Deck 16: The South and the Slavery Controversy
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/63
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 16: The South and the Slavery Controversy
1
In society's basement in the South of 1860 were nearly ____ black human chattels.
A) 1 million
B) 2 million
C) 4 million
D) 8 million
E) none of these choices
A) 1 million
B) 2 million
C) 4 million
D) 8 million
E) none of these choices
4 million
2
Some southern slaves gained their freedom as a result of
A) the prohibition of the Atlantic slave trade after 1807.
B) purchase by northern abolitionists.
C) fleeing to mountain hideaways.
D) purchasing themselves out of slavery.
E) having been taken by their masters into free territories.
A) the prohibition of the Atlantic slave trade after 1807.
B) purchase by northern abolitionists.
C) fleeing to mountain hideaways.
D) purchasing themselves out of slavery.
E) having been taken by their masters into free territories.
purchasing themselves out of slavery.
3
The majority of southern whites owned no slaves because
A) they opposed slavery.
B) they could not afford the purchase price.
C) slavery was not profitable on small farms.
D) their racism would not allow them to work alongside African Americans.
E) they feared the possibility of slave revolts.
A) they opposed slavery.
B) they could not afford the purchase price.
C) slavery was not profitable on small farms.
D) their racism would not allow them to work alongside African Americans.
E) they feared the possibility of slave revolts.
they could not afford the purchase price.
4
Members of the planter aristocracy
A) focused on cultural gentility rather than politics.
B) dominated society and politics in the South.
C) provided democratic rule in the South.
D) promoted tax-supported public education.
E) kept up with developments in modern thought.
A) focused on cultural gentility rather than politics.
B) dominated society and politics in the South.
C) provided democratic rule in the South.
D) promoted tax-supported public education.
E) kept up with developments in modern thought.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 63 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
As a result of the introduction of the cotton gin,
A) fewer slaves were needed on the plantations.
B) the textile industry expanded in the South.
C) slavery was reinvigorated.
D) the center of cotton production shifted to Tennessee and Missouri.
E) the African slave trade was legalized.
A) fewer slaves were needed on the plantations.
B) the textile industry expanded in the South.
C) slavery was reinvigorated.
D) the center of cotton production shifted to Tennessee and Missouri.
E) the African slave trade was legalized.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 63 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
All of the following were weaknesses of the slave plantation system except that
A) it relied on a one-crop economy.
B) it repelled a large-scale European immigration.
C) it stimulated racism among poor whites.
D) it created an aristocratic political elite.
E) it was economically unprofitable.
A) it relied on a one-crop economy.
B) it repelled a large-scale European immigration.
C) it stimulated racism among poor whites.
D) it created an aristocratic political elite.
E) it was economically unprofitable.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 63 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
The great increase of the slave population in the first half of the nineteenth century was largely due to
A) the reopening of the African slave trade in 1808.
B) imports of slaves from the West Indies.
C) natural reproduction.
D) reenslavement of free blacks.
E) the deliberate "breeding" of slaves by plantation owners.
A) the reopening of the African slave trade in 1808.
B) imports of slaves from the West Indies.
C) natural reproduction.
D) reenslavement of free blacks.
E) the deliberate "breeding" of slaves by plantation owners.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 63 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Plantation owners generally treated their slaves as
A) worthless beings to be brutally whipped and beaten.
B) valuable capital assets to be used to generate profits.
C) "children" within the master's family.
D) potentially dangerous rebels.
E) a skilled labor force to be trained and educated.
A) worthless beings to be brutally whipped and beaten.
B) valuable capital assets to be used to generate profits.
C) "children" within the master's family.
D) potentially dangerous rebels.
E) a skilled labor force to be trained and educated.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 63 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
The plantation system of the Cotton South was
A) increasingly monopolized by a few large planters.
B) efficient at utilizing natural resources.
C) financially stable.
D) attractive to European immigrants.
E) unable to expand westward.
A) increasingly monopolized by a few large planters.
B) efficient at utilizing natural resources.
C) financially stable.
D) attractive to European immigrants.
E) unable to expand westward.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 63 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Most white southerners were
A) planter aristocrats.
B) small slaveowners.
C) urban mill workers.
D) "poor white trash."
E) nonslaveowning subsistence farmers.
A) planter aristocrats.
B) small slaveowners.
C) urban mill workers.
D) "poor white trash."
E) nonslaveowning subsistence farmers.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 63 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Uncle Tom's Cabin was written by
A) Susan B.Anthony.
B) Lucrecia Mott.
C) Harriet Beecher Stowe.
D) Margaret Fuller.
E) Harriet Tubman.
A) Susan B.Anthony.
B) Lucrecia Mott.
C) Harriet Beecher Stowe.
D) Margaret Fuller.
E) Harriet Tubman.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 63 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
The contingent of southerners most opposed to both the wealthy planters and African American slaves were the
A) "poor white trash."
B) mountain whites.
C) small slaveowners.
D) nonslaveowning subsistence farmers.
E) citizens of the border states.
A) "poor white trash."
B) mountain whites.
C) small slaveowners.
D) nonslaveowning subsistence farmers.
E) citizens of the border states.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 63 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Plantation agriculture was wasteful largely because
A) it relied heavily on artificial fertilizers.
B) it required leaving cropland fallow every other year.
C) excessive water was used for irrigation.
D) everything but the single crop had to be imported.
E) excessive cultivation of cotton led to "land butchery."
A) it relied heavily on artificial fertilizers.
B) it required leaving cropland fallow every other year.
C) excessive water was used for irrigation.
D) everything but the single crop had to be imported.
E) excessive cultivation of cotton led to "land butchery."

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 63 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Plantation mistresses
A) had little contact with slaves.
B) were often active in the women's rights movement.
C) frequently had moral doubts about slavery.
D) commanded a sizable household staff of mostly female slaves.
E) tended to be harsh in their treatment of slaves.
A) had little contact with slaves.
B) were often active in the women's rights movement.
C) frequently had moral doubts about slavery.
D) commanded a sizable household staff of mostly female slaves.
E) tended to be harsh in their treatment of slaves.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 63 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
European immigration to the South was discouraged by
A) competition with slave labor.
B) southern anti-Catholicism.
C) Irish antislavery groups.
D) immigration barriers enacted by southern states.
E) their inability to tolerate the hot climate.
A) competition with slave labor.
B) southern anti-Catholicism.
C) Irish antislavery groups.
D) immigration barriers enacted by southern states.
E) their inability to tolerate the hot climate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 63 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Northern attitudes toward free blacks can best be described as
A) supporting their right to full citizenship.
B) disliking the race but liking individual blacks.
C) advocating black movement into the new territories.
D) politically sympathetic but socially segregationist.
E) race prejudice, not humanitarian.
A) supporting their right to full citizenship.
B) disliking the race but liking individual blacks.
C) advocating black movement into the new territories.
D) politically sympathetic but socially segregationist.
E) race prejudice, not humanitarian.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 63 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
For free blacks living in the North,
A) the Midwest was a more hospitable place to live than New England.
B) cities were more hospitable than small towns.
C) good jobs were plentiful.
D) education opened the door to economic opportunity.
E) discrimination was common.
A) the Midwest was a more hospitable place to live than New England.
B) cities were more hospitable than small towns.
C) good jobs were plentiful.
D) education opened the door to economic opportunity.
E) discrimination was common.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 63 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
The profitable southern slave system
A) hobbled the economic development of the region as a whole.
B) saw many slaves moving to the upper South.
C) promoted economic equality among the whites.
D) relied almost totally on importing slaves to meet the unquenchable demand for labor.
E) enabled the South to afford economic and educational progress.
A) hobbled the economic development of the region as a whole.
B) saw many slaves moving to the upper South.
C) promoted economic equality among the whites.
D) relied almost totally on importing slaves to meet the unquenchable demand for labor.
E) enabled the South to afford economic and educational progress.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 63 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Plantation agriculture
A) had become largely unprofitable by the time of the Civil War.
B) succeeded in a great variety of crops and climates.
C) was financially risky and ecologically wasteful.
D) brought many immigrants to the South.
E) encouraged southern democracy.
A) had become largely unprofitable by the time of the Civil War.
B) succeeded in a great variety of crops and climates.
C) was financially risky and ecologically wasteful.
D) brought many immigrants to the South.
E) encouraged southern democracy.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 63 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
As their main crop, southern subsistence farmers raised
A) cotton.
B) tobacco.
C) corn.
D) rice.
E) sugar cane.
A) cotton.
B) tobacco.
C) corn.
D) rice.
E) sugar cane.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 63 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
William Lloyd Garrison pledged his dedication to
A) shipping freed blacks back to Africa.
B) a gradual emancipation of all southern slaves.
C) preventing the expansion of slavery beyond the South.
D) forming an antislavery political party.
E) the immediate abolition of slavery in the South.
A) shipping freed blacks back to Africa.
B) a gradual emancipation of all southern slaves.
C) preventing the expansion of slavery beyond the South.
D) forming an antislavery political party.
E) the immediate abolition of slavery in the South.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 63 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
As a substitute for the wage-incentive system, slaveowners most often used
A) the lure that slaves might eventually purchase their freedom.
B) the protection of slave families.
C) the threat of sale or family disruption.
D) whipping and flogging.
E) incentive of free time for holidays.
A) the lure that slaves might eventually purchase their freedom.
B) the protection of slave families.
C) the threat of sale or family disruption.
D) whipping and flogging.
E) incentive of free time for holidays.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 63 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Most African American slaves were raised
A) without the benefit of a stable home life.
B) never knowing anything about their relatives.
C) without religion.
D) knowing both African languages and English.
E) in stable two-parent households.
A) without the benefit of a stable home life.
B) never knowing anything about their relatives.
C) without religion.
D) knowing both African languages and English.
E) in stable two-parent households.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 63 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
The idea of transporting blacks back to Africa was
A) a recognition of blacks' desire to preserve their culture.
B) never carried out.
C) advocated by Frederick Douglass.
D) proposed by the African nation of Liberia.
E) an expression of widespread American racism.
A) a recognition of blacks' desire to preserve their culture.
B) never carried out.
C) advocated by Frederick Douglass.
D) proposed by the African nation of Liberia.
E) an expression of widespread American racism.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 63 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Those in the North who opposed the abolitionists believed that these opponents of slavery
A) were creating disorder in America.
B) were defending the American way of life.
C) deserved the right to speak freely.
D) had turned their backs on religion.
E) were undermining fundamental American beliefs.
A) were creating disorder in America.
B) were defending the American way of life.
C) deserved the right to speak freely.
D) had turned their backs on religion.
E) were undermining fundamental American beliefs.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 63 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Which one of the following has least in common with the other four?
A) Nat Turner
B) David Walker
C) Crispus Attucks
D) Denmark Vesey
E) Gabriel
A) Nat Turner
B) David Walker
C) Crispus Attucks
D) Denmark Vesey
E) Gabriel

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 63 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
As a result of white southerners' brutal treatment of their slaves and their fear of potential slave rebellions, the South
A) formed alliances with white imperialists in Africa.
B) began demanding federal military protection of the "peculiar institution."
C) began discussing sending blacks back to Africa.
D) started turning its back on Christianity.
E) developed a theory of biological racial superiority.
A) formed alliances with white imperialists in Africa.
B) began demanding federal military protection of the "peculiar institution."
C) began discussing sending blacks back to Africa.
D) started turning its back on Christianity.
E) developed a theory of biological racial superiority.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 63 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
In some counties of the deep South, especially along the lower Mississippi River, blacks accounted for more than ____ percent of the population.
A) 25
B) 50
C) 75
D) 90
E) none of these choices
A) 25
B) 50
C) 75
D) 90
E) none of these choices

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 63 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
In the pre-Civil War South, the most uncommon and least successful form of slave resistance was
A) feigned laziness.
B) sabotage of plantation equipment.
C) running away.
D) armed insurrection.
E) stealing food and other goods.
A) feigned laziness.
B) sabotage of plantation equipment.
C) running away.
D) armed insurrection.
E) stealing food and other goods.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 63 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Slavery's greatest psychological horror, which served as the theme of Harriet Beecher Stowe's Uncle Tom's Cabin, was
A) the forced separation of families in slave auctions.
B) slaveowners' frequent use of the whip.
C) the deliberate "breeding" of slave women.
D) the isolation of slaves on remote frontier plantations.
E) forcible sexual assault by slaveowners.
A) the forced separation of families in slave auctions.
B) slaveowners' frequent use of the whip.
C) the deliberate "breeding" of slave women.
D) the isolation of slaves on remote frontier plantations.
E) forcible sexual assault by slaveowners.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 63 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Arrange the following in chronological order: the founding of the (A) American Colonization Society, (B) American Anti-Slavery Society, (C) Liberty party.
A) A, B, C
B) C, A, B
C) B, C, A
D) A, C, B
E) C, B, A
A) A, B, C
B) C, A, B
C) B, C, A
D) A, C, B
E) C, B, A

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 63 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
By 1860, slaves were concentrated in the
A) border states of Delaware, Kentucky, Missouri, and Maryland.
B) Deep South states of South Carolina, Georgia, Alabama, Mississippi, and Louisiana.
C) Atlantic coast states of Virginia, North Carolina, and Florida.
D) new Southwest states of Texas, Arkansas, and Indian Territory.
E) mountain regions of Tennessee, West Virginia, and Kentucky.
A) border states of Delaware, Kentucky, Missouri, and Maryland.
B) Deep South states of South Carolina, Georgia, Alabama, Mississippi, and Louisiana.
C) Atlantic coast states of Virginia, North Carolina, and Florida.
D) new Southwest states of Texas, Arkansas, and Indian Territory.
E) mountain regions of Tennessee, West Virginia, and Kentucky.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 63 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Many abolitionists turned to political action in 1840 when they backed the presidential candidate of the
A) Free Soil party.
B) Republican party.
C) Know-Nothing party.
D) Liberty party.
E) Anti-Mason party.
A) Free Soil party.
B) Republican party.
C) Know-Nothing party.
D) Liberty party.
E) Anti-Mason party.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 63 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
The voice of white southern abolitionism fell silent at the beginning of the
A) 1790s.
B) 1820s.
C) 1830s.
D) 1840s.
E) 1850s.
A) 1790s.
B) 1820s.
C) 1830s.
D) 1840s.
E) 1850s.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 63 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Match each abolitionist below with his role in the movement. 
A) A-4, B-2, C-l, D-3
B) A-3, B-4, C-2, D-1
C) A-1, B-3, C-4, D-2
D) A-2, B-1, C-4, D-3
E) A-3, B-2, C-1, D-4

A) A-4, B-2, C-l, D-3
B) A-3, B-4, C-2, D-1
C) A-1, B-3, C-4, D-2
D) A-2, B-1, C-4, D-3
E) A-3, B-2, C-1, D-4

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 63 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
All of the following were characteristics of slaves in the mid-nineteenth century United States except
A) slaves had no civil or political rights.
B) slaves usually toiled from dawn to dusk in the fields.
C) they had minimal protection from murder or unusually cruel punishment.
D) slaves were forbidden to testify in court and their marriages were not legal.
E) floggings were very uncommon and rare.
A) slaves had no civil or political rights.
B) slaves usually toiled from dawn to dusk in the fields.
C) they had minimal protection from murder or unusually cruel punishment.
D) slaves were forbidden to testify in court and their marriages were not legal.
E) floggings were very uncommon and rare.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 63 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
"Varying Viewpoints" notes that Ulrich B.Phillips, in his book American Negro Slavery (1918) made certain claims about slavery that have been challenged in recent years.Which of the following is not one of his conclusions?
A) Slaves were racially inferior.
B) Slavery was an unprofitable economic institution.
C) Planters treated their slaves with kindly paternalism.
D) Slaves were passive by nature and did not abhor slavery.
E) Slavery was comparable to the Nazi concentration camps.
A) Slaves were racially inferior.
B) Slavery was an unprofitable economic institution.
C) Planters treated their slaves with kindly paternalism.
D) Slaves were passive by nature and did not abhor slavery.
E) Slavery was comparable to the Nazi concentration camps.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 63 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Match each abolitionist below with his publication. 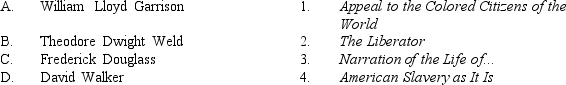
A) A-4, B-1, C-3, D-2
B) A-2, B-4, C-3, D-1
C) A-3, B-2, C-4, D-1
D) A-1, B-3, C-2, D-4
E) A-4, B-2, C-1, D-3
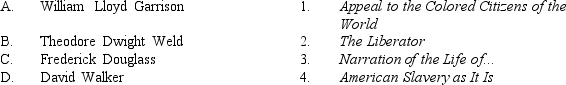
A) A-4, B-1, C-3, D-2
B) A-2, B-4, C-3, D-1
C) A-3, B-2, C-4, D-1
D) A-1, B-3, C-2, D-4
E) A-4, B-2, C-1, D-3

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 63 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Slaves fought the system of slavery in all of the following ways except by
A) slowing down the work pace.
B) conducting periodic successful slave rebellions.
C) sabotaging expensive equipment.
D) pilfering goods that their labor had produced.
E) running away from their masters.
A) slowing down the work pace.
B) conducting periodic successful slave rebellions.
C) sabotaging expensive equipment.
D) pilfering goods that their labor had produced.
E) running away from their masters.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 63 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
After 1830, southerners increasingly argued that
A) slavery was a positive good endorsed by the Bible and Aristotle.
B) slavery was morally problematic but economically necessary.
C) slavery could not be ended because emancipation would deepen racial conflict.
D) poorer whites as well as blacks could be enslaved.
E) leading European intellectuals accepted slavery on racial grounds.
A) slavery was a positive good endorsed by the Bible and Aristotle.
B) slavery was morally problematic but economically necessary.
C) slavery could not be ended because emancipation would deepen racial conflict.
D) poorer whites as well as blacks could be enslaved.
E) leading European intellectuals accepted slavery on racial grounds.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 63 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
Compare and contrast the ways in which African Americans respond to life under slavery? How did they manage to maintain dignity and culture under such conditions?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 63 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Until the eve of the Civil War, most people in the North
A) believed that the Constitution sanctioned slavery.
B) felt that they had little economic stake in slavery one way or the other.
C) were alarmed by the radicalism of abolitionists like William Lloyd Garrison.
D) expected that slavery would be abolished through gradual emancipation.
E) believed that Christianity and slavery were incompatible.
A) believed that the Constitution sanctioned slavery.
B) felt that they had little economic stake in slavery one way or the other.
C) were alarmed by the radicalism of abolitionists like William Lloyd Garrison.
D) expected that slavery would be abolished through gradual emancipation.
E) believed that Christianity and slavery were incompatible.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 63 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
What were the benefits and costs of the cotton plantation system for the pre-Civil War South?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 63 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
Some have argued that slavery in the southern United States, unlike that in some other countries, was characterized more by an attitude of "paternalism" than by raw exploitation and frequent violence (as was common in some slave countries).What arguments are there for this perspective? What criticisms would you make of such an argument?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 63 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Cotton became important to the prosperity of the North as well as the South because
A) about three-fourths of the southern cotton crop was sold to New England textile mills.
B) northern merchants handled the shipping of southern cotton.
C) cotton accounted for about half the value of all United States exports after 1840.
D) northern farmers profited from selling their foodstuffs to feed southern slaves.
E) northern investors and commodities traders controlled the cotton futures markets.
A) about three-fourths of the southern cotton crop was sold to New England textile mills.
B) northern merchants handled the shipping of southern cotton.
C) cotton accounted for about half the value of all United States exports after 1840.
D) northern farmers profited from selling their foodstuffs to feed southern slaves.
E) northern investors and commodities traders controlled the cotton futures markets.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 63 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
After 1830, the abolitionist movement took a new, more energetic tone, encouraged by the
A) British abolition of slavery in the British West Indies.
B) religious spirit of the Second Great Awakening.
C) success of the American Colonization Society.
D) growing movement of voluntary emancipation by slave masters.
E) growing political strength of the antislavery Liberty party.
A) British abolition of slavery in the British West Indies.
B) religious spirit of the Second Great Awakening.
C) success of the American Colonization Society.
D) growing movement of voluntary emancipation by slave masters.
E) growing political strength of the antislavery Liberty party.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 63 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
Before the Civil War, free blacks
A) were far more numerous in the North than in the South.
B) were often the mulatto offspring of white fathers and black mothers.
C) were often forbidden basic civil rights.
D) found their greatest friends and sympathizers among poor Irish immigrants.
E) were disliked in the North as well as the South.
A) were far more numerous in the North than in the South.
B) were often the mulatto offspring of white fathers and black mothers.
C) were often forbidden basic civil rights.
D) found their greatest friends and sympathizers among poor Irish immigrants.
E) were disliked in the North as well as the South.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 63 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
What was the relationship between slavery and racism in the pre-Civil War South? What did the existence of free blacks reveal about the character of American attitudes in both North and South?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 63 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
African American culture under slavery was characterized by
A) single mothers raising families without fathers.
B) frequent marriage between close relatives.
C) a form of evangelical Christianity with strong African influences.
D) widespread illiteracy among slaves.
E) subtle forms of resistance to slavery.
A) single mothers raising families without fathers.
B) frequent marriage between close relatives.
C) a form of evangelical Christianity with strong African influences.
D) widespread illiteracy among slaves.
E) subtle forms of resistance to slavery.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 63 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
The South's "positive good" argument for slavery claimed that
A) slavery was supported by the authority of both the Bible and the Constitution.
B) slavery was good for Africans because it had introduced them to Christianity.
C) slaves benefited from receiving education and job training.
D) slaves were usually treated as members of the family.
E) slaves were better off than most northern wage earners.
A) slavery was supported by the authority of both the Bible and the Constitution.
B) slavery was good for Africans because it had introduced them to Christianity.
C) slaves benefited from receiving education and job training.
D) slaves were usually treated as members of the family.
E) slaves were better off than most northern wage earners.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 63 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
Compare and contrast the "moral abolitionism" of William Lloyd Garrison (and others) and the more political abolitionism advocated by Frederick Douglass and the Liberty, Free Soil, and Republican parties.What were the advantages and disadvantages of each position as efforts to contain or end slavery?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 63 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
Explain why the "Gag Resolution" symbolized the threat that slavery constituted for all Americans, North and South.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 63 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
The pre-Civil War South was characterized by
A) political domination by a planter oligarchy.
B) the lack of free, tax-supported public education.
C) a widening gap between rich and poor.
D) plantation mistresses who ran large slave households.
E) a dependence on northern and European manufactured goods.
A) political domination by a planter oligarchy.
B) the lack of free, tax-supported public education.
C) a widening gap between rich and poor.
D) plantation mistresses who ran large slave households.
E) a dependence on northern and European manufactured goods.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 63 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
Assess the validity of the following statement, "slaves were better off than both wage earners in northern industry and free blacks back in Africa."

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 63 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
To what extent did the existence of slavery shape the entire social structure and culture of the South? Why did slavery so deeply affect even the vast majority of southerners who held no slaves?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 63 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
Slaves were
A) regarded by their owners primarily as financial investments.
B) the primary form of wealth in the South.
C) profitable for their owners.
D) exploited in the most difficult and dangerous jobs.
E) denied any kind of family life.
A) regarded by their owners primarily as financial investments.
B) the primary form of wealth in the South.
C) profitable for their owners.
D) exploited in the most difficult and dangerous jobs.
E) denied any kind of family life.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 63 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
Even those who did not own slaves in the pre-Civil War South supported that institution because they
A) dreamed of one day owning slaves themselves.
B) presumed themselves racially superior to black slaves.
C) were almost always economically better off than the slaves.
D) admired the virtues and values of the plantation aristocracy.
E) benefited from the economic growth of the region.
A) dreamed of one day owning slaves themselves.
B) presumed themselves racially superior to black slaves.
C) were almost always economically better off than the slaves.
D) admired the virtues and values of the plantation aristocracy.
E) benefited from the economic growth of the region.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 63 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
How did slavery affect both white and black families in the South? What justification was there for the saying that southerners liked blacks personally even while looking down on the race?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 63 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
The South became the Cotton Kingdom in the early nineteenth century because of
A) Eli Whitney's invention of the cotton gin.
B) the new profitability of short-staple cotton.
C) the opening of rich river bottomlands in the Gulf Coast states.
D) the eradication of the boll weevil.
E) the growth of textile production in the region.
A) Eli Whitney's invention of the cotton gin.
B) the new profitability of short-staple cotton.
C) the opening of rich river bottomlands in the Gulf Coast states.
D) the eradication of the boll weevil.
E) the growth of textile production in the region.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 63 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
What explains the outburst of abolitionism after about 1830? Could slavery have been abolished peacefully before that time?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 63 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
Why did the North, on the whole, react negatively to the radical abolitionists? Did the abolitionist arguments really affect northern public opinion?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 63 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
Based on "Varying Viewpoints," discuss how new perspectives, including women's history, have altered the understanding of actual human relationships under slavery.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 63 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
Was the southern "positive good" argument for slavery essentially a guilty and defensive response to abolitionist attack? Or were southerners convinced that slavery was a moral and benevolent institution?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 63 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



