Deck 2: Voltage, Current, and Resistance
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/69
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 2: Voltage, Current, and Resistance
1
The Nickel-Metal Hydride battery is an example of a secondary battery.
True
2
Resistance is the opposition to the flow of current.
True
3
An elementW ith a relatively large amount of electrons in the valence ring is considered to be a good conductor.
False
4
A ormally Open Push Button switch can carry currentW hen not pushed.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
The movement of free electrons through a conductor is called current

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
A resistor color coded with yellow, violet and orange bands has a value of 4.7 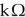
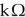

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Electrons have a positive charge.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
For electrical current to flow in a circuit voltage must be applied to that circuit.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Electrons attract each other.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
A(n)________ is a material that has many free electrons.
A)semiconductor
B)insulator
C)poor conductor
D)conductor
A)semiconductor
B)insulator
C)poor conductor
D)conductor

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Electromotive force is measured in volts.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
A resistor with orange, orange, red and gold bands has a value and tolerance of___________
A)
B)
C)
D)
A)
B)
C)
D)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
To measure the current through a resistor, place the ammeter so the current must pass through the meter.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
If a resistor is color coded with red, red, orange and silver bands, the resistance equals __________,the lower tolerance limit equals________, and the upper tolerance limit equals______
A)
B)
C)
D)
A)
B)
C)
D)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
A SPST switch is used to control one circuit.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
The opposition to the flow of current is called ________.
A)current
B)resistance
C)voltage
D)capacitance
A)current
B)resistance
C)voltage
D)capacitance

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
The ohm is the basic unit of resistance.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
An insulator is a materialW ith ________.
A)very many free electrons
B)some free electrons
C)very few free electrons
D)all free electrons
A)very many free electrons
B)some free electrons
C)very few free electrons
D)all free electrons

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
A resistor color-coded with brown, black and orange bands has a value of 10,000 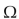
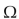

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
A generator converts electrical energy into mechanical energy.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
(a)

(b)

(c)

(d)

(e)

Figure
-Which switch in Figure 2-1 could be used to open a circuit momentarily?
A)graph (a)
B)graph (b)
C)graph (c)
D)graph (d)
E)graph (e)

(b)

(c)

(d)

(e)

Figure
-Which switch in Figure 2-1 could be used to open a circuit momentarily?
A)graph (a)
B)graph (b)
C)graph (c)
D)graph (d)
E)graph (e)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
(a)

(b)

(c)

(d)

(e)

Figure
-Which switch in Figure 2-1 could be used to simultaneously open or simultaneously close two circuits?
A)graph (a)
B)graph (b)
C)graph (c)
D)graph (d)
E)graph (e)

(b)

(c)

(d)

(e)

Figure
-Which switch in Figure 2-1 could be used to simultaneously open or simultaneously close two circuits?
A)graph (a)
B)graph (b)
C)graph (c)
D)graph (d)
E)graph (e)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
A source, a path, and a load ________.
A)make up a basic circuit
B)do not make up a complete circuit
C)can only be an open circuit
D)will allow current to flow if the switch is open
A)make up a basic circuit
B)do not make up a complete circuit
C)can only be an open circuit
D)will allow current to flow if the switch is open

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
(a)

(b)

(c)

(d)

(e)

Figure
-Identify the Normally Closed Push Button switch in Figure 2-1.
A)graph (a)
B)graph (b)
C)graph (c)
D)graph (d)
E)graph (e)

(b)

(c)

(d)

(e)

Figure
-Identify the Normally Closed Push Button switch in Figure 2-1.
A)graph (a)
B)graph (b)
C)graph (c)
D)graph (d)
E)graph (e)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Which unit of charge contains 6.25 × 1018 electrons?
A)a coulomb
B)an ampere
C)aVolt
D)a joule
A)a coulomb
B)an ampere
C)aVolt
D)a joule

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
What do you call a diagram that shows the electrical connections of a circuitʹs components?
A)a pictorial diagram
B)an electrical diagram
C)a schematic diagram
D)a block diagram
A)a pictorial diagram
B)an electrical diagram
C)a schematic diagram
D)a block diagram

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
To measure a circuitʹs source voltage, the voltmeter must ________.
A)be placed across the source
B)be placed in series in the circuit
C)have the red lead towards the negative side of the source
D)have the black lead towards the positive side of the source
A)be placed across the source
B)be placed in series in the circuit
C)have the red lead towards the negative side of the source
D)have the black lead towards the positive side of the source

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
(a)

(b)

(c)

(d)

(e)

Figure
-Identify the Rotary switch in Figure 2-1.
A)graph (a)
B)graph (b)
C)graph (c)
D)graph (d)
E)graph (e)

(b)

(c)

(d)

(e)

Figure
-Identify the Rotary switch in Figure 2-1.
A)graph (a)
B)graph (b)
C)graph (c)
D)graph (d)
E)graph (e)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
(a)

(b)

(c)

(d)

(e)

Figure
-Identify the DPDT switch in Figure 2-1.
A)graph (a)
B)graph (b)
C)graph (c)
D)graph (d)
E)graph (e)

(b)

(c)

(d)

(e)

Figure
-Identify the DPDT switch in Figure 2-1.
A)graph (a)
B)graph (b)
C)graph (c)
D)graph (d)
E)graph (e)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
(a)

(b)

(c)

(d)

(e)

Figure
-Identify the Normally Open Push Button switch in Figure 2-1.
A)graph (a)
B)graph (b)
C)graph (c)
D)graph (d)
E)graph (e)

(b)

(c)

(d)

(e)

Figure
-Identify the Normally Open Push Button switch in Figure 2-1.
A)graph (a)
B)graph (b)
C)graph (c)
D)graph (d)
E)graph (e)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
(a)

(b)

(c)

(d)

(e)

Figure
-Identify the DPST switch in Figure 2-1.
A)graph (a)
B)graph (b)
C)graph (c)
D)graph (d)
E)graph (e)

(b)

(c)

(d)

(e)

Figure
-Identify the DPST switch in Figure 2-1.
A)graph (a)
B)graph (b)
C)graph (c)
D)graph (d)
E)graph (e)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
A conductor is a material that has ________.
A)few free electrons
B)many free electrons
C)a positive charge
D)a structure similar to semiconductors
A)few free electrons
B)many free electrons
C)a positive charge
D)a structure similar to semiconductors

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
(a)

(b)

(c)

(d)

(e)

Figure
-The Rotary switch in Figure 2-1 is most likely to be used as ________.
A)a selector for differentVoltages in a power supply.
B)a range selector switch in an analogV
Oltmeter.
C)an old manual TV channel selector.
D)all of the above

(b)

(c)

(d)

(e)

Figure
-The Rotary switch in Figure 2-1 is most likely to be used as ________.
A)a selector for differentVoltages in a power supply.
B)a range selector switch in an analogV
Oltmeter.
C)an old manual TV channel selector.
D)all of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
(a)

(b)

(c)

(d)

(e)

Figure
-Which switch in Figure 2-1 could be used to switch two inputs to different output positions?
A)graph (a)
B)graph (b)
C)graph (c)
D)graph (d)
E)graph (e)

(b)

(c)

(d)

(e)

Figure
-Which switch in Figure 2-1 could be used to switch two inputs to different output positions?
A)graph (a)
B)graph (b)
C)graph (c)
D)graph (d)
E)graph (e)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
(a)

(b)

(c)

(d)

(e)

Figure
-Which switch in Figure 2-1W ould probably be used to control a light and a fan at the same time?
A)graph (a)
B)graph (b)
C)graph (c)
D)graph (d)
E)graph (e)

(b)

(c)

(d)

(e)

Figure
-Which switch in Figure 2-1W ould probably be used to control a light and a fan at the same time?
A)graph (a)
B)graph (b)
C)graph (c)
D)graph (d)
E)graph (e)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
If the current in a circuit equals 0 A, it is likely that the ________.
A)voltage is too high
B)circuit has a short
C)resistance is too low
D)circuit is open
A)voltage is too high
B)circuit has a short
C)resistance is too low
D)circuit is open

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
(a)

(b)

(c)

(d)

(e)

Figure
-Which switch in Figure 2-1 is usually used to control a doorbell?
A)graph (a)
B)graph (b)
C)graph (c)
D)graph (d)
E)graph (e)

(b)

(c)

(d)

(e)

Figure
-Which switch in Figure 2-1 is usually used to control a doorbell?
A)graph (a)
B)graph (b)
C)graph (c)
D)graph (d)
E)graph (e)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
If a resistor equals 1.2 , its color code is________
A) brown, red, silver, gold
B) brown, red, gold, gold
C) brown, black, gold, silver
D) brown, black, red, gold
A) brown, red, silver, gold
B) brown, red, gold, gold
C) brown, black, gold, silver
D) brown, black, red, gold

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
If the measured circuit current is zero, it is likely that the ________.
A)circuitVoltage isV
Ery high
B)voltage is turned off
C)circuit has a short
D)resistance isV
Ery low
A)circuitVoltage isV
Ery high
B)voltage is turned off
C)circuit has a short
D)resistance isV
Ery low

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Voltage is ________.
A)the force that exists between charged particles
B)the force that causesW
Ater to flow
C)the movement of free electrons
D)the opposition to the flow of current
A)the force that exists between charged particles
B)the force that causesW
Ater to flow
C)the movement of free electrons
D)the opposition to the flow of current

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
An ohmmeter should ________.
A)be inserted into the circuit so the current flows through it
B)have the polarity carefully checked before its use
C)be connected across a circuitW
Ith the power on
D)be placed across the resistor after the resistor has been disconnected from the circuit
A)be inserted into the circuit so the current flows through it
B)have the polarity carefully checked before its use
C)be connected across a circuitW
Ith the power on
D)be placed across the resistor after the resistor has been disconnected from the circuit

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
On a resistorW ith five bands of color code, the fifth band may represent that:
A)the resistor is a precision resistor.
B)the reliability in percentage of failure.
C)the tolerance in percentage ofV
Alue.
D)all of these.
A)the resistor is a precision resistor.
B)the reliability in percentage of failure.
C)the tolerance in percentage ofV
Alue.
D)all of these.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
Most DMMsW ill measure ________ ________ and ________.
A)frequency,Voltage, current
B)voltage, current, resistance
C)voltage, frequency, resistance
D)voltage, current, capacitance
A)frequency,Voltage, current
B)voltage, current, resistance
C)voltage, frequency, resistance
D)voltage, current, capacitance

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
Every electrical circuit must contain ________.
A)a source, a load and a path
B)a battery, a path and a switch
C)a source, a load and a resistor
D)a battery, a resistor and a capacitor
A)a source, a load and a path
B)a battery, a path and a switch
C)a source, a load and a resistor
D)a battery, a resistor and a capacitor

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
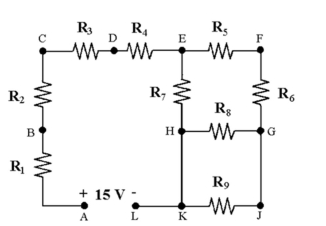
-In Figure 2-2 , the voltage VCE is the same as________
A)
B)
C)
D)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
In order to measure the current in a circuit, an ammeter must ________.
A)be placed so the current must pass through the meter
B)be placed across the load
C)be placed across the source
D)all of these
A)be placed so the current must pass through the meter
B)be placed across the load
C)be placed across the source
D)all of these

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
A 100 resistor is color coded___________
A) brown, black, yellow, gold
B) brown, black, yellow, silver
C) brown, green, black, gold
D) black, brown, yellow, silver
A) brown, black, yellow, gold
B) brown, black, yellow, silver
C) brown, green, black, gold
D) black, brown, yellow, silver

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48

-In Figure 2-2, if you place a voltmeter?s red lead on point E and its black lead on point H, youW ill be measuring ________.
A)
B)
C)
D)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
Interpret the following mixed numbers and letters 4R7 on a resistor to the correct resistance of:
A)4.7 Kilohms.
B)47 ohms.
C)4.7 Megohms.
D)4.7 ohms.
A)4.7 Kilohms.
B)47 ohms.
C)4.7 Megohms.
D)4.7 ohms.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
On a resistorW ith four bands of color code, the fourth band represents:
A)the multiplierV
Alue.
B)theVoltage rating.
C)theW
Attage rating.
D)the tolerance percentage.
A)the multiplierV
Alue.
B)theVoltage rating.
C)theW
Attage rating.
D)the tolerance percentage.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
Interpret the following mixed numbers and letters 3M3 on a resistor to the correct resistance of:
A)330 Kilohms.
B)33 Kilohms.
C)3.3 Kilohms.
D)3300 Kilohms.
A)330 Kilohms.
B)33 Kilohms.
C)3.3 Kilohms.
D)3300 Kilohms.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
A resistor with yellow, violet, orange and silver bands equals_____
A)
B)
C)
D)
A)
B)
C)
D)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
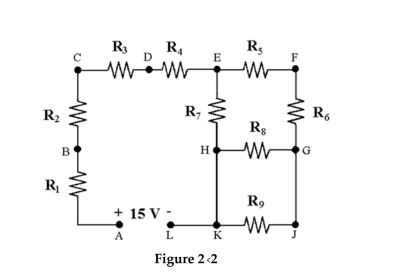
To measure the current that flows through R6 in Figure 2-2, the circuit must be opened and the ammeter placed at point ________.
A)H
B)G
C)E
D)F

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54

-In Figure 2-2 , the voltage is the same as_______
A)
B)
C)
D)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55

In Figure 2-2, the voltage VGH is the same as ________.
A)VR5
B)VR7
C)VR6
D)VR8

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
An analog meter has ________.
A)a digital readout
B)a needle and a scale to indicate theV
Alue
C)a high degree of accuracy
D)no moving parts
A)a digital readout
B)a needle and a scale to indicate theV
Alue
C)a high degree of accuracy
D)no moving parts

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57

-In Figure 2-2, a voltmeter placed across points C and D will measure_______
A)
B)
C)
D)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
A resistor with yellow, violet, orange, and gold bands equals_______
A)
B)
C)
D)
A)
B)
C)
D)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
If a resistor is color codedW ith orange, orange, orange and silver bands, the resistance equals ________, the lower tolerance limit equals ________ and the upper tolerance limit equals ________.
A)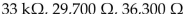
B)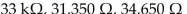
C)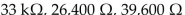
D)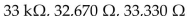
A)
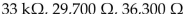
B)
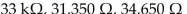
C)
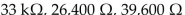
D)
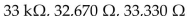

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
On a resistorW ith numbers and letters, the position of the letter in the sequence represents:
A)the tolerance.
B)the numerical total.
C)the decimal point.
D)the resistanceV
Alue.
A)the tolerance.
B)the numerical total.
C)the decimal point.
D)the resistanceV
Alue.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
In the AmericanW ire Gauge sizes, as the numerical value of AWG goes higher, the cross sectional area of theW ire:
A)doubles.
B)halves.
C)increases.
D)decreases.
A)doubles.
B)halves.
C)increases.
D)decreases.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
What is the key differenceW hen taking voltage measurementsW ith an analog meter versus a digital meter?
A)where the negative lead is placed
B)proper choice of the scale on the display
C)safety procedure in taking the measurement
D)adjustment of the scale
A)where the negative lead is placed
B)proper choice of the scale on the display
C)safety procedure in taking the measurement
D)adjustment of the scale

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
The voltage measured directly across an open switch in a circuitW ill be:
A)unpredictable.
B)half of applied Voltage.
C)0 V
D)full applied Voltage.
A)unpredictable.
B)half of applied Voltage.
C)0 V
D)full applied Voltage.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
(a)
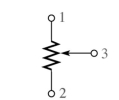
(b)
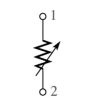
(c)
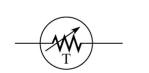
(d)
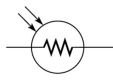
Figure
-What does the schematic symbol (b)represent in Figure 2-3?
A)photoconductive cell
B)rheostat
C)thermistor
D)potentiometer

(b)

(c)

(d)

Figure
-What does the schematic symbol (b)represent in Figure 2-3?
A)photoconductive cell
B)rheostat
C)thermistor
D)potentiometer

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
Which type of resistor is used for high power applications?
A)wireW
Ound
B)surface mount
C)carbon composition
D)film
A)wireW
Ound
B)surface mount
C)carbon composition
D)film

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
Potentiometers and rheostats differ in that:
A)potentiometers utilize linear and nonlinear tapers,wHile rheostats usually utilize only lineartapers.
B)potentiometers utilize three terminals,while rheostats usually use only two terminals.
C)potentiometers are used to vary Voltages,while rheostats vary currents.
D)all of these.
A)potentiometers utilize linear and nonlinear tapers,wHile rheostats usually utilize only lineartapers.
B)potentiometers utilize three terminals,while rheostats usually use only two terminals.
C)potentiometers are used to vary Voltages,while rheostats vary currents.
D)all of these.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
A common type of resistors are:
A)carbon-composition.
B)carbon film.
C)metal film.
D)wirewound.
A)carbon-composition.
B)carbon film.
C)metal film.
D)wirewound.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
(a)

(b)

(c)

(d)

Figure
-Which of the following is not a type of variable resistor?
A)photoconductive cell
B)thermistor
C)potentiometer
D)All are types ofV
Ariable resistors.

(b)

(c)

(d)

Figure
-Which of the following is not a type of variable resistor?
A)photoconductive cell
B)thermistor
C)potentiometer
D)All are types ofV
Ariable resistors.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
The basic difference between a fuse and a circuit breaker is that:
A)a fuse is faster.
B)a circuit breaker is more reliable.
C)a circuit breaker is reusable.
D)a fuse is reusable.
A)a fuse is faster.
B)a circuit breaker is more reliable.
C)a circuit breaker is reusable.
D)a fuse is reusable.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



