Deck 4: The Origin of Modern Astronomy
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/109
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 4: The Origin of Modern Astronomy
1
The geometry of an ellipse is described by two numbers: the ____ which is half the longest diameter of the ellipse and the ____ which tells us the shape of the ellipse.
A) radius, eccentricity
B) radius, deferent
C) semimajor axis, deferent
D) semimajor axis, epicycle
E) semimajor axis, eccentricity
A) radius, eccentricity
B) radius, deferent
C) semimajor axis, deferent
D) semimajor axis, epicycle
E) semimajor axis, eccentricity
semimajor axis, eccentricity
2
Spring tides occur
A) at new moon and first quarter moon.
B) at first quarter and third quarter moons.
C) at new moon and full moon.
D) at third quarter and full moons.
E) at noon and midnight.
A) at new moon and first quarter moon.
B) at first quarter and third quarter moons.
C) at new moon and full moon.
D) at third quarter and full moons.
E) at noon and midnight.
at new moon and full moon.
3
A(n) ____ is a commonly accepted set of scientific ideas and assumptions.
A) theory
B) paradigm
C) hypothesis
D) natural law
E) model
A) theory
B) paradigm
C) hypothesis
D) natural law
E) model
paradigm
4
Tycho Brahe's greatest contribution to astronomy was
A) his model of the universe.
B) his telescopic observations.
C) his discovery of three laws of motion.
D) his 20 years of careful observations of the planets.
E) a and b above
A) his model of the universe.
B) his telescopic observations.
C) his discovery of three laws of motion.
D) his 20 years of careful observations of the planets.
E) a and b above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
A(n) ____ is a small circle whose center is located on the circumference of another larger circle.
A) equant
B) deferent
C) retrograde loop
D) ellipse
E) epicycle
A) equant
B) deferent
C) retrograde loop
D) ellipse
E) epicycle

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
The Copernican system was no more accurate than the Ptolemaic system in predicting the positions of the planets because ___________just as in the Ptolemaic system.
A) the Copernican system assumed the Earth was at rest at the center
B) the Copernican system used elliptical planetary orbits
C) the Copernican system used uniform circular motion
D) the Copernican system assumed all planets orbited the sun
A) the Copernican system assumed the Earth was at rest at the center
B) the Copernican system used elliptical planetary orbits
C) the Copernican system used uniform circular motion
D) the Copernican system assumed all planets orbited the sun

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Tycho failed to detect ______ for the nova of 1572 indicating it was ______.
A) parallax; beyond the orbit of Earth's moon
B) parallax; inside the Earth's atmosphere close to Earth
C) light; beyond the orbit of Earth's moon
D) light; inside the Earth's atmosphere close to Earth
A) parallax; beyond the orbit of Earth's moon
B) parallax; inside the Earth's atmosphere close to Earth
C) light; beyond the orbit of Earth's moon
D) light; inside the Earth's atmosphere close to Earth

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Ptolemy's model of the universe
A) was heliocentric.
B) included elliptical orbits.
C) contained epicycles.
D) all of the above.
E) none of the above.
A) was heliocentric.
B) included elliptical orbits.
C) contained epicycles.
D) all of the above.
E) none of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Tycho's universe was the same as the Copernican universe except that
A) Earth did not move.
B) the sun did not move.
C) the moon orbited the sun.
D) the orbits were elliptical with the sun at one focus.
E) the orbits followed uniform circular motion.
A) Earth did not move.
B) the sun did not move.
C) the moon orbited the sun.
D) the orbits were elliptical with the sun at one focus.
E) the orbits followed uniform circular motion.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Retrograde motion (east to west among the stars) is observed
A) for some planets as Earth passes between that planet and the sun.
B) for the sun during the entire year.
C) for Earth's moon during an entire month.
D) none of the above.
A) for some planets as Earth passes between that planet and the sun.
B) for the sun during the entire year.
C) for Earth's moon during an entire month.
D) none of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
A(n) ____ is a single conjecture that can be tested.
A) hypothesis
B) paradigm
C) natural law
D) model
E) theory
A) hypothesis
B) paradigm
C) natural law
D) model
E) theory

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
____ orbit is one in which an object orbiting Earth has an orbital period equal to the rotation period of Earth.
A) A daily
B) A lunar
C) An epicycle
D) A geosynchronous
E) An open
A) A daily
B) A lunar
C) An epicycle
D) A geosynchronous
E) An open

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Parallax is
A) the apparent motion of an object due to the motion of the observer.
B) the distance between two foci of an ellipse.
C) the small circle that the planets slid along in Ptolemy's geocentric universe.
D) the circular orbits used in Copernicus' heliocentric universe.
E) half the length of the shortest diameter of an ellipse.
A) the apparent motion of an object due to the motion of the observer.
B) the distance between two foci of an ellipse.
C) the small circle that the planets slid along in Ptolemy's geocentric universe.
D) the circular orbits used in Copernicus' heliocentric universe.
E) half the length of the shortest diameter of an ellipse.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Galileo's telescopic discoveries of mountains on the moon and spots on the sun were controversial because they suggested that the sun and moon
A) were the same kind of object.
B) were not perfect spheres.
C) were inhabited.
D) orbited each other.
E) did not orbit Earth.
A) were the same kind of object.
B) were not perfect spheres.
C) were inhabited.
D) orbited each other.
E) did not orbit Earth.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Which of the following people did NOT accept a heliocentric model for the universe?
A) Kepler
B) Copernicus
C) Tycho
D) Galileo
E) Newton
A) Kepler
B) Copernicus
C) Tycho
D) Galileo
E) Newton

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
The semimajor axis of an ellipse is
A) the ratio of the longest diameter of the ellipse to that of the shortest diameter of the ellipse.
B) half the length of the shortest diameter of the ellipse.
C) half the length of the longest diameter of the ellipse.
D) the distance between the two foci of the ellipse.
E) the ratio of the distance between the two foci to the length of half the longest diameter of the ellipse.
A) the ratio of the longest diameter of the ellipse to that of the shortest diameter of the ellipse.
B) half the length of the shortest diameter of the ellipse.
C) half the length of the longest diameter of the ellipse.
D) the distance between the two foci of the ellipse.
E) the ratio of the distance between the two foci to the length of half the longest diameter of the ellipse.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
The book "De Revolutionibus Orbium Coelestium"
A) describes how Galileo's observations and Kepler's calculations proved the Copernican theory.
B) describes the construction of Galileo's telescope and his observations.
C) is a dialog written to convince the general public of the merits of the Copernican theory.
D) first described the Copernican theory.
E) describes the Tychonian theory.
A) describes how Galileo's observations and Kepler's calculations proved the Copernican theory.
B) describes the construction of Galileo's telescope and his observations.
C) is a dialog written to convince the general public of the merits of the Copernican theory.
D) first described the Copernican theory.
E) describes the Tychonian theory.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
A(n) ____ is well supported (observationally and/or experimentally) system of rules and principles that can be applied to a wide variety of circumstances.
A) hypothesis
B) paradigm
C) theory
D) model
A) hypothesis
B) paradigm
C) theory
D) model

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
____ occur when the moon is first or third quarter.
A) Neap tides
B) Spring tides
C) Total solar eclipses
D) Annular eclipses
E) A coppery red moon will
A) Neap tides
B) Spring tides
C) Total solar eclipses
D) Annular eclipses
E) A coppery red moon will

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Galileo's observations of a complete set of phases of Venus proved
A) that Venus orbited the sun.
B) that Earth orbited the sun.
C) that all of the planets orbited the sun.
D) that the moon orbited Earth.
E) that Venus had an atmosphere.
A) that Venus orbited the sun.
B) that Earth orbited the sun.
C) that all of the planets orbited the sun.
D) that the moon orbited Earth.
E) that Venus had an atmosphere.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
If the mass of the Earth decreased by a factor of two with no change in radius, your weight would
A) increase by a factor of 4.
B) increase by a factor of 2.
C) stay the same.
D) decrease by a factor of 2.
E) decrease by a factor of 4.
A) increase by a factor of 4.
B) increase by a factor of 2.
C) stay the same.
D) decrease by a factor of 2.
E) decrease by a factor of 4.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Gravity obeys an inverse square relation. This statement implies that the force due to gravity between two masses
A) will increase as the distance between the two masses increases.
B) will decrease as the square of the distance between the two masses increases.
C) will cause the two masses to move away from each other.
D) will cause the two masses to move in a straight line.
E) will cause the two masses to orbit each other.
A) will increase as the distance between the two masses increases.
B) will decrease as the square of the distance between the two masses increases.
C) will cause the two masses to move away from each other.
D) will cause the two masses to move in a straight line.
E) will cause the two masses to orbit each other.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Halley's comet has an orbital period of 76 years, what is the average distance of Comet Halley from the sun?
A) 51 AU
B) 18 AU
C) 114 AU
D) 660 AU
E) 38 AU
A) 51 AU
B) 18 AU
C) 114 AU
D) 660 AU
E) 38 AU

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
The force of gravity from one object extends to infinity never going to zero. When we say that gravitation is universal we mean that
A) the Earth exerts gravitational force on objects on its surface.
B) the Earth exerts a gravitational force on its moon and vice versa.
C) the Earth, moon, and sun exert gravitational forces on each other.
D) all material objects in the universe exert gravitational forces on one another.
A) the Earth exerts gravitational force on objects on its surface.
B) the Earth exerts a gravitational force on its moon and vice versa.
C) the Earth, moon, and sun exert gravitational forces on each other.
D) all material objects in the universe exert gravitational forces on one another.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
The force due to gravity between two objects depends on 
A) I & II
B) I & III
C) II & IV
D) I, II, & III
E) I, II, III, & IV

A) I & II
B) I & III
C) II & IV
D) I, II, & III
E) I, II, III, & IV

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
An apparent westward motion of a planet in the sky compared to the background stars (as viewed from Earth) when observed on successive nights is referred to as
A) epicycle.
B) retrograde motion.
C) prograde motion.
D) heliocentric motion.
E) deferent.
A) epicycle.
B) retrograde motion.
C) prograde motion.
D) heliocentric motion.
E) deferent.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
The purpose of using epicycles and deferents to explain the motion of the planets in the night sky was to account for
A) prograde motion.
B) Mercury's and Venus's limited angular distance from the sun.
C) retrograde motion.
D) non-uniform speed of the planets in their orbits.
E) precession of the equinoxes.
A) prograde motion.
B) Mercury's and Venus's limited angular distance from the sun.
C) retrograde motion.
D) non-uniform speed of the planets in their orbits.
E) precession of the equinoxes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Newton concluded that a force from the Earth had to act on the moon because
A) a force is needed to keep the moon in motion in its orbit.
B) a force is needed to pull the moon outward.
C) a force is needed to accelerate the moon toward Earth away from straight-line motion.
D) the moon moved at a constant velocity in a straight line.
E) all of the above.
A) a force is needed to keep the moon in motion in its orbit.
B) a force is needed to pull the moon outward.
C) a force is needed to accelerate the moon toward Earth away from straight-line motion.
D) the moon moved at a constant velocity in a straight line.
E) all of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
The diagram below illustrates a portion of the model for the universe described by 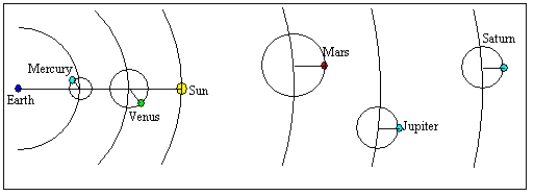
A) Kepler.
B) Tycho.
C) Ptolemy.
D) Copernicus.
E) Galileo.

A) Kepler.
B) Tycho.
C) Ptolemy.
D) Copernicus.
E) Galileo.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Kepler's second law implies that
A) a planet should move at its greatest speed when it is closest to the sun.
B) the most massive planets will have the greatest speed in their orbits.
C) the speed of a planet in its orbit depends on the size of the epicycle.
D) the mass of the planet determines how far the planet is from the sun.
E) the deferent and the epicycle have to be attached to the sun and not Earth.
A) a planet should move at its greatest speed when it is closest to the sun.
B) the most massive planets will have the greatest speed in their orbits.
C) the speed of a planet in its orbit depends on the size of the epicycle.
D) the mass of the planet determines how far the planet is from the sun.
E) the deferent and the epicycle have to be attached to the sun and not Earth.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Which of the following books of tabulated predicted planet positions was not based on uniform circular motion?
A) the Rudolphine Tables by Kepler
B) the Prutenic Tables based on Copernicus' model
C) the Alphonsine Tables based on Ptolemy's observations and calculations
A) the Rudolphine Tables by Kepler
B) the Prutenic Tables based on Copernicus' model
C) the Alphonsine Tables based on Ptolemy's observations and calculations

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Saturn is on average 10 AU from the sun. What is the approximate orbital period of Saturn?
A) 10 years
B) 32 years
C) 100 years
D) 1000 years
E) 1,000,000 years
A) 10 years
B) 32 years
C) 100 years
D) 1000 years
E) 1,000,000 years

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
The period of Jupiter's orbit around the sun is approximately 12 years. What is the approximate distance from the sun to Jupiter?
A) 144 AU
B) 1728 AU
C) 42 AU
D) 5.2 AU
E) 2.3 AU
A) 144 AU
B) 1728 AU
C) 42 AU
D) 5.2 AU
E) 2.3 AU

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Which of the following objects cannot transit (i.e., pass in front of) the sun as seen from Jupiter?
A) Mars
B) Earth
C) Saturn
D) Mercury
E) Venus
A) Mars
B) Earth
C) Saturn
D) Mercury
E) Venus

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
The ____ of an object is a measure of the amount of matter it contains. On the other hand ____ is a measure of the gravitational force on an object.
A) weight; mass
B) mass; weight
C) energy; force
D) force; energy
E) momentum; energy
A) weight; mass
B) mass; weight
C) energy; force
D) force; energy
E) momentum; energy

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
An object has been located orbiting the sun at a distance from the sun of 65 AU. What is the approximate orbital period of this object?
A) 65 years
B) 275,000 years
C) 4225 years
D) 8.1 years
E) 524 years
A) 65 years
B) 275,000 years
C) 4225 years
D) 8.1 years
E) 524 years

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
In pre-Copernican astronomy, it was almost universally believed that
A) the planets traveled in elliptical orbits about Earth.
B) the center of the universe was the sun with the Milky Way representing other distant planets.
C) the sun was at the center of the universe.
D) Earth was at the center of the universe.
E) None of the above was believed.
A) the planets traveled in elliptical orbits about Earth.
B) the center of the universe was the sun with the Milky Way representing other distant planets.
C) the sun was at the center of the universe.
D) Earth was at the center of the universe.
E) None of the above was believed.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Kepler's first law of planetary motion implies that
A) the planets move at a constant speed at all points in their orbits.
B) the planets all move around Earth in elliptical orbits.
C) uniform circular motion is adequate to describe the motion of all planets.
D) planets move in elliptical orbits around the sun.
A) the planets move at a constant speed at all points in their orbits.
B) the planets all move around Earth in elliptical orbits.
C) uniform circular motion is adequate to describe the motion of all planets.
D) planets move in elliptical orbits around the sun.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
When Mars is located directly behind Earth with respect to the sun in its orbit, it is
A) at the midpoint in the sky between east and west at sunset.
B) at the midpoint in the sky between east and west at midnight.
C) at the midpoint in the sky between east and west at sunrise.
D) at the midpoint in the sky between east and west at noon.
E) not visible in the night sky.
A) at the midpoint in the sky between east and west at sunset.
B) at the midpoint in the sky between east and west at midnight.
C) at the midpoint in the sky between east and west at sunrise.
D) at the midpoint in the sky between east and west at noon.
E) not visible in the night sky.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Which of the following planets can be seen as a crescent phase from Earth?
A) Mercury
B) Venus
C) Mars
D) both a and b
E) all of the above
A) Mercury
B) Venus
C) Mars
D) both a and b
E) all of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
The orbit of the planet Jupiter is an ellipse with the sun at one focus. What is located at the other focus?
A) the asteroid belt
B) Earth
C) Saturn
D) Jupiter
E) nothing
A) the asteroid belt
B) Earth
C) Saturn
D) Jupiter
E) nothing

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
What is the circular velocity of an object orbiting Earth at a distance of 100,000 km from Earth's center? 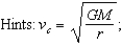 G = 6.67*10-11 m3.kg-1.s-2; MEarth = 5.98*1024kg
G = 6.67*10-11 m3.kg-1.s-2; MEarth = 5.98*1024kg
A) 2 m/s
B) 20 m/s
C) 200 m/s
D) 2000 m/s
E) 20,000 m/s
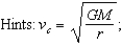 G = 6.67*10-11 m3.kg-1.s-2; MEarth = 5.98*1024kg
G = 6.67*10-11 m3.kg-1.s-2; MEarth = 5.98*1024kgA) 2 m/s
B) 20 m/s
C) 200 m/s
D) 2000 m/s
E) 20,000 m/s

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
Kepler used Tycho's observations to show that the planets
A) followed perfectly circular orbits.
B) followed perfectly cubical orbits.
C) all circled the earth.
D) followed elliptical orbits.
A) followed perfectly circular orbits.
B) followed perfectly cubical orbits.
C) all circled the earth.
D) followed elliptical orbits.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
Direct motion of a planet is its normal motion ____________ among the stars.
A) west to east along the ecliptic
B) east to west along the ecliptic
C) west to east along the celestial equator
D) east to west along the celestial equator
A) west to east along the ecliptic
B) east to west along the ecliptic
C) west to east along the celestial equator
D) east to west along the celestial equator

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Why did Galileo's observations of moons orbiting Jupiter disagree with geocentric model of the universe of his time?
A) The moons moved in non-circular orbits about Jupiter.
B) The moons did not appear to orbit the sun.
C) The moons did not appear to orbit Earth.
D) The moons appeared to be too small, and therefore too far away, to be considered part of the solar system.
A) The moons moved in non-circular orbits about Jupiter.
B) The moons did not appear to orbit the sun.
C) The moons did not appear to orbit Earth.
D) The moons appeared to be too small, and therefore too far away, to be considered part of the solar system.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
The eccentricity of a planet's orbit describes
A) westward motion in the night sky when observed on successive nights.
B) the deviation in shape when compared to a circle.
C) its tilt with respect to the ecliptic plane.
D) the tilt of the planet's rotational axis with respect to the ecliptic.
A) westward motion in the night sky when observed on successive nights.
B) the deviation in shape when compared to a circle.
C) its tilt with respect to the ecliptic plane.
D) the tilt of the planet's rotational axis with respect to the ecliptic.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
The vernal equinox is the point on the sky where the sun crosses the ____________ going north and east.
A) north celestial pole
B) south celestial pole
C) celestial equator
D) horizon
A) north celestial pole
B) south celestial pole
C) celestial equator
D) horizon

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
The greatest inaccuracy in Copernicus's model of the solar system was that the planets
A) traveled in circular orbits with uniform motion.
B) traveled on epicycles whose centers followed orbits around the sun.
C) traveled in elliptical orbits.
D) were allowed to travel backwards in their orbits.
E) orbited the sun.
A) traveled in circular orbits with uniform motion.
B) traveled on epicycles whose centers followed orbits around the sun.
C) traveled in elliptical orbits.
D) were allowed to travel backwards in their orbits.
E) orbited the sun.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
Galileo's telescopic discovery of moons orbiting Jupiter was important because it showed that
A) the universe could contain centers of motion other than Earth.
B) Earth might move along an orbit and not leave the moon behind.
C) Jupiter was much more massive than Earth.
D) all of the above.
E) a and b above.
A) the universe could contain centers of motion other than Earth.
B) Earth might move along an orbit and not leave the moon behind.
C) Jupiter was much more massive than Earth.
D) all of the above.
E) a and b above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
Tides occur because the gravitational force of the moon on Earth ____ with increasing distance from the moon.
A) stays constant
B) increases
C) decreases
A) stays constant
B) increases
C) decreases

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
The Almagest
A) is the book that first described the heliocentric solar system.
B) is a collection of the science and mathematics of the Greeks.
C) caused the author to be sentenced to house arrest.
D) is a book of astrological myths and predictions produced by the Arabs.
E) first described the Copernican theory.
A) is the book that first described the heliocentric solar system.
B) is a collection of the science and mathematics of the Greeks.
C) caused the author to be sentenced to house arrest.
D) is a book of astrological myths and predictions produced by the Arabs.
E) first described the Copernican theory.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
Galileo used a telescope to discover
A) spots on the sun.
B) craters on the moon.
C) moons around Jupiter.
D) moon-like phases of Venus.
E) all of these.
A) spots on the sun.
B) craters on the moon.
C) moons around Jupiter.
D) moon-like phases of Venus.
E) all of these.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
The ____ produce(s) tides on the Earth.
A) moon alone
B) sun alone
C) moon and sun
A) moon alone
B) sun alone
C) moon and sun

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
Newton's law of gravitational force is expressed as follows:
A) An object with no force on it moves in a straight line with constant velocity.
B) An object with a force on it is accelerated in the direction of the force an amount inversely proportional to its mass and directly proportional to the size of the force.
C) For every action there is an equal and opposite reaction.
D) The force between two objects is directly proportional to the product of their masses and inversely proportional to the distance between them squared.
A) An object with no force on it moves in a straight line with constant velocity.
B) An object with a force on it is accelerated in the direction of the force an amount inversely proportional to its mass and directly proportional to the size of the force.
C) For every action there is an equal and opposite reaction.
D) The force between two objects is directly proportional to the product of their masses and inversely proportional to the distance between them squared.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
In Ptolemy's view of the universe, a planet moves on an epicycle whose center moves around the Earth on the deferent circle.
A) Correct
B) FALSE; Ptolemy put the sun at the center.
C) FALSE; The planet stays on the deferent circle.
D) FALSE; Earth is at the center of the epicycle.
E) FALSE; Both c and d are correct.
A) Correct
B) FALSE; Ptolemy put the sun at the center.
C) FALSE; The planet stays on the deferent circle.
D) FALSE; Earth is at the center of the epicycle.
E) FALSE; Both c and d are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
A comet in a highly elliptical orbit is found to have a semimajor axis equal to one astronomical unit (AU). According to Kepler's 3rd law, what would be the sidereal period of this comet?
A) more than one year
B) one year
C) less than one year
D) 76 years; the same for every comet
E) Not enough information is given to determine this.
A) more than one year
B) one year
C) less than one year
D) 76 years; the same for every comet
E) Not enough information is given to determine this.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
Which type of curve would accurately represent a closed orbit?
A) ellipse
B) hyperbola
C) parabola
D) straight line
A) ellipse
B) hyperbola
C) parabola
D) straight line

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
Which of the following statements best describes Kepler's 3rd law of planetary motion?
A) The smaller the diameter of a planet, the faster its rotational period is.
B) The orbital period of a planet is directly proportional to the diameter of the planet.
C) The smaller the orbit, the longer its orbital period is.
D) The larger the orbit, the longer its orbital period is.
A) The smaller the diameter of a planet, the faster its rotational period is.
B) The orbital period of a planet is directly proportional to the diameter of the planet.
C) The smaller the orbit, the longer its orbital period is.
D) The larger the orbit, the longer its orbital period is.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
A(n) ____ orbit is one where the orbiting object is always above the same location on Earth's surface.
A) elliptical
B) geosynchronous
C) closed
D) hyperbolic
E) parabolic
A) elliptical
B) geosynchronous
C) closed
D) hyperbolic
E) parabolic

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
The circular velocity of a satellite orbiting Earth is given by 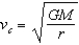 . In this equation,
. In this equation,
A) M represents the mass of the satellite, and r is its radius.
B) M represents the mass of Earth, and r the radius of Earth.
C) M represents the mass of the satellite, and r the distance from Earth to the satellite.
D) M represents the mass of Earth, and r the distance from Earth to the satellite.
E) M represents the mass of the satellite, and r the distance from Earth's surface to the satellite.
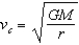 . In this equation,
. In this equation,A) M represents the mass of the satellite, and r is its radius.
B) M represents the mass of Earth, and r the radius of Earth.
C) M represents the mass of the satellite, and r the distance from Earth to the satellite.
D) M represents the mass of Earth, and r the distance from Earth to the satellite.
E) M represents the mass of the satellite, and r the distance from Earth's surface to the satellite.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
Copernicus proposed that Earth moved around the sun.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
The Copernican model of the solar system has the planets orbit the sun along elliptical paths.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
Once a theory has been tested thoroughly and is confidently believed by scientists, it becomes a ____________________.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
According to Kepler's third law, a planet's orbital period ____________________ is equal to its average distance from the sun ____________________.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
Classical Greek astronomers believed the motions of the heavens could be described by uniform circular motion.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
Tables based on a heliocentric model of the universe which used elliptical orbits for the planets were more accurate than ____________________.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
The ____________________ Tables were based on a heliocentric model of the universe and used elliptical orbits for the planets.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
The Ptolemaic model of the universe was heliocentric.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
The first observations of objects in the solar system that orbited neither the sun nor Earth were made by ____________________.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
When two objects of unequal masses orbit each other, the center of mass is
A) at the center of the more massive object.
B) at the center of the least massive object.
C) half way between the centers of each object.
D) always closer to the less massive of the two objects.
E) always closer to the more massive of the two objects.
A) at the center of the more massive object.
B) at the center of the least massive object.
C) half way between the centers of each object.
D) always closer to the less massive of the two objects.
E) always closer to the more massive of the two objects.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
____________________ made very accurate observations of the positions and movements of the planets that were later used to help develop the Rudolphine Tables.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
Uranus's orbital period is 84 years. How far is Uranus from the sun?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
A scientific model can never be exactly correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
Which planets are never visible near the eastern horizon at sunset?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
A(n) ____________________ is a circle whose center moves in a circular orbit around the Earth.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
The first modern astronomer to propose a heliocentric model for the solar system was ____________________.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
____________________ is a description of the Ptolemaic model of the solar system.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
Many classical Greek astronomers believed Earth could not move because they detected no parallax.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
Ptolemy formulated a(n) ____________________ model of the solar system to predict positions of the sun, moon, and planets.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
Ocean tides of low amplitude that occur at first and third quarter moons are called ____________________.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



