Deck 9: International Agreements: Trade, Labor, and the Environment
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/179
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 9: International Agreements: Trade, Labor, and the Environment
1
If we allow free trade in a small nation's industry where there is a
Domestic monopolist, the monopoly firm:
A)gains even more power.
B)sees its profits rise.
C)becomes a price taker, is not able to charge a higher price, and behaves like a competitive firm.
D)is able to charge a higher price.
Domestic monopolist, the monopoly firm:
A)gains even more power.
B)sees its profits rise.
C)becomes a price taker, is not able to charge a higher price, and behaves like a competitive firm.
D)is able to charge a higher price.
C
2
A foreign discriminating monopolist is engaging in:
A)infant industry protection.
B)dumping its product.
C)giving preferential treatment to domestic consumers.
D)charging higher prices to foreign consumers.
A)infant industry protection.
B)dumping its product.
C)giving preferential treatment to domestic consumers.
D)charging higher prices to foreign consumers.
B
3
The tariff imposed to punish a foreign discriminating monopolist is
Called:
A)antidumping duty.
B)a subsidy.
C)punitive damages.
D)a fine.
Called:
A)antidumping duty.
B)a subsidy.
C)punitive damages.
D)a fine.
A
4
If a monopoly suddenly became a perfectly competitive industry,
Equilibrium output would _________, and the equilibrium price would
_________.
A)increase; increase
B)decrease; decrease
C)increase; decrease
D)decrease; increase
Equilibrium output would _________, and the equilibrium price would
_________.
A)increase; increase
B)decrease; decrease
C)increase; decrease
D)decrease; increase

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 179 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
SCENARIO: A MONOPOLIST
A monopolist faces a demand curve given by P = 20 - Q and has total
Costs given by TC = Q2.By using a bit of calculus, you should be able
To determine that the firm's marginal revenue is MR = 20 - 2Q and its
Marginal cost is MC = 2Q.
Reference: Ref 93
(Scenario: A Monopolist) Now suppose that the country in which this
Monopolist is located decides to engage in international trade.The
World price of the product produced by the monopolist is $12.What is
The monopolist's profitmaximizing output level?
A)5
B)6
C)7
D)8
A monopolist faces a demand curve given by P = 20 - Q and has total
Costs given by TC = Q2.By using a bit of calculus, you should be able
To determine that the firm's marginal revenue is MR = 20 - 2Q and its
Marginal cost is MC = 2Q.
Reference: Ref 93
(Scenario: A Monopolist) Now suppose that the country in which this
Monopolist is located decides to engage in international trade.The
World price of the product produced by the monopolist is $12.What is
The monopolist's profitmaximizing output level?
A)5
B)6
C)7
D)8

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 179 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
The notrade equilibrium in a perfectly competitive market occurs
Where:
A)marginal revenue = price.
B)marginal cost = total revenue.
C)market quantity demanded = market quantity supplied.
D)average revenue = price.
Where:
A)marginal revenue = price.
B)marginal cost = total revenue.
C)market quantity demanded = market quantity supplied.
D)average revenue = price.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 179 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
The smallcountry monopolist's freetrade equilibrium occurs:
A)where MC = MR, where MR is declining and below price.
B)at the "world" price, which becomes a perfectly elastic demand curve for the monopoly firm and the firm's marginal cost curve.
C)where the home demand is completely satisfied by foreign importers.
D)at minimum marginal cost.
A)where MC = MR, where MR is declining and below price.
B)at the "world" price, which becomes a perfectly elastic demand curve for the monopoly firm and the firm's marginal cost curve.
C)where the home demand is completely satisfied by foreign importers.
D)at minimum marginal cost.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 179 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Figure: The Home Market 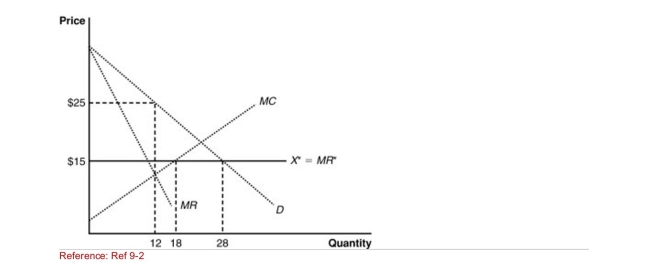 (Figure: The Home Market) If the world price is $15, the domestic
(Figure: The Home Market) If the world price is $15, the domestic
Monopolist will produce ______ and the country will import
________.
A)18; 10
B)12; 6
C)18; 16
D)12; 16
 (Figure: The Home Market) If the world price is $15, the domestic
(Figure: The Home Market) If the world price is $15, the domesticMonopolist will produce ______ and the country will import
________.
A)18; 10
B)12; 6
C)18; 16
D)12; 16

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 179 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
The smallcountry monopolist's freetrade equilibrium features a
Marginal revenue curve equal to __________ and coincident with
_____________.
A)marginal cost; the consumer's demand curve for the product
B)the world price; the new competitive demand curve for the firm
C)one; profits
D)imports at each price; the supply curve
Marginal revenue curve equal to __________ and coincident with
_____________.
A)marginal cost; the consumer's demand curve for the product
B)the world price; the new competitive demand curve for the firm
C)one; profits
D)imports at each price; the supply curve

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 179 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
If a perfectly competitive industry suddenly became a monopolist,
Equilibrium output would _________, and the equilibrium price would
_________.
A)increase; increase
B)decrease; decrease
C)increase; decrease
D)decrease; increase
Equilibrium output would _________, and the equilibrium price would
_________.
A)increase; increase
B)decrease; decrease
C)increase; decrease
D)decrease; increase

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 179 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Comparing the monopoly firm with a perfectly competitive firm reveals
That:
A)the competitive firm sells less quantity.
B)the monopoly firm charges a lower price.
C)the competitive firm's price is above MC.
D)None of these is revealed when the two firm are compared.
That:
A)the competitive firm sells less quantity.
B)the monopoly firm charges a lower price.
C)the competitive firm's price is above MC.
D)None of these is revealed when the two firm are compared.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 179 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
A profitmaximizing monopolist will produce at the point where:
A)total revenue = total costs.
B)marginal revenue = marginal cost.
C)average revenue = average cost.
D)the difference between average revenue and average cost is maximized.
A)total revenue = total costs.
B)marginal revenue = marginal cost.
C)average revenue = average cost.
D)the difference between average revenue and average cost is maximized.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 179 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
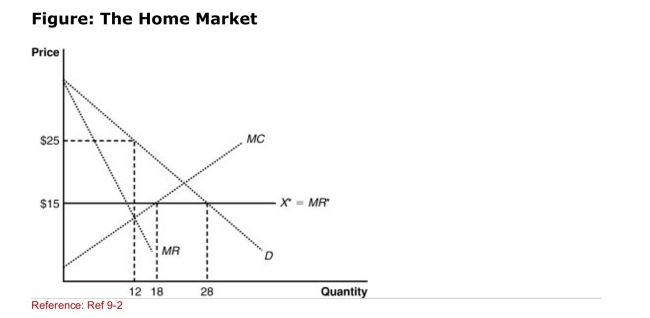 (Figure: The Home Market) Under conditions of notrade, the domestic
(Figure: The Home Market) Under conditions of notrade, the domesticMonopolist will produce and sell _______ at a price of _________.
A)18; $15
B)28; $15
C)12; $25
D)12; $15

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 179 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
SCENARIO: A MONOPOLIST
A monopolist faces a demand curve given by P = 20 - Q and has total
Costs given by TC = Q2.By using a bit of calculus, you should be able
To determine that the firm's marginal revenue is MR = 20 - 2Q and its
Marginal cost is MC = 2Q.
Reference: Ref 91
(Scenario: A Monopolist) If the firm's profitmaximizing output level is
5 and its profit maximizing price is $15, what are its monopoly profits
At this price and quantity?
A)$25
B)$50
C)$75
D)$100
A monopolist faces a demand curve given by P = 20 - Q and has total
Costs given by TC = Q2.By using a bit of calculus, you should be able
To determine that the firm's marginal revenue is MR = 20 - 2Q and its
Marginal cost is MC = 2Q.
Reference: Ref 91
(Scenario: A Monopolist) If the firm's profitmaximizing output level is
5 and its profit maximizing price is $15, what are its monopoly profits
At this price and quantity?
A)$25
B)$50
C)$75
D)$100

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 179 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
A monopoly firm will sell ________output and charge a ________
Price than a perfectly competitive firm.
A)less; higher
B)more; higher
C)more; lower
D)less; lower
Price than a perfectly competitive firm.
A)less; higher
B)more; higher
C)more; lower
D)less; lower

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 179 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
A monopoly firm operating with no trade will produce the profit
Maximizing quantity where:
A)the firm's MC = MR, where MR is declining and below price.
B)MR begins to increase and MC begins to decrease.
C)P = MC.
D)the firm's MC = MR, where MR is declining and equal to price.
Maximizing quantity where:
A)the firm's MC = MR, where MR is declining and below price.
B)MR begins to increase and MC begins to decrease.
C)P = MC.
D)the firm's MC = MR, where MR is declining and equal to price.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 179 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
SCENARIO: A MONOPOLIST
A monopolist faces a demand curve given by P = 20 - Q and has total
Costs given by TC = Q2.By using a bit of calculus, you should be able
To determine that the firm's marginal revenue is MR = 20 - 2Q and its
Marginal cost is MC = 2Q.
Reference: Ref 91
(Scenario: A Monopolist) What is its profitmaximizing output level?
A)5
B)6
C)7
D)8
A monopolist faces a demand curve given by P = 20 - Q and has total
Costs given by TC = Q2.By using a bit of calculus, you should be able
To determine that the firm's marginal revenue is MR = 20 - 2Q and its
Marginal cost is MC = 2Q.
Reference: Ref 91
(Scenario: A Monopolist) What is its profitmaximizing output level?
A)5
B)6
C)7
D)8

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 179 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
SCENARIO: A MONOPOLIST
A monopolist faces a demand curve given by P = 20 - Q and has total
Costs given by TC = Q2.By using a bit of calculus, you should be able
To determine that the firm's marginal revenue is MR = 20 - 2Q and its
Marginal cost is MC = 2Q.
Reference: Ref 91
(Scenario: A Monopolist) What is its profitmaximizing price?
A)$20
B)$15
C)$10
D)$5
A monopolist faces a demand curve given by P = 20 - Q and has total
Costs given by TC = Q2.By using a bit of calculus, you should be able
To determine that the firm's marginal revenue is MR = 20 - 2Q and its
Marginal cost is MC = 2Q.
Reference: Ref 91
(Scenario: A Monopolist) What is its profitmaximizing price?
A)$20
B)$15
C)$10
D)$5

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 179 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
The notrade equilibrium in a monopolistic market occurs where:
A)marginal revenue = price.
B)marginal cost = marginal revenue.
C)market demand = market supply.
D)marginal cost = average revenue.
A)marginal revenue = price.
B)marginal cost = marginal revenue.
C)market demand = market supply.
D)marginal cost = average revenue.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 179 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
What will happen to domestic monopolists' prices and outputs when a
Small country engages in international trade?
A)Prices will rise and outputs will fall.
B)Prices will rise and outputs will rise.
C)Prices will fall and outputs will rise.
D)Prices will fall and outputs will fall.
Small country engages in international trade?
A)Prices will rise and outputs will fall.
B)Prices will rise and outputs will rise.
C)Prices will fall and outputs will rise.
D)Prices will fall and outputs will fall.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 179 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
SCENARIO: HOME MONOPOLIST
A monopolist faces a demand curve given by P = 60 -2Q and has total
Costs given by TC = Q2.Its marginal revenue is MR = 60 - 4Q and its
Marginal cost is MC = 2Q.
Reference: Ref 95
(Scenario: Home Monopolist) Compared with the notrade equilibrium,
Consumer surplus ___________ when the monopolist engages in free
Trade.
A)increases
B)decreases
C)remains the same
D)first decreases, then increases
A monopolist faces a demand curve given by P = 60 -2Q and has total
Costs given by TC = Q2.Its marginal revenue is MR = 60 - 4Q and its
Marginal cost is MC = 2Q.
Reference: Ref 95
(Scenario: Home Monopolist) Compared with the notrade equilibrium,
Consumer surplus ___________ when the monopolist engages in free
Trade.
A)increases
B)decreases
C)remains the same
D)first decreases, then increases

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 179 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
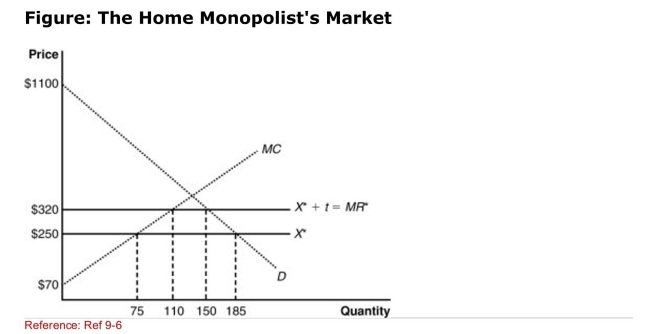 (Figure: The Home Monopolist's Market) The graph shows a home
(Figure: The Home Monopolist's Market) The graph shows a homeMonopolist market with the imposition of a tariff.According to the
Graph, the home country imposed a tariff of _____, and the new
Quantity of imports is _____.
A)$70; 40
B)$70; 75
C)$320; 185
D)$250; 110

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 179 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
With free trade, the demand curve facing a smallcountry monopolist:
A)is horizontal at the world price.
B)shifts upward by the amount of imports demanded.
C)shifts downward by the amount of imports demanded.
D)is horizontal at the firm's MC.
A)is horizontal at the world price.
B)shifts upward by the amount of imports demanded.
C)shifts downward by the amount of imports demanded.
D)is horizontal at the firm's MC.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 179 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
SCENARIO: HOME MONOPOLIST
A monopolist faces a demand curve given by P = 60 -2Q and has total
Costs given by TC = Q2.Its marginal revenue is MR = 60 - 4Q and its
Marginal cost is MC = 2Q.
Reference: Ref 95
(Scenario: Home Monopolist) What price does the monopolist charge
With no trade?
A)$5
B)$10
C)$15
D)$20
A monopolist faces a demand curve given by P = 60 -2Q and has total
Costs given by TC = Q2.Its marginal revenue is MR = 60 - 4Q and its
Marginal cost is MC = 2Q.
Reference: Ref 95
(Scenario: Home Monopolist) What price does the monopolist charge
With no trade?
A)$5
B)$10
C)$15
D)$20

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 179 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
SCENARIO: A MONOPOLIST
A monopolist faces a demand curve given by P = 20 - Q and has total
Costs given by TC = Q2.By using a bit of calculus, you should be able
To determine that the firm's marginal revenue is MR = 20 - 2Q and its
Marginal cost is MC = 2Q.
Reference: Ref 93
(Scenario: A Monopolist) Now suppose that the country in which this
Monopolist is located decides to engage in international trade.The
World price of the product produced by the monopolist is $12.What is
Its profitmaximizing price?
A)$20
B)$15
C)$12
D)$10
A monopolist faces a demand curve given by P = 20 - Q and has total
Costs given by TC = Q2.By using a bit of calculus, you should be able
To determine that the firm's marginal revenue is MR = 20 - 2Q and its
Marginal cost is MC = 2Q.
Reference: Ref 93
(Scenario: A Monopolist) Now suppose that the country in which this
Monopolist is located decides to engage in international trade.The
World price of the product produced by the monopolist is $12.What is
Its profitmaximizing price?
A)$20
B)$15
C)$12
D)$10

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 179 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
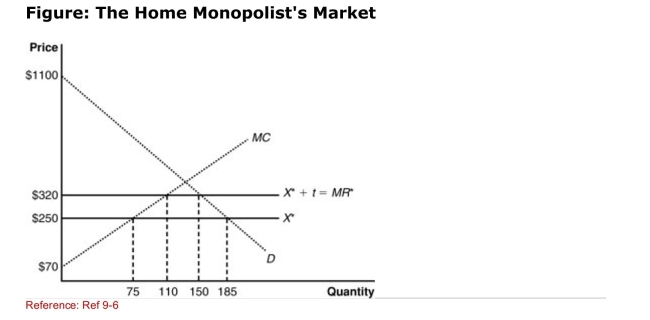 (Figure: The Home Monopolist's Market) The graph shows a home
(Figure: The Home Monopolist's Market) The graph shows a homeMonopolist market with the imposition of a tariff.According to the
Graph, the consumer surplus under free trade is:
A)$150,000.
B)$157,250.
C)$78,625.
D)$850.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 179 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
SCENARIO: HOME MONOPOLIST
A monopolist faces a demand curve given by P = 60 -2Q and has total
Costs given by TC = Q2.Its marginal revenue is MR = 60 - 4Q and its
Marginal cost is MC = 2Q.
Reference: Ref 95
(Scenario: Home Monopolist) Compared with the notrade equilibrium,
Producer surplus ___________ when the monopolist engages in free
Trade.
A)increases
B)decreases
C)remains the same
D)first increases, then decreases
A monopolist faces a demand curve given by P = 60 -2Q and has total
Costs given by TC = Q2.Its marginal revenue is MR = 60 - 4Q and its
Marginal cost is MC = 2Q.
Reference: Ref 95
(Scenario: Home Monopolist) Compared with the notrade equilibrium,
Producer surplus ___________ when the monopolist engages in free
Trade.
A)increases
B)decreases
C)remains the same
D)first increases, then decreases

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 179 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
When a domestic monopolist becomes subject to international
Competition, it faces:
A)a perfectly inelastic demand curve.
B)a unitary elastic demand curve.
C)a perfectly elastic demand curve.
D)no demand curve.
Competition, it faces:
A)a perfectly inelastic demand curve.
B)a unitary elastic demand curve.
C)a perfectly elastic demand curve.
D)no demand curve.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 179 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
SCENARIO: HOME MONOPOLIST
A monopolist faces a demand curve given by P = 60 -2Q and has total
Costs given by TC = Q2.Its marginal revenue is MR = 60 - 4Q and its
Marginal cost is MC = 2Q.
Reference: Ref 95
(Scenario: Home Monopolist) Now suppose that the country in which
This monopolist is located decides to engage in international trade.The
World price of the product produced by the monopolist is $10.
Calculate the value of the firm's profits.
A)$400
B)$1,200
C)-$1,600
D)$25
A monopolist faces a demand curve given by P = 60 -2Q and has total
Costs given by TC = Q2.Its marginal revenue is MR = 60 - 4Q and its
Marginal cost is MC = 2Q.
Reference: Ref 95
(Scenario: Home Monopolist) Now suppose that the country in which
This monopolist is located decides to engage in international trade.The
World price of the product produced by the monopolist is $10.
Calculate the value of the firm's profits.
A)$400
B)$1,200
C)-$1,600
D)$25

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 179 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
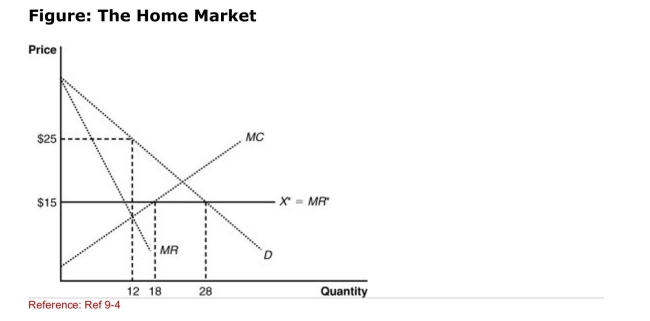 (Figure: The Home Market) With free trade, the consumer surplus is
(Figure: The Home Market) With free trade, the consumer surplus is_________ than in the case of notrade domestic monopoly.
A)lower
B)higher
C)constant
D)More information is needed to answer this question.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 179 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
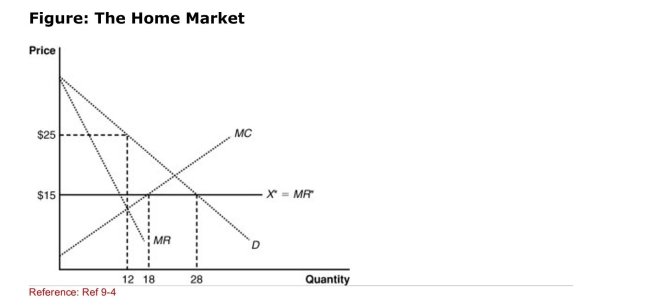 (Figure: The Home Market) For a home monopolist, free trade results
(Figure: The Home Market) For a home monopolist, free trade resultsIn:
A)more control over the domestic market.
B)more control over the foreign market.
C)an inability to control prices.
D)no change in the monopolistic behavior.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 179 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
SCENARIO: HOME MONOPOLIST
A monopolist faces a demand curve given by P = 60 -2Q and has total
Costs given by TC = Q2.Its marginal revenue is MR = 60 - 4Q and its
Marginal cost is MC = 2Q.
Reference: Ref 95
(Scenario: Home Monopolist) In autarky, what is the firm's equilibrium
Output?
A)5
B)10
C)15
D)20
A monopolist faces a demand curve given by P = 60 -2Q and has total
Costs given by TC = Q2.Its marginal revenue is MR = 60 - 4Q and its
Marginal cost is MC = 2Q.
Reference: Ref 95
(Scenario: Home Monopolist) In autarky, what is the firm's equilibrium
Output?
A)5
B)10
C)15
D)20

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 179 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
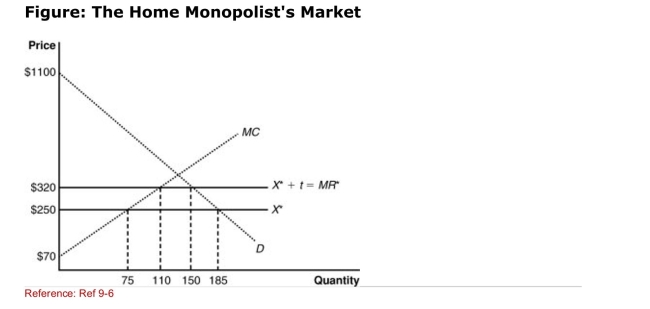 (Figure: The Home Monopolist's Market) The graph shows a home
(Figure: The Home Monopolist's Market) The graph shows a homeMonopolist market with the imposition of a tariff.Under free trade, the
Home country will produce ________ and import ________.
A)110, 185
B)75; 110
C)150; 185
D)75; 75

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 179 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
In comparison to the case of a perfectly competitive home market, the
Welfare effects of a tariff under a home monopoly are _______, and
The deadweight loss for the home monopoly is ________.
A)the same; the same
B)higher; lower
C)lower; higher
D)lower; lower
Welfare effects of a tariff under a home monopoly are _______, and
The deadweight loss for the home monopoly is ________.
A)the same; the same
B)higher; lower
C)lower; higher
D)lower; lower

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 179 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
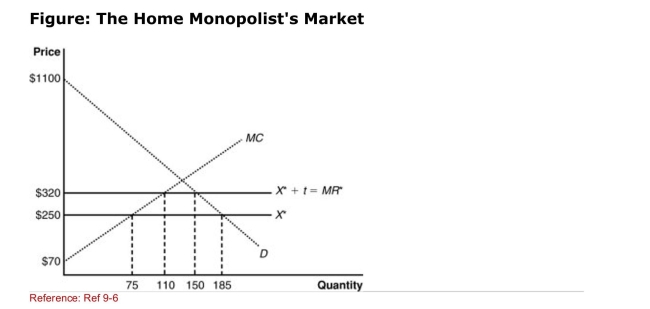 (Figure: The Home Monopolist's Market) The graph shows a home
(Figure: The Home Monopolist's Market) The graph shows a homeMonopolist market with the imposition of a tariff.According to the
Graph, the decrease in consumer surplus due to the tariff is:
A)$58,500.
B)$78,625.
C)$20,125.
D)$11,725.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 179 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
The small country monopolist's freetrade equilibrium occurs:
A)where MC = MR and where MC is greater than the world price.
B)at the same price as in autarky.
C)at a higher price than the autarkic price.
D)where MC = the world price.
A)where MC = MR and where MC is greater than the world price.
B)at the same price as in autarky.
C)at a higher price than the autarkic price.
D)where MC = the world price.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 179 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
SCENARIO: HOME MONOPOLIST
A monopolist faces a demand curve given by P = 60 -2Q and has total
Costs given by TC = Q2.Its marginal revenue is MR = 60 - 4Q and its
Marginal cost is MC = 2Q.
Reference: Ref 95
(Scenario: Home Monopolist) Now suppose that the country in which
This monopolist is located decides to engage in international trade.The
World price of the product produced by the monopolist is $10.What is
The firm's profitmaximizing output level?
A)5
B)20
C)30
D)40
A monopolist faces a demand curve given by P = 60 -2Q and has total
Costs given by TC = Q2.Its marginal revenue is MR = 60 - 4Q and its
Marginal cost is MC = 2Q.
Reference: Ref 95
(Scenario: Home Monopolist) Now suppose that the country in which
This monopolist is located decides to engage in international trade.The
World price of the product produced by the monopolist is $10.What is
The firm's profitmaximizing output level?
A)5
B)20
C)30
D)40

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 179 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
If the home nation allows free trade but imposes a tariff on a product
Currently produced by a home firm monopoly, what is the outcome?
A)The home firm then will regain its monopoly control over the price.
B)The home firm will be able to charge a higher price (world price + tariff), but it will become a price taker, just like a competitive firm.
C)The home nation's firm will be able to limit quantity and charge a higher price.
D)The monopoly firm will lower price, increase sales, and undercut the foreign competition.
Currently produced by a home firm monopoly, what is the outcome?
A)The home firm then will regain its monopoly control over the price.
B)The home firm will be able to charge a higher price (world price + tariff), but it will become a price taker, just like a competitive firm.
C)The home nation's firm will be able to limit quantity and charge a higher price.
D)The monopoly firm will lower price, increase sales, and undercut the foreign competition.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 179 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
If we allow free trade in a small nation's industry where there is a
Domestic monopolist, the monopoly firm:
A)gains even more power.
B)earns higher profits.
C)charges a lower price and produces more output.
D)charges a higher price and produces less output.
Domestic monopolist, the monopoly firm:
A)gains even more power.
B)earns higher profits.
C)charges a lower price and produces more output.
D)charges a higher price and produces less output.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 179 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Because the smallcountry monopolist loses the ability to control the
Market price, consumers enjoy more quantity, competitive prices,
And:
A)a bonus because the foreign goods are of higher quality.
B)a loss because the monopoly loses profits.
C)higher consumer surplus because the monopolist's producer surplus is reduced.
D)a loss because now unions have less power than before.
Market price, consumers enjoy more quantity, competitive prices,
And:
A)a bonus because the foreign goods are of higher quality.
B)a loss because the monopoly loses profits.
C)higher consumer surplus because the monopolist's producer surplus is reduced.
D)a loss because now unions have less power than before.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 179 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
Figure: The Home Monopolist's Market 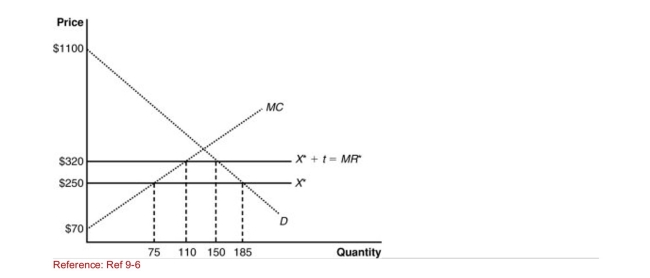 (Figure: The Home Monopolist's Market) The graph shows a home
(Figure: The Home Monopolist's Market) The graph shows a home
Monopolist market with the imposition of a tariff.The deadweight loss
Due to the tariff is:
A)$1,225.
B)$4,900.
C)$2,450.
D)$1,000.
 (Figure: The Home Monopolist's Market) The graph shows a home
(Figure: The Home Monopolist's Market) The graph shows a homeMonopolist market with the imposition of a tariff.The deadweight loss
Due to the tariff is:
A)$1,225.
B)$4,900.
C)$2,450.
D)$1,000.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 179 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Figure: Supply and Demand at Home 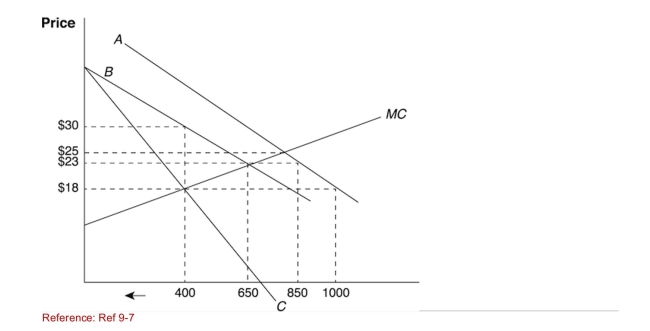 (Figure: Supply and Demand at Home) With a quota of 200 units,
(Figure: Supply and Demand at Home) With a quota of 200 units,
What would be the total quantity available to consumers in a home
Monopoly situation?
A)400
B)600
C)650
D)850
 (Figure: Supply and Demand at Home) With a quota of 200 units,
(Figure: Supply and Demand at Home) With a quota of 200 units,What would be the total quantity available to consumers in a home
Monopoly situation?
A)400
B)600
C)650
D)850

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 179 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
How does the demand curve facing a home monopolist compare in a
Notrade situation to a situation in which a quota protects the
Monopolist's output?
A)They are identical.
B)The quotaprotected demand curve lies to the right of the notrade demand curve.
C)The quotaprotected demand curve lies to the left of the notrade demand curve.
D)The notrade demand curve is perfectly price elastic at the world price; the quotaprotected demand curve has a negative slope.
Notrade situation to a situation in which a quota protects the
Monopolist's output?
A)They are identical.
B)The quotaprotected demand curve lies to the right of the notrade demand curve.
C)The quotaprotected demand curve lies to the left of the notrade demand curve.
D)The notrade demand curve is perfectly price elastic at the world price; the quotaprotected demand curve has a negative slope.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 179 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
When a country imposes a tariff to protect a domestic monopolist from
International competition, it will produce _______ output and charge
_______ in a perfectly competitive domestic industry.
A)more; a higher price than
B)the same; the same price as
C)less; a higher price than
D)less; a lower price than
International competition, it will produce _______ output and charge
_______ in a perfectly competitive domestic industry.
A)more; a higher price than
B)the same; the same price as
C)less; a higher price than
D)less; a lower price than

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 179 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
With a home monopolist, the imposition of a tariff results in:
A)a higher deadweight loss than a quota.
B)a higher price for consumers than a quota.
C)a lower deadweight loss than a quota.
D)the same welfare effects as a quota.
A)a higher deadweight loss than a quota.
B)a higher price for consumers than a quota.
C)a lower deadweight loss than a quota.
D)the same welfare effects as a quota.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 179 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
For a home monopolist, a quota allows the firm to charge
_______________ the tariff.
A)a higher price than
B)a lower price than
C)the same price as
D)Not enough information is provided to answer the question.
_______________ the tariff.
A)a higher price than
B)a lower price than
C)the same price as
D)Not enough information is provided to answer the question.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 179 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
Figure: The Home Monopolist's Market 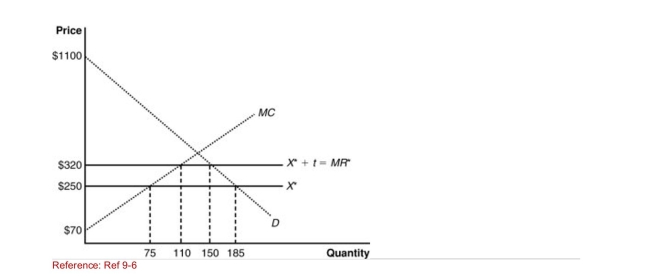 (Figure: The Home Monopolist's Market) The graph shows a home
(Figure: The Home Monopolist's Market) The graph shows a home
Monopolist market with the imposition of a tariff.After the imposition
Of the tariff, the home monopolist saw an increase in production of
______ and the producer surplus increased by ________.
A)55 units; $5,250
B)75 units; $1,225
C)100 units; $6,475
D)35 units; $6,475
 (Figure: The Home Monopolist's Market) The graph shows a home
(Figure: The Home Monopolist's Market) The graph shows a homeMonopolist market with the imposition of a tariff.After the imposition
Of the tariff, the home monopolist saw an increase in production of
______ and the producer surplus increased by ________.
A)55 units; $5,250
B)75 units; $1,225
C)100 units; $6,475
D)35 units; $6,475

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 179 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
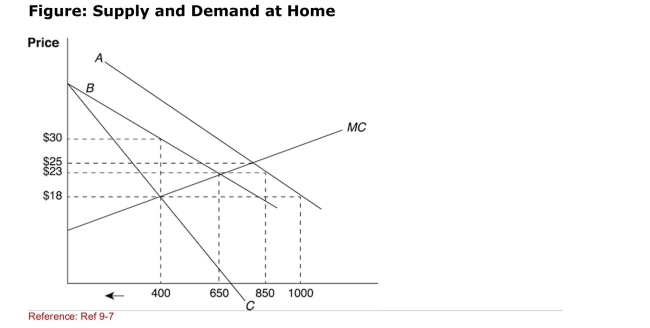 (Figure: Supply and Demand at Home) With a quota of 200 units,
(Figure: Supply and Demand at Home) With a quota of 200 units,What would be the price in a home monopoly situation?
A)$18
B)$23
C)$25
D)$30

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 179 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
The WTO has encouraged nations to replace their import quotas with
Tariffs.Why?
A)Quotas are more difficult to administer for the customs people.
B)Quotas are more discriminatory.
C)Quotas hurt domestic firms more than tariffs.
D)Quotas result in larger losses than tariffs with equivalent protection on domestic monopolists.
Tariffs.Why?
A)Quotas are more difficult to administer for the customs people.
B)Quotas are more discriminatory.
C)Quotas hurt domestic firms more than tariffs.
D)Quotas result in larger losses than tariffs with equivalent protection on domestic monopolists.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 179 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
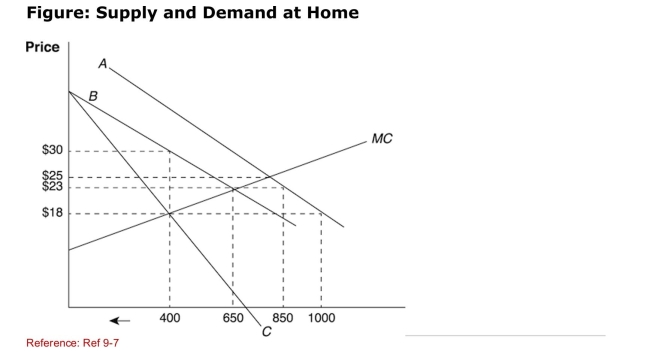 (Figure: Supply and Demand at Home) In the situation illustrated by
(Figure: Supply and Demand at Home) In the situation illustrated byThe figure, the monopoly firm's quantity produced after a quota is
Imposed ________, thus leading to a worse situation for the
Employees of the firm compared with a freetrade situation.
A)increases
B)decreases
C)remains the same
D)changes to different products

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 179 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
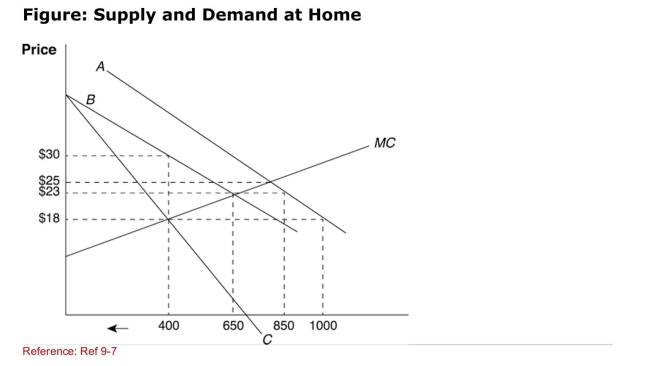 (Figure: Supply and Demand at Home) How many units will be
(Figure: Supply and Demand at Home) How many units will beImported after the quota is imposed?
A)50
B)100
C)150
D)200

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 179 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
When the monopoly firm is able to charge a higher price, the amount
Of ________ also increases, thus magnifying the importing nation's
__________.
A)quota rents; losses
B)comparative advantage; gains from trade
C)profits; welfare
D)protection; employment gains
Of ________ also increases, thus magnifying the importing nation's
__________.
A)quota rents; losses
B)comparative advantage; gains from trade
C)profits; welfare
D)protection; employment gains

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 179 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
When the home country is small, how will an increase in a tariff
Protecting a home monopolist affect the home country's demand
Curve?
A)There will be an upward parallel shift in the demand curve.
B)The demand curve will pivot upwards from its vertical intercept.
C)There will be a downward parallel shift in the demand curve.
D)The demand curve will pivot downwards from its vertical intercept.
Protecting a home monopolist affect the home country's demand
Curve?
A)There will be an upward parallel shift in the demand curve.
B)The demand curve will pivot upwards from its vertical intercept.
C)There will be a downward parallel shift in the demand curve.
D)The demand curve will pivot downwards from its vertical intercept.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 179 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
Figure: Supply and Demand at Home 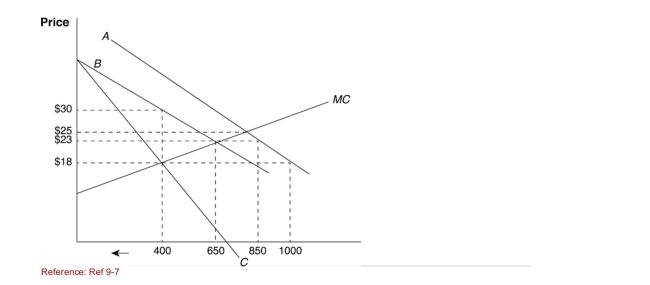 (Figure: Supply and Demand at Home) With a quota of 200 units,
(Figure: Supply and Demand at Home) With a quota of 200 units,
What would be the price if the home market were competitive?
A)$18
B)$23
C)$25
D)$30
 (Figure: Supply and Demand at Home) With a quota of 200 units,
(Figure: Supply and Demand at Home) With a quota of 200 units,What would be the price if the home market were competitive?
A)$18
B)$23
C)$25
D)$30

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 179 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
Comparing a tariff levied on an import where the home firm is a
Monopoly to a situation where the home firms are competitive, we
Find:
A)the exact same result-both firms charge world price + tariff and both firms produce Q where MC = MR = world price + tariff.
B)that the monopoly firm will be able to charge a higher price and limit its quantity.
C)that the competitive firm will not be able to survive the impact of the tariff.
D)that quantity is not the issue; the monopoly firm will pay its workers less and earn higher profits.
Monopoly to a situation where the home firms are competitive, we
Find:
A)the exact same result-both firms charge world price + tariff and both firms produce Q where MC = MR = world price + tariff.
B)that the monopoly firm will be able to charge a higher price and limit its quantity.
C)that the competitive firm will not be able to survive the impact of the tariff.
D)that quantity is not the issue; the monopoly firm will pay its workers less and earn higher profits.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 179 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
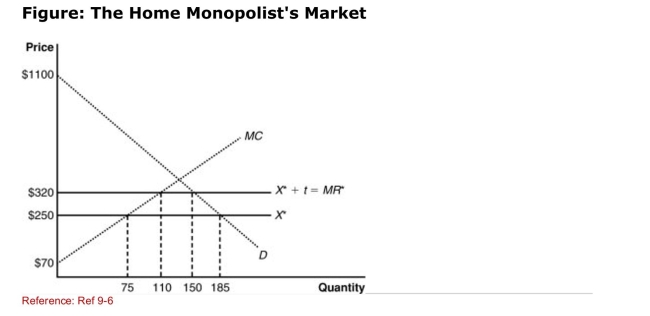 (Figure: The Home Monopolist's Market) The graph shows a home
(Figure: The Home Monopolist's Market) The graph shows a homeMonopolist market with the imposition of a tariff.Because of the tariff,
The home government collects ______ in tariff revenue.
A)$5,600
B)$2,800
C)$1,000
D)$3,200

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 179 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
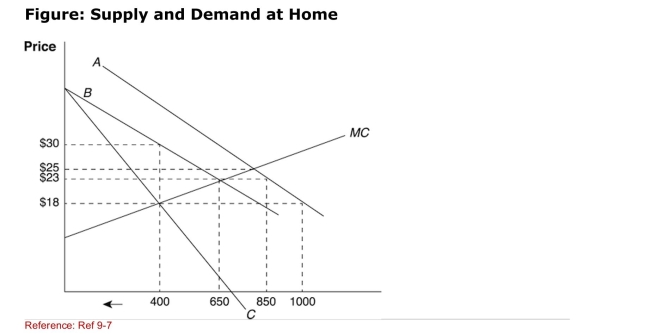 (Figure: Supply and Demand at Home) Suppose the world price is
(Figure: Supply and Demand at Home) Suppose the world price is$18, which line in the graph describes the "new" demand curve for the
Monopolist after a quota is imposed?
A)A
B)B
C)C
D)None of the answers is correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 179 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
What will happen to profits and domestic prices when a quota is used
To protect a domestic monopolist from international competition?
A)Profits will fall; domestic prices will fall.
B)Profits will fall; domestic prices will rise.
C)Profits will rise; domestic prices will rise.
D)Profits will rise; domestic prices will fall.
To protect a domestic monopolist from international competition?
A)Profits will fall; domestic prices will fall.
B)Profits will fall; domestic prices will rise.
C)Profits will rise; domestic prices will rise.
D)Profits will rise; domestic prices will fall.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 179 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
How do the deadweight losses of a tariff differ when the domestic
Industry is perfectly competitive from when it is a monopoly?
A)They are the same.
B)Deadweight losses are larger for a perfectly competitive industry than for a monopoly.
C)Deadweight losses are larger for a monopoly than for a perfectly competitive industry.
D)It is not possible to compare deadweight losses of a monopoly with those of a perfectly competitive industry.
Industry is perfectly competitive from when it is a monopoly?
A)They are the same.
B)Deadweight losses are larger for a perfectly competitive industry than for a monopoly.
C)Deadweight losses are larger for a monopoly than for a perfectly competitive industry.
D)It is not possible to compare deadweight losses of a monopoly with those of a perfectly competitive industry.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 179 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
Figure: Supply and Demand at Home 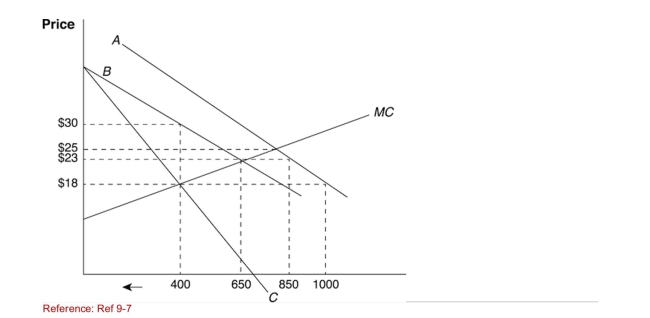 (Figure: Supply and Demand at Home) Which line describes the new
(Figure: Supply and Demand at Home) Which line describes the new
MR curve after the quota is imposed?
A)A
B)B
C)C
D)D
 (Figure: Supply and Demand at Home) Which line describes the new
(Figure: Supply and Demand at Home) Which line describes the newMR curve after the quota is imposed?
A)A
B)B
C)C
D)D

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 179 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
Will a home monopolist prefer a quota or a tariff to protect its output?
A)The home monopolist will prefer a tariff, because a tariff allows it to earn higher profits than a quota.
B)The home monopolist will prefer a quota, because a quota may allow it to earn higher profits than a tariff.
C)It is immaterial to the home monopolist because it will earn the same higher profits with each form of protection.
D)The home monopolist will prefer neither, because it earns higher profits in a freetrade situation.
A)The home monopolist will prefer a tariff, because a tariff allows it to earn higher profits than a quota.
B)The home monopolist will prefer a quota, because a quota may allow it to earn higher profits than a tariff.
C)It is immaterial to the home monopolist because it will earn the same higher profits with each form of protection.
D)The home monopolist will prefer neither, because it earns higher profits in a freetrade situation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 179 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
The WTO opposes quotas.Why did the WTO not stop the U.S.
Japanese quota during the 1980s?
A)There was a loophole in the GATT (at the time) that did not restrict nations from "voluntarily" curtailing their own exports.
B)Quotas are permitted under the GATT and WTO-as long as they are implemented for an approved reason.
C)The political situation at the time was tense; the GATT did not want to take on the powerhouses of the United States and Japan over such
A small issue.
D)The WTO operates by consensus; all parties wanted the quotas.
Japanese quota during the 1980s?
A)There was a loophole in the GATT (at the time) that did not restrict nations from "voluntarily" curtailing their own exports.
B)Quotas are permitted under the GATT and WTO-as long as they are implemented for an approved reason.
C)The political situation at the time was tense; the GATT did not want to take on the powerhouses of the United States and Japan over such
A small issue.
D)The WTO operates by consensus; all parties wanted the quotas.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 179 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
The voluntary export restraint that the United States negotiated with
Japan:
A)violated provisions of the GATT that encouraged countries to avoid using quotas.
B)exploited a loophole in the GATT because the quota was administered by the exporting country.
C)did not allow U.S.auto producers to raise their prices.
D)did not impose any deadweight losses on the United States.
Japan:
A)violated provisions of the GATT that encouraged countries to avoid using quotas.
B)exploited a loophole in the GATT because the quota was administered by the exporting country.
C)did not allow U.S.auto producers to raise their prices.
D)did not impose any deadweight losses on the United States.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 179 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
Suppose that a foreign monopolist supplies the entire domestic market
(there is no domestic production).The home country then applies a
5% tariff on imports from the foreign monopolist.How will the tariff
Affect the price in the home market?
A)It will increase by more than 5%.
B)It will increase by 5%.
C)It will increase by less than 5%.
D)It will not change.
(there is no domestic production).The home country then applies a
5% tariff on imports from the foreign monopolist.How will the tariff
Affect the price in the home market?
A)It will increase by more than 5%.
B)It will increase by 5%.
C)It will increase by less than 5%.
D)It will not change.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 179 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
A case study of Japanese auto imports during the 1980s focuses on an
Agreement between Japan and the United States to undertake:
A)a coordinated effort to improve gas mileage.
B)a study of wage concessions by Japanese carmakers in the United States.
C)a review of unionization and employee benefits in both nations.
D)a voluntary export restraint.
Agreement between Japan and the United States to undertake:
A)a coordinated effort to improve gas mileage.
B)a study of wage concessions by Japanese carmakers in the United States.
C)a review of unionization and employee benefits in both nations.
D)a voluntary export restraint.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 179 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
If a foreign country imposes a voluntary export restraint, then the:
A)consumer surplus will be lower than would be so if the home country imposes a tariff
B)producer surplus will be lower than would be so if the home country imposes a tariff.
C)area of government revenue will be taken by the foreign country.
D)deadweight loss is smaller than would be so if the home country imposes a tariff.
A)consumer surplus will be lower than would be so if the home country imposes a tariff
B)producer surplus will be lower than would be so if the home country imposes a tariff.
C)area of government revenue will be taken by the foreign country.
D)deadweight loss is smaller than would be so if the home country imposes a tariff.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 179 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
When there is a foreign monopoly exporting to the home nation, under
Free trade it will sell a quantity where the home ______ is just equal
To the foreign ______.
A)MC; MR
B)supply; demand
C)demand; supply
D)MR; MC
Free trade it will sell a quantity where the home ______ is just equal
To the foreign ______.
A)MC; MR
B)supply; demand
C)demand; supply
D)MR; MC

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 179 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
A country is more likely to have net welfare gains when it imposes a
Tariff on a foreign monopolist if:
A)the tariff is small.
B)the tariff is large.
C)the tariff revenues are large.
D)the deadweight losses are large.
Tariff on a foreign monopolist if:
A)the tariff is small.
B)the tariff is large.
C)the tariff revenues are large.
D)the deadweight losses are large.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 179 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
What will a home monopolist prefer?
A)high quotas
B)low quotas
C)low tariffs
D)It would like all of these equally; that is, they are equivalent.
A)high quotas
B)low quotas
C)low tariffs
D)It would like all of these equally; that is, they are equivalent.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 179 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
When a tariff is applied to a good exported by a foreign monopoly
(with no home producer), the price net of the tariff received by the
Seller is _________.
A)lower than under free trade
B)higher than under free trade
C)the same as under free trade
D)so high that no sales are possible
(with no home producer), the price net of the tariff received by the
Seller is _________.
A)lower than under free trade
B)higher than under free trade
C)the same as under free trade
D)so high that no sales are possible

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 179 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
When a tariff is applied to a good exported by a foreign monopoly
(with no home producer), the increase in the equilibrium price is
________ the tariff applied.
A)more than
B)less than
C)the same as
D)more than twice as much as
(with no home producer), the increase in the equilibrium price is
________ the tariff applied.
A)more than
B)less than
C)the same as
D)more than twice as much as

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 179 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
A country's net welfare will increase when it imposes a tariff on a
Foreign monopolist if its:
A)termsoftrade gain is greater than its increase in tariff revenues.
B)termsoftrade gain is less than its increase in tariff revenues.
C)termsoftrade gain is greater than its lost consumer surplus.
D)increase in tariff revenues is greater than its lost consumer surplus.
Foreign monopolist if its:
A)termsoftrade gain is greater than its increase in tariff revenues.
B)termsoftrade gain is less than its increase in tariff revenues.
C)termsoftrade gain is greater than its lost consumer surplus.
D)increase in tariff revenues is greater than its lost consumer surplus.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 179 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
Under the voluntary export restraints, the Japanese government
Allocated each Japanese auto producer a certain number of cars that
They could export to the United States.As a result, Japanese auto
Producers exported:
A)fewer and more luxurious cars to the United States.
B)fewer and less luxurious cars to the United States.
C)more luxurious cars to the United States.
D)less luxurious cars to the United States.
Allocated each Japanese auto producer a certain number of cars that
They could export to the United States.As a result, Japanese auto
Producers exported:
A)fewer and more luxurious cars to the United States.
B)fewer and less luxurious cars to the United States.
C)more luxurious cars to the United States.
D)less luxurious cars to the United States.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 179 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
Under the VER of the 1980s, U.S.automakers:
A)continued their downward slide.
B)could not recover because they were also faced with other issues, such as labor unrest, increased oil and steel prices, and higher taxes.
C)were able to raise prices and improve quality to get even higher prices.
D)were able, with the quota, to ignore world market conditions.
A)continued their downward slide.
B)could not recover because they were also faced with other issues, such as labor unrest, increased oil and steel prices, and higher taxes.
C)were able to raise prices and improve quality to get even higher prices.
D)were able, with the quota, to ignore world market conditions.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 179 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
Roughly ________ of the increased prices of Japanese automobiles
During the 1980s was due to the voluntary export restraints.
A)25%
B)35%
C)50%
D)95%
During the 1980s was due to the voluntary export restraints.
A)25%
B)35%
C)50%
D)95%

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 179 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
In order to avoid congressional action in the United States, in the
Early 1980s the Japanese resorted to:
A)infant industry protection.
B)dumping of automobiles.
C)voluntary export restraint (VER).
D)price discrimination.
Early 1980s the Japanese resorted to:
A)infant industry protection.
B)dumping of automobiles.
C)voluntary export restraint (VER).
D)price discrimination.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 179 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
If a country imposes a $10 tariff on a foreign monopolist, the price
Received by the monopolist, net of the tariff, will:
A)fall by $10.
B)fall by less than $10.
C)fall by more than $10.
D)fall by $0.
Received by the monopolist, net of the tariff, will:
A)fall by $10.
B)fall by less than $10.
C)fall by more than $10.
D)fall by $0.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 179 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
Under the VER of the 1980s, Japan's automakers received:
A)additional quota rents of about $2.2 billion.
B)approximately 10% lower prices.
C)censure by the WTO for failing to behave in a competitive manner.
D)wage concessions from their U.S.employees to keep plants open in the United States.
A)additional quota rents of about $2.2 billion.
B)approximately 10% lower prices.
C)censure by the WTO for failing to behave in a competitive manner.
D)wage concessions from their U.S.employees to keep plants open in the United States.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 179 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
The effect of a tariff on a foreign monopolist is similar to a large nation
Imposing a tariff on a small nation.What is the implication for the
Welfare of the home nation?
A)Only very large tariffs bring any benefit to the home nation.
B)No tariffs are the best policy; all tariffs have a deadweight net loss.
C)Small tariffs can be beneficial, but only to a certain point.
D)The foreign producer may actually raise prices to make the tariff impossible to impose.
Imposing a tariff on a small nation.What is the implication for the
Welfare of the home nation?
A)Only very large tariffs bring any benefit to the home nation.
B)No tariffs are the best policy; all tariffs have a deadweight net loss.
C)Small tariffs can be beneficial, but only to a certain point.
D)The foreign producer may actually raise prices to make the tariff impossible to impose.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 179 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
If a country imposes a $10 tariff on a foreign monopolist, the domestic
Price will rise by:
A)more than $10.
B)$10.
C)less than $10.
D)$0.
Price will rise by:
A)more than $10.
B)$10.
C)less than $10.
D)$0.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 179 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



