Deck 13: Decision Analysis
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/36
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 13: Decision Analysis
1
To find the EVSI,
A) use the EVPI to calculate sample information probabilities.
B) use indicator probabilities to calculate prior probabilities.
C) use prior and sample information probabilities to calculate revised probabilities.
D) use sample information to revise the sample information probabilities.
A) use the EVPI to calculate sample information probabilities.
B) use indicator probabilities to calculate prior probabilities.
C) use prior and sample information probabilities to calculate revised probabilities.
D) use sample information to revise the sample information probabilities.
C
2
Sample information with an efficiency rating of 100% is perfect information.
True
3
For a minimization problem, the optimistic approach is often referred to as the
A) minimax approach
B) maximin approach
C) maximax approach
D) minimum approach
A) minimax approach
B) maximin approach
C) maximax approach
D) minimum approach
D
4
The efficiency of sample information is
A) EVSI*(100%)
B) EVSI/EVPI*(100%)
C) EVwoSI/EVwoPI*(100%)
D) EVwSI/EVwoSI*(100%)
A) EVSI*(100%)
B) EVSI/EVPI*(100%)
C) EVwoSI/EVwoPI*(100%)
D) EVwSI/EVwoSI*(100%)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 36 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
In an influence diagram, decision nodes are represented by
A) circles or ovals
C) diamonds
B) squares or rectangles
D) triangles
A) circles or ovals
C) diamonds
B) squares or rectangles
D) triangles

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 36 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
For a minimization problem, the conservative approach is often referred to as the
A) minimax approach
B) maximin approach
C) maximax approach
D) minimum approach
A) minimax approach
B) maximin approach
C) maximax approach
D) minimum approach

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 36 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
States of nature
A) can describe uncontrollable natural events such as floods or freezing temperatures.
B) can be selected by the decision maker.
C) cannot be enumerated by the decision maker.
D) All of the alternatives are true.
A) can describe uncontrollable natural events such as floods or freezing temperatures.
B) can be selected by the decision maker.
C) cannot be enumerated by the decision maker.
D) All of the alternatives are true.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 36 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
For a maximization problem, the optimistic approach is often referred to as the
A) minimax approach
B) maximin approach
C) maximax approach
D) minimum approach
A) minimax approach
B) maximin approach
C) maximax approach
D) minimum approach

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 36 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
A decision tree
A) presents all decision alternatives first and follows them with all states of nature.
B) presents all states of nature first and follows them with all decision alternatives.
C) alternates the decision alternatives and states of nature.
D) arranges decision alternatives and states of nature in their natural chronological order.
A) presents all decision alternatives first and follows them with all states of nature.
B) presents all states of nature first and follows them with all decision alternatives.
C) alternates the decision alternatives and states of nature.
D) arranges decision alternatives and states of nature in their natural chronological order.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 36 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
States of nature should be defined so that one and only one will actually occur.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 36 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Decision alternatives are structured so that several could occur simultaneously.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 36 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Decision tree probabilities refer to
A) the probability of finding the optimal strategy
B) the probability of the decision being made
C) the probability of overlooked choices
D) the probability of an uncertain event occurring
A) the probability of finding the optimal strategy
B) the probability of the decision being made
C) the probability of overlooked choices
D) the probability of an uncertain event occurring

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 36 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
If P(high) = .3, P(low) = .7, P(favorable | high) = .9, and P(unfavorable | low) = .6, then P(favorable) =
A) .10
B) .27
C) .30
D) .55
A) .10
B) .27
C) .30
D) .55

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 36 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
For a maximization problem, the conservative approach is often referred to as the
A) minimax approach
B) maximin approach
C) maximax approach
D) minimum approach
A) minimax approach
B) maximin approach
C) maximax approach
D) minimum approach

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 36 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Which of the methods for decision making best protects the decision maker from undesirable results?
A) the optimistic approach
B) the conservative approach
C) minimum regret
D) minimax regret
A) the optimistic approach
B) the conservative approach
C) minimum regret
D) minimax regret

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 36 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Sensitivity analysis considers
A) how sensitive the decision maker is to risk.
B) changes in the number of states of nature.
C) changes in the values of the payoffs.
D) changes in the available alternatives.
A) how sensitive the decision maker is to risk.
B) changes in the number of states of nature.
C) changes in the values of the payoffs.
D) changes in the available alternatives.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 36 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Making a good decision
A) requires probabilities for all states of nature.
B) requires a clear understanding of decision alternatives, states of nature, and payoffs.
C) implies that a desirable outcome will occur.
D) All of the alternatives are true.
A) requires probabilities for all states of nature.
B) requires a clear understanding of decision alternatives, states of nature, and payoffs.
C) implies that a desirable outcome will occur.
D) All of the alternatives are true.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 36 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Which of the following approaches to decision making requires knowledge of the probabilities of the states of nature?
A) minimax regret
C) expected value
B) maximin
D) conservative
A) minimax regret
C) expected value
B) maximin
D) conservative

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 36 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
A payoff
A) is always measured in profit.
B) is always measured in cost.
C) exists for each pair of decision alternative and state of nature.
D) exists for each state of nature.
A) is always measured in profit.
B) is always measured in cost.
C) exists for each pair of decision alternative and state of nature.
D) exists for each state of nature.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 36 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
The options from which a decision maker chooses a course of action are
A) called the decision alternatives.
B) under the control of the decision maker.
C) not the same as the states of nature.
D) All of the alternatives are true.
A) called the decision alternatives.
B) under the control of the decision maker.
C) not the same as the states of nature.
D) All of the alternatives are true.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 36 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Maximizing the expected payoff and minimizing the expected opportunity loss result in the same recommended decision.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 36 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Fold back this decision tree. Clearly state the decision strategy you determine. 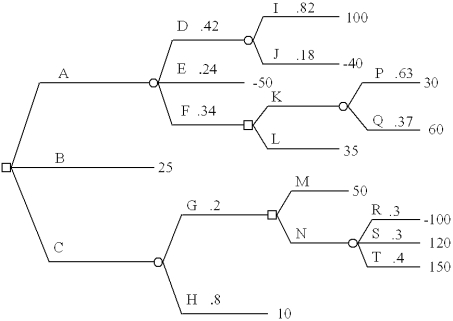


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 36 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Expected value is the sum of the weighted payoff possibilities at a circular node in a decision tree.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 36 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
The expected value approach is more appropriate for a one-time decision than a repetitive decision.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 36 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
EVPI equals the expected regret associated with the minimax decision.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 36 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
EVPI is always greater than or equal to EVSI.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 36 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Square nodes in a decision tree indicate that a decision must be made.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 36 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
A decision strategy is a sequence of decisions and chance outcomes, where the decisions chosen depend on the yet to be determined outcomes of chance events.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 36 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
The expected value of an alternative can never be negative.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 36 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
The expected value of sample information can never be less than the expected value of perfect information.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 36 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
The minimum expected opportunity loss provides the best decision, regardless of whether the decision analysis involves minimization or maximization.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 36 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
After all probabilities and payoffs are placed on a decision tree, the decision maker calculates expected values at state of nature nodes and makes selections at decision nodes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 36 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Circular nodes in a decision tree indicate that it would be incorrect to choose a path from the node.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 36 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Fold back the decision tree and state what strategy should be followed. 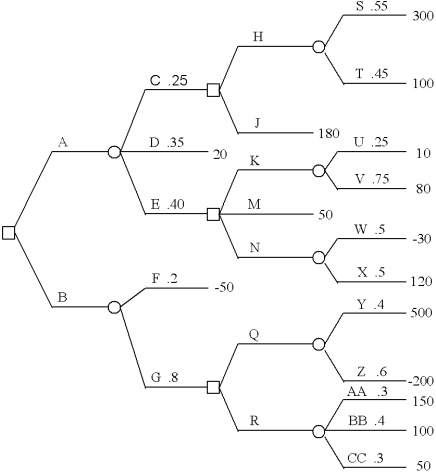


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 36 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
If sample information is obtained, the result of the sample information will be either positive or negative. No matter which result occurs, the choice to select option A or option B exists. And no matter which option is chosen, the eventual outcome will be good or poor. Complete the table.



Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 36 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Risk analysis helps the decision maker recognize the difference between the expected value of a decision alternative and the payoff that may actually occur.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 36 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



