
True
4
An increase in household wealth increases the risk premium of corporate bonds.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
, a junk bond has a lower risk premium than other bonds.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
A change in the risk of a bond affects the bond's risk premium.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
A CCC bond has higher interest rate risk than a BBB bond.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
A change in the profit opportunities of a company affects the risk premium of that company's bonds.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
The liquidity premium is included in calculations of the yield curve to account for default risk.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Government bonds are more liquid than corporate bonds.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
If a positive liquidity premium is included in the formula for the term structure, a downward sloping yield curve is impossible.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Positive spreads (long term rates - short term rates) indicate a possible future recession.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
An AAA bond has lower default risk than a BBB bond.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
A two-year bond is a perfect substitute for two consecutive one-year bonds.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
A downward sloping yield curve indicates a possible future recession.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
A blue chip bond has greater default risk than a high yield corporate bond.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
An increase in expected inflation has an ambiguous effect on the risk premium of corporate bonds.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
An increase in expected inflation increases the risk premium of corporate bonds.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
The U.S. Federal government has never defaulted on its bonds.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
, a blue chip bond has a lower risk premium than other bonds.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
The yield on a one-year bond is currently 3% and the expected yield for the next three years is also 3%. If the term premium is 0.5, then the yield curve
A) is upward sloping.
B) is flat.
C) is downward sloping.
D) cannot be determined.
A) is upward sloping.
B) is flat.
C) is downward sloping.
D) cannot be determined.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
, a junk bond has a higher yield and higher risk premium than other bonds.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
If a company gets concessions from labor in union negotiations, one would expect a(n) _____ in the risk premia on its bonds due to an increase in
A) increase; default risk.
B) decrease; default risk.
C) increase; liquidity.
D) decrease; liquidity.
A) increase; default risk.
B) decrease; default risk.
C) increase; liquidity.
D) decrease; liquidity.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
If a company gets concessions from labor in union negotiations, one would expect a(n) _____ in the risk premia on its bonds due to a shift in the ____ its bonds.
A) increase; demand for
B) decrease; demand for
C) increase; supply of
D) decrease; supply of
A) increase; demand for
B) decrease; demand for
C) increase; supply of
D) decrease; supply of

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
If a company gets concessions from labor in union negotiations, one would expect a(n) _____ in yields on its bonds due to an increase in
A) increase; default risk.
B) decrease; default risk.
C) increase; liquidity.
D) decrease; liquidity.
A) increase; default risk.
B) decrease; default risk.
C) increase; liquidity.
D) decrease; liquidity.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
The recent increase in U.S. government debt could lead to a(n) _____ in yields due to an increase in
A) increase; default risk.
B) decrease; default risk.
C) increase; liquidity.
D) decrease; liquidity.
A) increase; default risk.
B) decrease; default risk.
C) increase; liquidity.
D) decrease; liquidity.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
, an AAA bond has a lower term premium than other bonds.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Which of the following factors could explain difference in yields on bonds with the same time to maturity?
A) default risk
B) tax considerations
C) liquidity
D) all of the above
A) default risk
B) tax considerations
C) liquidity
D) all of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Municipal bonds tend to have lower yields than other bonds, ceteris paribus, due to
A) higher default risk.
B) higher taxes.
C) higher liquidity.
D) none of the above.
A) higher default risk.
B) higher taxes.
C) higher liquidity.
D) none of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
If S&P upgrades a corporate bond its yield will _____ and its risk premium will
A) rise; rise.
B) rise; fall.
C) fall; rise.
D) fall; fall.
A) rise; rise.
B) rise; fall.
C) fall; rise.
D) fall; fall.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
During crises, flight to quality, investors are driven to sell riskier assets and move to safe ones.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Which of the following factors could explain difference in yields on bonds with the same time to maturity?
A) default risk
B) interest rate risk
C) credit risk
D) all of the above
A) default risk
B) interest rate risk
C) credit risk
D) all of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
If yields on one-year bonds are expected to rise and the liquidity premium is zero, the yield curve will be
A) upward sloping.
B) flat.
C) downward sloping.
D) cannot be determined.
A) upward sloping.
B) flat.
C) downward sloping.
D) cannot be determined.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
You cannot post-dict the changes in rank order between different types of bonds.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
The yield curve plots yield against maturity.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Which of the following factors could explain difference in yields on bonds with the same time to maturity?
A) the risk that the issuer will not make future payments
B) differences in the taxation of the bonds
C) ease of finding buyers and sellers of a bond
D) all of the above
A) the risk that the issuer will not make future payments
B) differences in the taxation of the bonds
C) ease of finding buyers and sellers of a bond
D) all of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
If S&P upgrades a corporate bond the _____ for the bond will shift and its risk premium will
A) demand; rise.
B) demand; fall.
C) supply; rise.
D) supply; fall.
A) demand; rise.
B) demand; fall.
C) supply; rise.
D) supply; fall.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Municipal bonds tend to have lower yields than other bonds, ceteris paribus, due to
A) higher default risk.
B) lower taxes.
C) higher liquidity.
D) none of the above.
A) higher default risk.
B) lower taxes.
C) higher liquidity.
D) none of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
If yields on one-year bonds are expected to fall and the liquidity premium increases with the time to maturity, the yield curve
A) will be upward sloping.
B) will be flat.
C) will be downward sloping.
D) cannot be determined.
A) will be upward sloping.
B) will be flat.
C) will be downward sloping.
D) cannot be determined.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Which of the following factors could explain difference in yields on bonds with the same time to maturity?
A) interest rate risk
B) credit risk
C) liquidity
D) none of the above
A) interest rate risk
B) credit risk
C) liquidity
D) none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
What is the difference between risk and term structure?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
If the government budget deficit rises, explain the impact on the risk premia of corporate bonds.
As the supply of government (risk-free) bonds increases, the yields on those bonds rise, reducing the risk premia for corporate bonds.
As the supply of government (risk-free) bonds increases, the yields on those bonds rise, reducing the risk premia for corporate bonds.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
If the government makes it easier to buy its bonds online, the risk premia for corporate bonds will
A) increase.
B) decrease.
C) stay the same.
D) cannot be determined.
A) increase.
B) decrease.
C) stay the same.
D) cannot be determined.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
The yield on a one-year bond is currently 4% and the expected yield on one-year bonds for the next two years is 5% and 6%. If the liquidity premium is 0.5%, what is the yield on a bond with two years to maturity?
A) 4.5%
B) 5%
C) 5.5%
D) 6%
A) 4.5%
B) 5%
C) 5.5%
D) 6%

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Blue chip bonds tend to have
A) higher yields.
B) higher risk premia.
C) both of the above.
D) neither of the above.
A) higher yields.
B) higher risk premia.
C) both of the above.
D) neither of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
If interest rates on one-year bonds are expected to stay at 3% and the term premium is 1%, what would the yield curve look like?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
Default risk is measured by the
A) term premium.
B) risk premium.
C) credit premium.
D) none of the above.
A) term premium.
B) risk premium.
C) credit premium.
D) none of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
The yield curve indicates a possible future recession if it is
A) upward sloping.
B) flat.
C) downward sloping.
D) none of the above.
A) upward sloping.
B) flat.
C) downward sloping.
D) none of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
If a corporate bond loses its listing on a centralized exchange, explain the effect on the risk premium in terms of the supply and demand for bonds.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
Interest rate risk is measured by the
A) term premium.
B) risk premium.
C) rate of inflation.
D) none of the above.
A) term premium.
B) risk premium.
C) rate of inflation.
D) none of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
Term structure models the yields of bonds with
A) with the same times to maturity.
B) with different times to maturity.
C) both of the above.
D) neither of the above.
A) with the same times to maturity.
B) with different times to maturity.
C) both of the above.
D) neither of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
If Moody's upgrades a corporate bond to AAA, explain the impact on the risk premium.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
Which theory that suggests short and long term bonds are partial substitutes?
A) preferred habitat.
B) the yield curve.
C) substitute preference.
D) none of the above.
A) preferred habitat.
B) the yield curve.
C) substitute preference.
D) none of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
Risk structure models the yields of bonds
A) with the same times to maturity.
B) with different times to maturity.
C) both of the above.
D) neither of the above.
A) with the same times to maturity.
B) with different times to maturity.
C) both of the above.
D) neither of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
Ceteris paribus, an increase in the government budget deficit will cause the risk premia on corporate bonds to
A) increase.
B) decrease.
C) stay the same.
D) cannot be determined.
A) increase.
B) decrease.
C) stay the same.
D) cannot be determined.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
Junk bonds tend to have
A) higher risk premia.
B) higher yields.
C) higher default risk.
D) all of the above.
A) higher risk premia.
B) higher yields.
C) higher default risk.
D) all of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
If a corporate bond becomes traded on an exchange (as opposed to OTC), the demand for the bond shifts to the _____ and its risk premia
A) right; rises.
B) right; falls.
C) left; rises.
D) left; falls.
A) right; rises.
B) right; falls.
C) left; rises.
D) left; falls.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
Ratings from Moody's and S&P measure
A) liquidity risk.
B) interest rate risk.
C) default risk.
D) all of the above.
A) liquidity risk.
B) interest rate risk.
C) default risk.
D) all of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
Structure of interest rates explains why bonds issued by _____ but of _____ sometimes have different yields.
A) the same economic entity, different maturities
B) different economic entities, the same maturities
C) different economic entities, different maturities
D) none of the above.
A) the same economic entity, different maturities
B) different economic entities, the same maturities
C) different economic entities, different maturities
D) none of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
Which theory that suggests that investors typically prefer more liquid, shorter-term bonds?
A) preferred habitat.
B) the yield curve.
C) liquidity preference.
D) none of the above.
A) preferred habitat.
B) the yield curve.
C) liquidity preference.
D) none of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
A strike against United Airlines puts the company's long term solvency in question. Using a graph, show (and explain) the effect on its risk premium.
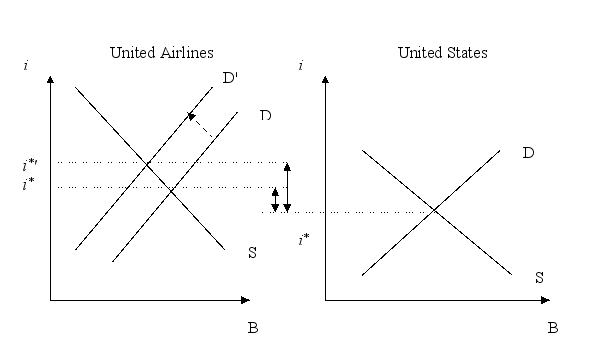


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
If Congress removed the tax exemption for municipal bonds, how would the risk premium on those bonds be affected? Use a graph to help explain.
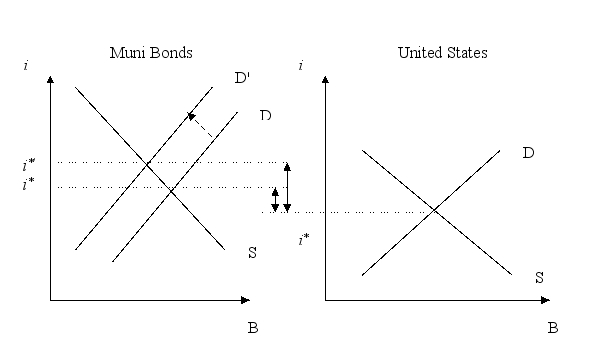


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
Explain the liquidity preference and its impact on the yield curve.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
The current and expected future yields on the one year Treasury bond is 7%. The liquidity premium is 0.5( is the number years to maturity on the bond. Sketch the yield curve covering the next four years. Briefly explain your work.
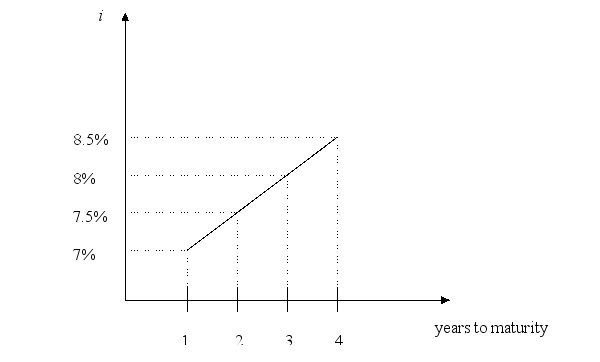


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
Does the information in the table about the yield curve indicate a possible recession?
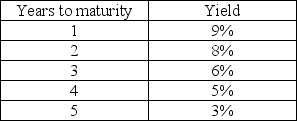


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
The yield on a one-year bond is currently 5% and the liquidity premium is 0.5( is the years to maturity. You are told that the spread between two- and one-year bonds is positive. What does that tell you about the yield on the two-year bond?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
The yield on a one-year bond is currently 6% and the expected yield on one-year bonds for the next three years is 4%, 2% and 1%. If the liquidity premium is 1%, what are the yields on a bond with two, three and four years to maturity?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
The use of auctions should make the cost of issuing bonds cheaper for corporations. Show the expected impact on risk premia for corporate bonds with a graph.
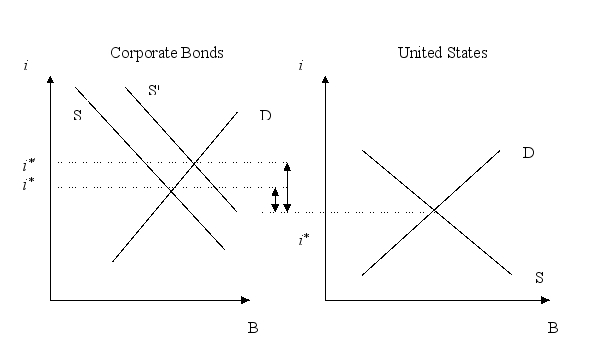


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
Does the information in the table about the yield curve indicate a possible recession?
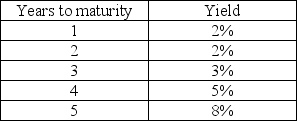


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
Explain the concept of flight to quality.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



