Deck 5: Conditional Convergence and Long-Run Economic Growth
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/60
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 5: Conditional Convergence and Long-Run Economic Growth
1
In the Solow growth model transition, the growth rate of output per worker is negatively related to:
A)the initial capital stock per worker, k(0).
B)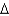 y/y.
y/y.
C)the optimum output per worker, y*
D)all of the above.
A)the initial capital stock per worker, k(0).
B)
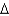 y/y.
y/y.C)the optimum output per worker, y*
D)all of the above.
the initial capital stock per worker, k(0).
2
In the Solow growth model transition, the growth rate of capital per worker is negatively related to:
A)the initial capital stock per worker, k(0).
B)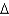 k/k.
k/k.
C)the optimum output per worker, k*
D)all of the above.
A)the initial capital stock per worker, k(0).
B)
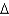 k/k.
k/k.C)the optimum output per worker, k*
D)all of the above.
the initial capital stock per worker, k(0).
3
In the key equation for convergence 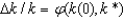 , k* is:
, k* is:
A)the initial level of capital.
B)the initial level of capital per worker.
C)the optimum level of capital.
D)the optimum level of capital per worker.
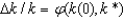 , k* is:
, k* is:A)the initial level of capital.
B)the initial level of capital per worker.
C)the optimum level of capital.
D)the optimum level of capital per worker.
the optimum level of capital per worker.
4
In the key equation for convergence 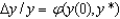 , y* is:
, y* is:
A)the initial level of output.
B)the initial level of output per worker.
C)the optimum level of output.
D)the optimum level of output per worker.
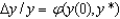 , y* is:
, y* is:A)the initial level of output.
B)the initial level of output per worker.
C)the optimum level of output.
D)the optimum level of output per worker.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
In the Solow growth model the growth rate of capital per worker is positively related to the initial level of capital per worker.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
The Solow growth model with technological progress has continuous output per worker growth in the steady state.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
In the key equation for convergence 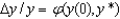 , y(0) is:
, y(0) is:
A)the initial level of output.
B)the initial level of output per worker.
C)the optimum level of output.
D)the optimum level of output per worker.
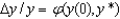 , y(0) is:
, y(0) is:A)the initial level of output.
B)the initial level of output per worker.
C)the optimum level of output.
D)the optimum level of output per worker.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
In the Solow growth model transition, the growth rate of output per worker is positively related to:
A)the initial capital stock per worker, k(0).
B)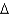 y/y.
y/y.
C)the optimum output per worker, y*
D)all of the above.
A)the initial capital stock per worker, k(0).
B)
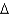 y/y.
y/y.C)the optimum output per worker, y*
D)all of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Convergence can be seen in the data of all countries together if one holds constant:
A)the saving rate.
B)the fertility rate.
C)the degree the rule of law is maintained.
D)all of the above.
A)the saving rate.
B)the fertility rate.
C)the degree the rule of law is maintained.
D)all of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Ideas are rival goods.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Governments grant patents and copyrights to encourage firms to engage in research and development.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
In the Solow growth model, the growth rate of capital per worker is positively related to the optimum capital per worker.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
The key equation for conditional convergence for output per worker is:
A)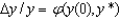
B)Y = A•F(K,L)
C)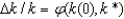
D)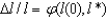
A)
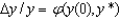
B)Y = A•F(K,L)
C)
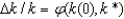
D)
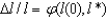

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Conditional convergence is the tendency of economies to converge:
A)all the time.
B)when they are similar.
C)only when economic conditions are good.
D)only when currencies are stable.
A)all the time.
B)when they are similar.
C)only when economic conditions are good.
D)only when currencies are stable.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Convergence can be seen in the data of all countries together if one holds constant:
A)the degree that democracy is maintained.
B)changes in the terms of trade.
C)the average rate of inflation.
D)all of the above.
A)the degree that democracy is maintained.
B)changes in the terms of trade.
C)the average rate of inflation.
D)all of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Absolute convergence is the tendency of economies to converge:
A)all the time.
B)when they are similar.
C)only when economic conditions are good.
D)only when currencies are stable.
A)all the time.
B)when they are similar.
C)only when economic conditions are good.
D)only when currencies are stable.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Convergence can be seen in the data of all countries together if one holds constant:
A)the size of government.
B)the extent of international openness.
C)investment in education and health.
D)all of the above.
A)the size of government.
B)the extent of international openness.
C)investment in education and health.
D)all of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
In the key equation for convergence 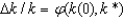 , k(0) is:
, k(0) is:
A)the initial level of capital.
B)the initial level of capital per worker.
C)the optimum level of capital.
D)the optimum level of capital per worker.
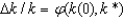 , k(0) is:
, k(0) is:A)the initial level of capital.
B)the initial level of capital per worker.
C)the optimum level of capital.
D)the optimum level of capital per worker.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
The key equation for conditional convergence for capital per worker is:
A)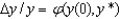
B)Y = A•F(K,L)
C)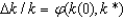
D)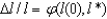
A)
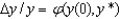
B)Y = A•F(K,L)
C)
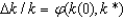
D)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
In the Solow growth model transition, the growth rate of capital per worker is positively related to:
A)the initial capital stock per worker, k(0).
B)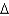 k/k.
k/k.
C)the optimum output per worker, k*
D)all of the above.
A)the initial capital stock per worker, k(0).
B)
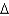 k/k.
k/k.C)the optimum output per worker, k*
D)all of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
If sA > s 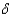 + n in the model with constant average product of capital, the long run growth rate is:
+ n in the model with constant average product of capital, the long run growth rate is:
A)constant.
B)positive
C)negative.
D)cyclical.
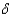 + n in the model with constant average product of capital, the long run growth rate is:
+ n in the model with constant average product of capital, the long run growth rate is:A)constant.
B)positive
C)negative.
D)cyclical.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
In the Solow growth model, the long run rate of growth of output per worker is:
A)zero
B)negative.
C)cyclical.
D)positive.
A)zero
B)negative.
C)cyclical.
D)positive.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
A problem with the constant average product of capital growth model is that:
A)a common view among economist is that the average product of capital eventually starts to fall as capital rises.
B)output per worker grows in the long run.
C)the Y/K ratio grows.
D)all of the above.
A)a common view among economist is that the average product of capital eventually starts to fall as capital rises.
B)output per worker grows in the long run.
C)the Y/K ratio grows.
D)all of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
To encourage firms to engage in research and development (R&D), governments grant temporary monopolies in the production of the word or symbol based goods like books and computer code that result from R&D called:
A)cartels.
B)copyrights.
C)anti-trust exemptions.
D)all of the above.
A)cartels.
B)copyrights.
C)anti-trust exemptions.
D)all of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
The private return from research and development might be less than the social return because:
A)others than just the inventor can use inventions that come out of research and development.
B)it is encouraged by patents and copyrights.
C)it is funded by the government.
D)all of the above.
A)others than just the inventor can use inventions that come out of research and development.
B)it is encouraged by patents and copyrights.
C)it is funded by the government.
D)all of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
An example of a non-rival good is:
A)an output like a pizza.
B)a machine like a printing press.
C)an idea like a new chemical formula for a drug.
D)all of the above.
A)an output like a pizza.
B)a machine like a printing press.
C)an idea like a new chemical formula for a drug.
D)all of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
An example of non-rival good is:
A)mathematical formulas in calculus.
B)a machine like a laser printer.
C)an output like a dress.
D)all of the above.
A)mathematical formulas in calculus.
B)a machine like a laser printer.
C)an output like a dress.
D)all of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
An example of a non-rival good is:
A)an output like a shirt.
B)code for computer software.
C)a structure like a factory.
D)all of the above.
A)an output like a shirt.
B)code for computer software.
C)a structure like a factory.
D)all of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
In the Solow growth model with technological progress,
A)k* is constant.
B)k* is growing
C)k* is cyclical.
D)k* is declining.
A)k* is constant.
B)k* is growing
C)k* is cyclical.
D)k* is declining.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
In the Solow growth model with technological progress in the optimal amount of capital per worker is
A)growing.
B)shrinking.
C)cyclical.
D)fluctuating.
A)growing.
B)shrinking.
C)cyclical.
D)fluctuating.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
If sA > s 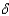 + n in the model with constant average product of capita, the long run growth rate is:
+ n in the model with constant average product of capita, the long run growth rate is:
A)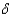
B)Ak
C)sA - (s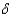 +N)
+N)
D)none of the above.
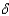 + n in the model with constant average product of capita, the long run growth rate is:
+ n in the model with constant average product of capita, the long run growth rate is:A)
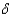
B)Ak
C)sA - (s
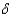 +N)
+N)D)none of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
An example of a rival capital good is:
A)an employee like an R&D engineer.
B)a machine like a printing press.
C)a structure like a factory.
D)all of the above.
A)an employee like an R&D engineer.
B)a machine like a printing press.
C)a structure like a factory.
D)all of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
The rewards to private R&D depend on:
A)the costs of R&D.
B)the rewards from the results of R&D.
C)the security of intellectual property rights.
D)all of the above.
A)the costs of R&D.
B)the rewards from the results of R&D.
C)the security of intellectual property rights.
D)all of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
A growth model with continuing output per worker growth in the long run is:
A)the production function.
B)the Ak model of constant average product of capital.
C)the Solow growth model.
D)all of the above.
A)the production function.
B)the Ak model of constant average product of capital.
C)the Solow growth model.
D)all of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
To encourage firms to engage in research and development (R&D), governments grant temporary monopolies in the production of the goods that result from R&D called:
A)patents.
B)land grants.
C)anti-trust exemptions.
D)all of the above.
A)patents.
B)land grants.
C)anti-trust exemptions.
D)all of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
In endogenous growth models, technological progress comes from:
A)outside the system.
B)research and development.
C)increases in the capital stock.
D)all of the above.
A)outside the system.
B)research and development.
C)increases in the capital stock.
D)all of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
An example of a non-rival good is:
A)mathematical formulas in calculus.
B)codes for computer software.
C)an idea like a new chemical formula for a drug.
D)all of the above.
A)mathematical formulas in calculus.
B)codes for computer software.
C)an idea like a new chemical formula for a drug.
D)all of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
An example of a rival capital good is:
A)infrastructure like roads.
B)a machine like a printing press.
C)an idea like a new chemical formula for a drug.
D)all of the above.
A)infrastructure like roads.
B)a machine like a printing press.
C)an idea like a new chemical formula for a drug.
D)all of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
A problem with the constant average product of capital growth model is that:
A)output per worker grows in the long run.
B)there is no convergence.
C)the Y/K ratio grows.
D)all of the above.
A)output per worker grows in the long run.
B)there is no convergence.
C)the Y/K ratio grows.
D)all of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
In the Solow growth model with technological progress in the steady state:
A)capital per worker is constant.
B)capital per worker is cyclical.
C)capital per worker is increasing.
D)capital per worker is declining.
A)capital per worker is constant.
B)capital per worker is cyclical.
C)capital per worker is increasing.
D)capital per worker is declining.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
What happens when exogenous technological change is modeled in the Solow growth model?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
A business may not seek a patent on an idea or invention because:
A)patents are not valuable.
B)approval is costly.
C)ideas and inventions are non-rival.
D)all of the above.
A)patents are not valuable.
B)approval is costly.
C)ideas and inventions are non-rival.
D)all of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
With steady state growth:
A)the optimal output per worker grows faster than optimal capital per worker.
B)the steady state growth rate of real GDP per worker is less than the rate of technological progress.
C)the average product of capital is constant.
D)all of the above.
A)the optimal output per worker grows faster than optimal capital per worker.
B)the steady state growth rate of real GDP per worker is less than the rate of technological progress.
C)the average product of capital is constant.
D)all of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
If intellectual property rights become better secured, then:
A)the costs of R&D are greater.
B)the costs of R&D are smaller.
C)the private returns to R&D are greater.
D)the private returns to R&D are smaller.
A)the costs of R&D are greater.
B)the costs of R&D are smaller.
C)the private returns to R&D are greater.
D)the private returns to R&D are smaller.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
What is conditional convergence?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
With steady state growth:
A)there is absolute convergence.
B)y/k is constant.
C)k* growth fluctuates.
D)all of the above.
A)there is absolute convergence.
B)y/k is constant.
C)k* growth fluctuates.
D)all of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
Steady state growth is when:
A)when the average product of capital, y/k, is unchanging as k increases at a constant rate.
B)when the rate of growth of capital per worker is constant at zero.
C)when the rate growth of output per worker is constant at zero.
D)all of the above.
A)when the average product of capital, y/k, is unchanging as k increases at a constant rate.
B)when the rate of growth of capital per worker is constant at zero.
C)when the rate growth of output per worker is constant at zero.
D)all of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
What are the steady-state growth results of a constant average product of capital model of growth and what are the problems of such a model?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
What is the key equation for conditional convergence and what are the direction of influences?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
With steady state growth:
A)the optimal output per worker grows faster than the optimal capital per worker.
B)the steady state growth rate of real GDP per worker is greater than the rate of technological progress.
C)the average product of capital is falling.
D)all of the above.
A)the optimal output per worker grows faster than the optimal capital per worker.
B)the steady state growth rate of real GDP per worker is greater than the rate of technological progress.
C)the average product of capital is falling.
D)all of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
With steady state growth:
A)(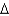 y/y)* = (
y/y)* = ( 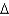 k/k)*
k/k)*
B)y/k is constant.
C)(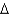 y/y)*= g/(1-
y/y)*= g/(1- 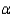 )
)
D)all of the above.
A)(
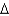 y/y)* = (
y/y)* = ( 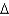 k/k)*
k/k)*B)y/k is constant.
C)(
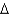 y/y)*= g/(1-
y/y)*= g/(1- 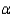 )
)D)all of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
With steady state growth:
A)(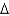 y/y)* = (
y/y)* = ( 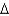 k/k)*.
k/k)*.
B)k* = 0.
C)y* = 0.
D)all of the above.
A)(
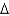 y/y)* = (
y/y)* = ( 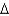 k/k)*.
k/k)*.B)k* = 0.
C)y* = 0.
D)all of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
With steady state growth:
A)the optimal output per worker and capital per worker grow at the same rate.
B)the steady state growth rate of real GDP per worker is equal to the rate of technological progress.
C)the average product of capital falls.
D)all of the above.
A)the optimal output per worker and capital per worker grow at the same rate.
B)the steady state growth rate of real GDP per worker is equal to the rate of technological progress.
C)the average product of capital falls.
D)all of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
With steady state growth:
A)k* growth fluctuates.
B)there is absolute convergence.
C)(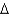 y/y)*= g/(1-
y/y)*= g/(1- 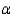 )
)
D)all of the above.
A)k* growth fluctuates.
B)there is absolute convergence.
C)(
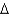 y/y)*= g/(1-
y/y)*= g/(1- 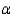 )
)D)all of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
The rewards to private R&D are positively related to:
A)the costs of R&D.
B)growth rate of capital per worker.
C)the security of intellectual property rights.
D)all of the above.
A)the costs of R&D.
B)growth rate of capital per worker.
C)the security of intellectual property rights.
D)all of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
The ability to control the inventions from R&D spending is known as
A)greed.
B)a rival good.
C)intellectual property rights.
D)all of the above.
A)greed.
B)a rival good.
C)intellectual property rights.
D)all of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
With steady state growth:
A)the optimal output per worker and capital per worker grow at the same rate.
B)the steady state growth rate of real GDP per worker is greater than the rate of technological progress.
C)the average product of capital is constant.
D)all of the above.
A)the optimal output per worker and capital per worker grow at the same rate.
B)the steady state growth rate of real GDP per worker is greater than the rate of technological progress.
C)the average product of capital is constant.
D)all of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
Diffusion of technology means:
A)how many industries a technology can be used in.
B)describes the imitation and adaptation of technology from country to country.
C)how expensive a technology is.
D)how many scientists had to work on a technology.
A)how many industries a technology can be used in.
B)describes the imitation and adaptation of technology from country to country.
C)how expensive a technology is.
D)how many scientists had to work on a technology.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
The rewards to private R&D are negatively related to:
A)the costs of R&D.
B)the rewards from the results of R&D.
C)the security of intellectual property rights.
D)all of the above.
A)the costs of R&D.
B)the rewards from the results of R&D.
C)the security of intellectual property rights.
D)all of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
What variables must be held constant to find convergence in the data on all countries.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



