Deck 5: Centre of Mass and Linear Momentum
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/42
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 5: Centre of Mass and Linear Momentum
1
A net force of 100.0 N is applied to a certain object. As a result, the object accelerates with an acceleration of G)What is the mass of the object?
A)7.2 kg
B)10.2 kg
C)14.4 kg
D)20.4 kg
A)7.2 kg
B)10.2 kg
C)14.4 kg
D)20.4 kg
10.2 kg
2
The mass of a human leg below the knee is 0.60 of the mass above the knee, and its centre of mass is located at 0.3 of the length of the lower leg from the knee joint. When the leg is bent from straight to a right angle at the knee, by what amount does the centre of mass of the leg shift? Express your answer in terms of the length of the leg below the knee.
A)0.68
B)0.50
C)0.38
D)0.11
A)0.68
B)0.50
C)0.38
D)0.11
0.11
3
Two cars of equal mass, one travelling north and the other east, collide at the same speed at right angles to each other. Assuming the collision is inelastic, what is the velocity following the collision?
A)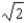 times initial speed, at 45° east of north
times initial speed, at 45° east of north
B)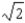 times initial speed, at 45° east of south
times initial speed, at 45° east of south
C)the initial speed, at 45° east of north
D)twice the initial speed, at 45° east of south
A)
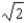 times initial speed, at 45° east of north
times initial speed, at 45° east of northB)
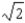 times initial speed, at 45° east of south
times initial speed, at 45° east of southC)the initial speed, at 45° east of north
D)twice the initial speed, at 45° east of south
the initial speed, at 45° east of north
4
There are 15 billiard balls in a rack. The rack is removed. The balls are in triangular formation with the tip toward the cue ball. The cue ball is shot into the ball on the tip of the triangle. Assuming all balls have the same mass, in which direction does the net velocity vector of the set of balls point soon after the cue ball strikes them?
A)opposite to the cue ball's velocity before collision
B)same direction as the cue ball's velocity before collision
C)net velocity vector of the balls in the rack is zero
D)not enough information
A)opposite to the cue ball's velocity before collision
B)same direction as the cue ball's velocity before collision
C)net velocity vector of the balls in the rack is zero
D)not enough information

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 42 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
A source of alpha particles bombards a target of gold. A small fraction of alpha particles return in a direction opposite to that of the ingoing source particles. Which of the following statements accurately describes the cause of this phenomenon?
A)There is electrostatic repulsion between the alpha particles meeting a gold nucleus head-on.
B)The alpha particles are randomly scattered, and some return in the opposite direction.
C)The alpha particles feel the combined electrostatic forces of several gold nuclei acting in the opposite direction.
D)This never happens because the gold atoms are electrically neutral.
A)There is electrostatic repulsion between the alpha particles meeting a gold nucleus head-on.
B)The alpha particles are randomly scattered, and some return in the opposite direction.
C)The alpha particles feel the combined electrostatic forces of several gold nuclei acting in the opposite direction.
D)This never happens because the gold atoms are electrically neutral.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 42 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
A railway boxcar is moving toward a stationary boxcar on a rail with negligible friction. The stationary boxcar is twice the mass of the moving one. On collision, the boxcars couple to each other. After the collision, what is the velocity of the more massive boxcar? Express your answer as a fraction of the velocity of the less massive boxcar before the collision.
A)1/2
B)1/3
C)-1/3
D)-1/2
A)1/2
B)1/3
C)-1/3
D)-1/2

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 42 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
3. A 1 kg ball travels at velocity v = +5 m/s horizontally to the right, hits a vertical wall, and bounces back to the left with velocity v = -5 m/s. What is the impulse exerted on the ball?
A)+10 kg m/s
B)-10 kg m/s
C)+5 kg m/s
D)-5 kg m/s
A)+10 kg m/s
B)-10 kg m/s
C)+5 kg m/s
D)-5 kg m/s

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 42 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Three railway cars of equal mass are on the same (frictionless) track. The one on the left is moving with velocity V toward the other two which are stationary. As the cars undergo successive collisions, they couple and move together. What is the velocity of the final configuration of the three coupled cars?
A)V
B)V/2
C)V/3
D)V/4
A)V
B)V/2
C)V/3
D)V/4

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 42 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Assuming a classical picture of the atom, an electron is captured into a circular orbit about a spherically shaped, singly charged ion, thus neutralizing it. In the frame of reference of the ion, the neutral atom acquires a component of velocity that is
A)in the opposite direction to that of the incoming electron.
B)equal to zero.
C)in the same direction as that of the incoming electron.
D)unpredictable because insufficient information has been given.
A)in the opposite direction to that of the incoming electron.
B)equal to zero.
C)in the same direction as that of the incoming electron.
D)unpredictable because insufficient information has been given.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 42 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
A fireman is sliding down a fire pole. As he speeds up, he tightens his grip on the pole, thus increasing the vertical frictional force that the pole exerts on the fireman. When this force equals the weight of the fireman, which of the following happens?
A)The fireman comes to a stop.
B)The fireman descends at slower and slower speed.
C)The fireman descends with a smaller acceleration.
D)The fireman continues to descend, but at a constant speed.
A)The fireman comes to a stop.
B)The fireman descends at slower and slower speed.
C)The fireman descends with a smaller acceleration.
D)The fireman continues to descend, but at a constant speed.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 42 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
An object is moving with constant velocity. Which of these statements accurately describes this?
A)There is a constant force being applied to the object in the direction of its motion.
B)The net force on the object is zero.
C)There are no forces acting on the object.
D)There is no frictional force on the object.
A)There is a constant force being applied to the object in the direction of its motion.
B)The net force on the object is zero.
C)There are no forces acting on the object.
D)There is no frictional force on the object.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 42 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
A squid ejects a bolus of water in order to escape a predator. The squid has a mass of 0.4 kg with its water cavity empty, and needs to escape with a speed of at least 0.8 m/s. If the ejected water has a mass of 0.1 kg, how fast must it be ejected in order for the squid to escape?
A)4.0 m/s
B)3.2 m/s
C)1.6 m/s
D)0.8 m/s
A)4.0 m/s
B)3.2 m/s
C)1.6 m/s
D)0.8 m/s

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 42 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
A car of mass m travelling at 40.0 km/hr collides head-on with a stationary car of equal mass, and stays attached until the pair come to a stop. The car in motion does NOT apply the brakes, whereas the stationary car has a braking force of 0.2mg. At what distance from the collision site does the pair of cars come to rest?
A)4.0 m
B)7.9 m
C)11 m
D)16 m
A)4.0 m
B)7.9 m
C)11 m
D)16 m

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 42 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
You are falling from your tree house. Which of these actions could slow the fall? Ignore the effects of air resistance.
A)You can rotate and slow linear motion by increasing rotational motion.
B)You can stretch your body abruptly upward to change the motion of the centre of the mass.
C)You can stretch your body abruptly sideways to change the motion of centre of the mass.
D)No internal forces can change the motion of the centre of the mass.
A)You can rotate and slow linear motion by increasing rotational motion.
B)You can stretch your body abruptly upward to change the motion of the centre of the mass.
C)You can stretch your body abruptly sideways to change the motion of centre of the mass.
D)No internal forces can change the motion of the centre of the mass.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 42 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
A ball rolls in a straight line without friction across the horizontal floor of a descending elevator. As the elevator comes to a stop, which of the following happens to the ball?
A)It accelerates.
B)It decelerates.
C)It comes to a stop.
D)It continues its horizontal motion unchanged.
A)It accelerates.
B)It decelerates.
C)It comes to a stop.
D)It continues its horizontal motion unchanged.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 42 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
A spaceship and docking module travelling in parallel come alongside each other at the same speed. The module fires a small rocket at a right angle to its motion to bring the module into contact with the spaceship for docking. On docking, which one of these effects does this have on the motion of the combined craft?
A)none
B)Their speed decreases.
C)They acquire a small component of velocity perpendicular to the original motion.
D)They continue with increased velocity in the same direction.
A)none
B)Their speed decreases.
C)They acquire a small component of velocity perpendicular to the original motion.
D)They continue with increased velocity in the same direction.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 42 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
A 1000 kg car moving at 20 km/hr collides inelastically and head-on with a 10000 kg truck moving at 2 km/hr. Which one of these statements correctly describes the motion of the two vehicles after the collision?
A)The car and truck continue moving in the original direction of the truck.
B)The car and truck continue moving in the original direction of the car.
C)The car and truck stop moving.
D)The car and truck separate and move in opposite directions.
A)The car and truck continue moving in the original direction of the truck.
B)The car and truck continue moving in the original direction of the car.
C)The car and truck stop moving.
D)The car and truck separate and move in opposite directions.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 42 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
A fish swimming with speed of 1.00 m/s is chasing its prey of 0.100 of its mass. It captures its prey when their relative velocity is 0.10 m/s. If the fish were to capture its prey when their relative velocity was 0.20 m/s, what would be the velocity of the fish in the second case relative to the first case?
A)0.90
B)0.99
C)1.09
D)1.11
A)0.90
B)0.99
C)1.09
D)1.11

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 42 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
The thigh has a mass of 21.5 units, and its centre of mass is 9.6 units from the hip joint. The corresponding mass and length units for the knee are 9.6, 33.9; and for the ankle, 3.4, 50.3. Where is the centre of mass of the outstretched leg located relative to the hip bone?
A)38.2 units
B)20.4 units
C)17.1 units
D)15.2 units
A)38.2 units
B)20.4 units
C)17.1 units
D)15.2 units

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 42 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
A pair of railway boxcars are moving toward each other on a rail with negligible friction. One boxcar is twice the mass of the other. On collision, the boxcars couple to each other. In order for the coupled pair to have zero velocity (relative to a bystander next to the track) after the collision, what is the ratio of velocities of the more massive to the less massive boxcar before the collision?
A)1/2
B)1/3
C)-1/3
D)-1/2
A)1/2
B)1/3
C)-1/3
D)-1/2

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 42 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
An object moving at constant speed does not have force acting on it.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 42 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
If the gravitational forces of bodies outside the solar system were neglected, the Sun would move at a constant velocity.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 42 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
An astronaut in a space capsule is experiencing "weightlessness"; therefore, he does not have to exert any force in order to throw a ball, which is also weightless.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 42 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Two balls of equal mass are thrown toward each other with the same speed and at the same angle to the horizontal by two people standing a certain distance apart on the ground. Following an elastic collision, the balls will always return to their respective throwers with the same speed.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 42 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
When firing a rifle, you experience a force against your shoulder. Explain why.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 42 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
One to simulate gravity in a spaceship is to set the spaceship into rotation at constant angular velocity. Describe what shape the spaceship would have in order for this to work.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 42 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
When you catch a ball, you feel a force against your hand. Explain why.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 42 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
The metal head of a hammer is loose. In order to get the hammerhead tight again, you should drop the hammer with the head end down.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 42 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
A person inside an elevator throws a ball horizontally through the air. Describe under what conditions the ball would travel in a straight line.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 42 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
A ball rolling across the centre line of a long level table collides with a second ball of equal mass also on the centre line. Both balls fall off the edge of the table at the same instant of time.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 42 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
A standard man (m = 70 kg) is holding a 300 g marble in his hand. The values for the masses of the hand, forearm, and upper arm, expressed as the percentage of full body mass, are as follow: hand 0.65%, forearm 1.87%, and upper arm 3.25%. Each segment's weight acts as if the mass is concentrated in the centre of mass of a segment. The points at which the weight of each segment is acting are shown in Fig. 5.1. Calculate the centre of mass of the arm. 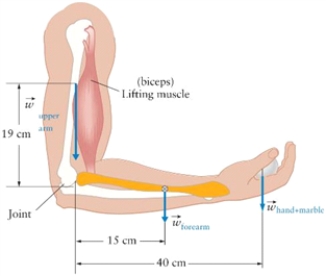


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 42 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Impulse is a vector.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 42 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
For a single rigid body, its centre of mass always lies inside the body.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 42 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
A snowball moving with a certain velocity in interstellar space evaporates molecules from its surface at an equal rate in all directions. The velocity of the snowball remains constant throughout the evaporation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 42 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Interplanetary spaceships can be sent to distant parts of the solar system by means of the "gravitational slingshot" method. The spaceship makes a brief close encounter with a massive planet and is flung away in a different direction of travel. Assuming the approach and post-encounter directions of the spaceship, as seen from the planet, are opposite to each other, describe how the spaceship may increase its overall velocity relative to the Sun.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 42 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Explain whether someone inside a closed box on the ground would be able to tell the difference from being in a spaceship accelerating at g perpendicular to the ground.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 42 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
In order for a rigid body suspended by a pivot to be in rotational equilibrium, its point of suspension must be vertically above its centre of gravity.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 42 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
An astronaut in a space capsule is experiencing "weightlessness." Does the astronaut have to exert any effort to throw a bowling ball, since the bowling ball is also weightless?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 42 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Discuss the advantages to passenger safety if a car undergoes an inelastic collision with another car compared to an elastic collision.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 42 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Find the centre of mass of a water molecule. Angles and distances are shown in Fig. 5.2. The mass of a hydrogen atom is 1.0 u, and the mass of an oxygen atom is 16 u, where u is the atomic mass unit. Choose an appropriate coordinate system. 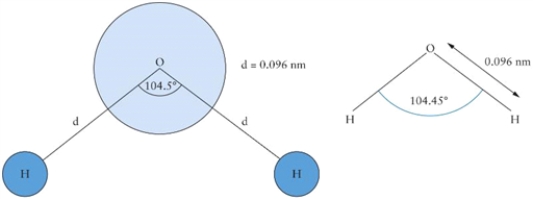


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 42 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
Describe the mechanical principle of why air bags are used in cars.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 42 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Explain why Newton's second law is expressed in terms of momentum rather than "mass times acceleration." Give an example of where this difference matters.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 42 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



