Deck 1: Thinking About Macroeconomics
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/50
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 1: Thinking About Macroeconomics
1
Macroeconomists study:
A)the determination of real GDP.
B)the production of specific goods.
C)the relative production in different markets.
D)all of the above.
A)the determination of real GDP.
B)the production of specific goods.
C)the relative production in different markets.
D)all of the above.
the determination of real GDP.
2
Macroeconomists study the amount of employment and unemployment.
True
3
Macroeconomics deals with:
A)how individual markets work.
B)the overall performance of the economy.
C)relative prices in different markets.
D)substitution of one good for another good.
A)how individual markets work.
B)the overall performance of the economy.
C)relative prices in different markets.
D)substitution of one good for another good.
the overall performance of the economy.
4
Monetary policy involves:
A)the government's expenditure.
B)taxation.
C)determining the quantity of money.
D)the fiscal deficit.
A)the government's expenditure.
B)taxation.
C)determining the quantity of money.
D)the fiscal deficit.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
During recessions the unemployment rate:
A)declines.
B)increases.
C)is stable.
D)is unmeasurable.
A)declines.
B)increases.
C)is stable.
D)is unmeasurable.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Macroeconomists study:
A)the determination of the economy's total production.
B)unemployment
C)the general price level.
D)all of the above.
A)the determination of the economy's total production.
B)unemployment
C)the general price level.
D)all of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Among the prices that macroeconomists study are:
A)the wage rate.
B)the interest rate.
C)the exchange rate.
D)all of the above.
A)the wage rate.
B)the interest rate.
C)the exchange rate.
D)all of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Fiscal policy involves:
A)determining exchange rates.
B)government expenditures.
C)interest rates.
D)all of the above.
A)determining exchange rates.
B)government expenditures.
C)interest rates.
D)all of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
The unemployment rate is:
A)the fraction of the population with no job.
B)the fraction of those seeking work with no job.
C)the rate of growth of those with no job.
D)the rate of growth of those seeking work.
A)the fraction of the population with no job.
B)the fraction of those seeking work with no job.
C)the rate of growth of those with no job.
D)the rate of growth of those seeking work.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
The unemployment rate in France was highest in:
A)1990
B)1994
C)2001
D)2009
A)1990
B)1994
C)2001
D)2009

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Macroeconomists study the price of individual products like beer.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
When real GDP falls toward a low point or trough it is called a[n]:
A)boom.
B)recession.
C)inflation.
D)expansion.
A)boom.
B)recession.
C)inflation.
D)expansion.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
When GDP is expanding toward a high point it is called a[n]:
A)depression.
B)boom.
C)recession.
D)inflation.
A)depression.
B)boom.
C)recession.
D)inflation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
If price is below equilibrium in a market, then quantity supplied will be less than quantity demanded.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
A recession is when GDP is falling toward a trough.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Variations in real GDP are called:
A)inflation.
B)deflation.
C)economic fluctuations.
D)all of the above.
A)inflation.
B)deflation.
C)economic fluctuations.
D)all of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
The rate of growth of GDP for period t is:
A)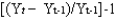
B)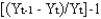
C)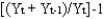
D)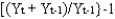
A)
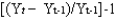
B)
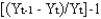
C)
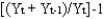
D)
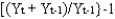

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
When the gross domestic product is growing, it is called inflation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Among the prices that macroeconomist study are:
A)the price of coffee.
B)the price of tea.
C)the interest rate.
D)all of the above.
A)the price of coffee.
B)the price of tea.
C)the interest rate.
D)all of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Macroeconomics includes the study of:
A)the general price level.
B)the price of individual goods.
C)the relative price of goods.
D)all of the above.
A)the general price level.
B)the price of individual goods.
C)the relative price of goods.
D)all of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
A possible order of events in an economy over time is:
A)expansion, recession, peak, expansion.
B)recession, trough, expansion, peak.
C)expansion, peak, trough, recession.
D)recession, trough, peak, expansion.
A)expansion, recession, peak, expansion.
B)recession, trough, expansion, peak.
C)expansion, peak, trough, recession.
D)recession, trough, peak, expansion.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
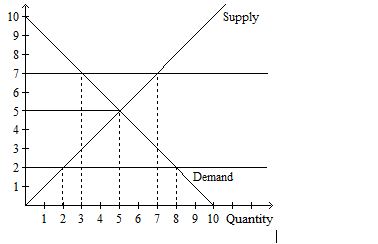
In Figure1.1 if the price is 2, then:
A)the market is in equilibrium.
B)there is excess quantity supplied.
C)there is excess quantity demanded.
D)the market clears.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
The inflation rate for year t is:
A)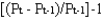
B)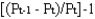
C)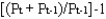
D)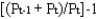
A)
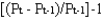
B)
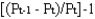
C)
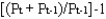
D)
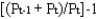

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24

In Figure1.1 the equilibrium quantity is
A)5
B)2
C)7
D)8

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
A peak in an economy is when the economy:
A)is growing.
B)reaches a low point.
C)is contracting.
D)reaches a high point.
A)is growing.
B)reaches a low point.
C)is contracting.
D)reaches a high point.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26

In Figure1.1, if price is 7, then quantity demanded is:
A) 2.
B) 7.
C) 3.
D) 8.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
The price of labour is the:
A)exchange rate.
B)wage rate.
C)interest rate.
D)the rental price.
A)exchange rate.
B)wage rate.
C)interest rate.
D)the rental price.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28

In Figure1.1 the equilibrium price is:
A)2
B)5
C)7
D)0

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29

In Figure1.1 if price is 7, then
A)the market is in equilibrium.
B)there is excess quantity supplied.
C)there is excess quantity demanded.
D)the market clears.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30

In Figure1.1, if price is 2, then quantity demanded is:
A) 2.
B) 7.
C) 3.
D) 8.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
A trough in an economy is when the economy:
A)is growing.
B)reaches a low point.
C)is contracting.
D)reaches a high point.
A)is growing.
B)reaches a low point.
C)is contracting.
D)reaches a high point.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32

In Figure1.1, if price is 5, then quantity demanded is:
A) 2.
B) 7.
C) 3.
D) 5.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
A variable that macroeconomists want to model is a[n]
A)endogenous variable.
B)dummy variable.
C)exogenous variable.
D)predetermined variable.
A)endogenous variable.
B)dummy variable.
C)exogenous variable.
D)predetermined variable.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34

In Figure1.1, if price is 2, then quantity supplied is:
A) 2.
B) 7.
C) 3.
D) 8.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35

In Figure1.1, if price is 7, then quantity supplied is:
A) 2.
B) 7.
C) 3.
D) 8.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36

In Figure1.1, if demand falls, then equilibrium:
A)price and quantity fall.
B)price and quantity rise.
C)price falls and quantity rises.
D)prices rises and quantity falls.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37

In Figure1.1, if price is 7, then quantity demanded is:
A) 2.
B) 7.
C) 3.
D) 8.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
A variable taken as given in a model is a[n]
A)endogenous variable.
B)dummy variable.
C)exogenous variable.
D)dichotomous variable.
A)endogenous variable.
B)dummy variable.
C)exogenous variable.
D)dichotomous variable.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39

In Figure1.1 if supply increases, then equilibrium:
A)price and quantity fall.
B)price and quantity rise.
C)price rises and quantity falls.
D)price falls and quantity rises.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
The euro price paid to use capital is known as:
A)the interest rate.
B)the exchange rate.
C)the rental price of capital.
D)the general price level.
A)the interest rate.
B)the exchange rate.
C)the rental price of capital.
D)the general price level.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
What are exogenous and endogenous variables?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
What is the rate of growth of real GDP?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
What types of economic issues do macroeconomists study?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
If prices are sticky:
A)the market quickly sticks at equilibrium.
B)the market clears quickly.
C)the market only slowly moves toward equilibrium.
D)all of the above.
A)the market quickly sticks at equilibrium.
B)the market clears quickly.
C)the market only slowly moves toward equilibrium.
D)all of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
In an economic model:
A)endogenous variables feed into a model to affect exogenous variable.
B)exogenous variables feed into a model to affect endogenous variables.
C)exogenous and endogenous variables feed into the model.
D)none of the above.
A)endogenous variables feed into a model to affect exogenous variable.
B)exogenous variables feed into a model to affect endogenous variables.
C)exogenous and endogenous variables feed into the model.
D)none of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
Describe what happens when demand or supply increase in a market.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
A possible order of economic fluctuations is:
A)recession, boom, expansion, trough.
B)expansion, recession, boom, trough.
C)recession, trough, expansion, peak.
D)expansion, trough, recession, peak.
A)recession, boom, expansion, trough.
B)expansion, recession, boom, trough.
C)recession, trough, expansion, peak.
D)expansion, trough, recession, peak.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
A macroeconomist would study the:
A)price of cars.
B)the market for shoes.
C)the sales of beer.
D)none of the above.
A)price of cars.
B)the market for shoes.
C)the sales of beer.
D)none of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
A price taker:
A)takes the price to the market.
B)controls the market price.
C)accepts the market price and decides whether and how much to buy or sell.
D)accepts the market quantity and sets price.
A)takes the price to the market.
B)controls the market price.
C)accepts the market price and decides whether and how much to buy or sell.
D)accepts the market quantity and sets price.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
How is the annual inflation rate calculated?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



