Deck 3: Electric Potential
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/49
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 3: Electric Potential
1
A charged particle (q = -8.0 mC), which moves in a region where the only force acting on the particle is an electric force, is released from rest at point A.At point B the kinetic energy of the particle is equal to 4.8 J.What is the electric potential difference VB - VA?
A)(-0.60 kV)
B)+0.60 kV
C)+0.80 kV
D)(-0.80 kV)
E)+0.48 kV
A)(-0.60 kV)
B)+0.60 kV
C)+0.80 kV
D)(-0.80 kV)
E)+0.48 kV
+0.60 kV
2
A particle (charge = Q) is kept in a fixed position at point P, and a second particle (charge = q) is released from rest when it is a distance R from P.If Q = +2.0 mC, q = -1.5 mC, and R = 30 cm, what is the kinetic energy of the moving particle after it has moved a distance of 10 cm?
A)60 kJ
B)45 kJ
C)75 kJ
D)90 kJ
E)230 kJ
A)60 kJ
B)45 kJ
C)75 kJ
D)90 kJ
E)230 kJ
45 kJ
3
Points A [at (3, 6) m] and B [at (8, -3) m] are in a region where the electric field is uniform and given by N/C.What is the electric potential difference VA -VB? ![<strong>Points A [at (3, 6) m] and B [at (8, -3) m] are in a region where the electric field is uniform and given by N/C.What is the electric potential difference VA -VB? </strong> A)+60 V B)(-60 V) C)+80 V D)(-80 V) E)+50 V](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB8846/11eb8aea_0743_3f23_8952_1362e0619ca1_TB8846_11.jpg)
A)+60 V
B)(-60 V)
C)+80 V
D)(-80 V)
E)+50 V
![<strong>Points A [at (3, 6) m] and B [at (8, -3) m] are in a region where the electric field is uniform and given by N/C.What is the electric potential difference VA -VB? </strong> A)+60 V B)(-60 V) C)+80 V D)(-80 V) E)+50 V](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB8846/11eb8aea_0743_3f23_8952_1362e0619ca1_TB8846_11.jpg)
A)+60 V
B)(-60 V)
C)+80 V
D)(-80 V)
E)+50 V
+60 V
4
A particle (q = +5.0 C) is released from rest when it is 2.0 m from a charged particle which is held at rest.After the positively charged particle has moved 1.0 m toward the fixed particle, it has a kinetic energy of 50 mJ.What is the charge on the fixed particle?
A)(-2.2 C)
B)+6.7 C
C)(-2.7 C)
D)+8.0 C
E)(-1.1 C)
A)(-2.2 C)
B)+6.7 C
C)(-2.7 C)
D)+8.0 C
E)(-1.1 C)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Points A [at (2, 3) m] and B [at (5, 7) m] are in a region where the electric field is uniform and given by N/C.What is the potential difference VA - VB? ![<strong>Points A [at (2, 3) m] and B [at (5, 7) m] are in a region where the electric field is uniform and given by N/C.What is the potential difference VA - VB? </strong> A)33 V B)27 V C)30 V D)24 V E)11 V](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB8846/11eb8aea_0742_a2e2_8952_cb276d0cf7ca_TB8846_11.jpg)
A)33 V
B)27 V
C)30 V
D)24 V
E)11 V
![<strong>Points A [at (2, 3) m] and B [at (5, 7) m] are in a region where the electric field is uniform and given by N/C.What is the potential difference VA - VB? </strong> A)33 V B)27 V C)30 V D)24 V E)11 V](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB8846/11eb8aea_0742_a2e2_8952_cb276d0cf7ca_TB8846_11.jpg)
A)33 V
B)27 V
C)30 V
D)24 V
E)11 V

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Identical point charges (+30 C) are placed at the corners of a rectangle (4.0 m * 6.0 m).How much external energy is required to bring a charge of 55 C from infinity to the midpoint of one of the 6.0-m long sides of the rectangle?
A)22 J
B)16 J
C)13 J
D)19 J
E)8.0 J
A)22 J
B)16 J
C)13 J
D)19 J
E)8.0 J

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
A particle (charge = 40 C) moves directly toward a second particle (charge = 80 C) which is held in a fixed position.At an instant when the distance between the two particles is 2.0 m, the kinetic energy of the moving particle is 16 J.Determine the distance separating the two particles when the moving particle is momentarily stopped.
A)0.75 m
B)0.84 m
C)0.95 m
D)0.68 m
E)0.56 m
A)0.75 m
B)0.84 m
C)0.95 m
D)0.68 m
E)0.56 m

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Three identical point charges (+2.0 nC) are placed at the corners of an equilateral triangle with sides of 2.0-m length.If the electric potential is taken to be zero at infinity, what is the potential at the midpoint of any one of the sides of the triangle?
A)16 V
B)10 V
C)70 V
D)46 V
E)44 V
A)16 V
B)10 V
C)70 V
D)46 V
E)44 V

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
A charge per unit length given by (x) = bx, where b = 12 nC/m2, is distributed along the x axis from x = +9.0 cm to x = +16 cm.If the electric potential at infinity is taken to be zero, what is the electric potential at the point P on the y axis at y = 12 cm?
A)5.4 V
B)7.2 V
C)9.0 V
D)9.9 V
E)16 V
A)5.4 V
B)7.2 V
C)9.0 V
D)9.9 V
E)16 V

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
A charge of +3.0 C is distributed uniformly along the circumference of a circle with a radius of 20 cm.How much external energy is required to bring a charge of 25 C from infinity to the centre of the circle?
A)5.4 J
B)3.4 J
C)4.3 J
D)2.7 J
E)6.8 J
A)5.4 J
B)3.4 J
C)4.3 J
D)2.7 J
E)6.8 J

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Several charges in the neighbourhood of point P produce an electric potential of 6.0 kV (relative to zero at infinity) and an electric field of N/C at point P.Determine the work required of an external agent to move a 3.0- C charge along the x axis from infinity to point P without any net change in the kinetic energy of the particle. 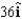
A)21 mJ
B)18 mJ
C)24 mJ
D)27 mJ
E)12 mJ
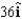
A)21 mJ
B)18 mJ
C)24 mJ
D)27 mJ
E)12 mJ

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
If a = 30 cm, b = 20 cm, q = +2.0 nC, and Q = -3.0 nC in the figure, what is the potential difference VA - VB? 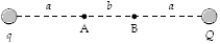
A)+60 V
B)+72 V
C)+84 V
D)+96 V
E)+48 V
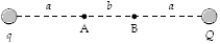
A)+60 V
B)+72 V
C)+84 V
D)+96 V
E)+48 V

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
An alpha particle (m = 6.7 * 10-27 kg, q = +3.2 *10-19 C) has a speed of 20 km/s at point A and moves to point B where it momentarily stops.Only electric forces act on the particle during this motion.Determine the electric potential difference VA -VB.
A)+4.2 V
B)(-4.2 V)
C)(-9.4 V)
D)+9.4 V
E)(-8.4 V)
A)+4.2 V
B)(-4.2 V)
C)(-9.4 V)
D)+9.4 V
E)(-8.4 V)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Two identical particles, each with a mass of 2.0 g and a charge of 25 nC, are released simultaneously from rest when the two are 4.0 cm apart.What is the speed of either particle at the instant when the two are separated by 10 cm?
A)7.3 m/s
B)9.8 m/s
C)9.2 m/s
D)6.5 m/s
E)4.6 m/s
A)7.3 m/s
B)9.8 m/s
C)9.2 m/s
D)6.5 m/s
E)4.6 m/s

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
A particle (mass = 6.7 *10-27 kg, charge = 3.2 * 10-19 C) moves along the positive x axis with a speed of 4.8 *105 m/s.It enters a region of uniform electric field parallel to its motion and comes to rest after moving 2.0 m into the field.What is the magnitude of the electric field?
A)2.0 kN/C
B)1.5 kN/C
C)1.2 kN/C
D)3.5 kN/C
E)2.4 kN/C
A)2.0 kN/C
B)1.5 kN/C
C)1.2 kN/C
D)3.5 kN/C
E)2.4 kN/C

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Two identical particles, each with a mass of 4.5 g and a charge of 30 nC, are moving directly toward each other with equal speeds of 4.0 m/s at an instant when the distance separating the two is equal to 25 cm.How far apart will they be when closest to one another?
A)9.8 cm
B)12 cm
C)7.8 cm
D)15 cm
E)20 cm
A)9.8 cm
B)12 cm
C)7.8 cm
D)15 cm
E)20 cm

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
What is the speed of a proton that has been accelerated from rest through a potential difference of 4.0 kV?
A)1.1 * 106 m/s
B)9.8 * 105 m/s
C)8.8 * 105 m/s
D)1.2 * 106 m/s
E)6.2 * 105 m/s
A)1.1 * 106 m/s
B)9.8 * 105 m/s
C)8.8 * 105 m/s
D)1.2 * 106 m/s
E)6.2 * 105 m/s

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Four identical point charges (+4.0 C) are placed at the corners of a square which has 20-cm sides.How much work is required to assemble this charge arrangement starting with each of the charges a very large distance from any of the other charges?
A)+2.9 J
B)+3.9 J
C)+2.2 J
D)+4.3 J
E)+1.9 J
A)+2.9 J
B)+3.9 J
C)+2.2 J
D)+4.3 J
E)+1.9 J

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Through what potential difference must an electron (starting from rest) be accelerated if it is to reach a speed of 3.0 *107 m/s?
A)5.8 kV
B)2.6 kV
C)7.1 kV
D)8.6 kV
E)5.1 kV
A)5.8 kV
B)2.6 kV
C)7.1 kV
D)8.6 kV
E)5.1 kV

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Point charges of equal magnitudes (25 nC) and opposite signs are placed on (diagonally) opposite corners of a 60-cm *80-cm rectangle.If point A is the corner of this rectangle nearest the positive charge and point B is located at the intersection of the diagonals of the rectangle, determine the potential difference, VB - VA.
A)(-47 V)
B)+94 V
C)zero
D)(-94 V)
E)+47 V
A)(-47 V)
B)+94 V
C)zero
D)(-94 V)
E)+47 V

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Which of the following represents the equipotential lines of a dipole?
A)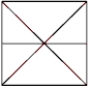
B)
C)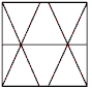
D)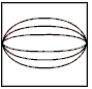
E)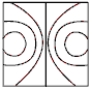
A)

B)

C)

D)

E)


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Two large parallel conducting plates are 8.0 cm apart and carry equal but opposite charges on their facing surfaces.The magnitude of the surface charge density on either of the facing surfaces is 2.0 nC/m2.Determine the magnitude of the electric potential difference between the plates.
A)36 V
B)27 V
C)18 V
D)45 V
E)16 V
A)36 V
B)27 V
C)18 V
D)45 V
E)16 V

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
A charge of 10 nC is distributed uniformly along the x axis from x =-2 m to x = +3 m.Which of the following integrals is correct for the electric potential (relative to zero at infinity) at the point x = +5 m on the x axis?
A)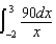
B)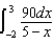
C)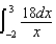
D)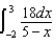
E)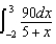
A)
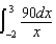
B)
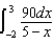
C)
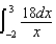
D)
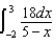
E)
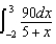

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
A charge is placed on a spherical conductor of radius r1.This sphere is then connected to a distant sphere of radius r2 (not equal to r1) by a conducting wire.After the charges on the spheres are in equilibrium:
A)the electric fields at the surfaces of the two spheres are equal.
B)the amount of charge on each sphere is q/2.
C)both spheres are at the same potential.
D)the potentials are in the ratio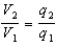
E)the potentials are in the ratio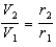
A)the electric fields at the surfaces of the two spheres are equal.
B)the amount of charge on each sphere is q/2.
C)both spheres are at the same potential.
D)the potentials are in the ratio
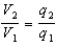
E)the potentials are in the ratio
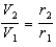

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
A rod (length = 2.0 m) is uniformly charged and has a total charge of 5.0 nC.What is the electric potential (relative to zero at infinity) at a point which lies along the axis of the rod and is 3.0 m from the centre of the rod?
A)22 V
B)19 V
C)16 V
D)25 V
E)12 V
A)22 V
B)19 V
C)16 V
D)25 V
E)12 V

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
The electric field in a region of space is given by Ex = (3.0x) N/C, Ey = Ez = 0, where x is in m.Points A and B are on the x axis at xA = 3.0 m and xB = 5.0 m.Determine the potential difference VB - VA.
A)(-24 V)
B)+24 V
C)(-18 V)
D)+30 V
E)(-6.0 V)
A)(-24 V)
B)+24 V
C)(-18 V)
D)+30 V
E)(-6.0 V)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
When a charged particle is moved along an electric field line:
A)the electric field does no work on the charge.
B)the electrical potential energy of the charge does not change.
C)the electrical potential energy of the charge undergoes the maximum change in magnitude.
D)the voltage changes, but there is no change in electrical potential energy.
E)the electrical potential energy undergoes the maximum change, but there is no change in voltage.
A)the electric field does no work on the charge.
B)the electrical potential energy of the charge does not change.
C)the electrical potential energy of the charge undergoes the maximum change in magnitude.
D)the voltage changes, but there is no change in electrical potential energy.
E)the electrical potential energy undergoes the maximum change, but there is no change in voltage.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Charge of uniform density (3.5 nC/m) is distributed along the circular arc shown.Determine the electric potential (relative to zero at infinity) at point P. 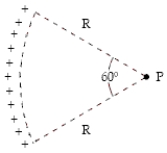
A)61 V
B)42 V
C)52 V
D)33 V
E)22 V

A)61 V
B)42 V
C)52 V
D)33 V
E)22 V

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Charge of uniform linear density 6.0 nC/m is distributed along the x axis from x = 0 to x = +3 m.Which of the following integrals is correct for the electric potential (relative to zero at infinity) at the point y = +4 m on the y axis?
A)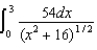
B)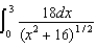
C)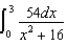
D)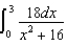
E)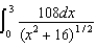
A)
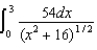
B)
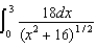
C)
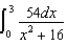
D)
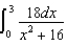
E)
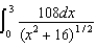

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
A series of 3 uncharged concentric shells surround a small central charge q.The charge distributed on the outside of the third shell is:
A)(-3q.)
B)(-(ln 3)q.)
C)+q.
D)+(ln 3)q.
E)+3q.
A)(-3q.)
B)(-(ln 3)q.)
C)+q.
D)+(ln 3)q.
E)+3q.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
A solid conducting sphere (radius = 5.0 cm) has a charge of 0.25 nC distributed uniformly on its surface.If point A is located at the centre of the sphere and point B is 15 cm from the centre, what is the magnitude of the electric potential difference between these two points?
A)23 V
B)30 V
C)15 V
D)45 V
E)60 V
A)23 V
B)30 V
C)15 V
D)45 V
E)60 V

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Equipotentials are lines along which:
A)the electric field is constant in magnitude and direction.
B)the electric charge is constant in magnitude and direction.
C)maximum work against electrical forces is required to move a charge at constant speed.
D)a charge may be moved at constant speed without work against electrical forces.
E)charges move by themselves.
A)the electric field is constant in magnitude and direction.
B)the electric charge is constant in magnitude and direction.
C)maximum work against electrical forces is required to move a charge at constant speed.
D)a charge may be moved at constant speed without work against electrical forces.
E)charges move by themselves.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
The electric potential inside a charged solid spherical conductor in equilibrium:
A)is always zero.
B)is constant and equal to its value at the surface.
C)decreases from its value at the surface to a value of zero at the centre.
D)increases from its value at the surface to a value at the centre that is a multiple of the potential at the surface.
E)is equal to the charge passing through the surface per unit time divided by the resistance.
A)is always zero.
B)is constant and equal to its value at the surface.
C)decreases from its value at the surface to a value of zero at the centre.
D)increases from its value at the surface to a value at the centre that is a multiple of the potential at the surface.
E)is equal to the charge passing through the surface per unit time divided by the resistance.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Can the lines in the figure below be equipotential lines? 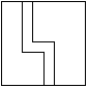
A)No, because there are sharp corners.
B)No, because they are isolated lines.
C)Yes, because any lines within a charge distribution are equipotential lines.
D)Yes, they might be boundary lines of the two surfaces of a conductor.
E)It is not possible to say without further information.

A)No, because there are sharp corners.
B)No, because they are isolated lines.
C)Yes, because any lines within a charge distribution are equipotential lines.
D)Yes, they might be boundary lines of the two surfaces of a conductor.
E)It is not possible to say without further information.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Two charges lie on the x axis, +3q at the origin, and -2q at x = 5.0 m.The point on the x axis where the electric potential has a zero value (when the value at infinity is also zero) is:
A)1.0 m.
B)2.0 m.
C)2.5 m.
D)3.0 m.
E)4.0 m.
A)1.0 m.
B)2.0 m.
C)2.5 m.
D)3.0 m.
E)4.0 m.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
A linear charge of non-uniform density = bx, where b = 2.1 nC/m2, is distributed along the x axis from x = 2.0 m to x = 3.0 m.Determine the electric potential (relative to zero at infinity) of the point y = 4.0 m on the y axis.
A)36 V
B)95 V
C)10 V
D)17 V
E)15 V
A)36 V
B)95 V
C)10 V
D)17 V
E)15 V

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
When a positive charge is released and moves along an electric field line, it moves to a position of:
A)lower potential and lower potential energy.
B)lower potential and higher potential energy.
C)higher potential and lower potential energy.
D)higher potential and higher potential energy.
E)greater magnitude of the electric field.
A)lower potential and lower potential energy.
B)lower potential and higher potential energy.
C)higher potential and lower potential energy.
D)higher potential and higher potential energy.
E)greater magnitude of the electric field.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Charge of uniform density 90 nC/m3 is distributed throughout the inside of a long non-conducting cylindrical rod (radius = 2.0 cm).Determine the magnitude of the potential difference of point A (2.0 cm from the axis of the rod) and point B (4.0 cm from the axis).
A)1.9 V
B)1.4 V
C)2.2 V
D)2.8 V
E)4.0 V
A)1.9 V
B)1.4 V
C)2.2 V
D)2.8 V
E)4.0 V

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
When a negative charge is released and moves along an electric field line, it moves to a position of:
A)lower potential and lower potential energy.
B)lower potential and higher potential energy.
C)higher potential and lower potential energy.
D)higher potential and higher potential energy.
E)decreasing magnitude of the electric field.
A)lower potential and lower potential energy.
B)lower potential and higher potential energy.
C)higher potential and lower potential energy.
D)higher potential and higher potential energy.
E)decreasing magnitude of the electric field.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Charge of uniform density 12 nC/m is distributed along the x axis from x = 2.0 m to x = 5.0 m.What is the electric potential (relative to zero at infinity) at the origin (x = 0)?
A)91 V
B)99 V
C)82 V
D)74 V
E)140 V
A)91 V
B)99 V
C)82 V
D)74 V
E)140 V

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
When introduced into a region where an electric field is present, an electron with initial velocity will eventually move: 
A)along an electric field line, in the positive direction of the line.
B)along an electric field line, in the negative direction of the line.
C)to a point of decreased potential.
D)to a point of increased potential.
E)as described in both (b) and (d).
A)along an electric field line, in the positive direction of the line.
B)along an electric field line, in the negative direction of the line.
C)to a point of decreased potential.
D)to a point of increased potential.
E)as described in both (b) and (d).

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
How much electrical charge is needed to raise an isolated metal sphere of radius 1.0 m to a potential of 1.0 * 106 V?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
The Bohr model pictures a hydrogen atom in its ground state as a proton and an electron separated by the distance a0 = 0.529 *10-10 m.The electric potential created by the proton at the position of the electron is:
A)(F-13.6 V.)
B)+13.6 V.
C)(-27.2 V.)
D)+27.2 V.
E)+5.12 *109 V.
A)(F-13.6 V.)
B)+13.6 V.
C)(-27.2 V.)
D)+27.2 V.
E)+5.12 *109 V.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
To recharge a 12-V battery, a battery charger must move 3.6 * 105 C of charge from the negative to the positive terminal.What amount of work is done by the battery charger? How many kilowatt hours is this?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
For the potential , what is the corresponding electric field at the point (2,2,2)? 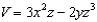
A)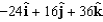
B)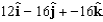
C)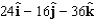
D)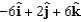
E)The correct answer is not given.
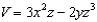
A)
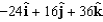
B)
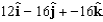
C)
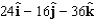
D)
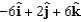
E)The correct answer is not given.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
A system consisting of a positively-charged particle and an electric field:
A)loses potential difference and kinetic energy when the charged particle moves in the direction of the field.
B)loses electric potential energy when the charged particle moves in the direction of the field.
C)loses kinetic energy when the charged particle moves in the direction of the field.
D)gains electric potential energy when the charged particle moves in the direction of the field.
E)gains potential difference and electric potential energy when the charged particle moves in the direction of the field.
A)loses potential difference and kinetic energy when the charged particle moves in the direction of the field.
B)loses electric potential energy when the charged particle moves in the direction of the field.
C)loses kinetic energy when the charged particle moves in the direction of the field.
D)gains electric potential energy when the charged particle moves in the direction of the field.
E)gains potential difference and electric potential energy when the charged particle moves in the direction of the field.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
Four electrons move from point A to point B in a uniform electric field as shown below.Rank the electrons in diagrams I through IV by the changes in potential energy from most positive to most negative when travelling from A to B. 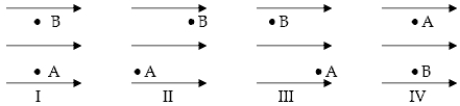
A)I = II = III = IV.
B)II = III > I > IV.
C)III > I = IV > II.
D)II > I = IV > III.
E)I > II = III > IV.

A)I = II = III = IV.
B)II = III > I > IV.
C)III > I = IV > II.
D)II > I = IV > III.
E)I > II = III > IV.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
The gap between electrodes in a spark plug is 0.06 cm.In order to produce an electric spark in a gasoline-air mixture, the electric field must reach a value of 3 *106 V/m.What minimum voltage must be supplied by the ignition circuit when starting the car?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
An infinite plane of charge with is tilted at a 45 angle to the vertical direction as shown below.The potential difference, VB -VA, in volts, between points A and B, a 4.50 m distance apart, is: 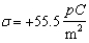

A)(-7.06.)
B)(F-9.98.)
C)(-14.11.)
D)+7.06.
E)+9.98.
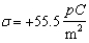

A)(-7.06.)
B)(F-9.98.)
C)(-14.11.)
D)+7.06.
E)+9.98.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



