Deck 15: Carbohydrates
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/54
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 15: Carbohydrates
1
Which group of carbohydrates cannot be hydrolyzed to give smaller molecules?
A)oligosaccharides
B)trisaccharides
C)disaccharides
D)monosaccharides
E)polysaccharides
A)oligosaccharides
B)trisaccharides
C)disaccharides
D)monosaccharides
E)polysaccharides
monosaccharides
2
The breakdown of carbohydrates to carbon dioxide and water in the body is called
A)photosynthesis.
B)respiration.
C)anabolism.
D)mutarotation.
E)reduction.
A)photosynthesis.
B)respiration.
C)anabolism.
D)mutarotation.
E)reduction.
respiration.
3
Which of the following is an example of an aldopentose?
A)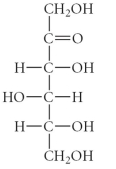
B)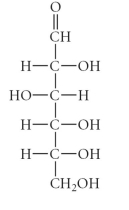
C)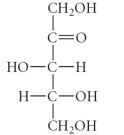
D)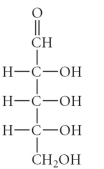
E)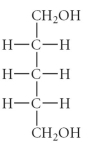
A)

B)

C)

D)

E)


4
The breakdown of glucose to chemical energy for the cells to do work is an example of
A)mutarotation.
B)reduction.
C)anabolism.
D)oxidation.
E)respiration.
A)mutarotation.
B)reduction.
C)anabolism.
D)oxidation.
E)respiration.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Ribulose has the following structural formula. To what carbohydrate class does ribulose belong? 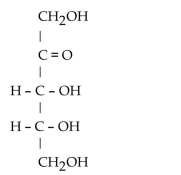
A)ketopentose
B)aldopentose
C)aldotetrose
D)ketohexose
E)ketotetrose
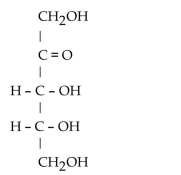
A)ketopentose
B)aldopentose
C)aldotetrose
D)ketohexose
E)ketotetrose

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Chiral drugs consist of only one enantiomer. The benefits of using a pure enantiomer, rather than a mixture, include
A)reduced chances of drug interactions.
B)elimination of side effects.
C)higher potency (lower total dose of drug).
D)All of the above.
E)None of the above.
A)reduced chances of drug interactions.
B)elimination of side effects.
C)higher potency (lower total dose of drug).
D)All of the above.
E)None of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
A monosaccharide that contains 4 carbon atoms, one of which is in an aldehyde group, is classified as a(n)
A)aldopentose.
B)aldohexose.
C)aldotetrose.
D)ketopentose.
E)ketotetrose.
A)aldopentose.
B)aldohexose.
C)aldotetrose.
D)ketopentose.
E)ketotetrose.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
An enantiomer is
A)a stereoisomer that is not a mirror image of another molecule.
B)a diastereoisomer.
C)a stereoisomer that is a mirror image of another molecule.
D)a structural isomer.
E)a cis-trans isomer.
A)a stereoisomer that is not a mirror image of another molecule.
B)a diastereoisomer.
C)a stereoisomer that is a mirror image of another molecule.
D)a structural isomer.
E)a cis-trans isomer.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Which molecule below has stereoisomers with different biological effects?
A)carvone
B)naproxen
C)epinephrine
D)nicotine
E)All of the above.
A)carvone
B)naproxen
C)epinephrine
D)nicotine
E)All of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
A carbohydrate that gives two molecules when it is completely hydrolyzed is known as a
A)polysaccharide.
B)monosaccharide.
C)starch.
D)trisaccharide.
E)disaccharide.
A)polysaccharide.
B)monosaccharide.
C)starch.
D)trisaccharide.
E)disaccharide.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
A monosaccharide that consists of 5 carbon atoms, one of which is in a ketone group, is classified as a(n)
A)ketopentose.
B)ketotetrose.
C)aldotetrose.
D)aldopentose.
E)aldohexose.
A)ketopentose.
B)ketotetrose.
C)aldotetrose.
D)aldopentose.
E)aldohexose.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
During photosynthesis, carbon dioxide and water are converted to glucose and oxygen by
A)mushrooms.
B)insects.
C)green plants.
D)large animals
E)earthworms.
A)mushrooms.
B)insects.
C)green plants.
D)large animals
E)earthworms.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
How many different substituents are required on a carbon atom for it to be chiral?
A)one
B)two
C)three
D)four
E)Any number from 1 to 4; chirality does not depend on substitution.
A)one
B)two
C)three
D)four
E)Any number from 1 to 4; chirality does not depend on substitution.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Chirality occurs when stereoisomers have mirror images that are
A)not superimposable.
B)identical.
C)superimposable.
D)not visible to one another.
E)the same.
A)not superimposable.
B)identical.
C)superimposable.
D)not visible to one another.
E)the same.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
In the L- isomer of a Fischer projection of a monosaccharide, the -OH group furthest from the carbonyl is written
A)on the left of the bottom chiral carbon.
B)on the right of the top chiral carbon.
C)on the left of the middle chiral carbon.
D)on the right of the bottom chiral carbon.
E)on the left of the top chiral carbon.
A)on the left of the bottom chiral carbon.
B)on the right of the top chiral carbon.
C)on the left of the middle chiral carbon.
D)on the right of the bottom chiral carbon.
E)on the left of the top chiral carbon.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Photosynthesis uses ________ as an energy source.
A)sunlight
B)glucose
C)oxygen
D)carbon dioxide
E)chlorophyll
A)sunlight
B)glucose
C)oxygen
D)carbon dioxide
E)chlorophyll

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Which of the following is an example of a ketopentose?
A)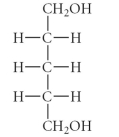
B)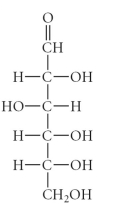
C)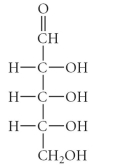
D)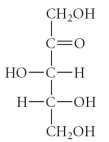
E)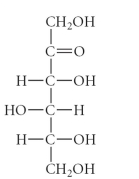
A)

B)

C)

D)

E)


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Which of the following is an example of an aldohexose?
A)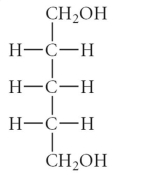
B)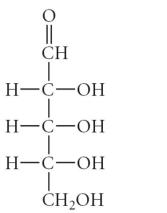
C)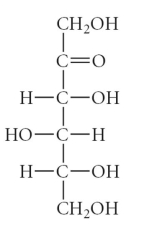
D)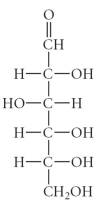
E)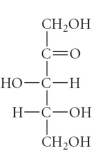
A)

B)

C)

D)

E)


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
One difference between D-glucose and L-glucose is
A)L-glucose cannot form a closed structure.
B)L-glucose has a 5-membered ring, and D-glucose has a 6-membered ring.
C)the open-chain form of L-glucose does not exist.
D)it is not possible to make L-glucose.
E)only D-glucose is more commonly found in disaccharides and polysaccharides.
A)L-glucose cannot form a closed structure.
B)L-glucose has a 5-membered ring, and D-glucose has a 6-membered ring.
C)the open-chain form of L-glucose does not exist.
D)it is not possible to make L-glucose.
E)only D-glucose is more commonly found in disaccharides and polysaccharides.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Fructose does not undergo hydrolysis because it is a(n)
A)aldose.
B)disaccharide.
C)hexose.
D)monosaccharide.
E)reducing sugar.
A)aldose.
B)disaccharide.
C)hexose.
D)monosaccharide.
E)reducing sugar.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
The oxidation of monosaccharides produces
A)sugar alcohols.
B)polysaccharides.
C)trisaccharides.
D)disaccharides.
E)sugar acids.
A)sugar alcohols.
B)polysaccharides.
C)trisaccharides.
D)disaccharides.
E)sugar acids.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Hyperglycemia is a condition in which
A)the glucose level in the blood is higher than normal.
B)the glucose level in the blood is about 90 mg/dL.
C)the amount of glucose in the urine is lower than normal.
D)the glucose level in the pancreas is lower than normal.
E)the glucose level in the liver is lower than normal.
A)the glucose level in the blood is higher than normal.
B)the glucose level in the blood is about 90 mg/dL.
C)the amount of glucose in the urine is lower than normal.
D)the glucose level in the pancreas is lower than normal.
E)the glucose level in the liver is lower than normal.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Which sugar is NOT a reducing sugar?
A)glucose
B)galactose
C)sucrose
D)fructose
E)maltose
A)glucose
B)galactose
C)sucrose
D)fructose
E)maltose

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Refer to the disaccharides below to answer the question(s)that follow. 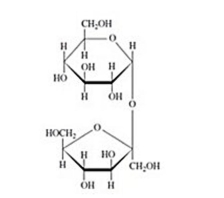
Hydrolysis of the disaccharide above gives the monosaccharides
A)ribose and glucose.
B)fructose and lactose.
C)fructose and ribose.
D)fructose and glucose.
E)ribose and galactose.

Hydrolysis of the disaccharide above gives the monosaccharides
A)ribose and glucose.
B)fructose and lactose.
C)fructose and ribose.
D)fructose and glucose.
E)ribose and galactose.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Which of the following contains a 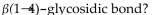
A)galactose
B)maltose
C)sucrose
D)lactose
E)amylose
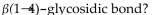
A)galactose
B)maltose
C)sucrose
D)lactose
E)amylose

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Which of the following contains 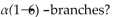
A)cellulose
B)amylose
C)maltose
D)glycogen
E)sucrose
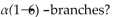
A)cellulose
B)amylose
C)maltose
D)glycogen
E)sucrose

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Refer to the disaccharides below to answer the question(s)that follow. 
In the figure above, the monosaccharide unit at the top is a(n)
A)aldopentose.
B)aldoheptose.
C)ketohexose.
D)ketopentose.
E)aldohexose.

In the figure above, the monosaccharide unit at the top is a(n)
A)aldopentose.
B)aldoheptose.
C)ketohexose.
D)ketopentose.
E)aldohexose.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
A glycosidic bond between two monosaccharides can also be classified as a(n)
A)double bond.
B)ester bond.
C)alcohol bond.
D)ether bond.
E)achiral bond.
A)double bond.
B)ester bond.
C)alcohol bond.
D)ether bond.
E)achiral bond.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Galactose is one of the products of enzymatic hydrolysis of
A)sucrose.
B)lactose.
C)glucose.
D)maltose.
E)erythrose.
A)sucrose.
B)lactose.
C)glucose.
D)maltose.
E)erythrose.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
The disaccharide above contains a(n) ______- glycosidic linkage.
A)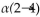
B)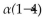
C)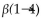
D)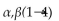
E)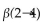
A)
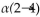
B)
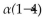
C)
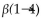
D)
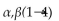
E)
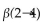

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
The reduction of monosaccharides produces
A)disaccharides.
B)sugar acids.
C)polysaccharides.
D)trisaccharides.
E)sugar alcohols.
A)disaccharides.
B)sugar acids.
C)polysaccharides.
D)trisaccharides.
E)sugar alcohols.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
In a disaccharide, two monosaccharides are joined by what kind of bond?
A)rotational
B)double
C)glycosidic
D)alcohol
E)anomeric
A)rotational
B)double
C)glycosidic
D)alcohol
E)anomeric

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Hypoglycemia is a condition in which
A)the glucose level in the blood is higher than normal.
B)the amount of glucose in the urine is higher than normal.
C)the glucose level in the pancreas is higher than normal.
D)the glucose level in the blood is lower than normal.
E)the glucose level in the blood is about 100 mg/dL.
A)the glucose level in the blood is higher than normal.
B)the amount of glucose in the urine is higher than normal.
C)the glucose level in the pancreas is higher than normal.
D)the glucose level in the blood is lower than normal.
E)the glucose level in the blood is about 100 mg/dL.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Galactose has the structure shown below. It can be classified as a 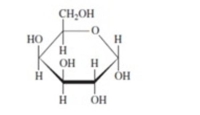
A)ketone.
B)ribose.
C)disaccharide.
D)ketose.
E)monosaccharide.

A)ketone.
B)ribose.
C)disaccharide.
D)ketose.
E)monosaccharide.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Maltose is a
A)trisaccharide.
B)phosphosaccharide.
C)disaccharide.
D)polysaccharide.
E)monosaccharide.
A)trisaccharide.
B)phosphosaccharide.
C)disaccharide.
D)polysaccharide.
E)monosaccharide.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
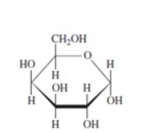
36
Mannose has the structure shown below. Which isomer is shown?
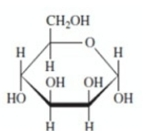
A)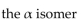
B)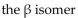
C) the D isomer
D) the L isomer
E) none of the above

A)
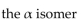
B)
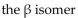
C) the D isomer
D) the L isomer
E) none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Refer to the disaccharides below to answer the question(s)that follow. 
In the figure above, the monosaccharide unit on the bottom is a(n)
A)ketopentose.
B)aldohexose.
C)aldoheptose.
D)aldopentose.
E)ketohexose.

In the figure above, the monosaccharide unit on the bottom is a(n)
A)ketopentose.
B)aldohexose.
C)aldoheptose.
D)aldopentose.
E)ketohexose.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
The sugar also known as dextrose and blood sugar is
A)lactose.
B)sucrose.
C)glucose.
D)galactose.
E)fructose.
A)lactose.
B)sucrose.
C)glucose.
D)galactose.
E)fructose.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
The conversion between α and β isomers occurs during a process called
A)reduction.
B)hydrolysis.
C)glycoside.
D)mutarotation.
E)oxidation.
A)reduction.
B)hydrolysis.
C)glycoside.
D)mutarotation.
E)oxidation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Maltose can be classified as a(n)
A)polysaccharide.
B)disaccharide.
C)ketose.
D)pentose.
E)oligosaccharide.
A)polysaccharide.
B)disaccharide.
C)ketose.
D)pentose.
E)oligosaccharide.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
State whether each of these structures is the 
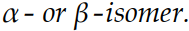


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Identify each Fischer projection as the D- or L-isomer.
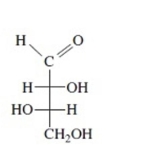


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
Under acid hydrolysis conditions, starch is ultimately converted to
A)fructose.
B)galactose.
C)xylose.
D)maltose.
E)glucose.
A)fructose.
B)galactose.
C)xylose.
D)maltose.
E)glucose.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
State whether each of these structures is the 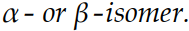
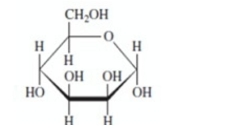


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
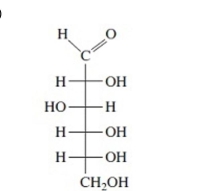
Identify each Fischer projection as the D- or L-isomer.


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
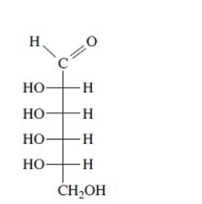
Identify each Fischer projection as the D- or L-isomer.


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
Humans cannot digest cellulose because they
A) lack the necessary enzymes to digest
B) are poisoned by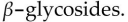
C) are allergic to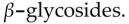
D) have intestinal flora which use up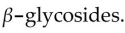
E) cannot digest chlorophyll.
A) lack the necessary enzymes to digest
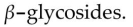
B) are poisoned by
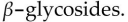
C) are allergic to
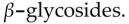
D) have intestinal flora which use up
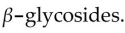
E) cannot digest chlorophyll.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
State whether each of these structures is the 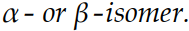
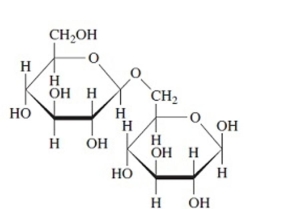


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
Identify each Fischer projection as the D- or L-isomer.
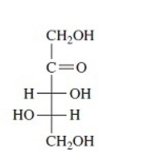


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
State whether each of these structures is the 
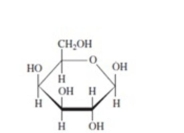
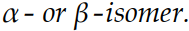


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
Amylose is a polysaccharide which has
A) only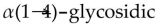 bonds glucose units.
bonds glucose units.
B) hemiacetal links joining glucose units.
C) carbon-carbon bonds joining glucose units.
D) both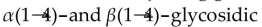 bonds between glucose units.
bonds between glucose units.
E) only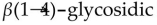 bonds between glucose units.
bonds between glucose units.
A) only
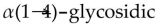 bonds glucose units.
bonds glucose units.B) hemiacetal links joining glucose units.
C) carbon-carbon bonds joining glucose units.
D) both
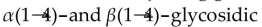 bonds between glucose units.
bonds between glucose units.E) only
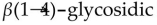 bonds between glucose units.
bonds between glucose units.
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
Amylopectin is a polysaccharide which has
A) only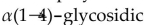 bonds glucose units.
bonds glucose units.
B) both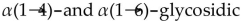 bonds between glucose units.
bonds between glucose units.
C) carbon-carbon bonds joining glucose units.
D) both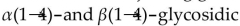 bonds between glucose units.
bonds between glucose units.
E) only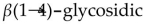 bonds between glucose units.
bonds between glucose units.
A) only
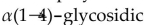 bonds glucose units.
bonds glucose units.B) both
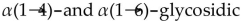 bonds between glucose units.
bonds between glucose units.C) carbon-carbon bonds joining glucose units.
D) both
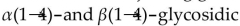 bonds between glucose units.
bonds between glucose units.E) only
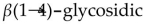 bonds between glucose units.
bonds between glucose units.
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
Identify each Fischer projection as the D- or L-isomer.
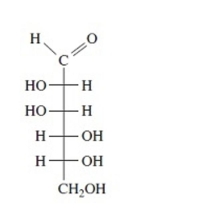


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
Cellulose is not digestible by humans because it contains glucose units linked by _____-glycosidic bonds.
A)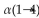
B)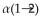
C)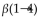
D)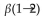
E)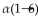
A)
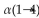
B)
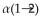
C)
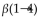
D)
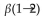
E)
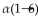

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



