Deck 9: Confidence Intervals Based on a Single Sample
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/51
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 9: Confidence Intervals Based on a Single Sample
1
A random sample of 33 pitches from a pitching machine set to throw at 80 mph yields an average speed of 79.25 mph.If we know that the standard deviation of speed from this machine is 2.22 mph, what is a 98% confidence interval for the mean pitch speed?
A) (78.255, 80.245)
B) (78.493, 80.007)
C) (78.351, 80.149)
D) (78.477, 80.023)
A) (78.255, 80.245)
B) (78.493, 80.007)
C) (78.351, 80.149)
D) (78.477, 80.023)
(78.351, 80.149)
2
Prior to the 1999-2000 NBA season, rules were changed in an effort to increase scoring and make basketball games more exciting.Previously, the league averaged 183.2 points per games.A random sample of 25 games played during December 1999 had a sample mean of 195.88 points per game, with a sample standard deviation of 20.27 points per game.What is a 95% confidence interval for the mean number of points per game after the rule change? Does this interval provide evidence of an increase in the average number of points per game?
A) (187.51, 204.25).No, but this does not contradict the idea that the average number of points per game has increased.
B) (187.51, 204.25).Yes, this provides firm evidence that the average number of points per game has increased.
C) (174.83, 191.57).No, but this does not contradict the idea that the average number of points per game has increased.
D) (174.83, 191.57).Yes, this provides firm evidence that the average number of points per game has increased.
A) (187.51, 204.25).No, but this does not contradict the idea that the average number of points per game has increased.
B) (187.51, 204.25).Yes, this provides firm evidence that the average number of points per game has increased.
C) (174.83, 191.57).No, but this does not contradict the idea that the average number of points per game has increased.
D) (174.83, 191.57).Yes, this provides firm evidence that the average number of points per game has increased.
(187.51, 204.25).No, but this does not contradict the idea that the average number of points per game has increased.
3
A biased estimator may be preferable to an unbiased estimator if:
A) the unbiased estimator has substantially less variability than the biased one.
B) the biased estimator has more variability than the unbiased one.
C) the biased estimator has substantially less variability than the unbiased one.
D) The only occasion where one would use a biased estimator is if an unbiased estimator did not exist.
A) the unbiased estimator has substantially less variability than the biased one.
B) the biased estimator has more variability than the unbiased one.
C) the biased estimator has substantially less variability than the unbiased one.
D) The only occasion where one would use a biased estimator is if an unbiased estimator did not exist.
the biased estimator has substantially less variability than the unbiased one.
4
Psychologists wish to evaluate the consistency of a standardized behavioral test.The test is designed to have a variance of 225.Twenty randomly sampled tests yield a variance of 240.Assuming the underlying population is normal, what is a 90% confidence interval for the variance of this test?
A) (151.276, 450.727)
B) (12.300, 21.230)
C) (190.542, 328.899)
D) (138.803, 511.986)
A) (151.276, 450.727)
B) (12.300, 21.230)
C) (190.542, 328.899)
D) (138.803, 511.986)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 51 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Why is a point estimate alone insufficient for providing a probabilistic estimate of a parameter?
A) Because a point estimate only estimates the parameter, it will never provide us with its value.
B) Although the point estimate provides a good guess for the parameter, it is a single value and, for a continuous variable, the probability the parameter equals this single value is 0.
C) The calculation of the point estimate is too fraught with uncertainty to provide an accurate probability estimate.
D) A point estimate is too static to accurately estimate a dynamic parameter.
A) Because a point estimate only estimates the parameter, it will never provide us with its value.
B) Although the point estimate provides a good guess for the parameter, it is a single value and, for a continuous variable, the probability the parameter equals this single value is 0.
C) The calculation of the point estimate is too fraught with uncertainty to provide an accurate probability estimate.
D) A point estimate is too static to accurately estimate a dynamic parameter.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 51 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
The chi-square distribution is:
A) symmetric around zero.
B) positively skewed.
C) negatively skewed.
D) mound-shaped.
A) symmetric around zero.
B) positively skewed.
C) negatively skewed.
D) mound-shaped.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 51 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Adult IQs are normally distributed, with a standard deviation of 15.We sample 10 adults and find 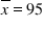 .What is a 95% confidence interval for the mean adult IQ?
.What is a 95% confidence interval for the mean adult IQ?
A) (65.6, 124.4)
B) (85.703, 104.297)
C) (83.967, 106.033)
D) (85.513, 104.487)
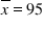 .What is a 95% confidence interval for the mean adult IQ?
.What is a 95% confidence interval for the mean adult IQ?A) (65.6, 124.4)
B) (85.703, 104.297)
C) (83.967, 106.033)
D) (85.513, 104.487)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 51 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
What critical value would be appropriate for a 98% confidence interval on a mean where σ is unknown if the sample size is 10 and the population is normally distributed?
A) 2.8214
B) 2.7638
C) 1.3830
D) 2.3263
A) 2.8214
B) 2.7638
C) 1.3830
D) 2.3263

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 51 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
A rule used to produce a point estimate of a population parameter is called a(n):
A) estimator.
B) probability estimate.
C) axiom.
D) maximum likelihood calculation.
A) estimator.
B) probability estimate.
C) axiom.
D) maximum likelihood calculation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 51 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Researchers with the state Department of Natural Resources (DNR) wish to estimate the mean flow rate of water through a stream.From previous research conducted on similar streams, they know that the variance of flow rate is 27,556 gpm2.If the DNR researchers wish to create an interval that they are 99% confident will contain the mean flow rate with a bound on the error of estimation of 40 gpm, how many flow samples do they need?
A) 114
B) 3,148,739
C) 165
D) 115
A) 114
B) 3,148,739
C) 165
D) 115

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 51 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
A random sample of 20 observations is selected from a normally distributed population.The sample variance is 12.In the 95% confidence interval for the population standard deviation, the upper limit will be:
A) 2.634.
B) 2.750.
C) 4.747.
D) 5.060.
A) 2.634.
B) 2.750.
C) 4.747.
D) 5.060.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 51 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
A local library is evaluating the possibility of expanding its hours of operation.The library staff want to estimate the mean number of persons who patronize the library during the peak weekday hours from 3:30 P.M.to 5:00 P.M.They randomly sample 12 weekdays and find an average attendance of 220.15, with a standard deviation of 22.4.What is a 90% confidence interval for the true mean weekly patronage during the peak hours?
A) (208.627, 231.673)
B) (209.514, 230.787)
C) (179.920, 260.380)
D) (208.537, 231.763)
A) (208.627, 231.673)
B) (209.514, 230.787)
C) (179.920, 260.380)
D) (208.537, 231.763)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 51 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
The confidence level is the:
A) probability that the confidence interval encloses the population parameter in repeated samplings.
B) confidence coefficient expressed as a percentage.
C) maximum level of confidence possible for a given point estimate to accurately predict an unknown parameter.
D) minimum (worst-case) level of confidence possible for a given point estimate to accurately predict an unknown parameter.
A) probability that the confidence interval encloses the population parameter in repeated samplings.
B) confidence coefficient expressed as a percentage.
C) maximum level of confidence possible for a given point estimate to accurately predict an unknown parameter.
D) minimum (worst-case) level of confidence possible for a given point estimate to accurately predict an unknown parameter.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 51 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Fat-tailed sheep are a common sight in the Near East.Some fat-tailed sheep are spotted, whereas others are solid colored.Of those that have a solid color, a small percentage of these fat-tailed sheep are completely black.If we randomly observe 18 black fat-tailed sheep out of a total of 218 sheep, what interval can we be 90% certain contains the population proportion of black fat-tailed sheep?
A) (0.052, 0.113)
B) (0.046, 0.119)
C) (0.059, 0.107)
D) (0.039, 0.126)
A) (0.052, 0.113)
B) (0.046, 0.119)
C) (0.059, 0.107)
D) (0.039, 0.126)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 51 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Which of the following statements is false?
A) The width of a confidence interval of the population mean narrows when the sample size increases.
B) The width of a confidence interval of the population mean narrows when the value of the sample mean increases.
C) The width of a confidence interval of the population mean widens when the confidence level increases.
D) The width of a confidence interval of the population mean is affected by the choice of confidence level.
A) The width of a confidence interval of the population mean narrows when the sample size increases.
B) The width of a confidence interval of the population mean narrows when the value of the sample mean increases.
C) The width of a confidence interval of the population mean widens when the confidence level increases.
D) The width of a confidence interval of the population mean is affected by the choice of confidence level.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 51 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
A recent survey indicates that the proportion of season ticket holders for the Virginia Tech football team who renew their seats is approximately 0.80.Using this information, the sample size that is needed to estimate the true proportion who plan to renew their seats using 95% confidence with an error bound of 0.025 is:
A) 689.
B) 697.
C) 810.
D) 984.
A) 689.
B) 697.
C) 810.
D) 984.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 51 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
In general, unbiased estimators are preferred for inference because:
A) bias in inference is always bad and should be avoided at all costs, so using unbiased estimators is the only way to conduct objective inference.
B) unbiased estimators always have the least amount of variance of all possible estimators.
C) a biased estimator will almost always give very little insight into the parameter being estimated and, therefore, serves as a poor guess of the parameter's true value.
D) in many cases the most probable value of an unbiased estimator is the value of the parameter being estimated; thus, unbiased estimators typically converge on values near the parameter.
A) bias in inference is always bad and should be avoided at all costs, so using unbiased estimators is the only way to conduct objective inference.
B) unbiased estimators always have the least amount of variance of all possible estimators.
C) a biased estimator will almost always give very little insight into the parameter being estimated and, therefore, serves as a poor guess of the parameter's true value.
D) in many cases the most probable value of an unbiased estimator is the value of the parameter being estimated; thus, unbiased estimators typically converge on values near the parameter.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 51 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
The MVUE (minimum variance unbiased estimator) for a parameter:
A) always exists.
B) rarely exists.
C) is a good candidate to estimate the parameter.
D) is the smallest estimator that has the ability to objectively estimate the parameter.
A) always exists.
B) rarely exists.
C) is a good candidate to estimate the parameter.
D) is the smallest estimator that has the ability to objectively estimate the parameter.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 51 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
A 95% confidence interval estimate of the population mean μ can be interpreted to mean that:
A) if we repeatedly draw samples of the same size from the same population, 95% of the values of the sample means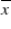 will result in a confidence interval that includes the population mean μ.
will result in a confidence interval that includes the population mean μ.
B) there is a 95% probability that the population mean μ will lie between the lower interval limit and the upper interval limit.
C) we are 95% confident that we have selected a sample whose range of values does not contain the population mean μ.
D) we are 95% confident that 5% of the values of the sample means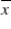 will result in a confidence interval that includes the population mean μ.
will result in a confidence interval that includes the population mean μ.
A) if we repeatedly draw samples of the same size from the same population, 95% of the values of the sample means
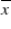 will result in a confidence interval that includes the population mean μ.
will result in a confidence interval that includes the population mean μ.B) there is a 95% probability that the population mean μ will lie between the lower interval limit and the upper interval limit.
C) we are 95% confident that we have selected a sample whose range of values does not contain the population mean μ.
D) we are 95% confident that 5% of the values of the sample means
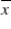 will result in a confidence interval that includes the population mean μ.
will result in a confidence interval that includes the population mean μ.
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 51 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
The cycle times for an electroplating machine are believed to be normally distributed.Twenty-one plating operations are randomly sampled, and cycle times are recorded.The sample average cycle time is 10.21 min, with a standard deviation of 0.59 min.What is a 95% confidence interval for the mean cycle time on this machine?
A) (9.958, 10.462)
B) (9.941, 10.479)
C) (8.979, 11.441)
D) (9.911, 10.509)
A) (9.958, 10.462)
B) (9.941, 10.479)
C) (8.979, 11.441)
D) (9.911, 10.509)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 51 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
The survival times of adult mosquitoes exposed to a commonly used synthetic pesticide (Phenothrin) follow a normal distribution, with a standard deviation of 15.18 sec.A random sample of 40 mosquitoes has an average survival time of 47.5 sec.What is a 99% confidence interval for the mean survival time?
A) (41.318, 53.682)
B) (41.916, 53.083)
C) (42.700, 52.300)
D) (8.399, 86.601)
A) (41.318, 53.682)
B) (41.916, 53.083)
C) (42.700, 52.300)
D) (8.399, 86.601)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 51 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
A fire occurs in a massive warehouse used to store apples prior to shipment.The apples are held in individual crates.The insurance company wishes to estimate the proportion of crates that were damaged by smoke from the fire.How many crates should the insurance adjustor analyze if she wishes to construct a 98% confidence interval with a bound on the error of estimation of 0.02?
A) 3383
B) 34
C) 2401
D) 4147
A) 3383
B) 34
C) 2401
D) 4147

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 51 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
A 99% confidence interval for the population mean μ is found to be (84.76, 92.17).If we were to use the same sample to construct a 95% confidence interval for this parameter, the 95% interval would be:
A) wider than the 99% confidence interval.
B) the same width as the 99% confidence interval.
C) narrower than the 99% confidence interval.
D) unrelated to the 99% confidence interval in terms of center and width.
A) wider than the 99% confidence interval.
B) the same width as the 99% confidence interval.
C) narrower than the 99% confidence interval.
D) unrelated to the 99% confidence interval in terms of center and width.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 51 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
A group of biologists wish to study the life span of the common housefly.They want to estimate the mean life span with 80% confidence and a width on the interval of estimation no greater than 1 hr.How many samples should they draw if a previous study indicates that the standard deviation of life span is 2.43 hr?
A) 10
B) 39
C) 230
D) 9
A) 10
B) 39
C) 230
D) 9

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 51 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
For any arbitrary parameter 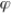 , a biased estimator of
, a biased estimator of 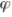 is any estimate where:
is any estimate where:
A) the expected value of the estimate equals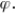
B) the expected value of the estimate differs from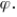
C) the expected value of the estimate is greater than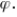
D) the expected value of the estimate is less than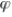 .
.
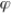 , a biased estimator of
, a biased estimator of 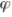 is any estimate where:
is any estimate where:A) the expected value of the estimate equals
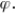
B) the expected value of the estimate differs from
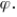
C) the expected value of the estimate is greater than
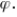
D) the expected value of the estimate is less than
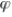 .
.
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 51 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Faculty members at a local university complain that achieving tenure at their university takes much longer than at comparable universities.They randomly sample nine tenured faculty members at their university and find that the average time of service prior to tenure was 13.55 years, with a standard deviation of 1.98 years.What is a 95% confidence interval for the mean number of years of service to achieve tenure at this university?
A) (12.028, 15.072)
B) (12.057, 15.043)
C) (12.256, 14.844)
D) (8.984, 18.116)
A) (12.028, 15.072)
B) (12.057, 15.043)
C) (12.256, 14.844)
D) (8.984, 18.116)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 51 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Which of the following statements about the error bound B (also called the margin of error) is false?
A) Statisticians routinely construct interval estimates by making their point estimate be the interval center and creating a range of other possible values, known as the error bound, below and above the center.
B) The error bound is a half-width of an interval estimate, equal to the difference between the point estimate on the one hand and either the lower or upper limit of the interval on the other hand.
C) The unknown parameter is presumed to lie at the center of the interval that the point estimate and the error bound create.
D) The error bound takes only sampling error into account, ignoring all other potential sources of error, such as bias in questions, selection bias, or miscalculations.
A) Statisticians routinely construct interval estimates by making their point estimate be the interval center and creating a range of other possible values, known as the error bound, below and above the center.
B) The error bound is a half-width of an interval estimate, equal to the difference between the point estimate on the one hand and either the lower or upper limit of the interval on the other hand.
C) The unknown parameter is presumed to lie at the center of the interval that the point estimate and the error bound create.
D) The error bound takes only sampling error into account, ignoring all other potential sources of error, such as bias in questions, selection bias, or miscalculations.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 51 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
To budget for the coming year, a community hospital must estimate the proportion of treated patients who will not be able to make payment in full.In a random sample of 2568 patients treated in the previous year, 381 failed to make payment in full.What is an 80% confidence interval for the proportion of patients who will not make full payment to the hospital?
A) (0.137, 0.160)
B) (0.125, 0.162)
C) (0.139, 0.157)
D) (0.132, 0.165)
A) (0.137, 0.160)
B) (0.125, 0.162)
C) (0.139, 0.157)
D) (0.132, 0.165)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 51 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Suppose we wish to estimate the proportion of classes skipped by seniors in a particular large class.How many samples should be drawn if we want a 90% confidence interval with a bound on the error of estimation of 3%?
A) 751
B) 1068
C) 752
D) 1067
A) 751
B) 1068
C) 752
D) 1067

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 51 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
After constructing a 95% confidence interval for a population mean μ, you decide that the interval is too wide to be of any value.To correct this problem, you need to:
A) increase the population size.
B) increase the confidence level.
C) increase the sample mean.
D) increase the sample size.
A) increase the population size.
B) increase the confidence level.
C) increase the sample mean.
D) increase the sample size.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 51 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Sales from a chain of computer stores are normally distributed, with an average monthly sales volume of $280,560.Estimating the amount of monthly variability in sales is of interest to help anticipate normal income fluctuations.A random sample of 8 months' sales data yields a standard deviation of $10,423.What is a 98% confidence interval for the standard deviation of monthly sales volume?
A) ($172,694.71, $666,866.84)
B) ($6152.47, $21,491.21)
C) ($6123.96, $27,725.40)
D) ($6415.73, $24,774.57)
A) ($172,694.71, $666,866.84)
B) ($6152.47, $21,491.21)
C) ($6123.96, $27,725.40)
D) ($6415.73, $24,774.57)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 51 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Consider an arbitrary parameter δ.If we identify an estimator 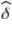 such that
such that 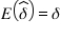 , then:
, then:
A)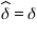 .
.
B)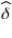 is unbiased for
is unbiased for 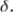
C) the maximum likelihood value for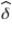 is
is 
D) the exponential value for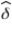 is
is 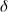 .
.
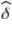 such that
such that 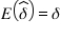 , then:
, then:A)
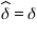 .
.B)
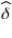 is unbiased for
is unbiased for 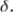
C) the maximum likelihood value for
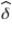 is
is 
D) the exponential value for
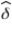 is
is 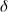 .
.
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 51 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
When we use estimation to determine the value of a parameter, we always use random sampling, rather than convenience sampling or judgment sampling, because random sampling:
A) avoids the errors inherent in judgment sampling.
B) avoids the errors inherent in convenience sampling.
C) avoids the errors inherent in voluntary response sampling.
D) eliminates the systematic error or bias that arises in nonrandom sampling.
A) avoids the errors inherent in judgment sampling.
B) avoids the errors inherent in convenience sampling.
C) avoids the errors inherent in voluntary response sampling.
D) eliminates the systematic error or bias that arises in nonrandom sampling.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 51 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
An unbiased estimator is:
A) any sample statistic used to approximate a population parameter.
B) a sample statistic that has an expected value equal to the value of the population parameter.
C) a sample statistic whose value is usually less than the value of the population parameter.
D) any estimator whose standard error is relatively small.
A) any sample statistic used to approximate a population parameter.
B) a sample statistic that has an expected value equal to the value of the population parameter.
C) a sample statistic whose value is usually less than the value of the population parameter.
D) any estimator whose standard error is relatively small.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 51 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
To perform diagnostics on the consistency of a laboratory scale, multiple measurements are taken using a reference weight over the course of several days.The variance observed over 20 repeated measures is 248.What is a 99% confidence interval for the measurement variance of this scale?
A) (122.129, 688.486)
B) (11.051, 26.239)
C) (117.809, 633.862)
D) (174.034, 413.213)
A) (122.129, 688.486)
B) (11.051, 26.239)
C) (117.809, 633.862)
D) (174.034, 413.213)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 51 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Previous research indicates that 20% of homeowners do not carry sufficient homeowners' insurance to adequately protect their investment.We wish to estimate the percentage of homeowners in a particular suburban area who do not have adequate insurance.How many homes should we sample if we desire a 95% confidence interval with a width of no more than 6%?
A) 171
B) 1068
C) 267
D) 683
A) 171
B) 1068
C) 267
D) 683

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 51 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Faculty at a local university randomly sampled nine tenured faculty at their university and found that a 99% confidence interval for the mean number of years of service to achieve tenure at this university is (11.335, 15.765).Based on this interval, does a faculty member who took 16 years to achieve tenure at this university have a reason to complain?
A) No, because the 99% confidence interval is wide and indicates it could take many years to achieve tenure.
B) No, because a sample of only nine faculty members is never reliable.We need to use a larger sample size.
C) Yes, because the interval indicates that the average time to achieve tenure should be less than 16 years with 99% confidence.
D) The interval does not allow us to answer this question.
A) No, because the 99% confidence interval is wide and indicates it could take many years to achieve tenure.
B) No, because a sample of only nine faculty members is never reliable.We need to use a larger sample size.
C) Yes, because the interval indicates that the average time to achieve tenure should be less than 16 years with 99% confidence.
D) The interval does not allow us to answer this question.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 51 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
An exit poll is conducted to estimate the proportion of voters who chose candidate A over candidate B.Out of 40 people surveyed, 12 indicated that they had voted for candidate A.What is a 95% confidence interval for the proportion of voters who chose candidate A?
A) (0.158, 0.442)
B) (0.181, 0.419)
C) (0.132, 0.469)
D) (0.154, 0.446)
A) (0.158, 0.442)
B) (0.181, 0.419)
C) (0.132, 0.469)
D) (0.154, 0.446)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 51 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
A random sample of size 25 taken from a normally distributed population resulted in a sample standard deviation of 0.93054.A 99% confidence interval for the population variance would be:
A) (9.886, 45.559).
B) (3.144, 6.750).
C) (0.678, 1.449).
D) (0.456, 2.102).
A) (9.886, 45.559).
B) (3.144, 6.750).
C) (0.678, 1.449).
D) (0.456, 2.102).

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 51 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
A _______________ for a population parameter is an interval of values constructed so that, given a specified degree of confidence, the value of the population parameter lies within this interval.
A) confidence level
B) confidence coefficient
C) convergence interval
D) confidence interval
A) confidence level
B) confidence coefficient
C) convergence interval
D) confidence interval

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 51 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
Whenever a sampled population is normally distributed or whenever the conditions of the Central Limit Theorem are fulfilled, the sample mean 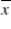 :
:
A) is a consistent estimator of the population mean μ because the mean of the sampling distribution of the sample mean equals μ.
B) is an efficient estimator of the population mean μ because the mean of the sampling distribution of the sample mean equals μ.
C) is an unbiased estimator of the population mean μ because the mean of the sampling distribution of the sample mean equals μ.
D) is a biased estimator of the population mean μ because the mean of the sampling distribution of the sample proportion equals p.
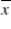 :
:A) is a consistent estimator of the population mean μ because the mean of the sampling distribution of the sample mean equals μ.
B) is an efficient estimator of the population mean μ because the mean of the sampling distribution of the sample mean equals μ.
C) is an unbiased estimator of the population mean μ because the mean of the sampling distribution of the sample mean equals μ.
D) is a biased estimator of the population mean μ because the mean of the sampling distribution of the sample proportion equals p.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 51 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Which of the following statements is correct?
A) A point estimate is an estimate of the range of a population parameter.
B) An interval estimate is an estimate of the range for a sample statistic.
C) A point estimate is a single-value estimate of the value of a population parameter.
D) A point estimate is an estimate of the midpoint of the range for a sample statistic.
A) A point estimate is an estimate of the range of a population parameter.
B) An interval estimate is an estimate of the range for a sample statistic.
C) A point estimate is a single-value estimate of the value of a population parameter.
D) A point estimate is an estimate of the midpoint of the range for a sample statistic.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 51 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
A random sample of 400 Texas A&M students was taken recently to determine an estimate of the proportion of all Texas A&M students who had attended at least three home football games.The estimate revealed that this proportion was between 0.372 and 0.458.Given this information, we can determine that the confidence coefficient was approximately:
A) 0.99.
B) 0.95.
C) 0.92.
D) 0.90.
A) 0.99.
B) 0.95.
C) 0.92.
D) 0.90.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 51 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
An estimator is a:
A) parameter and, therefore, a fixed characteristic of a data set.
B) statistic and, therefore, a random variable.
C) statistic and, therefore, a round variable.
D) parameter and, therefore, a random variable.
A) parameter and, therefore, a fixed characteristic of a data set.
B) statistic and, therefore, a random variable.
C) statistic and, therefore, a round variable.
D) parameter and, therefore, a random variable.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 51 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
What is t.01 if the distribution has 15 degrees of freedom?
A) 2.6025
B) 2.5835
C) 2.9467
D) 1.3406
A) 2.6025
B) 2.5835
C) 2.9467
D) 1.3406

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 51 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
When choosing between two unbiased estimators of the same parameter, the preferred estimator is:
A) the one that is most unbiased.
B) the one with the smaller variance.
C) the one that has an expected value equal to the parameter.
D) Either estimator is fine, as both are unbiased.
A) the one that is most unbiased.
B) the one with the smaller variance.
C) the one that has an expected value equal to the parameter.
D) Either estimator is fine, as both are unbiased.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 51 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
In a sample of 200 items, 12 items are defective.What is the point estimate of the population proportion that is defective?
A) 12
B) 0.06
C) 16.67
D) 0.12
A) 12
B) 0.06
C) 16.67
D) 0.12

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 51 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
A single number computed from a sample that serves as a guess for a parameter is called a(n):
A) point estimate.
B) approximate estimate.
C) confidence estimate.
D) confidence interval.
A) point estimate.
B) approximate estimate.
C) confidence estimate.
D) confidence interval.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 51 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
A 95% confidence interval for the population proportion of professional tennis players who earn more than $2 million per year is found to be between 0.82 and 0.88.Given this information, the sample size that was used was approximately:
A) 545.
B) 382.
C) 233.
D) 387.
A) 545.
B) 382.
C) 233.
D) 387.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 51 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
A shady operator wants to make sure the sample results are within the confidence interval.The easiest way to do this is to:
A) decrease the confidence level in the analysis.
B) increase the confidence level in the analysis.
C) decrease the sample size.
D) use a distribution other than the normal distribution.
A) decrease the confidence level in the analysis.
B) increase the confidence level in the analysis.
C) decrease the sample size.
D) use a distribution other than the normal distribution.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 51 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
In a study of typical student grade-point averages (GPAs), we sample 16 students and find an average GPA of 2.76, with a standard deviation of 0.48.Assuming the GPAs are normally distributed, what is an interval that we can be 80% certain contains the mean student GPA?
A) (2.12, 3.40)
B) (2.61, 2.91)
C) (2.60, 2.92)
D) (2.66, 2.86)
A) (2.12, 3.40)
B) (2.61, 2.91)
C) (2.60, 2.92)
D) (2.66, 2.86)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 51 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



