Deck 4: Newtons Laws
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/47
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 4: Newtons Laws
1
You jump off an airplane and fall freely for a while (before you open a parachute). Which of these statements describes what is happening in this situation?
A)There is always a net force acting on the body.
B)After a while, drag force in the air balances your weight and you fall with no net force acting on you.
C)Air resistance is always directed in the direction of your velocity.
D)You are continuously falling with accelerated motion.
A)There is always a net force acting on the body.
B)After a while, drag force in the air balances your weight and you fall with no net force acting on you.
C)Air resistance is always directed in the direction of your velocity.
D)You are continuously falling with accelerated motion.
After a while, drag force in the air balances your weight and you fall with no net force acting on you.
2
Figure 4.1

When a scale is pulled by two identical forces, 10 N each, as in Fig. 4.1, what will the scale read?
A)0 N
B)10 N
C)20 N
D)40 N

When a scale is pulled by two identical forces, 10 N each, as in Fig. 4.1, what will the scale read?
A)0 N
B)10 N
C)20 N
D)40 N
10 N
3
A seal is sunbathing on an inclined rock, and NOT slipping. Which one of these statements correctly describes the normal force?
A)The normal force is larger than the weight of the seal.
B)The normal force depends on a coefficient of friction.
C)The normal force is equal to the static friction force.
D)The normal force is smaller than the weight of the seal.
A)The normal force is larger than the weight of the seal.
B)The normal force depends on a coefficient of friction.
C)The normal force is equal to the static friction force.
D)The normal force is smaller than the weight of the seal.
The normal force is smaller than the weight of the seal.
4
Two flying squirrels of roughly the same size but with different masses, m1 = 110 g and m2 = 180 g, fly from a high tree. What is the ratio of terminal velocities v1 and v2 for the two squirrels?
A)v1 = 0.78v2
B)v2 = 0.78v1
C)v1 = 0.61v2
D)v2 = 0.61v1
A)v1 = 0.78v2
B)v2 = 0.78v1
C)v1 = 0.61v2
D)v2 = 0.61v1

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 47 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
A child holds a ball in her hand. Which of these forces is opposite but equal in magnitude to the weight of the ball?
A)the force of Earth on the ball
B)the force of her hand on the ball
C)the force of the ball on her hand
D)the force of the ball on Earth
A)the force of Earth on the ball
B)the force of her hand on the ball
C)the force of the ball on her hand
D)the force of the ball on Earth

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 47 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
The coefficient of static friction between a seal and a steep rock is 0.8. What is the steepest incline angle of a rock that the seal can lie on without slipping?
A)37°
B)39°
C)52°
D)We do not know the mass of the seal, so we cannot calculate the angle.
A)37°
B)39°
C)52°
D)We do not know the mass of the seal, so we cannot calculate the angle.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 47 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Figure 4.3 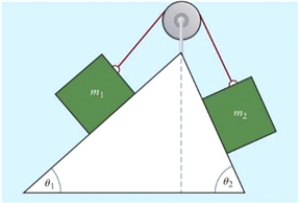 The figure shows two objects of masses m1 and m2, placed on two inclined surfaces of different angles è1 and è2. The connection between masses is a taut, massless string running over a massless and frictionless pulley.
The figure shows two objects of masses m1 and m2, placed on two inclined surfaces of different angles è1 and è2. The connection between masses is a taut, massless string running over a massless and frictionless pulley.
In Fig. 4.3, the two masses are the same (m1 = m2 = 10 kg); the incline angles are è1 = 30° and è2 = 50°. What are the magnitude and direction of the acceleration of the system, and the tension in the string, if both inclined surfaces are frictionless?
A)1.3 m/s2, 62 N
B)2.6 m/s2, 75 N
C)6.2 m/s2, 13 N
D)6.2 m/s2, 111 N
 The figure shows two objects of masses m1 and m2, placed on two inclined surfaces of different angles è1 and è2. The connection between masses is a taut, massless string running over a massless and frictionless pulley.
The figure shows two objects of masses m1 and m2, placed on two inclined surfaces of different angles è1 and è2. The connection between masses is a taut, massless string running over a massless and frictionless pulley.In Fig. 4.3, the two masses are the same (m1 = m2 = 10 kg); the incline angles are è1 = 30° and è2 = 50°. What are the magnitude and direction of the acceleration of the system, and the tension in the string, if both inclined surfaces are frictionless?
A)1.3 m/s2, 62 N
B)2.6 m/s2, 75 N
C)6.2 m/s2, 13 N
D)6.2 m/s2, 111 N

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 47 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
You charge a balloon by rubbing it on your hair and it sticks to the ceiling by electrostatic force. Which of these four free body diagrams describes all the forces acting on the balloon? The forces are labelled as follow: 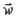 is the weight of the balloon,
is the weight of the balloon, 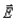 is electrostatic force, and
is electrostatic force, and 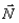 is a normal force.
is a normal force. 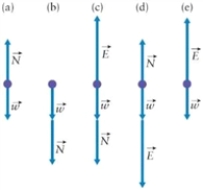
A)choice a
B)choice b
C)choice c
D)choice d
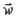 is the weight of the balloon,
is the weight of the balloon, 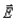 is electrostatic force, and
is electrostatic force, and 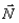 is a normal force.
is a normal force. 
A)choice a
B)choice b
C)choice c
D)choice d

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 47 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Figure 4.2 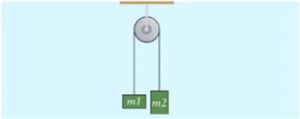 Two crates connected by a string passed through a pulley.
Two crates connected by a string passed through a pulley.
Two weights, one with mass 2 kg and the other with mass 4 kg, are attached to the ends of a massless string that hangs over an ideal pulley. The system is allowed to move freely. What is the value of acceleration of the system?
A)3.3 m/s2
B)9.8 m/s2
C)19.6 m/s2
D)29.0 m/s2
 Two crates connected by a string passed through a pulley.
Two crates connected by a string passed through a pulley.Two weights, one with mass 2 kg and the other with mass 4 kg, are attached to the ends of a massless string that hangs over an ideal pulley. The system is allowed to move freely. What is the value of acceleration of the system?
A)3.3 m/s2
B)9.8 m/s2
C)19.6 m/s2
D)29.0 m/s2

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 47 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Figure 4.3  The figure shows two objects of masses m1 and m2, placed on two inclined surfaces of different angles è1 and è2. The connection between masses is a taut, massless string running over a massless and frictionless pulley.
The figure shows two objects of masses m1 and m2, placed on two inclined surfaces of different angles è1 and è2. The connection between masses is a taut, massless string running over a massless and frictionless pulley.
In Fig. 4.3, masses are m1= 10 kg and m2 = 15 kg; incline angle is è1 = 30°. What is the value of è2 if the system is NOT moving?
A)71°
B)49°
C)41°
D)20°
 The figure shows two objects of masses m1 and m2, placed on two inclined surfaces of different angles è1 and è2. The connection between masses is a taut, massless string running over a massless and frictionless pulley.
The figure shows two objects of masses m1 and m2, placed on two inclined surfaces of different angles è1 and è2. The connection between masses is a taut, massless string running over a massless and frictionless pulley.In Fig. 4.3, masses are m1= 10 kg and m2 = 15 kg; incline angle is è1 = 30°. What is the value of è2 if the system is NOT moving?
A)71°
B)49°
C)41°
D)20°

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 47 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
You are moving in an elevator with constant speed, on the way up. Which of these statements correctly describes the normal force exerted by the floor of the elevator on you?
A)It is equal to your weight when you are off the elevator.
B)It is greater than your weight when you are off the elevator.
C)It is less than your weight when you are off the elevator.
D)It is equal to your mass when you are off the elevator.
A)It is equal to your weight when you are off the elevator.
B)It is greater than your weight when you are off the elevator.
C)It is less than your weight when you are off the elevator.
D)It is equal to your mass when you are off the elevator.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 47 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Figure 4.3  The figure shows two objects of masses m1 and m2, placed on two inclined surfaces of different angles è1 and è2. The connection between masses is a taut, massless string running over a massless and frictionless pulley.
The figure shows two objects of masses m1 and m2, placed on two inclined surfaces of different angles è1 and è2. The connection between masses is a taut, massless string running over a massless and frictionless pulley.
In Fig. 4.3, mass m1= 5 kg and incline angles are è1 = 30° and è2 = 50°. Both inclines are smooth frictionless surfaces. What is the value of m2 if the system is NOT moving?
A)7.7 kg
B)6.7 kg
C)3.7 kg
D)3.3 kg
 The figure shows two objects of masses m1 and m2, placed on two inclined surfaces of different angles è1 and è2. The connection between masses is a taut, massless string running over a massless and frictionless pulley.
The figure shows two objects of masses m1 and m2, placed on two inclined surfaces of different angles è1 and è2. The connection between masses is a taut, massless string running over a massless and frictionless pulley.In Fig. 4.3, mass m1= 5 kg and incline angles are è1 = 30° and è2 = 50°. Both inclines are smooth frictionless surfaces. What is the value of m2 if the system is NOT moving?
A)7.7 kg
B)6.7 kg
C)3.7 kg
D)3.3 kg

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 47 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
A sled is gliding down an incline with angleè. In the absence of friction, what component of the weight is driving the sled downward?
A)total mg
B)mgsinè
C)mgcosè
D)mgtanè
A)total mg
B)mgsinè
C)mgcosè
D)mgtanè

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 47 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Figure 4.4 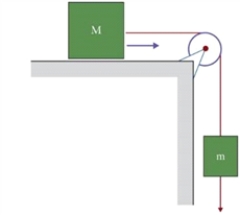 The figure shows two bodies of masses M and m, M placed on a horizontal surface and m hanging at the side, connected by a light cord over a massless and frictionless pulley.
The figure shows two bodies of masses M and m, M placed on a horizontal surface and m hanging at the side, connected by a light cord over a massless and frictionless pulley.
In Fig. 4.4, the masses are M = 3 kg and m = 5 kg. What is the minimum coefficient of static friction between the horizontal surface and M such that the system is NOT moving?
A)0.5
B)0.6
C)0.7
D)1.7
 The figure shows two bodies of masses M and m, M placed on a horizontal surface and m hanging at the side, connected by a light cord over a massless and frictionless pulley.
The figure shows two bodies of masses M and m, M placed on a horizontal surface and m hanging at the side, connected by a light cord over a massless and frictionless pulley.In Fig. 4.4, the masses are M = 3 kg and m = 5 kg. What is the minimum coefficient of static friction between the horizontal surface and M such that the system is NOT moving?
A)0.5
B)0.6
C)0.7
D)1.7

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 47 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
You exercise with a 5.0 kg dumbbell. You need to accelerate it downward with an acceleration of 3.0 m/s2. What are the magnitude and the direction of the force you need to push with?
A)15 N upward
B)15 N downward
C)24 N upward
D)49 N downward
A)15 N upward
B)15 N downward
C)24 N upward
D)49 N downward

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 47 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
A truck has a crate in its cargo bed. If the truck accelerates forward and the crate does NOT move, in which of these directions is the frictional force that the floor of the cargo bed exerts on the crate?
A)downward
B)forward
C)backward
D)There is no friction force because the crate is not moving with respect to the floor of the cargo bed.
A)downward
B)forward
C)backward
D)There is no friction force because the crate is not moving with respect to the floor of the cargo bed.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 47 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
If an object is falling freely, what is the gravitational force equal to?
A)the object's weight
B)weight - mass × acceleration
C)weight + mass × acceleration
D)zero
A)the object's weight
B)weight - mass × acceleration
C)weight + mass × acceleration
D)zero

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 47 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Figure 4.4  The figure shows two bodies of masses M and m, M placed on a horizontal surface and m hanging at the side, connected by a light cord over a massless and frictionless pulley.
The figure shows two bodies of masses M and m, M placed on a horizontal surface and m hanging at the side, connected by a light cord over a massless and frictionless pulley.
In Fig. 4.4, the masses are M = 10 kg and m = 20 kg. The coefficient of friction for the horizontal surface is ì = 0.4. What are the acceleration of the system and the tension in the string?
A)5.2 m/s2, 92 N
B)5.2 m/s2, 39 N
C)7.9 m/s2, 92 N
D)7.9 m/s2, 39 N
 The figure shows two bodies of masses M and m, M placed on a horizontal surface and m hanging at the side, connected by a light cord over a massless and frictionless pulley.
The figure shows two bodies of masses M and m, M placed on a horizontal surface and m hanging at the side, connected by a light cord over a massless and frictionless pulley.In Fig. 4.4, the masses are M = 10 kg and m = 20 kg. The coefficient of friction for the horizontal surface is ì = 0.4. What are the acceleration of the system and the tension in the string?
A)5.2 m/s2, 92 N
B)5.2 m/s2, 39 N
C)7.9 m/s2, 92 N
D)7.9 m/s2, 39 N

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 47 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Which of the following statements include all the essential elements of Newton's first law?
A)A body persists in its state of uniform motion in a straight line as long as the net external force remains constant.
B)A body persists in its state of rest as long as the net external force remains constant.
C)A body at rest persists in its state of rest unless acted on by a non-zero net external force.
D)A body persists in its state of rest or uniform motion in a straight line unless acted on by a non-zero net external force.
A)A body persists in its state of uniform motion in a straight line as long as the net external force remains constant.
B)A body persists in its state of rest as long as the net external force remains constant.
C)A body at rest persists in its state of rest unless acted on by a non-zero net external force.
D)A body persists in its state of rest or uniform motion in a straight line unless acted on by a non-zero net external force.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 47 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
A student in an elevator is checking Newton's laws using a scale. The scale is showing a reading lower than the student's actual weight. Which one of these statements explains this phenomenon?
A)The elevator moves upward with constant speed.
B)The elevator moves downward with constant speed.
C)The elevator moves upward with decreasing speed.
D)The elevator moves downward with decreasing speed.
A)The elevator moves upward with constant speed.
B)The elevator moves downward with constant speed.
C)The elevator moves upward with decreasing speed.
D)The elevator moves downward with decreasing speed.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 47 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Which one of these forces produces centripetal acceleration of a car on a flat circular track?
A)static friction
B)kinetic friction
C)normal force
D)centrifugal force
A)static friction
B)kinetic friction
C)normal force
D)centrifugal force

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 47 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Terminal velocity is the velocity with which a body falls through the air when the drag force equals all other forces acting on that body.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 47 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
If you are riding on a bus and the bus stops abruptly, you feel a tendency to go forward. There is a force that occurs at that moment pushing you forward.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 47 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
If you are riding on a bus and the bus stops abruptly, you feel a tendency to go forward. Is there a force that occurs at that moment pushing you forward? Describe the concept.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 47 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
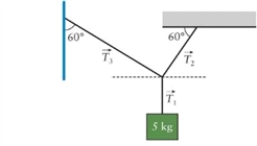
25
Figure 4.5 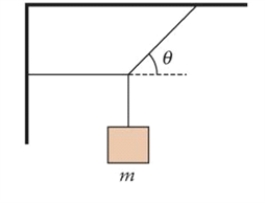 The figure shows a body hanging by two identical light cords.
The figure shows a body hanging by two identical light cords.
In Fig. 4.5, an alpinist with mass M = 80 kg is hanging between a wall and the ceiling of a cave. If angle è = 30°, is the rope, which was manufactured to withstand tension T = 2000 N, sufficiently strong to hold the alpinist?
 The figure shows a body hanging by two identical light cords.
The figure shows a body hanging by two identical light cords.In Fig. 4.5, an alpinist with mass M = 80 kg is hanging between a wall and the ceiling of a cave. If angle è = 30°, is the rope, which was manufactured to withstand tension T = 2000 N, sufficiently strong to hold the alpinist?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 47 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
You push a desk with force 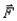 and the desk does not move. Force
and the desk does not move. Force 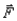 is one force in a pair of interaction forces. The other force is the friction force the floor exerts on you.
is one force in a pair of interaction forces. The other force is the friction force the floor exerts on you.
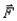 and the desk does not move. Force
and the desk does not move. Force 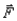 is one force in a pair of interaction forces. The other force is the friction force the floor exerts on you.
is one force in a pair of interaction forces. The other force is the friction force the floor exerts on you.
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 47 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
A squid moves through the water by means of ejecting a water jet. Explain, according to Newton's third law, the relationship between the direction of the water jet and the direction of the squid's motion.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 47 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Although a body is moving, net force acting on it can be zero.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 47 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
A truck has a crate in its cargo bed. If the truck stops abruptly and the crate does not move, the direction of the frictional force that the floor of the cargo bed exerts on the crate is backward.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 47 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
The utricular macula in the inner ear detects angular acceleration of human head.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 47 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
What are the similarity and the difference between static and dynamic equilibrium?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 47 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
A student in an elevator is checking Newton's laws using a scale. The elevator moves downward with decreasing speed. The scale is showing a reading larger than the student's actual weight.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 47 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
A student in an elevator is checking Newton's laws using a scale. The scale is showing a reading larger than the student's actual weight. Which one of these statements explains this phenomenon?
A)The elevator moves upward with constant speed.
B)The elevator moves downward with increasing speed.
C)The elevator moves upward with decreasing speed.
D)The elevator moves downward with decreasing speed.
A)The elevator moves upward with constant speed.
B)The elevator moves downward with increasing speed.
C)The elevator moves upward with decreasing speed.
D)The elevator moves downward with decreasing speed.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 47 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Figure 4.6
The figure shows a hanging body. The chords are massless.
In Fig. 4.6, an alpinist with mass M = 80 kg is hanging between a wall and the ceiling of a cave. If the rope is manufactured to withstand tension T = 500 N, is it sufficiently strong to hold the alpinist?

The figure shows a hanging body. The chords are massless.
In Fig. 4.6, an alpinist with mass M = 80 kg is hanging between a wall and the ceiling of a cave. If the rope is manufactured to withstand tension T = 500 N, is it sufficiently strong to hold the alpinist?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 47 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
The force of friction is parallel to the surface along which the body moves and opposite to the direction of motion.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 47 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
If an object is at rest, its velocity has to be zero.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 47 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Figure 4.7 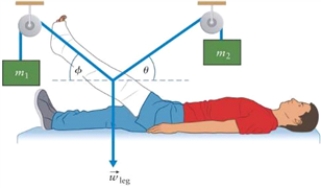
The leg and cast in Fig. 4.7 have mass mleg = 30 kg. Determine the mass of object m2 and the angleè for the system in balance. Mass m1 = 10 kg and ö = 30°.

The leg and cast in Fig. 4.7 have mass mleg = 30 kg. Determine the mass of object m2 and the angleè for the system in balance. Mass m1 = 10 kg and ö = 30°.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 47 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
The incline angle of a banked road is selected on the basis of an estimate of maximum mass of a vehicle that would be driven on the road.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 47 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
If a car stays parked on an inclined street without slipping, its total weight is balanced by the static friction force between the tires and the street.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 47 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Mass is a measure of inertia of a body.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 47 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
Figure 4.9 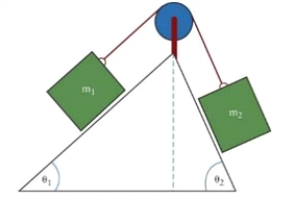 The figure shows two objects of masses m1 and m2 placed on two inclined surfaces of different angles, è1 and è2. The connection between the masses is a taut, massless string running over a massless and frictionless pulley.
The figure shows two objects of masses m1 and m2 placed on two inclined surfaces of different angles, è1 and è2. The connection between the masses is a taut, massless string running over a massless and frictionless pulley.
In Fig. 4.9, the masses are m1= 10 kg and m2 = 20 kg, and the incline angles are è1 = 30° and è2 = 50°. What are the magnitude and the direction of acceleration of the system and the tension in the string if the coefficient of friction for the surface under m1 is ì1 = 0.30 and under m2 it is ì2 = 0.40.
 The figure shows two objects of masses m1 and m2 placed on two inclined surfaces of different angles, è1 and è2. The connection between the masses is a taut, massless string running over a massless and frictionless pulley.
The figure shows two objects of masses m1 and m2 placed on two inclined surfaces of different angles, è1 and è2. The connection between the masses is a taut, massless string running over a massless and frictionless pulley.In Fig. 4.9, the masses are m1= 10 kg and m2 = 20 kg, and the incline angles are è1 = 30° and è2 = 50°. What are the magnitude and the direction of acceleration of the system and the tension in the string if the coefficient of friction for the surface under m1 is ì1 = 0.30 and under m2 it is ì2 = 0.40.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 47 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Figure 4.10 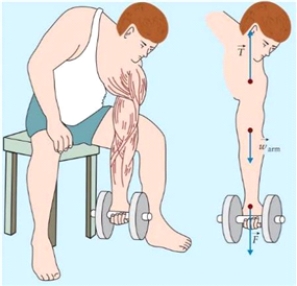 The figure shows a standard man working on concentration curls. A standard man is defined having body mass 70.0 kg, and mass of each arm 6.5% of the total body mass.
The figure shows a standard man working on concentration curls. A standard man is defined having body mass 70.0 kg, and mass of each arm 6.5% of the total body mass.
The standard man from Fig. 4.10 intends to exercise with a 4.0 kg dumbbell. When he is holding the weight vertically down, what are the magnitudes of tension in the shoulder and of the downward force pulling the fist?
 The figure shows a standard man working on concentration curls. A standard man is defined having body mass 70.0 kg, and mass of each arm 6.5% of the total body mass.
The figure shows a standard man working on concentration curls. A standard man is defined having body mass 70.0 kg, and mass of each arm 6.5% of the total body mass.The standard man from Fig. 4.10 intends to exercise with a 4.0 kg dumbbell. When he is holding the weight vertically down, what are the magnitudes of tension in the shoulder and of the downward force pulling the fist?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 47 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
Figure 4.11 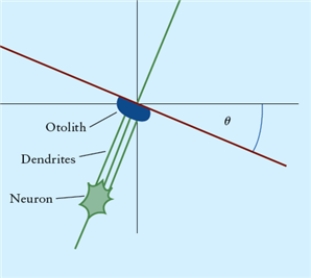
Fig. 4.11 illustrates an otolith near the membrane surface of the utricular macula, with the head tilted sideways by angle è. Dendrites near the otolith illustrate the geometry of the otolith-membrane-dendrite interaction. Sketch the free body diagram with three forces acting on it: its weight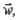 the normal force
the normal force 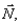 and a force parallel to the surface layer of the otolithic membrane
and a force parallel to the surface layer of the otolithic membrane 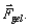 Give the reasoning behind your choice of any coordinate system chosen.
Give the reasoning behind your choice of any coordinate system chosen. 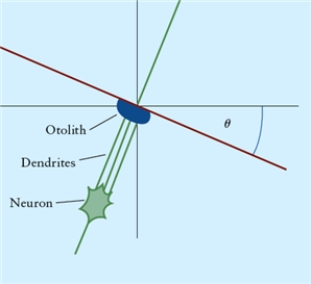

Fig. 4.11 illustrates an otolith near the membrane surface of the utricular macula, with the head tilted sideways by angle è. Dendrites near the otolith illustrate the geometry of the otolith-membrane-dendrite interaction. Sketch the free body diagram with three forces acting on it: its weight
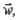 the normal force
the normal force 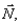 and a force parallel to the surface layer of the otolithic membrane
and a force parallel to the surface layer of the otolithic membrane 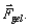 Give the reasoning behind your choice of any coordinate system chosen.
Give the reasoning behind your choice of any coordinate system chosen. 

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 47 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
A car goes around a banked curve of radius 1.2 km at a constant speed of 95 km/h. If no friction is required, at what angle should the curved portion be banked?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 47 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Figure 4.8 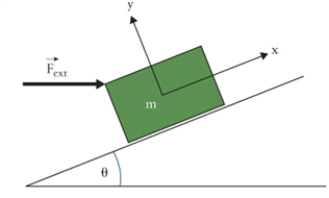 The figure shows an object on an inclined surface.
The figure shows an object on an inclined surface.
In Fig. 4.8, the object has a mass M = 5.0 kg, and the incline angle is è = 40°. What is the minimum force needed to prevent the body from sliding down if the coefficient of static friction between an object and the incline surface ì = 0.3?
 The figure shows an object on an inclined surface.
The figure shows an object on an inclined surface.In Fig. 4.8, the object has a mass M = 5.0 kg, and the incline angle is è = 40°. What is the minimum force needed to prevent the body from sliding down if the coefficient of static friction between an object and the incline surface ì = 0.3?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 47 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
A car goes around a banked curve of radius 1.2 km and with angle è = 4°. What is the safest speed (in km/h) going around the curve if the road is icy?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 47 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
A student in an elevator is checking Newton's laws using a scale. The elevator moves upward with decreasing speed. Is the scale showing a reading that is larger or less than the student's actual weight?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 47 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



