Deck 2: Trade and Technology: the Ricardian Model
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/173
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 2: Trade and Technology: the Ricardian Model
1
Which of the following is NOT considered to be a factor of production?
A)labor
B)capital
C)natural resources
D)government
A)labor
B)capital
C)natural resources
D)government
D
2
When a country requires more resources to produce a product than other
Countries, it is said to have a(n):
A)absolute disadvantage in the production of the product.
B)comparative disadvantage in the production of the product.
C)lower opportunity cost of producing the product.
D)higher opportunity cost of producing the product.
Countries, it is said to have a(n):
A)absolute disadvantage in the production of the product.
B)comparative disadvantage in the production of the product.
C)lower opportunity cost of producing the product.
D)higher opportunity cost of producing the product.
A
3
Mercantilists believed that:
A)exporting goods will leave fewer goods for the local economy.
B)importing goods is beneficial for the economy.
C)any kind of trade is a bad trade.
D)exports are good and imports are bad.
A)exporting goods will leave fewer goods for the local economy.
B)importing goods is beneficial for the economy.
C)any kind of trade is a bad trade.
D)exports are good and imports are bad.
D
4
Which of the following is the MOST likely explanation for a Detroit
Construction company's imports of Canadian concrete blocks made in
Windsor, Ontario?
A)the Ricardian model
B)offshoring
C)technology
D)proximity
Construction company's imports of Canadian concrete blocks made in
Windsor, Ontario?
A)the Ricardian model
B)offshoring
C)technology
D)proximity

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 173 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
The primary explanation of trade among nations is Ricardo's theory of:
A)offshoring.
B)resource abundance.
C)absolute advantage.
D)comparative advantage.
A)offshoring.
B)resource abundance.
C)absolute advantage.
D)comparative advantage.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 173 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
What is the MOST likely reason neighboring nations engage in trade?
A)labor availability
B)similar tastes and preferences
C)proximity
D)shared membership in a freetrade area
A)labor availability
B)similar tastes and preferences
C)proximity
D)shared membership in a freetrade area

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 173 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
According to the Ricardian principle of comparative advantage,
International trade increases a nation's total output because:
A)the nation's resources are used where they are most productive.
B)the output of the nation's trading partner declines.
C)the nation can produce to the exterior of its production possibilities frontier.
D)the nation is able to increase its consumption.
International trade increases a nation's total output because:
A)the nation's resources are used where they are most productive.
B)the output of the nation's trading partner declines.
C)the nation can produce to the exterior of its production possibilities frontier.
D)the nation is able to increase its consumption.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 173 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
David Ricardo's model, which provided an explanation of why nations
Trade, was based on:
A)labor productivity.
B)technology.
C)population.
D)government control.
Trade, was based on:
A)labor productivity.
B)technology.
C)population.
D)government control.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 173 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Ricardo's theory of trade discredited the idea that inflows of gold or silver
As a result of exporting helped a nation, while outflows of gold or silver
As a result of importing hurt a nation; that was known as:
A)export preference.
B)mercantilism.
C)monetary economics.
D)pricespecieflow mechanism.
As a result of exporting helped a nation, while outflows of gold or silver
As a result of importing hurt a nation; that was known as:
A)export preference.
B)mercantilism.
C)monetary economics.
D)pricespecieflow mechanism.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 173 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
The focus of the Ricardian model is on how:
A)countries' resource bases explain international trade.
B)countries' different technologies explain international trade.
C)transportation costs explain international trade.
D)different languages and cultures explain international trade.
A)countries' resource bases explain international trade.
B)countries' different technologies explain international trade.
C)transportation costs explain international trade.
D)different languages and cultures explain international trade.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 173 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
When a country requires fewer resources to produce a product than
Other countries, it is said to have a(n):
A)absolute advantage in the production of the product.
B)comparative advantage in the production of the product.
C)higher opportunity cost of producing the product.
D)lower opportunity cost of producing the product.
Other countries, it is said to have a(n):
A)absolute advantage in the production of the product.
B)comparative advantage in the production of the product.
C)higher opportunity cost of producing the product.
D)lower opportunity cost of producing the product.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 173 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Ricardo's theory made a number of assumptions, including which of the
Following?
A)Nations had balanced trade with their partners.
B)There were no barriers to trade (free trade).
C)There was no transfer of gold or silver.
D)Nations had balanced trade with their partners, and there were no barriers to trade (free trade).
Following?
A)Nations had balanced trade with their partners.
B)There were no barriers to trade (free trade).
C)There was no transfer of gold or silver.
D)Nations had balanced trade with their partners, and there were no barriers to trade (free trade).

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 173 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Ricardo's theory showed that if nations are allowed to trade freely, the
Result will be that:
A)all trading nations benefit by trade.
B)the manufacturing sector benefits but the consumers lose out.
C)workers benefit but the government loses tax revenue.
D)the gains from trade offset the losses from trade exactly.
Result will be that:
A)all trading nations benefit by trade.
B)the manufacturing sector benefits but the consumers lose out.
C)workers benefit but the government loses tax revenue.
D)the gains from trade offset the losses from trade exactly.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 173 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
David Ricardo believed that:
A)trade is a zerosum game; that is, a country benefits at the expense of other countries.
B)trade will benefit countries when it generates gold and silver for the national treasury.
C)all nations can gain from free international trade.
D)trade cannot increase the world's output of goods.
A)trade is a zerosum game; that is, a country benefits at the expense of other countries.
B)trade will benefit countries when it generates gold and silver for the national treasury.
C)all nations can gain from free international trade.
D)trade cannot increase the world's output of goods.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 173 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
The focus of the Ricardian model is on how differences in _________
Influence international trade patterns.
A)demand
B)comparative costs
C)absolute costs
D)transportation costs
Influence international trade patterns.
A)demand
B)comparative costs
C)absolute costs
D)transportation costs

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 173 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
When a firm in one nation purchases unfinished products internationally
And adds further processing to sell in the domestic market, this is known
As:
A)barter.
B)offshoring.
C)factor movement.
D)marketing arrangements.
And adds further processing to sell in the domestic market, this is known
As:
A)barter.
B)offshoring.
C)factor movement.
D)marketing arrangements.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 173 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
According to Ricardo:
A)all countries can gain from trade if they export goods for which they have an absolute advantage.
B)one country can gain from trade only at the expense of another country.
C)all countries can gain from trade if they export goods for which they have a comparative advantage.
D)all countries lose from international trade.
A)all countries can gain from trade if they export goods for which they have an absolute advantage.
B)one country can gain from trade only at the expense of another country.
C)all countries can gain from trade if they export goods for which they have a comparative advantage.
D)all countries lose from international trade.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 173 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
A country's factors of production include its:
A)labor.
B)capital.
C)natural resources.
D)labor, capital, and natural resources.
A)labor.
B)capital.
C)natural resources.
D)labor, capital, and natural resources.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 173 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
In trade, if-due to technology-a nation can produce a good (such as
Germany's production of snowboards) with fewest resources, it is known
As a(n):
A)absolute advantage.
B)technology advantage.
C)comparative advantage.
D)resource advantage.
Germany's production of snowboards) with fewest resources, it is known
As a(n):
A)absolute advantage.
B)technology advantage.
C)comparative advantage.
D)resource advantage.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 173 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Which of the following is NOT a reason why countries trade goods with
One another?
A)differences in technology used in different countries
B)differences in countries' total amount of resources
C)the proximity of countries to one another
D)differences in countries' languages and cultures
One another?
A)differences in technology used in different countries
B)differences in countries' total amount of resources
C)the proximity of countries to one another
D)differences in countries' languages and cultures

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 173 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Production possibilities frontiers in the Ricardian model:
A)are linear (i.e., straight lines), with end points showing a country's production when it produces only one or the other good.
B)are bowed out from the origin, with end points showing a country's production when it produces only one or the other good.
C)are linear and begin from the origin.
D)are curvilinear and increase at a decreasing rate.
A)are linear (i.e., straight lines), with end points showing a country's production when it produces only one or the other good.
B)are bowed out from the origin, with end points showing a country's production when it produces only one or the other good.
C)are linear and begin from the origin.
D)are curvilinear and increase at a decreasing rate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 173 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Figure: Home Production and Consumption 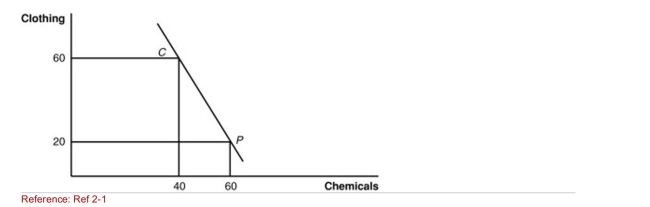 (Figure: Home Production and Consumption) The figure gives Home's
(Figure: Home Production and Consumption) The figure gives Home's
International trading pattern.Point P is production with trade, and point
C is consumption with trade.Which product does Home export?
A)clothing
B)chemicals
C)It exports neither chemicals nor clothing.
D)It exports both chemicals and clothing.
 (Figure: Home Production and Consumption) The figure gives Home's
(Figure: Home Production and Consumption) The figure gives Home'sInternational trading pattern.Point P is production with trade, and point
C is consumption with trade.Which product does Home export?
A)clothing
B)chemicals
C)It exports neither chemicals nor clothing.
D)It exports both chemicals and clothing.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 173 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Assume the MPLt = 5 tennis rackets and MPLb = 4 baseball bats.If the
Economy has 100 workers, then the economy can produce:
A)a maximum of 500 tennis rackets.
B)a maximum of 350 baseball bats.
C)500 tennis rackets and 400 baseball bats.
D)either 100 tennis rackets only or 100 baseball bats only.
Economy has 100 workers, then the economy can produce:
A)a maximum of 500 tennis rackets.
B)a maximum of 350 baseball bats.
C)500 tennis rackets and 400 baseball bats.
D)either 100 tennis rackets only or 100 baseball bats only.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 173 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
The Ricardian model assumes that the marginal product of labor is:
A)increasing.
B)decreasing.
C)constant.
D)zero.
A)increasing.
B)decreasing.
C)constant.
D)zero.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 173 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
The slope of the PPF can be expressed as:
A)the ratio of abundance of capital to labor.
B)the preferences of consumers in terms of marginal utility.
C)the ratio of the quantities of good 1 and good 2.
D)the negative of the ratio of the marginal products of labor in producing each good.
A)the ratio of abundance of capital to labor.
B)the preferences of consumers in terms of marginal utility.
C)the ratio of the quantities of good 1 and good 2.
D)the negative of the ratio of the marginal products of labor in producing each good.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 173 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
With the assumption that the marginal product of labor is constant and
That labor is the only variable resource, the slope of the PPF is:
A)positive and increasing.
B)negative and decreasing.
C)negative and constant.
D)unrelated to the issue at hand.
That labor is the only variable resource, the slope of the PPF is:
A)positive and increasing.
B)negative and decreasing.
C)negative and constant.
D)unrelated to the issue at hand.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 173 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
In the Ricardian model, the marginal product of labor:
A)first rises, then falls, as more labor is employed to produce a good.
B)first falls, then rises, as more labor is employed to produce a good.
C)continuously falls, as more labor is employed to produce a good.
D)does not change, as more labor is employed to produce a good.
A)first rises, then falls, as more labor is employed to produce a good.
B)first falls, then rises, as more labor is employed to produce a good.
C)continuously falls, as more labor is employed to produce a good.
D)does not change, as more labor is employed to produce a good.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 173 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
When the production possibilities frontier is a straight line, then
Production occurs under conditions of:
A)increasing costs.
B)decreasing costs.
C)constant costs.
D)increasing, then decreasing, then constant costs.
Production occurs under conditions of:
A)increasing costs.
B)decreasing costs.
C)constant costs.
D)increasing, then decreasing, then constant costs.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 173 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Figure: Home Production and Consumption 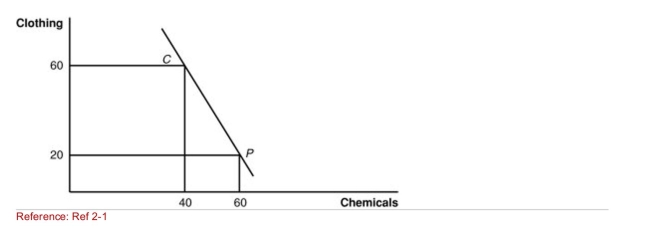 (Figure: Home Production and Consumption) The figure gives Home's
(Figure: Home Production and Consumption) The figure gives Home's
International trading pattern.Point P is production with trade, and point
C is consumption with trade.What is the international price of chemicals
According to the figure?
A)1/2 unit of clothing per unit of chemicals
B)one unit of clothing per unit of chemicals
C)two units of clothing per unit of chemicals
D)three units of clothing per unit of chemicals
 (Figure: Home Production and Consumption) The figure gives Home's
(Figure: Home Production and Consumption) The figure gives Home'sInternational trading pattern.Point P is production with trade, and point
C is consumption with trade.What is the international price of chemicals
According to the figure?
A)1/2 unit of clothing per unit of chemicals
B)one unit of clothing per unit of chemicals
C)two units of clothing per unit of chemicals
D)three units of clothing per unit of chemicals

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 173 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Figure: Home Production and Consumption 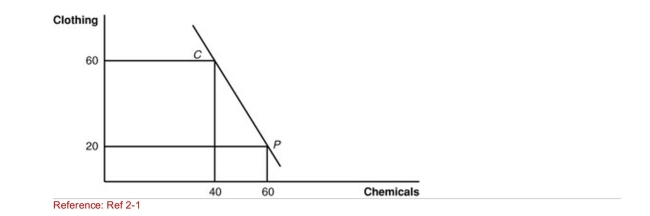 (Figure: Home Production and Consumption) The figure gives Home's
(Figure: Home Production and Consumption) The figure gives Home's
International trading pattern.Point P is production with trade, and point
C is consumption with trade.Which product does Home import?
A)clothing
B)chemicals
C)It imports neither chemicals nor clothing.
D)It imports both chemicals and clothing.
 (Figure: Home Production and Consumption) The figure gives Home's
(Figure: Home Production and Consumption) The figure gives Home'sInternational trading pattern.Point P is production with trade, and point
C is consumption with trade.Which product does Home import?
A)clothing
B)chemicals
C)It imports neither chemicals nor clothing.
D)It imports both chemicals and clothing.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 173 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
To complete the model of international trade using the PPF, we must also
Use the idea of indifference curves.These curves represent:
A)a set of alternate quantities of both goods (sloped negatively), whereby consumers are equally satisfied in their level of utility gained.
B)consumers who are indifferent to everything.
C)producers who do not care which production method is chosen.
D)a fixed quantity of one good (such as wheat) and a varying amount of the other good.
Use the idea of indifference curves.These curves represent:
A)a set of alternate quantities of both goods (sloped negatively), whereby consumers are equally satisfied in their level of utility gained.
B)consumers who are indifferent to everything.
C)producers who do not care which production method is chosen.
D)a fixed quantity of one good (such as wheat) and a varying amount of the other good.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 173 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Assume the MPLc = 2 cars and the MPLb = 5 boats.There are 150
Workers in this hypothetical economy.What is the maximum number of
Boats that can be produced?
A)30
B)300
C)750
D)150
Workers in this hypothetical economy.What is the maximum number of
Boats that can be produced?
A)30
B)300
C)750
D)150

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 173 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
As a consumer moves down one of her indifference curves, her
Satisfaction:
A)falls.
B)rises.
C)remains unchanged.
D)first falls, then levels out.
Satisfaction:
A)falls.
B)rises.
C)remains unchanged.
D)first falls, then levels out.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 173 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
If the maximum number of units of cloth produced is 300 and the
Maximum number of units of corn produced is 600, then with a MPLcloth
= 2, what is the MPLcorn?
A)4
B)5
C)6
D)7
Maximum number of units of corn produced is 600, then with a MPLcloth
= 2, what is the MPLcorn?
A)4
B)5
C)6
D)7

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 173 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
International trade allows countries to:
A)produce outside their PPF.
B)produce inside their PPF.
C)consume inside their PPF.
D)consume outside their PPF.
A)produce outside their PPF.
B)produce inside their PPF.
C)consume inside their PPF.
D)consume outside their PPF.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 173 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
If the maximum number of units of cloth produced is 300 and the
Maximum number of units of corn produced is 600, then with a MPLcloth
= 2, what is the number of workers in the economy?
A)100
B)200
C)150
D)600
Maximum number of units of corn produced is 600, then with a MPLcloth
= 2, what is the number of workers in the economy?
A)100
B)200
C)150
D)600

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 173 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
The Ricardian model employs the concept of alternate uses of economic
Resources in production.We refer to this technique as:
A)the production possibilities frontier.
B)the labor theory of value technique.
C)the leastcost option.
D)the labor productivity model.
Resources in production.We refer to this technique as:
A)the production possibilities frontier.
B)the labor theory of value technique.
C)the leastcost option.
D)the labor productivity model.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 173 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
The Ricardian model can be simplified and made more explanatory by
Assuming that there is only one resource used in producing goods.What
Did Ricardo assume the resource was?
A)capital
B)technology
C)labor
D)loanable funds
Assuming that there is only one resource used in producing goods.What
Did Ricardo assume the resource was?
A)capital
B)technology
C)labor
D)loanable funds

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 173 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
What is the marginal product of labor?
A)the average output of a unit of labor
B)the extra output obtained by using one more unit of labor
C)the average output obtained by using one more unit of labor
D)the total output obtained by using one more unit of labor
A)the average output of a unit of labor
B)the extra output obtained by using one more unit of labor
C)the average output obtained by using one more unit of labor
D)the total output obtained by using one more unit of labor

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 173 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
If a consumer moves to a higher indifference curve, her satisfaction:
A)falls.
B)rises.
C)remains unchanged.
D)first falls, then levels out.
A)falls.
B)rises.
C)remains unchanged.
D)first falls, then levels out.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 173 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
Figure: Home Equilibrium with No Trade 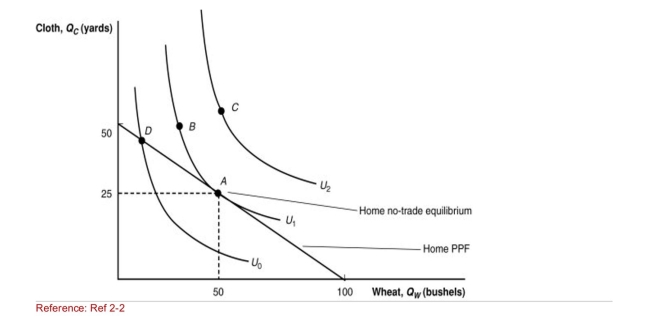 (Figure: Home Equilibrium with No Trade) Under the condition of no
(Figure: Home Equilibrium with No Trade) Under the condition of no
Trade, which combination of the following is NOT attainable?
A)A
B)B
C)C
D)D
 (Figure: Home Equilibrium with No Trade) Under the condition of no
(Figure: Home Equilibrium with No Trade) Under the condition of noTrade, which combination of the following is NOT attainable?
A)A
B)B
C)C
D)D

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 173 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Figure: Indifference Curves 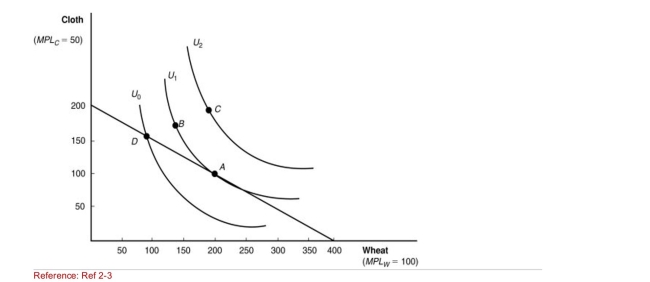 (Figure: Indifference Curves) Of the following points of consumption,
(Figure: Indifference Curves) Of the following points of consumption,
Which is LEAST desirable for consumers?
A)A
B)B
C)C
D)D
 (Figure: Indifference Curves) Of the following points of consumption,
(Figure: Indifference Curves) Of the following points of consumption,Which is LEAST desirable for consumers?
A)A
B)B
C)C
D)D

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 173 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
Figure: Indifference Curves 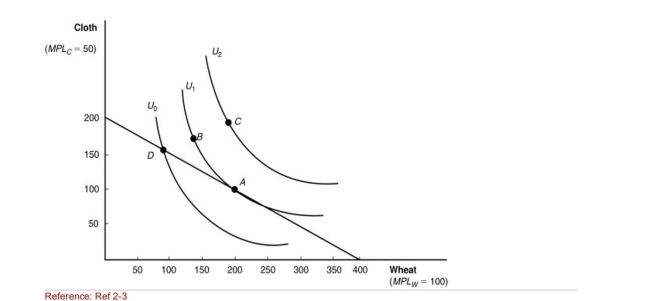 (Figure: Indifference Curves) Of the following points of consumption,
(Figure: Indifference Curves) Of the following points of consumption,
Which is MOST desirable for consumers?
A)A
B)B
C)C
D)D
 (Figure: Indifference Curves) Of the following points of consumption,
(Figure: Indifference Curves) Of the following points of consumption,Which is MOST desirable for consumers?
A)A
B)B
C)C
D)D

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 173 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
A country's indifference curve describes combinations of goods that:
A)a country can purchase.
B)yield equal satisfaction to a country.
C)yield satisfaction to a country.
D)a country can produce.
A)a country can purchase.
B)yield equal satisfaction to a country.
C)yield satisfaction to a country.
D)a country can produce.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 173 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
In order for the production possibilities frontier to be a straight line,
Production must exhibit:
A)increasing costs.
B)decreasing costs.
C)constant costs.
D)increasing, then decreasing, then constant costs.
Production must exhibit:
A)increasing costs.
B)decreasing costs.
C)constant costs.
D)increasing, then decreasing, then constant costs.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 173 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
Figure: Indifference Curves 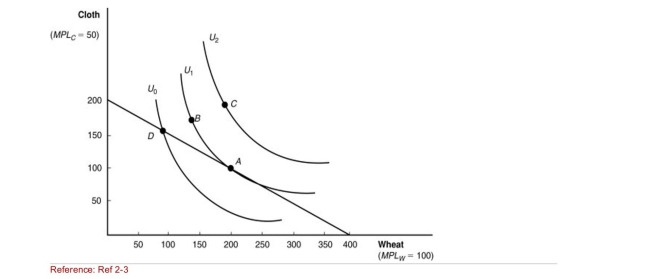 (Figure: Indifference Curves) Which point on the diagram represents the
(Figure: Indifference Curves) Which point on the diagram represents the
"home" equilibrium in the absence of international trade?
A)A
B)B
C)C
D)D
 (Figure: Indifference Curves) Which point on the diagram represents the
(Figure: Indifference Curves) Which point on the diagram represents the"home" equilibrium in the absence of international trade?
A)A
B)B
C)C
D)D

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 173 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
Among the indifference curves for an economy, to achieve higher utility:
A)you must move to the indifference curve farthest away from the origin.
B)you must move to the indifference curve closest to the origin.
C)It is necessary to always close the borders.
D)It does not matter which indifference curve you select; your utility is the same along every curve.
A)you must move to the indifference curve farthest away from the origin.
B)you must move to the indifference curve closest to the origin.
C)It is necessary to always close the borders.
D)It does not matter which indifference curve you select; your utility is the same along every curve.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 173 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
Assume the MPLc = 2 cars and the MPLb = 5 boats.There are 150
Workers in this hypothetical economy; the slope of the PPF for this
Economy is:
A)20/500.
B)200/50.
C)2/5.
D)1/5.
Workers in this hypothetical economy; the slope of the PPF for this
Economy is:
A)20/500.
B)200/50.
C)2/5.
D)1/5.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 173 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
In the absence of trade, a nation is in equilibrium where an indifference
Curve:
A)lies above its production possibilities frontier.
B)is tangent to its production possibilities frontier.
C)intersects its production possibilities frontier.
D)lies below its production possibilities frontier.
Curve:
A)lies above its production possibilities frontier.
B)is tangent to its production possibilities frontier.
C)intersects its production possibilities frontier.
D)lies below its production possibilities frontier.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 173 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
Assume a hypothetical economy where cloth and wheat can be produced.
What is the opportunity cost of producing wheat in this economy?
A)the amount of cloth that must be given up to produce one more unit of wheat
B)the amount of money received by selling wheat
C)the number of workers it takes to produce all the wheat
D)More information is needed to answer the question.
What is the opportunity cost of producing wheat in this economy?
A)the amount of cloth that must be given up to produce one more unit of wheat
B)the amount of money received by selling wheat
C)the number of workers it takes to produce all the wheat
D)More information is needed to answer the question.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 173 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
Figure: Indifference Curves 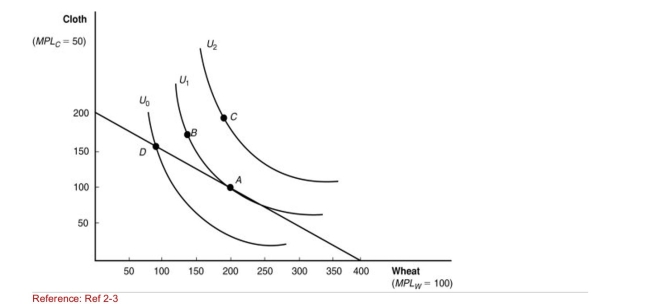 (Figure: Indifference Curves) What is the opportunity cost of cloth in
(Figure: Indifference Curves) What is the opportunity cost of cloth in
Terms of wheat in this example?
A)A unit of cloth may be obtained by foregoing a unit of wheat.
B)A unit of cloth "costs" 2 units of wheat.
C)A unit of cloth "costs" 1/2 unit of wheat.
D)Not enough information is given to answer.
 (Figure: Indifference Curves) What is the opportunity cost of cloth in
(Figure: Indifference Curves) What is the opportunity cost of cloth inTerms of wheat in this example?
A)A unit of cloth may be obtained by foregoing a unit of wheat.
B)A unit of cloth "costs" 2 units of wheat.
C)A unit of cloth "costs" 1/2 unit of wheat.
D)Not enough information is given to answer.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 173 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
Where will a nation that gains from trade find its consumption point
Located?
A)inside its production possibilities frontier
B)along its production possibilities frontier
C)outside its production possibilities frontier
D)at the center of its production possibilities frontier
Located?
A)inside its production possibilities frontier
B)along its production possibilities frontier
C)outside its production possibilities frontier
D)at the center of its production possibilities frontier

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 173 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
When a nation is in autarky (a notrade state) and maximizes its living
Standard, its consumption and production points are:
A)along its production possibilities frontier.
B)above its production possibilities frontier.
C)beneath production possibilities frontier.
D)along, above, or beneath its production possibilities frontier.
Standard, its consumption and production points are:
A)along its production possibilities frontier.
B)above its production possibilities frontier.
C)beneath production possibilities frontier.
D)along, above, or beneath its production possibilities frontier.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 173 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
If the opportunity cost is constant (the PPF is a straight line), then a
Country will:
A)partially specialize in the production of its exported product.
B)completely specialize in the production of its exported product.
C)not benefit from importing goods from another country.
D)benefit by raising trade barriers.
Country will:
A)partially specialize in the production of its exported product.
B)completely specialize in the production of its exported product.
C)not benefit from importing goods from another country.
D)benefit by raising trade barriers.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 173 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
A nation will gain from trade if it:
A)produces and consumes along its PPF.
B)produces outside its PPF and consumes along its PPF.
C)consumes outside its PPF and produces along its PPF.
D)produces and consumes outside its PPF.
A)produces and consumes along its PPF.
B)produces outside its PPF and consumes along its PPF.
C)consumes outside its PPF and produces along its PPF.
D)produces and consumes outside its PPF.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 173 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
Figure: Indifference Curves 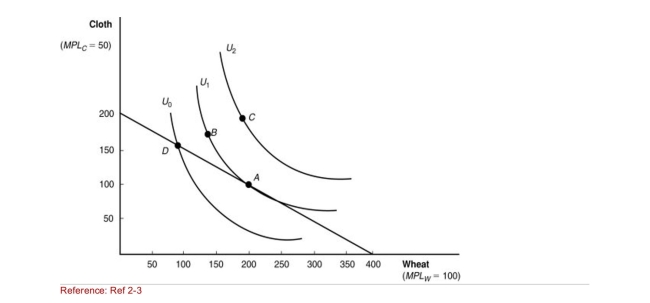 (Figure: Indifference Curves) If this economy produces no cloth, how
(Figure: Indifference Curves) If this economy produces no cloth, how
Many units of wheat are possible?
A)50
B)200
C)300
D)400
 (Figure: Indifference Curves) If this economy produces no cloth, how
(Figure: Indifference Curves) If this economy produces no cloth, howMany units of wheat are possible?
A)50
B)200
C)300
D)400

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 173 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
Figure: Home Equilibrium with No Trade 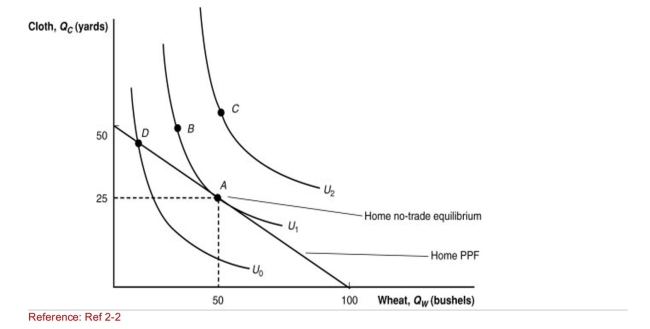 (Figure: Home Equilibrium with No Trade) Under the condition of no
(Figure: Home Equilibrium with No Trade) Under the condition of no
Trade, which combination gives the nation the MOST utility?
A)A
B)B
C)C
D)D
 (Figure: Home Equilibrium with No Trade) Under the condition of no
(Figure: Home Equilibrium with No Trade) Under the condition of noTrade, which combination gives the nation the MOST utility?
A)A
B)B
C)C
D)D

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 173 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
Figure: Indifference Curves 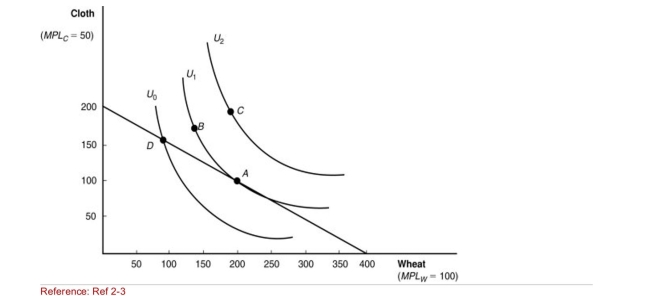 (Figure: Indifference Curves) Which combination of wheat and cloth is
(Figure: Indifference Curves) Which combination of wheat and cloth is
Represented by point A in the diagram?
A)200 units of wheat and 400 units of cloth
B)100 units of cloth and 200 units of wheat
C)200 units of cloth and 100 units of wheat
D)300 units of cloth and 150 units of wheat
 (Figure: Indifference Curves) Which combination of wheat and cloth is
(Figure: Indifference Curves) Which combination of wheat and cloth isRepresented by point A in the diagram?
A)200 units of wheat and 400 units of cloth
B)100 units of cloth and 200 units of wheat
C)200 units of cloth and 100 units of wheat
D)300 units of cloth and 150 units of wheat

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 173 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
Because the marginal product of labor measures the quantity of labor
Required to produce a unit of a good, the slope of the PPF can also be
Expressed as:
A)the ratio of abundance of labor to capital.
B)consumer utility.
C)the opportunity cost (in units of labor) to obtain an additional unit of good 1 in terms of what we give up of good 2.
D)the ratio of the marginal products of labor to the marginal product of capital.
Required to produce a unit of a good, the slope of the PPF can also be
Expressed as:
A)the ratio of abundance of labor to capital.
B)consumer utility.
C)the opportunity cost (in units of labor) to obtain an additional unit of good 1 in terms of what we give up of good 2.
D)the ratio of the marginal products of labor to the marginal product of capital.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 173 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
Moving to a lower indifference curve means that a country is:
A)better off.
B)worse off.
C)indifferent.
D)lowering production.
A)better off.
B)worse off.
C)indifferent.
D)lowering production.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 173 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
SCENARIO: ABSOLUTE AND COMPARATIVE ADVANTAGE
Poland requires 4 hours of labor to produce a ton of coal and 10 hours of
Labor to produce 10 bushels of wheat.The Czech Republic requires 6
Hours of labor to produce a ton of coal and 10 hours of labor to produce
10 bushels of wheat.
Reference: Ref 25
(Scenario: Absolute and Comparative Advantage) Which country has a
Comparative advantage in the production of coal?
A)Poland
B)the Czech Republic
C)Neither country has a comparative advantage.
D)Both countries have a comparative advantage.
Poland requires 4 hours of labor to produce a ton of coal and 10 hours of
Labor to produce 10 bushels of wheat.The Czech Republic requires 6
Hours of labor to produce a ton of coal and 10 hours of labor to produce
10 bushels of wheat.
Reference: Ref 25
(Scenario: Absolute and Comparative Advantage) Which country has a
Comparative advantage in the production of coal?
A)Poland
B)the Czech Republic
C)Neither country has a comparative advantage.
D)Both countries have a comparative advantage.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 173 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
SCENARIO: ABSOLUTE AND COMPARATIVE ADVANTAGE
Poland requires 4 hours of labor to produce a ton of coal and 10 hours of
Labor to produce 10 bushels of wheat.The Czech Republic requires 6
Hours of labor to produce a ton of coal and 10 hours of labor to produce
10 bushels of wheat.
Reference: Ref 25
(Scenario: Absolute and Comparative Advantage) Which country has an
Absolute advantage in the production of wheat?
A)Poland
B)the Czech Republic
C)Neither country has an absolute advantage.
D)Both countries have an absolute advantage.
Poland requires 4 hours of labor to produce a ton of coal and 10 hours of
Labor to produce 10 bushels of wheat.The Czech Republic requires 6
Hours of labor to produce a ton of coal and 10 hours of labor to produce
10 bushels of wheat.
Reference: Ref 25
(Scenario: Absolute and Comparative Advantage) Which country has an
Absolute advantage in the production of wheat?
A)Poland
B)the Czech Republic
C)Neither country has an absolute advantage.
D)Both countries have an absolute advantage.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 173 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
A nation will export the product in which it has a comparative advantage,
Which results from the good being relatively ____ than in the importing
Nation.
A)cheaper
B)more expensive
C)lower in quality
D)less available
Which results from the good being relatively ____ than in the importing
Nation.
A)cheaper
B)more expensive
C)lower in quality
D)less available

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 173 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
It can be shown that differences in "beforetrade" relative prices will
Determine:
A)which nation has the absolute advantage.
B)which good each nation will export or import.
C)the quantity traded by each nation.
D)which nation has the comparative advantage.
Determine:
A)which nation has the absolute advantage.
B)which good each nation will export or import.
C)the quantity traded by each nation.
D)which nation has the comparative advantage.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 173 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
SCENARIO: ABSOLUTE AND COMPARATIVE ADVANTAGE
Poland requires 4 hours of labor to produce a ton of coal and 10 hours of
Labor to produce 10 bushels of wheat.The Czech Republic requires 6
Hours of labor to produce a ton of coal and 10 hours of labor to produce
10 bushels of wheat.
Reference: Ref 25
(Scenario: Absolute and Comparative Advantage) Suppose that the
International price of coal is 4 1/4 bushels of wheat per ton of coal.
Which country is likely to have the larger gain from trade?
A)Poland
B)the Czech Republic
C)Neither country has the larger gain.
D)Both countries have the larger gain.
Poland requires 4 hours of labor to produce a ton of coal and 10 hours of
Labor to produce 10 bushels of wheat.The Czech Republic requires 6
Hours of labor to produce a ton of coal and 10 hours of labor to produce
10 bushels of wheat.
Reference: Ref 25
(Scenario: Absolute and Comparative Advantage) Suppose that the
International price of coal is 4 1/4 bushels of wheat per ton of coal.
Which country is likely to have the larger gain from trade?
A)Poland
B)the Czech Republic
C)Neither country has the larger gain.
D)Both countries have the larger gain.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 173 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
In competitive labor markets, the wage equals:
A)the marginal product of labor times the price of output.
B)the marginal product of labor minus the price of output.
C)the marginal product of labor plus the price of output.
D)the price of output.
A)the marginal product of labor times the price of output.
B)the marginal product of labor minus the price of output.
C)the marginal product of labor plus the price of output.
D)the price of output.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 173 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
In equilibrium, which of the following statements regarding the relative
Price of a tomato versus a book is CORRECT?
I)It is the opportunity cost of a tomato.
II)It is how much the production of books must fall in order to produce
Another tomato.
A)I
B)II
C)Neither is correct.
D)Both are correct.
Price of a tomato versus a book is CORRECT?
I)It is the opportunity cost of a tomato.
II)It is how much the production of books must fall in order to produce
Another tomato.
A)I
B)II
C)Neither is correct.
D)Both are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 173 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
SCENARIO: ABSOLUTE AND COMPARATIVE ADVANTAGE
Poland requires 4 hours of labor to produce a ton of coal and 10 hours of
Labor to produce 10 bushels of wheat.The Czech Republic requires 6
Hours of labor to produce a ton of coal and 10 hours of labor to produce
10 bushels of wheat.
Reference: Ref 25
(Scenario: Absolute and Comparative Advantage) In Poland, what is the
Marginal product of labor in coal production?
A)2.5 tons per hour
B)0.4 tons per hour
C)4 tons per hour
D)0.4 tons per bushel of wheat
Poland requires 4 hours of labor to produce a ton of coal and 10 hours of
Labor to produce 10 bushels of wheat.The Czech Republic requires 6
Hours of labor to produce a ton of coal and 10 hours of labor to produce
10 bushels of wheat.
Reference: Ref 25
(Scenario: Absolute and Comparative Advantage) In Poland, what is the
Marginal product of labor in coal production?
A)2.5 tons per hour
B)0.4 tons per hour
C)4 tons per hour
D)0.4 tons per bushel of wheat

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 173 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
SCENARIO: ABSOLUTE ADVANTAGE
The United States requires 20 hours of labor to produce a ton of steel
And 30 hours of labor to produce 1,000 board feet of lumber.In Canada,
20 hours of labor are required to produce a ton of steel and 25 hours of
Labor to produce 1,000 board feet of lumber.
Reference: Ref 24
(Scenario: Absolute Advantage) Which country has a comparative
Advantage in the production of lumber?
A)the United States
B)Canada
C)Neither the United States nor Canada has a comparative advantage.
D)Both the United States and Canada have a comparative advantage.
The United States requires 20 hours of labor to produce a ton of steel
And 30 hours of labor to produce 1,000 board feet of lumber.In Canada,
20 hours of labor are required to produce a ton of steel and 25 hours of
Labor to produce 1,000 board feet of lumber.
Reference: Ref 24
(Scenario: Absolute Advantage) Which country has a comparative
Advantage in the production of lumber?
A)the United States
B)Canada
C)Neither the United States nor Canada has a comparative advantage.
D)Both the United States and Canada have a comparative advantage.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 173 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
SCENARIO: ABSOLUTE AND COMPARATIVE ADVANTAGE
Poland requires 4 hours of labor to produce a ton of coal and 10 hours of
Labor to produce 10 bushels of wheat.The Czech Republic requires 6
Hours of labor to produce a ton of coal and 10 hours of labor to produce
10 bushels of wheat.
Reference: Ref 25
(Scenario: Absolute and Comparative Advantage) Which country has an
Absolute advantage in the production of coal?
A)Poland
B)the Czech Republic
C)Neither country has an absolute advantage.
D)Both countries have an absolute advantage.
Poland requires 4 hours of labor to produce a ton of coal and 10 hours of
Labor to produce 10 bushels of wheat.The Czech Republic requires 6
Hours of labor to produce a ton of coal and 10 hours of labor to produce
10 bushels of wheat.
Reference: Ref 25
(Scenario: Absolute and Comparative Advantage) Which country has an
Absolute advantage in the production of coal?
A)Poland
B)the Czech Republic
C)Neither country has an absolute advantage.
D)Both countries have an absolute advantage.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 173 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
SCENARIO: ABSOLUTE AND COMPARATIVE ADVANTAGE
Poland requires 4 hours of labor to produce a ton of coal and 10 hours of
Labor to produce 10 bushels of wheat.The Czech Republic requires 6
Hours of labor to produce a ton of coal and 10 hours of labor to produce
10 bushels of wheat.
Reference: Ref 25
(Scenario: Absolute and Comparative Advantage) Suppose that Poland
Has 1,000 hours of labor and that it completely specializes according to
Its comparative advantage.How many units of which product will it
Produce?
A)250 tons of coal
B)1,000 bushels of wheat
C)100 bushels of wheat
D)4,000 tons of coal
Poland requires 4 hours of labor to produce a ton of coal and 10 hours of
Labor to produce 10 bushels of wheat.The Czech Republic requires 6
Hours of labor to produce a ton of coal and 10 hours of labor to produce
10 bushels of wheat.
Reference: Ref 25
(Scenario: Absolute and Comparative Advantage) Suppose that Poland
Has 1,000 hours of labor and that it completely specializes according to
Its comparative advantage.How many units of which product will it
Produce?
A)250 tons of coal
B)1,000 bushels of wheat
C)100 bushels of wheat
D)4,000 tons of coal

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 173 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
SCENARIO: ABSOLUTE ADVANTAGE
The United States requires 20 hours of labor to produce a ton of steel
And 30 hours of labor to produce 1,000 board feet of lumber.In Canada,
20 hours of labor are required to produce a ton of steel and 25 hours of
Labor to produce 1,000 board feet of lumber.
Reference: Ref 24
(Scenario: Absolute Advantage) Which country has an absolute
Advantage in the production of steel?
A)the United States
B)Canada
C)Neither the United States nor Canada has an absolute advantage.
D)Both the United States and Canada have an absolute advantage.
The United States requires 20 hours of labor to produce a ton of steel
And 30 hours of labor to produce 1,000 board feet of lumber.In Canada,
20 hours of labor are required to produce a ton of steel and 25 hours of
Labor to produce 1,000 board feet of lumber.
Reference: Ref 24
(Scenario: Absolute Advantage) Which country has an absolute
Advantage in the production of steel?
A)the United States
B)Canada
C)Neither the United States nor Canada has an absolute advantage.
D)Both the United States and Canada have an absolute advantage.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 173 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
SCENARIO: ABSOLUTE AND COMPARATIVE ADVANTAGE
Poland requires 4 hours of labor to produce a ton of coal and 10 hours of
Labor to produce 10 bushels of wheat.The Czech Republic requires 6
Hours of labor to produce a ton of coal and 10 hours of labor to produce
10 bushels of wheat.
Reference: Ref 25
(Scenario: Absolute and Comparative Advantage) The international price
Of wheat must fall between which of the following two prices?
A)between 1/6 ton and 1/4 ton of coal per bushel of wheat
B)between 1 2/3 ton and 2 1/2 tons of coal per bushel of wheat
C)between 1/6 hour and 1/4 hour of labor per bushel of wheat
D)between 4 tons and 6 tons of coal per bushel of wheat
Poland requires 4 hours of labor to produce a ton of coal and 10 hours of
Labor to produce 10 bushels of wheat.The Czech Republic requires 6
Hours of labor to produce a ton of coal and 10 hours of labor to produce
10 bushels of wheat.
Reference: Ref 25
(Scenario: Absolute and Comparative Advantage) The international price
Of wheat must fall between which of the following two prices?
A)between 1/6 ton and 1/4 ton of coal per bushel of wheat
B)between 1 2/3 ton and 2 1/2 tons of coal per bushel of wheat
C)between 1/6 hour and 1/4 hour of labor per bushel of wheat
D)between 4 tons and 6 tons of coal per bushel of wheat

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 173 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
In the home equilibrium situation, the relative price of wheat is the same
As:
A)the relative price of cloth.
B)the slope of the PPF.
C)the marginal product of wheat.
D)the cost of labor to produce wheat.
As:
A)the relative price of cloth.
B)the slope of the PPF.
C)the marginal product of wheat.
D)the cost of labor to produce wheat.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 173 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
SCENARIO: ABSOLUTE ADVANTAGE
The United States requires 20 hours of labor to produce a ton of steel
And 30 hours of labor to produce 1,000 board feet of lumber.In Canada,
20 hours of labor are required to produce a ton of steel and 25 hours of
Labor to produce 1,000 board feet of lumber.
Reference: Ref 24
(Scenario: Absolute Advantage) Which country has a comparative
Advantage in the production of steel?
A)the United States
B)Canada
C)Neither the United States nor Canada has a comparative advantage.
D)Both the United States and Canada have a comparative advantage.
The United States requires 20 hours of labor to produce a ton of steel
And 30 hours of labor to produce 1,000 board feet of lumber.In Canada,
20 hours of labor are required to produce a ton of steel and 25 hours of
Labor to produce 1,000 board feet of lumber.
Reference: Ref 24
(Scenario: Absolute Advantage) Which country has a comparative
Advantage in the production of steel?
A)the United States
B)Canada
C)Neither the United States nor Canada has a comparative advantage.
D)Both the United States and Canada have a comparative advantage.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 173 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
SCENARIO: ABSOLUTE AND COMPARATIVE ADVANTAGE
Poland requires 4 hours of labor to produce a ton of coal and 10 hours of
Labor to produce 10 bushels of wheat.The Czech Republic requires 6
Hours of labor to produce a ton of coal and 10 hours of labor to produce
10 bushels of wheat.
Reference: Ref 25
(Scenario: Absolute and Comparative Advantage) What is the
Opportunity cost of coal in Poland?
A)0.25 hour of labor/ton of coal
B)2.5 bushels of wheat/ton of coal
C)4 hours of labor/ton of coal
D)0.4 bushels of wheat/ton of coal
Poland requires 4 hours of labor to produce a ton of coal and 10 hours of
Labor to produce 10 bushels of wheat.The Czech Republic requires 6
Hours of labor to produce a ton of coal and 10 hours of labor to produce
10 bushels of wheat.
Reference: Ref 25
(Scenario: Absolute and Comparative Advantage) What is the
Opportunity cost of coal in Poland?
A)0.25 hour of labor/ton of coal
B)2.5 bushels of wheat/ton of coal
C)4 hours of labor/ton of coal
D)0.4 bushels of wheat/ton of coal

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 173 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
SCENARIO: ABSOLUTE AND COMPARATIVE ADVANTAGE
Poland requires 4 hours of labor to produce a ton of coal and 10 hours of
Labor to produce 10 bushels of wheat.The Czech Republic requires 6
Hours of labor to produce a ton of coal and 10 hours of labor to produce
10 bushels of wheat.
Reference: Ref 25
(Scenario: Absolute and Comparative Advantage) Which country has a
Comparative advantage in the production of wheat?
A)Poland
B)the Czech Republic
C)Neither country has a comparative advantage.
D)Both countries have a comparative advantage.
Poland requires 4 hours of labor to produce a ton of coal and 10 hours of
Labor to produce 10 bushels of wheat.The Czech Republic requires 6
Hours of labor to produce a ton of coal and 10 hours of labor to produce
10 bushels of wheat.
Reference: Ref 25
(Scenario: Absolute and Comparative Advantage) Which country has a
Comparative advantage in the production of wheat?
A)Poland
B)the Czech Republic
C)Neither country has a comparative advantage.
D)Both countries have a comparative advantage.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 173 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
Whenever a nation has a lower opportunity cost of producing any good
Or service in relative terms, that nation is said to have:
A)an absolute advantage.
B)a comparative advantage.
C)low labor costs.
D)better technology to produce that good or service.
Or service in relative terms, that nation is said to have:
A)an absolute advantage.
B)a comparative advantage.
C)low labor costs.
D)better technology to produce that good or service.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 173 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
To explain why some nations purchase products from abroad, even when
They have an absolute advantage in production, we have to use the
Theory of:
A)absolute advantage.
B)relative pricing.
C)comparative advantage.
D)industrial advantage.
They have an absolute advantage in production, we have to use the
Theory of:
A)absolute advantage.
B)relative pricing.
C)comparative advantage.
D)industrial advantage.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 173 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
Which of the following statements describes the way our home
Equilibrium reflects the concepts of competitive markets?
I)The opportunity cost of each good is the inverse of the ratio of labor
Productivity.
II)Prices of each good reflect opportunity cost.
III)Wages are equal and reflect the value of the marginal product of
Labor (MPL × P) for each good.
A)I
B)II
C)III
D)I, II, and III
Equilibrium reflects the concepts of competitive markets?
I)The opportunity cost of each good is the inverse of the ratio of labor
Productivity.
II)Prices of each good reflect opportunity cost.
III)Wages are equal and reflect the value of the marginal product of
Labor (MPL × P) for each good.
A)I
B)II
C)III
D)I, II, and III

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 173 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



