Deck 17: Quantisation and Wave-Particle Duality
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/41
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 17: Quantisation and Wave-Particle Duality
1
A neutron has a mass of 1.67 *10-27 kg.The de Broglie wavelength is 1.4 * 10-10 m.How fast is the neutron going? (in m/s)
A)3.4 * 103
B)2.8 * 103
C)3.9 *103
D)2.6 *103
E)1.7 * 103
A)3.4 * 103
B)2.8 * 103
C)3.9 *103
D)2.6 *103
E)1.7 * 103
2.8 * 103
2
A solid state pulsed laser has an energy of 400 mJ per pulse.If its wavelength is 1.06 * 10-6 m, how many photons are in each pulse?
A)2 * 1025
B)2 * 1021
C)3 *1018
D)6 * 1038
E)2 * 1018
A)2 * 1025
B)2 * 1021
C)3 *1018
D)6 * 1038
E)2 * 1018
2 * 1018
3
What is the maximum kinetic energy (in eV) of a photoelectron when a surface, whose work function is 5.0 eV, is illuminated by photons whose wavelength is 400 nm?
A)3.1
B)(-1.9)
C)1.9
D)0
E)1.2
A)3.1
B)(-1.9)
C)1.9
D)0
E)1.2
0
4
The light intensity incident on a metallic surface with a work function of 3 eV produces photoelectrons with a maximum kinetic energy of 2 eV.The frequency of the light is doubled.Determine the maximum kinetic energy (in eV).
A)3
B)2
C)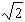
D)4
E)7
A)3
B)2
C)
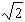
D)4
E)7

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 41 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
A helium-neon laser emits red light having a wavelength of 6.4 *10-7 m and a power of 0.5 mW.How many photons are emitted each second?
A)6.4*1038
B)1.6 *1021
C)3.2 * 1025
D)2.6* 1018
E)1.6 * 1015
A)6.4*1038
B)1.6 *1021
C)3.2 * 1025
D)2.6* 1018
E)1.6 * 1015

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 41 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
A stopping potential of 3.2 V is needed for radiation whose wavelength is 200 nm.What is the work function (in eV) of the material?
A)4.0
B)3.0
C)5.0
D)6.0
E)2.0
A)4.0
B)3.0
C)5.0
D)6.0
E)2.0

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 41 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
What wavelength (in m) is associated with the Paschen series for n = 4? (RH = 1.097 * 107 m-1)
A)320
B)530
C)2.7
D)1.9
E)0.5
A)320
B)530
C)2.7
D)1.9
E)0.5

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 41 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
How much energy is in an 89.7 MHz photon of FM-radiation?
A)2.2 *10-33 J
B)9.5 * 10-27 J
C)7.4 *10-42 J
D)5.9 * 10-26 J
E)3.7 * 10-25 J
A)2.2 *10-33 J
B)9.5 * 10-27 J
C)7.4 *10-42 J
D)5.9 * 10-26 J
E)3.7 * 10-25 J

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 41 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
A photon whose energy is 8.00 *10-15 J is scattered off an electron at a 90 angle.What is the wavelength of the scattered wave?
A)2.73 * 10-11 m
B)2.25 * 10-11 m
C)2.50 * 10-11 m
D)2.40 * 10-12 m
E)2.48 * 10-11 m
A)2.73 * 10-11 m
B)2.25 * 10-11 m
C)2.50 * 10-11 m
D)2.40 * 10-12 m
E)2.48 * 10-11 m

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 41 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
The light intensity incident on a metallic surface produces photoelectrons with a maximum kinetic energy of 2 eV.The light intensity is doubled.Determine the maximum kinetic energy of the photoelectrons (in eV).
A)4
B)2
C)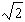
D)3
E)16
A)4
B)2
C)
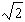
D)3
E)16

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 41 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
How much energy is in a 63 kHz photon of AM-radiation?
A)1.0 *10-38 J
B)6.6 * 10-30 J
C)4.2 * 10-29 J
D)3.1 *10-30 J
E)13 *10-29 J
A)1.0 *10-38 J
B)6.6 * 10-30 J
C)4.2 * 10-29 J
D)3.1 *10-30 J
E)13 *10-29 J

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 41 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
The threshold wavelength for photoelectric emission of a particular substance is 500 nm.What is the work function (in eV)?
A)4.2
B)4.0 *10-19
C)4.0 * 10-10
D)2.5 * 10-19
E)2.5
A)4.2
B)4.0 *10-19
C)4.0 * 10-10
D)2.5 * 10-19
E)2.5

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 41 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Your temperature is 98.6 F.Assuming your skin is a perfect radiator ( = 1), determine the wavelength corresponding to the largest intensity (in m).
A)8.0
B)9.3
C)3.0
D)5.7
E)29.4
A)8.0
B)9.3
C)3.0
D)5.7
E)29.4

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 41 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
What value of wavelength is associated with the Lyman series for n = 2? (RH = 1.097 * 107 m-1)
A)8.2 *106 m
B)1.2 * 10-7 m
C)2.7 *106 m
D)3.6 * 10-7 m
E)8.8 * 10-7 m
A)8.2 *106 m
B)1.2 * 10-7 m
C)2.7 *106 m
D)3.6 * 10-7 m
E)8.8 * 10-7 m

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 41 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
A photon collides with an electron.After the collision the wavelength of the scattered wave at a scattering angle greater than is: 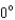
A)greater than or equal to the initial wavelength.
B)equal to the initial wavelength.
C)less than or equal to the initial wavelength.
D)greater than the initial wavelength.
E)less or greater depending on the scattering angle.
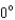
A)greater than or equal to the initial wavelength.
B)equal to the initial wavelength.
C)less than or equal to the initial wavelength.
D)greater than the initial wavelength.
E)less or greater depending on the scattering angle.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 41 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
A photon whose wavelength is = 5.0 * 10-11 m is scattered straight backward.What is the wavelength of the scattered wave?
A)5.0 *10-11 m
B)4.5 * 10-11 m
C)5.5 * 10-11 m
D)6.0 * 10-11 m
E)6.5 * 10-11 m
A)5.0 *10-11 m
B)4.5 * 10-11 m
C)5.5 * 10-11 m
D)6.0 * 10-11 m
E)6.5 * 10-11 m

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 41 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Assume electrons are accelerated through a potential difference of 25 000 V inside a TV picture tube.What is the minimum wavelength that could be produced when the electrons strike the phosphor? (1 Å = 10-10 m)
A)0.50 Å
B)1.0 Å
C)10 Å
D)100 Å
E)0.25 Å
A)0.50 Å
B)1.0 Å
C)10 Å
D)100 Å
E)0.25 Å

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 41 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
What is the maximum velocity (in km/s) of a photoelectron emitted from a surface whose work function is 5.0 eV when illuminated by a light whose wavelength is 200 nm?
A)460
B)650
C)420
D)550
E)1 480
A)460
B)650
C)420
D)550
E)1 480

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 41 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
What is the maximum kinetic energy (in eV) of a photoelectron emitted from a surface whose work function is 5.0 eV when illuminated by a light whose wavelength is 200 nm?
A)1.9
B)1.2
C)3.1
D)zero
E)6.2
A)1.9
B)1.2
C)3.1
D)zero
E)6.2

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 41 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Light is emitted by hydrogen atoms in the visible range for a hydrogen atom.Its wavelength is 656 nm.What value of n is associated with the light? (RH = 1.097 * 107 m-1)
A)5
B)2
C)4
D)3
E)6
A)5
B)2
C)4
D)3
E)6

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 41 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
A pendulum located where has a 0.500 kg bob and a 4.00 Hz oscillation frequency.If it is released from a point 0.150 m above the lowest point it reaches, the number of quanta in this oscillation is: 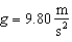
A)2.77 * 1032.
B)1.11 * 1033.
C)4.87 * 10-34.
D)0.184.
E)4.00.
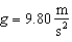
A)2.77 * 1032.
B)1.11 * 1033.
C)4.87 * 10-34.
D)0.184.
E)4.00.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 41 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
In electron diffraction, an electron moving at speed v << c acts like:
A)a particle with momentum mv.
B)a particle with position coordinate v/t.
C)a wave with wavelength v/t.
D)a wave with wavelength h/mv.
E)both a particle with position coordinate v/t and a wave with wavelength v/t.
A)a particle with momentum mv.
B)a particle with position coordinate v/t.
C)a wave with wavelength v/t.
D)a wave with wavelength h/mv.
E)both a particle with position coordinate v/t and a wave with wavelength v/t.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 41 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
The number of photons per second passing a plane perpendicular to a collimated monochromatic (one frequency) beam of light transporting power P is directly proportional to:
A)the wavelength of the light.
B)the frequency of the light.
C)the power of the beam.
D)increase the wavelength, frequency and power..
E)increase the wavelength and power but not the frequency.
A)the wavelength of the light.
B)the frequency of the light.
C)the power of the beam.
D)increase the wavelength, frequency and power..
E)increase the wavelength and power but not the frequency.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 41 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
A quantum particle:
A)can be localised in space.
B)can be represented by an infinitely long wave having a single frequency.
C)can be represented by a wave packet.
D)travels at the phase speed of the infinitely long wave having the highest frequency.
E)has the highest probability of being present in those regions of space where its component waves interfere destructively.
A)can be localised in space.
B)can be represented by an infinitely long wave having a single frequency.
C)can be represented by a wave packet.
D)travels at the phase speed of the infinitely long wave having the highest frequency.
E)has the highest probability of being present in those regions of space where its component waves interfere destructively.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 41 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Photoelectrons are ejected when monochromatic light shines on a freshly-prepared (oxide-free) sodium surface.In order to obtain the maximum increase in the number of electrons ejected per second, the experimenter needs to:
A)increase the frequency of the light.
B)increase the intensity of the light.
C)increase the area illuminated by the light.
D)increase the frequency and intensity of the light, and also the area illuminated.
E)increase the intensity of the light and the area illuminated, but not the frequency.
A)increase the frequency of the light.
B)increase the intensity of the light.
C)increase the area illuminated by the light.
D)increase the frequency and intensity of the light, and also the area illuminated.
E)increase the intensity of the light and the area illuminated, but not the frequency.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 41 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
In an experiment different wavelengths of light, all able to eject photoelectrons, shine on a freshly prepared (oxide-free) zinc surface.Which statement is true?
A)The number of photoelectrons emitted per second is independent of the intensity of the light for all the different wavelengths.
B)The number of photoelectrons emitted per second is directly proportional to the frequency for all the different wavelengths.
C)The maximum kinetic energy of the photoelectrons emitted is directly proportional to the frequency for each wavelength present.
D)The maximum kinetic energy of the photoelectrons has a linear relationship with the frequency for each wavelength present.
E)The maximum kinetic energy of the photoelectrons is proportional to the intensity of the light and independent of the frequency.
A)The number of photoelectrons emitted per second is independent of the intensity of the light for all the different wavelengths.
B)The number of photoelectrons emitted per second is directly proportional to the frequency for all the different wavelengths.
C)The maximum kinetic energy of the photoelectrons emitted is directly proportional to the frequency for each wavelength present.
D)The maximum kinetic energy of the photoelectrons has a linear relationship with the frequency for each wavelength present.
E)The maximum kinetic energy of the photoelectrons is proportional to the intensity of the light and independent of the frequency.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 41 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
The wavelength of a 45-kg teenager moving at 5 m/s on a skateboard is about:
A)5 * 10-37 m.
B)3 * 10-36 m.
C)7 * 10-34 m.
D)0.1 m.
E)5 m.
A)5 * 10-37 m.
B)3 * 10-36 m.
C)7 * 10-34 m.
D)0.1 m.
E)5 m.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 41 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
A neutron has a mass of 1.67 * 10-27 kg.Its de Broglie wavelength is 1.4 * 10-10 m.What temperature would it correspond to if we had a monatomic gas having the same average kinetic energy (in C)?
A)273
B)25
C)36
D)309
E)51
A)273
B)25
C)36
D)309
E)51

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 41 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
The experimental observation(s) below that require(s) a quantum explanation for the photoelectric effect:
A)is that more photoelectrons are emitted when the light frequency increases.
B)is that the maximum kinetic energy of the photoelectrons is related linearly to the frequency of the light.
C)is that every metal surface has a work function, a minimum amount of energy needed to free electrons.
D)is that the stopping potential measures the kinetic energy of the photoelectrons.
E)are all of the above.
A)is that more photoelectrons are emitted when the light frequency increases.
B)is that the maximum kinetic energy of the photoelectrons is related linearly to the frequency of the light.
C)is that every metal surface has a work function, a minimum amount of energy needed to free electrons.
D)is that the stopping potential measures the kinetic energy of the photoelectrons.
E)are all of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 41 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
An atomic level has a lifetime, 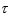 of.What is the linewidth, , of this level?
of.What is the linewidth, , of this level? 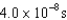
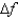
A)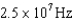
B)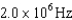
C)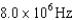
D)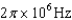
E)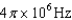
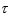 of.What is the linewidth, , of this level?
of.What is the linewidth, , of this level? 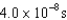
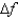
A)
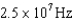
B)
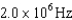
C)
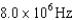
D)
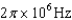
E)
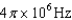

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 41 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
What is the energy in eV of a photon of yellow light? = 500 nm.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 41 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
What is the shortest x-ray wavelength that can be produced in a 12-keV x-ray machine?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 41 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
A wave packet can represent a quantum particle because:
A)it has the localised nature of a particle.
B)the group velocity is identical to the speed of the particle.
C)the waves that compose the packet can show interference and diffraction.
D)of all of the above.
E)of only (a) and (b) above.
A)it has the localised nature of a particle.
B)the group velocity is identical to the speed of the particle.
C)the waves that compose the packet can show interference and diffraction.
D)of all of the above.
E)of only (a) and (b) above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 41 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
On a bright and sunny day, the intensity of solar radiation on the Earth's surface is 1000 W/m2.If the average wavelength of the sunlight is 500 nm, how many photons are incident on a square metre of the Earth's surface per second?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 41 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
An electron is accelerated through a potential difference of 25 000 V.What is the de Broglie wavelength of the electron (in m)?
A)5.9 *10-12
B)6.8 * 10-12
C)6.5 *10-12
D)7.8 * 10-12
E)5.5 *10-12
A)5.9 *10-12
B)6.8 * 10-12
C)6.5 *10-12
D)7.8 * 10-12
E)5.5 *10-12

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 41 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Film behind a double slit is exposed to light in the following way: First one slit is opened and light is allowed to go through that slit for time t.Then it is closed and the other slit is opened and light is allowed to go through that slit for the same time t.When the film is developed the pattern will be:
A)one single slit pattern.
B)two superimposed single slit patterns, their centres displaced from each other by the distance between the two slits.
C)one double slit pattern.
D)two double slit patterns, their centres displaced from each other by the distance between the two slits.
E)random darkening of the film.(no pattern at all)
A)one single slit pattern.
B)two superimposed single slit patterns, their centres displaced from each other by the distance between the two slits.
C)one double slit pattern.
D)two double slit patterns, their centres displaced from each other by the distance between the two slits.
E)random darkening of the film.(no pattern at all)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 41 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
When a photon collides with a free electron at rest and the direction of motion of the photon changes:
A)the magnitude of the momentum of the photon does not change.
B)the momentum of the electron does not change.
C)the kinetic energy of the electron does not change.
D)the total energy of the photon does not change.
E)both the magnitude of the momentum and the total energy of the photon decrease.
A)the magnitude of the momentum of the photon does not change.
B)the momentum of the electron does not change.
C)the kinetic energy of the electron does not change.
D)the total energy of the photon does not change.
E)both the magnitude of the momentum and the total energy of the photon decrease.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 41 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
A neutron has a mass of 1.67 *10-27 kg.Its de Broglie wavelength is 1.4 * 10-10 m.What is its kinetic energy (in eV)?
A)4
B)0.4
C)0.04
D)40
E)0.08
A)4
B)0.4
C)0.04
D)40
E)0.08

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 41 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
If a rubidium surface is irradiated with blue light of wavelength 450.0 nm, what is the kinetic energy of the electrons emitted? (The work function for rubidium is = 2.09 eV.)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 41 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Microscopes are inherently limited by the wavelength of the light used.How much smaller (in order of magnitude) can we 'see' using an electron microscope whose electrons have been accelerated through a potential difference of 50 000 V than using red light (500 nm)?
A)3
B)4
C)5
D)6
E)14
A)3
B)4
C)5
D)6
E)14

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 41 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
The 'seeing ability' or resolution of radiation is determined by its wavelength.If an atom is approximately 10-10 m in diameter, how fast must an electron travel to have a wavelength smaller than the size of an atom?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 41 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



