Deck 3: The Chemistry of Life: Organic Compounds
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/95
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 3: The Chemistry of Life: Organic Compounds
1
Glucose dissolves in water because:
A) it ionizes.
B) it is a polysaccharide.
C) it has polar hydroxyl groups that interact with polar water molecules.
D) it has a very reactive primary structure.
E) it is hydrophobic.
A) it ionizes.
B) it is a polysaccharide.
C) it has polar hydroxyl groups that interact with polar water molecules.
D) it has a very reactive primary structure.
E) it is hydrophobic.
C
2
The highly polarized nature of compounds containing carboxyl groups can be attributed to the presence of two:
A) highly electronegative carbon atoms.
B) highly electropositive carbon atoms.
C) highly electronegative oxygen atoms.
D) highly electropositive oxygen atoms.
E) highly electropositive nitrogen atoms.
A) highly electronegative carbon atoms.
B) highly electropositive carbon atoms.
C) highly electronegative oxygen atoms.
D) highly electropositive oxygen atoms.
E) highly electropositive nitrogen atoms.
C
3
Figure 3-1
Use the figure below to answer the corresponding question(s).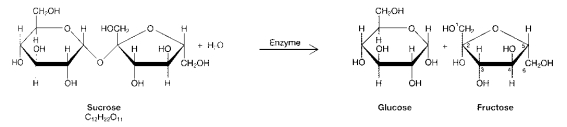
The products of the process in Figure 3-1 are:
A) amino acids.
B) molecules of glycerol.
C) representative of a glycoside linkage.
D) enzymes.
E) monosaccharides.
Use the figure below to answer the corresponding question(s).

The products of the process in Figure 3-1 are:
A) amino acids.
B) molecules of glycerol.
C) representative of a glycoside linkage.
D) enzymes.
E) monosaccharides.
E
4
Which of the following is not a property of carbon?
A) Carbon-to-carbon bonds are limited to single bonds.
B) Carbon has four valence electrons.
C) Carbon can form bonds to various other atoms.
D) Two carbon atoms can share three electron pairs with each other.
E) Carbon-to-carbon bonds are strong.
A) Carbon-to-carbon bonds are limited to single bonds.
B) Carbon has four valence electrons.
C) Carbon can form bonds to various other atoms.
D) Two carbon atoms can share three electron pairs with each other.
E) Carbon-to-carbon bonds are strong.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 95 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Which pair is mismatched?
A) monsaccharide-maltose
B) disaccharide-sucrose
C) polysaccharide-cellulose
D) hexose-glucose
E) pentose-ribose
A) monsaccharide-maltose
B) disaccharide-sucrose
C) polysaccharide-cellulose
D) hexose-glucose
E) pentose-ribose

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 95 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Hydrocarbons are hydrophobic because:
A) the covalent bonds between hydrogen and carbon are nonpolar.
B) they contain oxygen atoms.
C) they exist as isomers.
D) the covalent bonds between carbon atoms are polar.
E) the hydrogen bonds between hydrogen and carbon are nonpolar.
A) the covalent bonds between hydrogen and carbon are nonpolar.
B) they contain oxygen atoms.
C) they exist as isomers.
D) the covalent bonds between carbon atoms are polar.
E) the hydrogen bonds between hydrogen and carbon are nonpolar.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 95 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
The two molecules in the following figure represent: 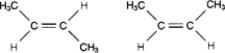
A) ionized structures.
B) enantiomers.
C) secondary structures.
D) geometric isomers.
E) polymers.

A) ionized structures.
B) enantiomers.
C) secondary structures.
D) geometric isomers.
E) polymers.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 95 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Carbohydrate molecules:
A) serve as structural components of human cell walls.
B) form the regulatory compounds known as enzymes.
C) are a source of energy.
D) help protect vital organs from damage.
E) contain the genetic information of a cell.
A) serve as structural components of human cell walls.
B) form the regulatory compounds known as enzymes.
C) are a source of energy.
D) help protect vital organs from damage.
E) contain the genetic information of a cell.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 95 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
The difference between a hexose and a pentose is that:
A) a hexose is saturated, and a pentose is undersaturated.
B) a hexose is hydrophilic, and a pentose is hydrophobic.
C) a hexose always has six hydroxyl groups, and a pentose always has five.
D) a hexose always has six carbons, but a pentose always has five carbons.
E) a hexose can be polymerized, but a pentose cannot.
A) a hexose is saturated, and a pentose is undersaturated.
B) a hexose is hydrophilic, and a pentose is hydrophobic.
C) a hexose always has six hydroxyl groups, and a pentose always has five.
D) a hexose always has six carbons, but a pentose always has five carbons.
E) a hexose can be polymerized, but a pentose cannot.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 95 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
A chemical reaction in which polymers are synthesized from their building blocks is called:
A) hydrolysis.
B) condensation.
C) oxidation.
D) reduction.
E) dissociation.
A) hydrolysis.
B) condensation.
C) oxidation.
D) reduction.
E) dissociation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 95 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
The chemical interactions of large organic molecules are largely determined by:
A) their solubility in water.
B) their functional groups.
C) their polar nature.
D) isomerization of these hydrocarbons into other forms.
E) the hydrogens bonded to the carbon atoms.
A) their solubility in water.
B) their functional groups.
C) their polar nature.
D) isomerization of these hydrocarbons into other forms.
E) the hydrogens bonded to the carbon atoms.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 95 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Amyloplasts are organelles that store:
A) fat.
B) starch.
C) protein.
D) lipids.
E) DNA.
A) fat.
B) starch.
C) protein.
D) lipids.
E) DNA.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 95 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Monosaccharides are water soluble because:
A) they contain a large number of methyl groups.
B) they have a large number of polar hydroxyl groups.
C) they have at least one double bond between adjacent carbons.
D) they have large numbers of nonpolar carbons in their backbones.
E) they can form ring structures.
A) they contain a large number of methyl groups.
B) they have a large number of polar hydroxyl groups.
C) they have at least one double bond between adjacent carbons.
D) they have large numbers of nonpolar carbons in their backbones.
E) they can form ring structures.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 95 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Figure 3-1
Use the figure below to answer the corresponding question(s).
The process illustrated in Figure 3-1 is called:
A) condensation.
B) protein synthesis.
C) hydrolysis.
D) dehydration synthesis.
E) denaturation.
Use the figure below to answer the corresponding question(s).

The process illustrated in Figure 3-1 is called:
A) condensation.
B) protein synthesis.
C) hydrolysis.
D) dehydration synthesis.
E) denaturation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 95 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Which of the following illustrates hydrolysis?
A) the reaction of two monosaccharides to form a disaccharide
B) the reaction of two amino acids to form a dipeptide
C) the reaction of a hydrogen atom and a hydroxide ion to form water
D) the reaction of a fat to form glycerol and fatty acids
E) the formation of ATP from ADP and inorganic phosphate
A) the reaction of two monosaccharides to form a disaccharide
B) the reaction of two amino acids to form a dipeptide
C) the reaction of a hydrogen atom and a hydroxide ion to form water
D) the reaction of a fat to form glycerol and fatty acids
E) the formation of ATP from ADP and inorganic phosphate

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 95 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Which one of the following carbohydrates is the most structurally complex?
A) sucrose
B) fructose
C) cellulose
D) glucose
E) a disaccharide
A) sucrose
B) fructose
C) cellulose
D) glucose
E) a disaccharide

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 95 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
The number of electron pairs shared between carbon 2 and 3 in the accompanying figure is: 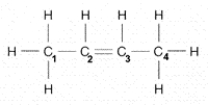
A) one.
B) one and a half.
C) two.
D) three.
E) four

A) one.
B) one and a half.
C) two.
D) three.
E) four

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 95 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
This functional group is weakly basic because it can accept an H+ ion:
A) hydroxyl
B) carbonyl
C) amino
D) phosphate
E) sulfhydryl
A) hydroxyl
B) carbonyl
C) amino
D) phosphate
E) sulfhydryl

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 95 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Which of these terms is most inclusive?
A) monosaccharide
B) starch
C) polysaccharide
D) disaccharide
E) carbohydrate
A) monosaccharide
B) starch
C) polysaccharide
D) disaccharide
E) carbohydrate

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 95 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Figure 3-1
Use the figure below to answer the corresponding question(s).
-In which of the following reactions must the equivalent of a water molecule be added in order to break a bond?
A) fatty acids + glycerol fat
B) glucose + fructose sucrose
C) glycogen glucose
D) alanine + glycine dipeptide
E) glucose cellulose
Use the figure below to answer the corresponding question(s).

-In which of the following reactions must the equivalent of a water molecule be added in order to break a bond?
A) fatty acids + glycerol fat
B) glucose + fructose sucrose
C) glycogen glucose
D) alanine + glycine dipeptide
E) glucose cellulose

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 95 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
The primary difference between the amino acids commonly found in proteins is in their:
A) R or variable groups.
B) number of potassium groups.
C) number of phosphate groups.
D) number of carbonyl groups.
E) number of asymmetric carbons.
A) R or variable groups.
B) number of potassium groups.
C) number of phosphate groups.
D) number of carbonyl groups.
E) number of asymmetric carbons.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 95 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
If you partially hydrogenate oleic acid, the resulting molecule most likely would:
A) decrease the risk of cardiovascular disease.
B) contain more double bonds.
C) lose a carbon atom.
D) lose a carboxyl group.
E) have a double bond changed from cis to trans.
A) decrease the risk of cardiovascular disease.
B) contain more double bonds.
C) lose a carbon atom.
D) lose a carboxyl group.
E) have a double bond changed from cis to trans.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 95 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Which of the following is responsible for the alpha-helical structure of proteins?
A) hydrophobic interactions
B) nonpolar covalent bonds
C) ionic interactions
D) hydrogen bonds
E) polar covalent bonds
A) hydrophobic interactions
B) nonpolar covalent bonds
C) ionic interactions
D) hydrogen bonds
E) polar covalent bonds

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 95 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
The hydrolysis of triacylglycerol will yield:
A) three fatty acids and one glycerol.
B) three glycerols and one fatty acid.
C) two fatty acids and three glycerols.
D) one fatty acid, one amino acid, and one glucose.
E) one fatty acid, one phosphate, and one glycerol.
A) three fatty acids and one glycerol.
B) three glycerols and one fatty acid.
C) two fatty acids and three glycerols.
D) one fatty acid, one amino acid, and one glucose.
E) one fatty acid, one phosphate, and one glycerol.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 95 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Proteins with alpha-helical forms exhibit this property:
A) strength.
B) elasticity.
C) heat stability.
D) rigidity.
E) hydrophobicity.
A) strength.
B) elasticity.
C) heat stability.
D) rigidity.
E) hydrophobicity.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 95 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
A molecule of a saturated triacylglycerol contains:
A) the maximum number of double bonds between carbons in the fatty acid chains.
B) the maximum number of triple bonds between carbons in the fatty acid chains.
C) the maximum number of hydrogen atoms in the fatty acid chains.
D) fatty acid chains with both amino and carboxyl groups.
E) alternating single and double bonds between carbons in the fatty acid chains.
A) the maximum number of double bonds between carbons in the fatty acid chains.
B) the maximum number of triple bonds between carbons in the fatty acid chains.
C) the maximum number of hydrogen atoms in the fatty acid chains.
D) fatty acid chains with both amino and carboxyl groups.
E) alternating single and double bonds between carbons in the fatty acid chains.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 95 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
What macromolecule is composed entirely of beta-glucose units?
A) starch
B) chitin
C) glycogen
D) cellulose
E) protein
A) starch
B) chitin
C) glycogen
D) cellulose
E) protein

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 95 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
At which level of protein structure are peptide bonds most important?
A) primary
B) secondary
C) tertiary
D) quaternary
E) globular
A) primary
B) secondary
C) tertiary
D) quaternary
E) globular

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 95 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
You isolate a compound that is insoluble in water, has alternating single and double bonds, and has a bright orange color.You correctly conclude that this compound is a:
A) protein.
B) nucleic acid.
C) polysaccharide.
D) steroid.
E) carotenoid.
A) protein.
B) nucleic acid.
C) polysaccharide.
D) steroid.
E) carotenoid.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 95 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
An amphipathic molecule has:
A) two polar ends.
B) two hydrophobic ends.
C) a hydrophobic and a hydrophilic portion.
D) only one hydrophobic end.
E) only one hydrophilic end.
A) two polar ends.
B) two hydrophobic ends.
C) a hydrophobic and a hydrophilic portion.
D) only one hydrophobic end.
E) only one hydrophilic end.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 95 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
The most abundant molecules in this structure are: 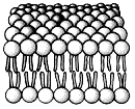
A) structural proteins.
B) polysaccharides.
C) triacylglycerols.
D) phospholipids.
E) polypeptides.

A) structural proteins.
B) polysaccharides.
C) triacylglycerols.
D) phospholipids.
E) polypeptides.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 95 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
The following amino acid would be characterized as __________ based on the chemical properties of its side chain. 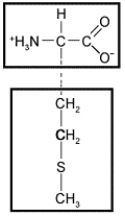
A) nonpolar
B) acidic
C) basic
D) hydrophilic
E) electrically charged

A) nonpolar
B) acidic
C) basic
D) hydrophilic
E) electrically charged

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 95 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
The major difference between a structural lipid, such as those in cell membranes, and a storage fat is the fact that the structural lipid:
A) most commonly contains phosphate.
B) does not contain glycerol.
C) has four fatty acids attached to glucose.
D) is entirely hydrophobic.
E) is nonpolar.
A) most commonly contains phosphate.
B) does not contain glycerol.
C) has four fatty acids attached to glucose.
D) is entirely hydrophobic.
E) is nonpolar.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 95 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Regulatory proteins:
A) defend against foreign invaders.
B) store nutrients.
C) catalyze a specific chemical reaction.
D) control the expression of specific genes.
E) strengthen and protect cells and tissues.
A) defend against foreign invaders.
B) store nutrients.
C) catalyze a specific chemical reaction.
D) control the expression of specific genes.
E) strengthen and protect cells and tissues.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 95 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Some proteins are important biological buffers because:
A) they react with water to produce carbon dioxide, which neutralizes acids.
B) they contain acidic as well as basic groups.
C) they are able to absorb great amounts of carbon dioxide during condensation reactions.
D) they produce carbonic acid upon hydrolysis.
E) they contain nonpolar groups that exclude water molecules.
A) they react with water to produce carbon dioxide, which neutralizes acids.
B) they contain acidic as well as basic groups.
C) they are able to absorb great amounts of carbon dioxide during condensation reactions.
D) they produce carbonic acid upon hydrolysis.
E) they contain nonpolar groups that exclude water molecules.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 95 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Which of the following statements concerning unsaturated fats is correct?
A) They are more common in animals.
B) They have no double bonds in the carbon chains of their fatty acids.
C) They are generally liquid at room temperature.
D) They contain more hydrogen than do saturated fats having the same number of carbon atoms.
E) They have fewer fatty acids per fat molecule than do saturated fats.
A) They are more common in animals.
B) They have no double bonds in the carbon chains of their fatty acids.
C) They are generally liquid at room temperature.
D) They contain more hydrogen than do saturated fats having the same number of carbon atoms.
E) They have fewer fatty acids per fat molecule than do saturated fats.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 95 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Which of the following is NOT true of lipids?
A) They store energy.
B) They function as structural components of cellular membranes.
C) They function as hormones.
D) They are nonpolar.
E) They have many oxygen-containing functional groups.
A) They store energy.
B) They function as structural components of cellular membranes.
C) They function as hormones.
D) They are nonpolar.
E) They have many oxygen-containing functional groups.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 95 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Which of the following molecules is not grouped with the lipids?
A) prostaglandins.
B) steroids.
C) cholesterol.
D) carotenoids.
E) glycoproteins
A) prostaglandins.
B) steroids.
C) cholesterol.
D) carotenoids.
E) glycoproteins

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 95 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
A carbohydrate energy storage molecule found in animal liver and muscle cells is:
A) starch.
B) glycogen.
C) cellulose.
D) a fatty acid.
E) cholesterol.
A) starch.
B) glycogen.
C) cellulose.
D) a fatty acid.
E) cholesterol.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 95 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Which of the following statements concerning steroids is FALSE?
A) They can function as hormones.
B) They are exemplified by cholesterol.
C) They consist of four attached carbon rings.
D) They are synthesized from isoprene units.
E) They contain phosphodiester linkages.
A) They can function as hormones.
B) They are exemplified by cholesterol.
C) They consist of four attached carbon rings.
D) They are synthesized from isoprene units.
E) They contain phosphodiester linkages.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 95 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
Which of the following statements is false?
A) DNA is usually composed of two nucleotide strands.
B) DNA contains deoxyribose.
C) DNA does not normally contain uracil.
D) The nucleotides of DNA are linked by phosphodiester linkages.
E) DNA does not normally contain a phosphate group.
A) DNA is usually composed of two nucleotide strands.
B) DNA contains deoxyribose.
C) DNA does not normally contain uracil.
D) The nucleotides of DNA are linked by phosphodiester linkages.
E) DNA does not normally contain a phosphate group.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 95 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
DNA most directly determines which __________ are made by a cell.
A) polysaccharides
B) polypeptides
C) nucleotides
D) triglycerides
E) fatty acids
A) polysaccharides
B) polypeptides
C) nucleotides
D) triglycerides
E) fatty acids

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 95 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
Figure 3-2
Use the figure below to answer the corresponding question(s).
Hydrophobic interactions would occur between the R groups of which two amino acids in Figure 3-2?
A) 1 and 4
B) 2 and 5
C) 3 and 6
D) 2 and 4
E) 3 and 5
Use the figure below to answer the corresponding question(s).

Hydrophobic interactions would occur between the R groups of which two amino acids in Figure 3-2?
A) 1 and 4
B) 2 and 5
C) 3 and 6
D) 2 and 4
E) 3 and 5

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 95 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
ATP is important in living organisms because:
A) like all other nucleic acids, it stores hereditary information.
B) like RNA, it acts as a source code for the formation of proteins.
C) it can transfer some of its energy to other chemicals.
D) it is an important structural component of cell membranes.
E) it is easily converted to starch for long-term storage.
A) like all other nucleic acids, it stores hereditary information.
B) like RNA, it acts as a source code for the formation of proteins.
C) it can transfer some of its energy to other chemicals.
D) it is an important structural component of cell membranes.
E) it is easily converted to starch for long-term storage.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 95 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
This molecule transmits heredity information:
A) cholesterol.
B) adenosine triphosphate.
C) nucleic acid.
D) fatty acid.
E) polysaccharide.
A) cholesterol.
B) adenosine triphosphate.
C) nucleic acid.
D) fatty acid.
E) polysaccharide.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 95 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
Which of the following statements is true of proteins?
A) Proteins lose some or all of their normal activity if their three-dimensional structure is disrupted.
B) Proteins are composed of ribose, phosphate, and a nitrogen-containing base.
C) The activity of proteins is independent of temperature and pH.
D) Denaturation is usually reversible.
E) All proteins are enzymes.
A) Proteins lose some or all of their normal activity if their three-dimensional structure is disrupted.
B) Proteins are composed of ribose, phosphate, and a nitrogen-containing base.
C) The activity of proteins is independent of temperature and pH.
D) Denaturation is usually reversible.
E) All proteins are enzymes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 95 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
This functional group forms bridges that help stabilize protein quaternary structure:
A) hydroxyl
B) carbonyl
C) amino
D) phosphate
E) sulfhydryl
A) hydroxyl
B) carbonyl
C) amino
D) phosphate
E) sulfhydryl

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 95 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
If tyrosine and isoleucine undergo condensation, the new bond that is formed is between the:
A) oxygen of the R group and the hydrogen of the amino group.
B) carbon of the R group and the nitrogen of the amino group.
C) carbon of the carboxyl group and the hydrogen of the R group.
D) carbon of the carboxyl group and the hydrogen of the amino group.
E) carbon of the carboxyl group and the nitrogen of the amino group.
A) oxygen of the R group and the hydrogen of the amino group.
B) carbon of the R group and the nitrogen of the amino group.
C) carbon of the carboxyl group and the hydrogen of the R group.
D) carbon of the carboxyl group and the hydrogen of the amino group.
E) carbon of the carboxyl group and the nitrogen of the amino group.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 95 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
Figure 3-2
Use the figure below to answer the corresponding question(s).
In Figure 3-2, ionic bonds would form between the R groups of which amino acids?
A) 1 and 3
B) 2 and 4
C) 3 and 5
D) 4 and 6
E) 3 and 6
Use the figure below to answer the corresponding question(s).

In Figure 3-2, ionic bonds would form between the R groups of which amino acids?
A) 1 and 3
B) 2 and 4
C) 3 and 5
D) 4 and 6
E) 3 and 6

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 95 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
Figure 3-3
Use the figure to answer the corresponding question(s).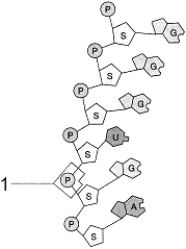
Analysis of a certain polymer shows that it contains phosphate groups, ribose groups, and pyrimidines.Based on this information, which of the following is the best description of this compound?
A) It is most likely ribonucleic acid.
B) It is DNA.
C) It is an inorganic compound.
D) It contains thymine.
E) It is a polypeptide.
Use the figure to answer the corresponding question(s).

Analysis of a certain polymer shows that it contains phosphate groups, ribose groups, and pyrimidines.Based on this information, which of the following is the best description of this compound?
A) It is most likely ribonucleic acid.
B) It is DNA.
C) It is an inorganic compound.
D) It contains thymine.
E) It is a polypeptide.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 95 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
Figure 3-3
Use the figure to answer the corresponding question(s).
The molecular fragment represented in Figure 3-3 is:
A) ATP.
B) RNA.
C) a protein.
D) a nucleotide.
E) a polysaccharide.
Use the figure to answer the corresponding question(s).

The molecular fragment represented in Figure 3-3 is:
A) ATP.
B) RNA.
C) a protein.
D) a nucleotide.
E) a polysaccharide.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 95 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
When a nucleic acid undergoes hydrolysis, the resulting subunits are:
A) amino acids.
B) monosaccharides.
C) nucleotides.
D) fatty acids.
E) carotenoids.
A) amino acids.
B) monosaccharides.
C) nucleotides.
D) fatty acids.
E) carotenoids.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 95 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
Figure 3-3
Use the figure to answer the corresponding question(s).
The type of connection between the atoms at the point labeled 1 in Figure 3-3 is:
A) a peptide bond.
B) a glycoside linkage.
C) a disulfide bond.
D) a phosphodiester linkage.
E) a hydrogen bond.
Use the figure to answer the corresponding question(s).

The type of connection between the atoms at the point labeled 1 in Figure 3-3 is:
A) a peptide bond.
B) a glycoside linkage.
C) a disulfide bond.
D) a phosphodiester linkage.
E) a hydrogen bond.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 95 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
If the differently shaded portions of this molecule represent different polypeptide chains, then this figure is representative of: 
A) an amino acid.
B) the quaternary structure of a protein.
C) a steroid hormone.
D) cellulose.
E) a carotenoid.

A) an amino acid.
B) the quaternary structure of a protein.
C) a steroid hormone.
D) cellulose.
E) a carotenoid.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 95 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
Which portion of the following molecule is most directly involved in transferring energy? 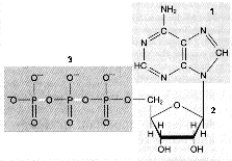
A) 1
B) 2
C) 3
D) 1 and 2
E) 2 and 3

A) 1
B) 2
C) 3
D) 1 and 2
E) 2 and 3

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 95 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
Which of the following statements best summarizes the differences between RNA and DNA?
A) RNA is a protein and DNA is a nucleic acid.
B) DNA is a polymer and RNA is a monomer.
C) DNA comprises the genes, while RNA is a direct participant in the process of protein synthesis.
D) RNA is a single-stranded form of DNA.
E) DNA is the primary energy currency of all cells.
A) RNA is a protein and DNA is a nucleic acid.
B) DNA is a polymer and RNA is a monomer.
C) DNA comprises the genes, while RNA is a direct participant in the process of protein synthesis.
D) RNA is a single-stranded form of DNA.
E) DNA is the primary energy currency of all cells.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 95 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
All of the following types of chemical bonds are responsible for maintaining the tertiary structure of this polypeptide except: 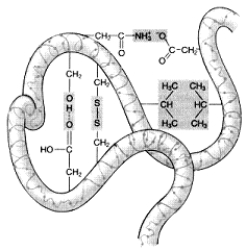
A) ionic bonds.
B) hydrogen bonds.
C) hydrophobic interactions.
D) disulfide bonds.
E) peptide bonds.

A) ionic bonds.
B) hydrogen bonds.
C) hydrophobic interactions.
D) disulfide bonds.
E) peptide bonds.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 95 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
Figure 3-2
Use the figure below to answer the corresponding question(s).
The tertiary structure of proteins is typified by the:
A) association of several polypeptide chains by weak bonds.
B) order in which amino acids are joined in a peptide chain.
C) bonding of two amino acids to form a dipeptide.
D) folding of a peptide chain to form an alpha helix.
E) three-dimensional shape of an individual polypeptide chain.
Use the figure below to answer the corresponding question(s).

The tertiary structure of proteins is typified by the:
A) association of several polypeptide chains by weak bonds.
B) order in which amino acids are joined in a peptide chain.
C) bonding of two amino acids to form a dipeptide.
D) folding of a peptide chain to form an alpha helix.
E) three-dimensional shape of an individual polypeptide chain.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 95 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
Which pair matches the correct macromolecule with the bond that joins its subunits?
A) polysaccharide-peptide bond
B) triacylglycerol-glycosidic linkage
C) nucleic acid-phosphodiester linkage
D) protein-ester linkage
E) steroid-peptide bond
A) polysaccharide-peptide bond
B) triacylglycerol-glycosidic linkage
C) nucleic acid-phosphodiester linkage
D) protein-ester linkage
E) steroid-peptide bond

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 95 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
Molecular chaperones are proteins that mediate the folding process of:
A) other proteins.
B) amino acids.
C) lipids.
D) DNA.
E) sugars.
A) other proteins.
B) amino acids.
C) lipids.
D) DNA.
E) sugars.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 95 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
Identify the levels of organization for protein molecules, and list the type(s) of bond(s) involved in establishing each structural level.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 95 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
A beta-pleated sheet is an example of a protein's tertiary structure.
__________________
__________________

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 95 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
Cyclic AMP is a type of nucleotide.
__________________
__________________

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 95 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
Molecular chaperones mediate the folding of other protein molecules.
__________________
__________________

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 95 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
A pyrimidine is double-ring molecule.
__________________
__________________

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 95 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
A disaccharide is composed of two monosaccharides joined by a glycosidic linkage.
__________________
__________________

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 95 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
The phosphate group is a nonpolar group.
__________________
__________________

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 95 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
When glucose and fructose undergo condensation, maltose is produced as a product.
__________________
__________________

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 95 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
Compare and contrast the structure, physical characteristics, and biological functions of two of the following: fats, steroids, and phospholipids.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 95 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
A single protein may have several domains.
__________________
__________________

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 95 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
Water is always released as a product in hydrolysis reactions.
__________________
__________________

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 95 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
Identify three functions of proteins other than enzymes and briefly discuss or describe each.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 95 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
Glycogen consists of beta-glucose monomers.
__________________
__________________

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 95 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
What does the term "functional group" mean in reference to the structure of organic molecules? Identify two types of functional groups and describe their chemical properties.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 95 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
Fats high in unsaturated fatty acids tend to be solid at room temperature.
__________________
__________________

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 95 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
By definition, geometric isomers are mirror images of each other.
__________________
__________________

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 95 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
Chitin is a polymer composed of N-acetyl glucosamine monomers.
__________________
__________________

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 95 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
Carotenoids are composed of isoprene subunits.
__________________
__________________

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 95 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
The carboxyl group can exist in an ionized form and also in a nonionized form.
__________________
__________________

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 95 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
An essential amino acid is one that the body cannot synthesize in sufficient amounts.
__________________
__________________

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 95 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



