Deck 5: Elasticity of Demand and Supply
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/86
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 5: Elasticity of Demand and Supply
1
) 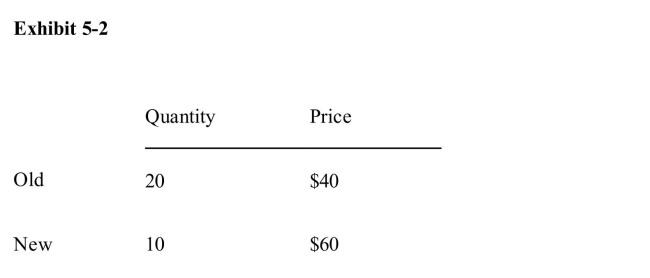 Based on the information in Exhibit 52, the demand for the good is__________ and an increase in price from $40 to $60 per unit will__________ total revenue.
Based on the information in Exhibit 52, the demand for the good is__________ and an increase in price from $40 to $60 per unit will__________ total revenue.
A)unit elastic; increase
B)elastic; decrease
C)unit elastic; not change
D)inelastic; increase
E)elastic; decrease
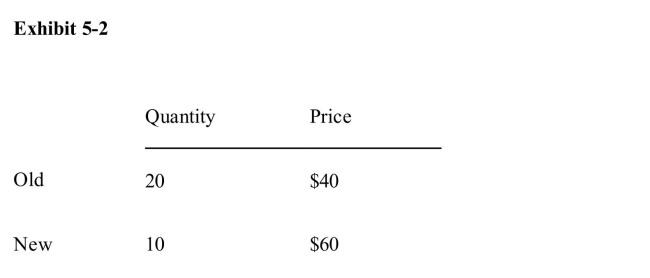 Based on the information in Exhibit 52, the demand for the good is__________ and an increase in price from $40 to $60 per unit will__________ total revenue.
Based on the information in Exhibit 52, the demand for the good is__________ and an increase in price from $40 to $60 per unit will__________ total revenue.A)unit elastic; increase
B)elastic; decrease
C)unit elastic; not change
D)inelastic; increase
E)elastic; decrease
B
2
The general term elasticity refers to a relationship between
A)quantity demanded and price only
B)quantity supplied and price only
C)quantity supplied or demanded and price only
D)quantity supplied or demanded and anything other than price
E)percentage changes in any two variables
A)quantity demanded and price only
B)quantity supplied and price only
C)quantity supplied or demanded and price only
D)quantity supplied or demanded and anything other than price
E)percentage changes in any two variables
E
3
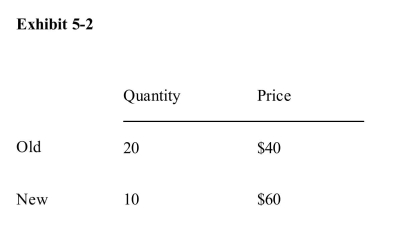 Use the information in Exhibit 52 to calculate the value of price elasticityof demand.
Use the information in Exhibit 52 to calculate the value of price elasticityof demand.A)2/3
B)1/3
C)3/5
D)5/3
E)0
D
4
The midpoint price between $20 and $40 is
A)$10
B)$20
C)$30
D)$15
E)$200
A)$10
B)$20
C)$30
D)$15
E)$200

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 86 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
)Elasticity is always
A)measured in dollars
B)measured in dollars per unit of quantity
C)measured in units of quantity
D)measured in units of quantity per dollar
E)independent of the units of measurement
A)measured in dollars
B)measured in dollars per unit of quantity
C)measured in units of quantity
D)measured in units of quantity per dollar
E)independent of the units of measurement

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 86 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
In calculating price elasticity of demand, which of the following is assumedto be constant?
A)the price of the product itself
B)the quantity demanded of the product
C)total revenue received from the sale of the product
D)the prices of all other products
E)none of the above
A)the price of the product itself
B)the quantity demanded of the product
C)total revenue received from the sale of the product
D)the prices of all other products
E)none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 86 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Elasticity measures
A)whether a price increase causes quantity demanded to increase or decrease
B)the strength of an economy's tendency to recover from recession
C)the responsiveness of decision makers to changes in prices, income, or other variables
D)the profitability of investment in an industry
E)the longrun flexibility of prices in the economy
A)whether a price increase causes quantity demanded to increase or decrease
B)the strength of an economy's tendency to recover from recession
C)the responsiveness of decision makers to changes in prices, income, or other variables
D)the profitability of investment in an industry
E)the longrun flexibility of prices in the economy

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 86 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
If the price of PepsiCola increases from 40 cents to 50 cents per can andthe quantity demanded decreases from 100 cans to 50 cans, then, accordingto the midpoint formula, the value of price elasticity of demand for PepsiCola is
A)0.5
B)0.25
C)1
D)3
E)2
A)0.5
B)0.25
C)1
D)3
E)2

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 86 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Price elasticity of demand is typically negative because
A)as price decreases, quantity demanded decreases
B)as price decreases, quantity demanded increases
C)as price decreases, demand decreases
D)as price decreases, demand increases
E)consumers rarely respond to a change in price
A)as price decreases, quantity demanded decreases
B)as price decreases, quantity demanded increases
C)as price decreases, demand decreases
D)as price decreases, demand increases
E)consumers rarely respond to a change in price

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 86 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
"More elastic" means
A)unchanging
B)less desirable
C)more desirable
D)less responsive
E)more responsive
A)unchanging
B)less desirable
C)more desirable
D)less responsive
E)more responsive

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 86 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
The midpoint quantity between 100 and 300 units is
A)100 units
B)200 units
C)300 units
D)150 units
E)20,000 units
A)100 units
B)200 units
C)300 units
D)150 units
E)20,000 units

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 86 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
When quantity is measured in gallons, the price elasticity of demand formilk will be __________ the price elasticity when quantity is measured inquarts.
A)the same as
B)four times
C)one quarter
D)two times
E)less than
A)the same as
B)four times
C)one quarter
D)two times
E)less than

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 86 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
The price elasticity of demand is equal to the slope of the demand curve.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 86 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
If a $1 increase in price leads to a 3unit decrease in quantity demanded,then demand must be elastic.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 86 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Price elasticity of demand is useful because it measures __________responsiveness to changes in __________.
A)taxpayers'; demand
B)producers'; supply
C)consumers'; price
D)consumers'; demand
E)producers'; income
A)taxpayers'; demand
B)producers'; supply
C)consumers'; price
D)consumers'; demand
E)producers'; income

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 86 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
If the value of the price elasticity of demand is 0.2, this means that a
A)20 percent decrease in price causes a 1 percent increase in quantity demanded
B)0.2 percent decrease in price causes a 1 percent increase in quantity demanded
C)5 percent decrease in price causes a 1 percent increase in quantity demanded
D)0.2 percent decrease in price causes a 0.2 percent increase in quantity demanded
E)100 percent decrease in price causes a 200 percent increase in quantity demanded
A)20 percent decrease in price causes a 1 percent increase in quantity demanded
B)0.2 percent decrease in price causes a 1 percent increase in quantity demanded
C)5 percent decrease in price causes a 1 percent increase in quantity demanded
D)0.2 percent decrease in price causes a 0.2 percent increase in quantity demanded
E)100 percent decrease in price causes a 200 percent increase in quantity demanded

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 86 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
If an increase in the price of a product from $1 to $2 per unit leads to adecrease in the quantity demanded from 100 to 80 units, then the value ofprice elasticity of demand is
A)elastic
B)inelastic
C)unit elastic
D)suggestive of an inferior good
E)equal to 20
A)elastic
B)inelastic
C)unit elastic
D)suggestive of an inferior good
E)equal to 20

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 86 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
A good synonym for elasticity would be
A)stability
B)volatility
C)stickiness
D)demand
E)responsiveness
A)stability
B)volatility
C)stickiness
D)demand
E)responsiveness

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 86 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Another word for elasticity is
A)responsiveness
B)happiness
C)bonus
D)profit
E)surplus
A)responsiveness
B)happiness
C)bonus
D)profit
E)surplus

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 86 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
The price elasticity of demand helps determine the effect of price changeson a firm's
A)property taxes
B)profits
C)quantity supplied
D)revenues
E)total costs
A)property taxes
B)profits
C)quantity supplied
D)revenues
E)total costs

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 86 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Unit elastic demand occurs when
A)a oneunit increase in price leads to a oneunit decrease in quantity demanded
B)a 1% increase in price leads to a oneunit decrease in quantity demanded
C)price elasticity of demand is positive
D)price elasticity of demand is exactly zero
E)price elasticity of demand is exactly 1
A)a oneunit increase in price leads to a oneunit decrease in quantity demanded
B)a 1% increase in price leads to a oneunit decrease in quantity demanded
C)price elasticity of demand is positive
D)price elasticity of demand is exactly zero
E)price elasticity of demand is exactly 1

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 86 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Demand is unit elastic whenever
A)price elasticity has an absolute value of 1
B)price elasticity has an absolute value greater than 1
C)price elasticity has an absolute value less than 1
D)price elasticity is negative
E)consumers always respond to a onedollar change in price by decreasing their quantity demanded by one
Unit
A)price elasticity has an absolute value of 1
B)price elasticity has an absolute value greater than 1
C)price elasticity has an absolute value less than 1
D)price elasticity is negative
E)consumers always respond to a onedollar change in price by decreasing their quantity demanded by one
Unit

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 86 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
The price elasticity of demand
A)is of no use to producers
B)tells producers what will happen to total profit if they change product price
C)tells producers what will happen to quantity supplied if they change product price
D)tells producers what will happen to total revenue if they change product price
E)tells producers what will happen to price in the following time period
A)is of no use to producers
B)tells producers what will happen to total profit if they change product price
C)tells producers what will happen to quantity supplied if they change product price
D)tells producers what will happen to total revenue if they change product price
E)tells producers what will happen to price in the following time period

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 86 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
As price decreases along a linear demand curve, price elasticity of demanddecreases.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 86 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Demand is inelastic if
A)the percentage change in price is greater than the percentage change in quantity demanded
B)the percentage change in price is less than the percentage change in quantity demanded
C)the percentage change in price is equal to the percentage change in quantity demanded
D)the value of price elasticity is equal to 1
E)the value of price elasticity is less than 1
A)the percentage change in price is greater than the percentage change in quantity demanded
B)the percentage change in price is less than the percentage change in quantity demanded
C)the percentage change in price is equal to the percentage change in quantity demanded
D)the value of price elasticity is equal to 1
E)the value of price elasticity is less than 1

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 86 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Demand is inelastic only if
A)price elasticity has an absolute value of 1
B)price elasticity has an absolute value greater than 1
C)price elasticity has an absolute value less than 1
D)price elasticity is negative
E)consumers do not respond to a change in price
A)price elasticity has an absolute value of 1
B)price elasticity has an absolute value greater than 1
C)price elasticity has an absolute value less than 1
D)price elasticity is negative
E)consumers do not respond to a change in price

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 86 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
If the price of PepsiCola increases from 50 cents to 60 cents per can andthe quantity demanded decreases from 100 cans to 50 cans, then the demandfor PepsiCola is
A)unit elastic
B)perfectly elastic
C)perfectly inelastic
D)relatively elastic
E)relatively inelastic
A)unit elastic
B)perfectly elastic
C)perfectly inelastic
D)relatively elastic
E)relatively inelastic

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 86 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
If demand is elastic, a decrease in price leads to a decrease in totalrevenue.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 86 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Suppose that you allow yourself $50 per month to spend on compact disks.You spend exactly this much every month regardless of the price ofcompact disks.Therefore, your demand for CDs
A)is elastic
B)is inelastic
C)is unit elastic
D)cannot be characterized unless we know the price of a disk
E)cannot be characterized unless we know the price and quantity of compact disks purchased
A)is elastic
B)is inelastic
C)is unit elastic
D)cannot be characterized unless we know the price of a disk
E)cannot be characterized unless we know the price and quantity of compact disks purchased

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 86 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
If demand is inelastic, the percentage change in price is greater than theresulting percentage change in quantity demanded.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 86 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
If a 5% increase in price leads to an 8% decrease in quantity demanded,demand is
A)perfectly elastic
B)elastic
C)unit elastic
D)inelastic
E)perfectly inelastic
A)perfectly elastic
B)elastic
C)unit elastic
D)inelastic
E)perfectly inelastic

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 86 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
) 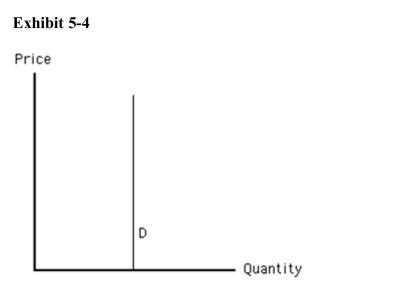 What is the price elasticity of demand in Exhibit 54?
What is the price elasticity of demand in Exhibit 54?
A)0
B)1
C)negative infinity
D)1
E)100
 What is the price elasticity of demand in Exhibit 54?
What is the price elasticity of demand in Exhibit 54?A)0
B)1
C)negative infinity
D)1
E)100

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 86 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Price elasticity of demand is calculated as
A)the percentage change in quantity demanded divided by the percentage change in price
B)the percentage change in price divided by the percentage change in quantity demanded
C)the absolute change in quantity demanded divided by the absolute change in price
D)the absolute change in price divided by the absolute change in quantity demanded
E)none of the above
A)the percentage change in quantity demanded divided by the percentage change in price
B)the percentage change in price divided by the percentage change in quantity demanded
C)the absolute change in quantity demanded divided by the absolute change in price
D)the absolute change in price divided by the absolute change in quantity demanded
E)none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 86 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Total revenue is the same for every pricequantity combination along a unitelastic demand curve.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 86 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
If an increase in the price of a product from $1 to $2 per unit leads to adecrease in the quantity demanded from 100 to 80 units, then the value ofprice elasticity of demand is
A)1/3
B)2 1/3
C)1/4
D)3
E)2/3
A)1/3
B)2 1/3
C)1/4
D)3
E)2/3

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 86 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
A perfectly elastic demand curve is
A)a vertical straight line
B)a horizontal straight line
C)a downwardsloping straight line
D)an upwardsloping straight line
E)not a straight line
A)a vertical straight line
B)a horizontal straight line
C)a downwardsloping straight line
D)an upwardsloping straight line
E)not a straight line

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 86 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
If a firm facing a perfectly elastic demand curve raises its price,
A)it will still sell exactly the same amount of output as it did at the lower price
B)it will lose some, but not all, of its sales
C)its sales will decrease to zero
D)its sales will increase
E)it is impossible to predict what will happen to its sales
A)it will still sell exactly the same amount of output as it did at the lower price
B)it will lose some, but not all, of its sales
C)its sales will decrease to zero
D)its sales will increase
E)it is impossible to predict what will happen to its sales

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 86 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Demand is elastic whenever
A)price elasticity has an absolute value of 1
B)price elasticity has an absolute value greater than 1
C)price elasticity has an absolute value less than 1
D)price elasticity is negative
E)consumers respond to a change in price
A)price elasticity has an absolute value of 1
B)price elasticity has an absolute value greater than 1
C)price elasticity has an absolute value less than 1
D)price elasticity is negative
E)consumers respond to a change in price

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 86 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
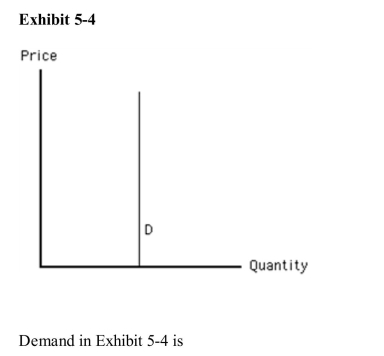
A)unit elastic
B)somewhat elastic
C)perfectly elastic
D)somewhat inelastic
E)perfectly inelastic

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 86 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
If an increase in the price of a product from $100 to $200 per unit leads to adecrease in the quantity demanded from 10 to 8 units, then demand is
A)elastic
B)inelastic
C)unit elastic
D)0
E)inferior
A)elastic
B)inelastic
C)unit elastic
D)0
E)inferior

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 86 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
If the demand for ptyalin is unit elastic, then
A)total revenue decreases as quantity demanded increases
B)total revenue increases as quantity demanded increases
C)total revenue increases as price increases
D)total revenue remains constant as price increases
E)total revenue decreases as price increases
A)total revenue decreases as quantity demanded increases
B)total revenue increases as quantity demanded increases
C)total revenue increases as price increases
D)total revenue remains constant as price increases
E)total revenue decreases as price increases

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 86 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
The absolute value of the price elasticity of demand at the midpoint of alinear demand curve is always
A)greater than one
B)less than one
C)one
D)zero
E)infinity
A)greater than one
B)less than one
C)one
D)zero
E)infinity

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 86 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
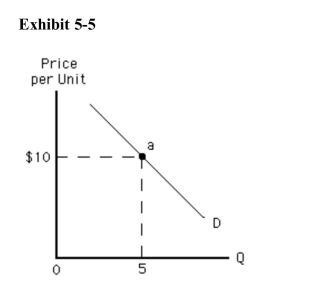 In Exhibit 55, what is the total revenue at point a?
In Exhibit 55, what is the total revenue at point a?A)$4
B)$5
C)$10
D)$50
E)$100

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 86 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
If the demand for swordfish is price elastic and the price of swordfishincreases, then
A)the quantity of swordfish demanded will increase
B)the total revenue from swordfish sales will decrease
C)the total revenue from swordfish sales will increase
D)the total revenue from swordfish sales will not change
E)whether total revenue rises or falls depends on how much the price of swordfish increases
A)the quantity of swordfish demanded will increase
B)the total revenue from swordfish sales will decrease
C)the total revenue from swordfish sales will increase
D)the total revenue from swordfish sales will not change
E)whether total revenue rises or falls depends on how much the price of swordfish increases

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 86 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Along a linear demand curve,
A)both the slope and price elasticity are constant
B)the price elasticity is constant, but the slope varies
C)total revenues are constant
D)the slope is constant, but the price elasticity varies
E)total revenues are negative
A)both the slope and price elasticity are constant
B)the price elasticity is constant, but the slope varies
C)total revenues are constant
D)the slope is constant, but the price elasticity varies
E)total revenues are negative

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 86 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
If the administration raises tuition on our campus in order to increaserevenue, it will
A)not be successful if the demand curve slopes downward
B)be successful if demand is elastic
C)be successful if demand is inelastic
D)be successful if supply is elastic
E)be successful if supply is inelastic
A)not be successful if the demand curve slopes downward
B)be successful if demand is elastic
C)be successful if demand is inelastic
D)be successful if supply is elastic
E)be successful if supply is inelastic

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 86 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
Wheat farmers in Kansas would benefit from a devastating crop failure inNorth Dakota (another major wheatproducing state) if the U.S.demand forwheat is
A)inelastic
B)elastic
C)unit elastic
D)downward sloping
E)perfectly elastic
A)inelastic
B)elastic
C)unit elastic
D)downward sloping
E)perfectly elastic

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 86 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
Which of the following describes a situation in which demand must beelastic?
A)Total revenue increases by 15 percent when the price of corndogs rises by 15 percent.
B)Total revenue increases by less than 15 percent when the price of corndogs rises by 15 percent.
C)Total revenue decreases by more than 15 percent when the price of corndogs rises by 15 percent.
D)Total revenue increases by $15 when the price of corndogs rises by $15.
E)Total revenue increases by more than $15 when the price of corndogs rises by $15.
A)Total revenue increases by 15 percent when the price of corndogs rises by 15 percent.
B)Total revenue increases by less than 15 percent when the price of corndogs rises by 15 percent.
C)Total revenue decreases by more than 15 percent when the price of corndogs rises by 15 percent.
D)Total revenue increases by $15 when the price of corndogs rises by $15.
E)Total revenue increases by more than $15 when the price of corndogs rises by $15.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 86 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
The total revenue from selling trucks is equal to
A)the price of a truck times the quantity sold
B)the change in quantity sold divided by the change in price
C)average cost times quantity produced
D)the price of a truck times the quantity produced
E)the price of a truck times the price elasticity of demand
A)the price of a truck times the quantity sold
B)the change in quantity sold divided by the change in price
C)average cost times quantity produced
D)the price of a truck times the quantity produced
E)the price of a truck times the price elasticity of demand

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 86 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
Elasticity rises as price falls along a linear, downwardsloping demandcurve.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 86 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
John spends exactly the same dollar amount on candy bars each week,regardless of their price.John's demand curve for candy bars is
A)upwardsloping
B)backwardbending
C)perfectly inelastic
D)perfectly elastic
E)unit elastic
A)upwardsloping
B)backwardbending
C)perfectly inelastic
D)perfectly elastic
E)unit elastic

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 86 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
If a price reduction leads to larger total revenue, demand is
A)perfectly inelastic
B)inelastic
C)unit elastic
D)elastic
E)perfectly elastic
A)perfectly inelastic
B)inelastic
C)unit elastic
D)elastic
E)perfectly elastic

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 86 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
Along a linear demand curve, as the price increases from zero,
A)demand decreases
B)demand increases
C)quantity demanded increases
D)total revenue first increases but eventually decreases
E)total revenue first decreases but eventually increases
A)demand decreases
B)demand increases
C)quantity demanded increases
D)total revenue first increases but eventually decreases
E)total revenue first decreases but eventually increases

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 86 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
Price elasticity is unit elastic at the midpoint of a linear, downwardslopingdemand curve.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 86 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
If the price of PepsiCola increases from 50 cents to 60 cents per can andthe quantity demanded decreases from 100 cans to 50 cans, then the PepsiCola Company could increase its total revenue by
A)lowering price
B)decreasing quantity supplied
C)leaving price the same
D)raising price
E)decreasing supply
A)lowering price
B)decreasing quantity supplied
C)leaving price the same
D)raising price
E)decreasing supply

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 86 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
If the demand for a product is price inelastic,
A)producers' revenues will increase if supply increases
B)producers' revenues will increase if supply decreases
C)a small change in price will cause a large shift in the demand curve
D)a large change in price will cause a small shift in the demand curve
E)a small change in price will cause a small shift in the demand curve
A)producers' revenues will increase if supply increases
B)producers' revenues will increase if supply decreases
C)a small change in price will cause a large shift in the demand curve
D)a large change in price will cause a small shift in the demand curve
E)a small change in price will cause a small shift in the demand curve

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 86 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
If demand is price elastic, total revenue is
A)directly related to quantity demanded
B)inversely related to quantity demanded
C)directly related to price
D)directly related to price and inversely related to quantity demanded
E)not related to either price or to quantity demanded
A)directly related to quantity demanded
B)inversely related to quantity demanded
C)directly related to price
D)directly related to price and inversely related to quantity demanded
E)not related to either price or to quantity demanded

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 86 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
Which of the following describes a situation in which demand must beinelastic?
A)Total revenue decreases by 10 percent when the price of spats rises by 10 percent.
B)Total revenue decreases by less than 10 percent when the price of spats rises by 10 percent.
C)Total revenue increases by more than 10 percent when the price of spats rises by 10 percent.
D)Total revenue decreases by $10 when the price of spats rises by $10.
E)Total revenue decreases by more than $10 when the price of spats rises by $10.
A)Total revenue decreases by 10 percent when the price of spats rises by 10 percent.
B)Total revenue decreases by less than 10 percent when the price of spats rises by 10 percent.
C)Total revenue increases by more than 10 percent when the price of spats rises by 10 percent.
D)Total revenue decreases by $10 when the price of spats rises by $10.
E)Total revenue decreases by more than $10 when the price of spats rises by $10.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 86 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
If a firm raises the price of its product, its total revenue will
A)always increase
B)increase only if demand is price inelastic
C)increase only if demand is price elastic
D)remain constant, regardless of price elasticity of demand
E)never increase
A)always increase
B)increase only if demand is price inelastic
C)increase only if demand is price elastic
D)remain constant, regardless of price elasticity of demand
E)never increase

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 86 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
Total revenue is maximized where demand is inelastic.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 86 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
) 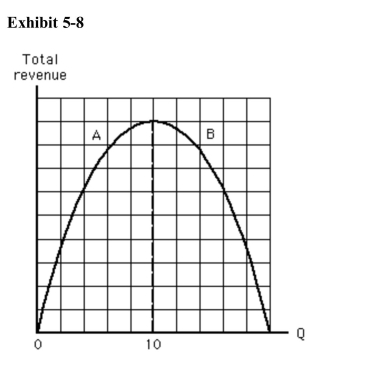 Which of the following is not true in the range of the total revenue curvelabeled A in Exhibit 58?
Which of the following is not true in the range of the total revenue curvelabeled A in Exhibit 58?
A)Demand is inelastic.
B)Total revenue is increasing.
C)Total revenue is positive.
D)Demand is elastic.
E)Demand elasticity decreases as total revenue increases.
 Which of the following is not true in the range of the total revenue curvelabeled A in Exhibit 58?
Which of the following is not true in the range of the total revenue curvelabeled A in Exhibit 58?A)Demand is inelastic.
B)Total revenue is increasing.
C)Total revenue is positive.
D)Demand is elastic.
E)Demand elasticity decreases as total revenue increases.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 86 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
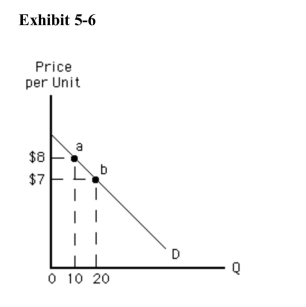 We can tell that demand is elastic as price falls between point a and point bin Exhibit 56 because
We can tell that demand is elastic as price falls between point a and point bin Exhibit 56 becauseA)quantity demanded is increasing
B)total revenue is increasing
C)total revenue is decreasing
D)total revenue is unchanged
E)the demand curve slopes downward

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 86 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
If the sellers in the cigarette industry formed a cartel and decided to setprice along a straightline downwardsloping demand curve, which pointwould they choose if they wanted to gain the highest total revenue?
A)The point nearest the vertical axis, where the price is highest.
B)The point nearest the horizontal axis, where quantity demanded is greatest.
C)One of the points higher up on the demand curve, where demand is elastic.
D)One of the points lower down on the demand curve, where demand is inelastic.
E)The point of unit elasticity, in the middle of the demand curve.
A)The point nearest the vertical axis, where the price is highest.
B)The point nearest the horizontal axis, where quantity demanded is greatest.
C)One of the points higher up on the demand curve, where demand is elastic.
D)One of the points lower down on the demand curve, where demand is inelastic.
E)The point of unit elasticity, in the middle of the demand curve.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 86 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
) 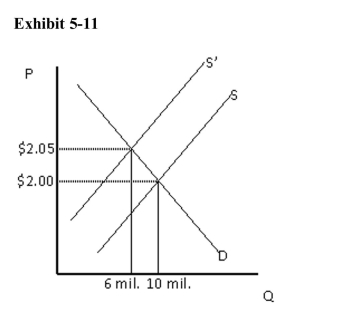 Refer to Exhibit 511.What can be said of the price elasticity of demand forthis good?
Refer to Exhibit 511.What can be said of the price elasticity of demand forthis good?
A)Demand is inelastic.
B)Demand is unit elastic.
C)Demand is elastic.
D)Demand is perfectly elastic.
E)Not enough information is given to determine elasticity.
 Refer to Exhibit 511.What can be said of the price elasticity of demand forthis good?
Refer to Exhibit 511.What can be said of the price elasticity of demand forthis good?A)Demand is inelastic.
B)Demand is unit elastic.
C)Demand is elastic.
D)Demand is perfectly elastic.
E)Not enough information is given to determine elasticity.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 86 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
) 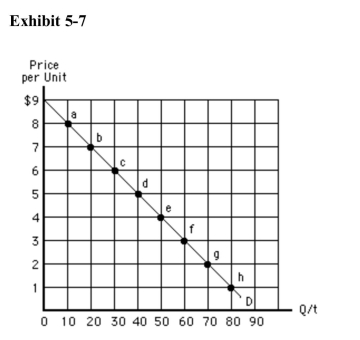 Between points b and c in Exhibit 57, price decreases by $1, quantitydemanded increases by 10,
Between points b and c in Exhibit 57, price decreases by $1, quantitydemanded increases by 10,
A)total revenue decreases by $1, and demand is elastic
B)total revenue decreases by $1, and demand is inelastic
C)total revenue increases by $40, and demand is elastic
D)total revenue increases by $40, and demand is inelastic
E)and total revenue increases by $80
 Between points b and c in Exhibit 57, price decreases by $1, quantitydemanded increases by 10,
Between points b and c in Exhibit 57, price decreases by $1, quantitydemanded increases by 10,A)total revenue decreases by $1, and demand is elastic
B)total revenue decreases by $1, and demand is inelastic
C)total revenue increases by $40, and demand is elastic
D)total revenue increases by $40, and demand is inelastic
E)and total revenue increases by $80

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 86 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
Exhibit 57 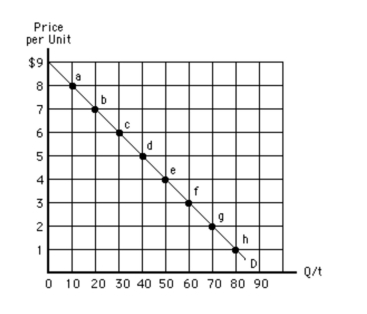 Which of the following is true between points g and h in Exhibit 57?
Which of the following is true between points g and h in Exhibit 57?
A)Total revenue remains constant at $180.
B)Total revenue falls by $12.
C)Total revenue falls by $60.
D)Total revenue falls by $180.
E)Demand is elastic.
 Which of the following is true between points g and h in Exhibit 57?
Which of the following is true between points g and h in Exhibit 57?A)Total revenue remains constant at $180.
B)Total revenue falls by $12.
C)Total revenue falls by $60.
D)Total revenue falls by $180.
E)Demand is elastic.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 86 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
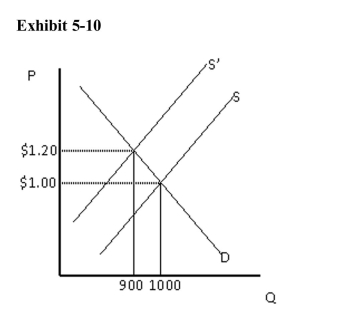 In Exhibit 510, between the two equilibrium prices shown, demand is
In Exhibit 510, between the two equilibrium prices shown, demand isA)price elastic
B)price inelastic
C)unit elastic
D)perfectly elastic
E)perfectly inelastic

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 86 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
Along a downwardsloping linear demand curve,
A)slope is constant and elasticity is changing
B)slope is changing and elasticity is constant
C)both slope and elasticity are constant
D)both slope and elasticity are changing
E)no generalizations can be made about slope
A)slope is constant and elasticity is changing
B)slope is changing and elasticity is constant
C)both slope and elasticity are constant
D)both slope and elasticity are changing
E)no generalizations can be made about slope

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 86 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
Along a linear demand curve, total revenue is maximized when demand is
A)elastic
B)inelastic
C)unit elastic
D)perfectly elastic
E)perfectly inelastic
A)elastic
B)inelastic
C)unit elastic
D)perfectly elastic
E)perfectly inelastic

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 86 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
) 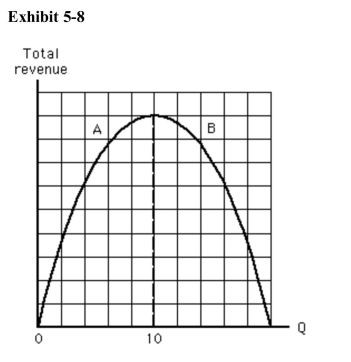 Which of the following statements is true in the range of the total revenuecurve labeled B in Exhibit 58?
Which of the following statements is true in the range of the total revenuecurve labeled B in Exhibit 58?
A)Demand is elastic.
B)Demand is inelastic.
C)Demand is unit elastic.
D)We cannot tell anything about elasticity of demand because this is a total revenue curve.
E)Demand is perfectly elastic.
 Which of the following statements is true in the range of the total revenuecurve labeled B in Exhibit 58?
Which of the following statements is true in the range of the total revenuecurve labeled B in Exhibit 58?A)Demand is elastic.
B)Demand is inelastic.
C)Demand is unit elastic.
D)We cannot tell anything about elasticity of demand because this is a total revenue curve.
E)Demand is perfectly elastic.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 86 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
Dusty Rags, Inc.provides janitorial services to retail stores.Dusty had beencharging $10 per hour and selling 400 hours of service per week at that rate.When he raised his price to $15 per hour, his customers cut back to 300weekly hours of service.Which of the following is true?
A)Revenue went from $4,000 per week to $4,500 per week, indicating that the demand curve for his services
Must have shifted to the right.
B)Revenue went from $4,000 per week to $4,500 per week, indicating that the demand for his services must
Be elastic.
C)Revenue went from $4,000 per week to $4,500 per week, indicating that the demand for his services must
Be inelastic.
D)Revenue went from $400 to $300 per week, indicating that demand must be elastic.
E)Revenue went from $10 to $15 per week, indicating that demand must be inelastic.
A)Revenue went from $4,000 per week to $4,500 per week, indicating that the demand curve for his services
Must have shifted to the right.
B)Revenue went from $4,000 per week to $4,500 per week, indicating that the demand for his services must
Be elastic.
C)Revenue went from $4,000 per week to $4,500 per week, indicating that the demand for his services must
Be inelastic.
D)Revenue went from $400 to $300 per week, indicating that demand must be elastic.
E)Revenue went from $10 to $15 per week, indicating that demand must be inelastic.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 86 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
Along a linear demand curve, as the price rises, demand becomes more
A)steep
B)elastic
C)inelastic
D)unit elastic
E)variable
A)steep
B)elastic
C)inelastic
D)unit elastic
E)variable

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 86 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
Along a straightline downwardsloping demand curve, elasticity is
A)constant, but its value cannot be determined without measurement
B)constant and equal to an absolute value of one
C)greater at higher prices
D)greater at lower prices
E)greater in the middle
A)constant, but its value cannot be determined without measurement
B)constant and equal to an absolute value of one
C)greater at higher prices
D)greater at lower prices
E)greater in the middle

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 86 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
The total revenue curve that corresponds to a downwardsloping lineardemand curve
A)slopes downward
B)slopes upward
C)is a horizontal line
D)first rises, then falls
E)first falls, then rises
A)slopes downward
B)slopes upward
C)is a horizontal line
D)first rises, then falls
E)first falls, then rises

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 86 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
Along a downwardsloping linear demand curve, total revenue is greatest ifdemand is
A)inelastic
B)elastic
C)inelastic when prices are high
D)elastic when prices are high
E)unit elastic
A)inelastic
B)elastic
C)inelastic when prices are high
D)elastic when prices are high
E)unit elastic

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 86 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
It has been suggested that if NHL hockey teams would lower ticket prices,they could increase revenue from ticket sales.Which of the followingassumptions forms the basis for this suggestion?
A)Both d and e are correct.
B)All of the following are correct.
C)Demand for NHL hockey is income inelastic.
D)Demand for NHL hockey is price elastic.
E)There are many substitutes for NHL hockey.
A)Both d and e are correct.
B)All of the following are correct.
C)Demand for NHL hockey is income inelastic.
D)Demand for NHL hockey is price elastic.
E)There are many substitutes for NHL hockey.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 86 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
) 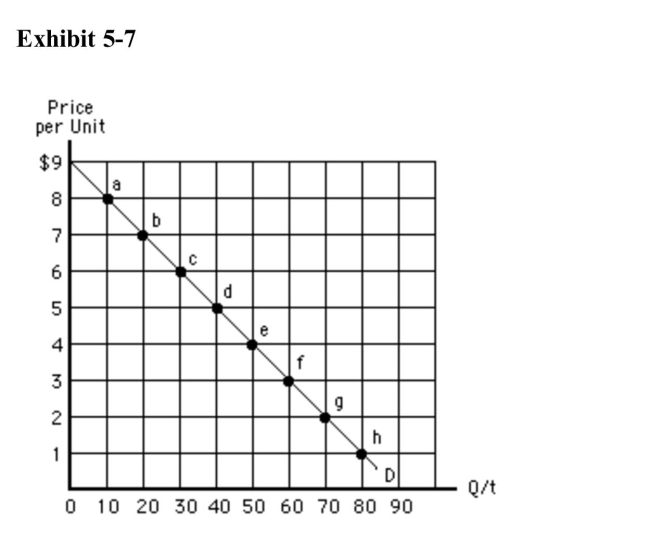 In Exhibit 57, demand is unit elastic
In Exhibit 57, demand is unit elastic
A)between points a and d
B)between points d and e
C)between points e and g
D)only at the top and bottom of the curve
E)anywhere along the curve
 In Exhibit 57, demand is unit elastic
In Exhibit 57, demand is unit elasticA)between points a and d
B)between points d and e
C)between points e and g
D)only at the top and bottom of the curve
E)anywhere along the curve

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 86 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
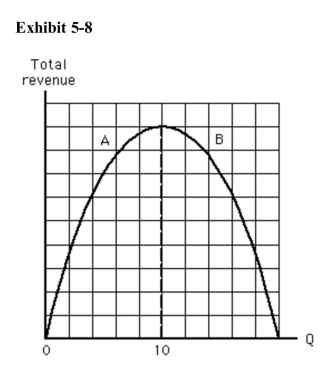 In Exhibit 58, which of the following statements is true at a quantity of 10?
In Exhibit 58, which of the following statements is true at a quantity of 10?A)Demand is elastic.
B)Demand is inelastic.
C)Demand is unit elastic.
D)We cannot tell anything about elasticity of demand because this is a total revenue curve.
E)Demand is perfectly elastic.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 86 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
Suppose consumers spent $42 million on Christmas trees last year when theaverage tree cost $30 and this year spent $42 million when the average treecosts $25.Assuming nothing else changed, this data suggests that
A)consumers bought the same number of Christmas trees this year as last year
B)the price of Christmas trees stayed the same
C)total revenues to tree producers rose this year
D)the demand for trees is unit elastic
E)the demand for trees is inelastic
A)consumers bought the same number of Christmas trees this year as last year
B)the price of Christmas trees stayed the same
C)total revenues to tree producers rose this year
D)the demand for trees is unit elastic
E)the demand for trees is inelastic

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 86 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
Exhibit 59 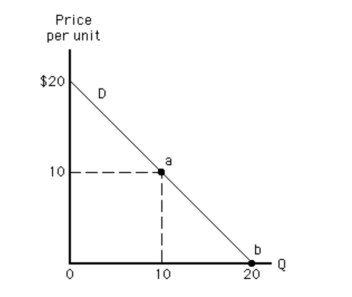 Between points a and b on the demand curve in Exhibit 59, demand is
Between points a and b on the demand curve in Exhibit 59, demand is
A)perfectly elastic
B)elastic
C)perfectly inelastic
D)inelastic
E)unit elastic
 Between points a and b on the demand curve in Exhibit 59, demand is
Between points a and b on the demand curve in Exhibit 59, demand isA)perfectly elastic
B)elastic
C)perfectly inelastic
D)inelastic
E)unit elastic

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 86 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



