Deck 2: Gausss Law
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/44
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 2: Gausss Law
1
Two charges of 15 pC and -40 pC are inside a cube with sides that are of 0.40-m length.Determine the net electric flux through the surface of the cube.
A)+2.8 N . m2/C
B)(-1.1 N . m2/C)
C)+1.1 N . m2/C
D)(-2.8 N . m2/C)
E)(-0.47 N.m2/C)
A)+2.8 N . m2/C
B)(-1.1 N . m2/C)
C)+1.1 N . m2/C
D)(-2.8 N . m2/C)
E)(-0.47 N.m2/C)
(-2.8 N . m2/C)
2
A hemispherical surface (half of a spherical surface) of radius R is located in a uniform electric field of magnitude E that is parallel to the axis of the hemisphere.What is the magnitude of the electric flux through the hemisphere surface?
A)( R2E)
B)4 R2E/3
C)2 R2E/3
D)( R2E/2)
E)( R2E/3)
A)( R2E)
B)4 R2E/3
C)2 R2E/3
D)( R2E/2)
E)( R2E/3)
( R2E)
3
Charge of uniform density (40 pC/m2) is distributed on a spherical surface (radius = 1.0 cm), and a second concentric spherical surface (radius = 3.0 cm) carries a uniform charge density of 60 pC/m2.What is the magnitude of the electric field at a point 4.0 cm from the centre of the two surfaces?
A)3.8 N/C
B)4.1 N/C
C)3.5 N/C
D)3.2 N/C
E)0.28 N/C
A)3.8 N/C
B)4.1 N/C
C)3.5 N/C
D)3.2 N/C
E)0.28 N/C
4.1 N/C
4
A solid non-conducting sphere (radius = 12 cm) has a charge of uniform density (30 nC/m3) distributed throughout its volume.Determine the magnitude of the electric field 15 cm from the centre of the sphere.
A)22 N/C
B)49 N/C
C)31 N/C
D)87 N/C
E)26 N/C
A)22 N/C
B)49 N/C
C)31 N/C
D)87 N/C
E)26 N/C

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 44 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
The xy plane is 'painted' with a uniform surface charge density which is equal to 40 nC/m2.Consider a spherical surface with a 4.0-cm radius that has a point in the xy plane as its centre.What is the electric flux through that part of the spherical surface for which z > 0?
A)14 N . m2/C
B)11 N . m2/C
C)17 N . m2/C
D)20 N . m2/C
E)23 N . m2/C
A)14 N . m2/C
B)11 N . m2/C
C)17 N . m2/C
D)20 N . m2/C
E)23 N . m2/C

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 44 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Charge of uniform density (80 nC/m3) is distributed throughout a hollow cylindrical region formed by two coaxial cylindrical surfaces of radii 1.0 mm and 3.0 mm.Determine the magnitude of the electric field at a point which is 2.0 mm from the symmetry axis.
A)7.9 N/C
B)9.0 N/C
C)5.9 N/C
D)6.8 N/C
E)18 N/C
A)7.9 N/C
B)9.0 N/C
C)5.9 N/C
D)6.8 N/C
E)18 N/C

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 44 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
The axis of a long hollow metallic cylinder (inner radius = 1.0 cm, outer radius = 2.0 cm) coincides with a long wire.The wire has a linear charge density of -8.0 pC/m, and the cylinder has a net charge per unit length of-4.0 pC/m.Determine the magnitude of the electric field 3.0 cm from the axis.
A)5.4 N/C
B)7.2 N/C
C)4.3 N/C
D)3.6 N/C
E)2.4 N/C
A)5.4 N/C
B)7.2 N/C
C)4.3 N/C
D)3.6 N/C
E)2.4 N/C

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 44 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
A 5.0-nC point charge is embedded at the centre of a non-conducting sphere (radius = 2.0 cm) which has a charge of -8.0 nC distributed uniformly throughout its volume.What is the magnitude of the electric field at a point that is 1.0 cm from the centre of the sphere?
A)1.8*105 N/C
B)9.0 * 104 N/C
C)3.6 * 105 N/C
D)2.7 *105 N/C
E)7.2 *105 N/C
A)1.8*105 N/C
B)9.0 * 104 N/C
C)3.6 * 105 N/C
D)2.7 *105 N/C
E)7.2 *105 N/C

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 44 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
A uniform linear charge density of 4.0 nC/m is distributed along the entire x axis.Consider a spherical (radius = 5.0 cm) surface centred on the origin.Determine the electric flux through this surface.
A)68 N . m2/C
B)62 N .m2/C
C)45 N . m2/C
D)79 N . m2/C
E)23 N . m2/C
A)68 N . m2/C
B)62 N .m2/C
C)45 N . m2/C
D)79 N . m2/C
E)23 N . m2/C

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 44 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Charge of uniform density (20 nC/m2) is distributed over a cylindrical surface (radius = 1.0 cm), and a second coaxial surface (radius = 3.0 cm) carries a uniform charge density of -12 nC/m2.Determine the magnitude of the electric field at a point 2.0 cm from the symmetry axis of the two surfaces.
A)2.3 kN/C
B)1.1 kN/C
C)1.7 kN/C
D)3.4 kN/C
E)4.5 kN/C
A)2.3 kN/C
B)1.1 kN/C
C)1.7 kN/C
D)3.4 kN/C
E)4.5 kN/C

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 44 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Charge of uniform linear density (4.0 nC/m) is distributed along the entire x axis.Determine the magnitude of the electric field on the y axis at y = 2.5 m.
A)36 N/C
B)29 N/C
C)43 N/C
D)50 N/C
E)58 N/C
A)36 N/C
B)29 N/C
C)43 N/C
D)50 N/C
E)58 N/C

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 44 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
A charge of 0.80 nC is placed at the centre of a cube that measures 4.0 m along each edge.What is the electric flux through one face of the cube?
A)90 N . m2/C
B)15 N . m2/C
C)45 N . m2/C
D)23 N . m2/C
E)64 N .m2/C
A)90 N . m2/C
B)15 N . m2/C
C)45 N . m2/C
D)23 N . m2/C
E)64 N .m2/C

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 44 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
A 4.0-pC point charge is placed at the centre of a hollow (inner radius = 2.0 cm, outer radius = 4.0 cm) conducting sphere which has a net charge of 4.0 pC.Determine the magnitude of the electric field at a point which is 6.0 cm from the point charge.
A)35 N/C
B)25 N/C
C)30 N/C
D)20 N/C
E)10 N/C
A)35 N/C
B)25 N/C
C)30 N/C
D)20 N/C
E)10 N/C

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 44 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Charge of uniform surface density (0.20 nC/m2) is distributed over the entire xy plane.Determine the magnitude of the electric field at any point having z = 2.0 m.
A)17 N/C
B)11 N/C
C)23 N/C
D)28 N/C
E)40 N/C
A)17 N/C
B)11 N/C
C)23 N/C
D)28 N/C
E)40 N/C

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 44 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
A long non-conducting cylinder (radius = 12 cm) has a charge of uniform density (5.0 nC/m3) distributed throughout its column.Determine the magnitude of the electric field 5.0 cm from the axis of the cylinder.
A)25 N/C
B)20 N/C
C)14 N/C
D)31 N/C
E)34 N/C
A)25 N/C
B)20 N/C
C)14 N/C
D)31 N/C
E)34 N/C

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 44 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Charge of a uniform density (8.0 nC/m2) is distributed over the entire xy plane.A charge of uniform density (3.0 nC/m2) is distributed over the parallel plane defined by z = 2.0 m.Determine the magnitude of the electric field for any point with z = 3.0 m.
A)0.79 kN/C
B)0.17 kN/C
C)0.62 kN/C
D)0.34 kN/C
E)0.28 kN/C
A)0.79 kN/C
B)0.17 kN/C
C)0.62 kN/C
D)0.34 kN/C
E)0.28 kN/C

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 44 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
A long cylindrical shell (radius = 2.0 cm) has a charge uniformly distributed on its surface.If the magnitude of the electric field at a point 8.0 cm radially outward from the axis of the shell is 85 N/C, how much charge is distributed on a 2.0-m length of the charged cylindrical surface?
A)0.38 nC
B)0.76 nC
C)0.19 nC
D)0.57 nC
E)0.98 nC
A)0.38 nC
B)0.76 nC
C)0.19 nC
D)0.57 nC
E)0.98 nC

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 44 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
A point charge +Q is located on the x axis at x = a, and a second point charge -Q is located on the x axis at x = -a.A Gaussian surface with radius r = 2a is centred at the origin.The flux through this Gaussian surface is:
A)zero because the negative flux over one hemisphere is equal to the positive flux over the other.
B)greater than zero.
C)zero because at every point on the surface the electric field has no component perpendicular to the surface.
D)zero because the electric field is zero at every point on the surface.
E)none of the above.
A)zero because the negative flux over one hemisphere is equal to the positive flux over the other.
B)greater than zero.
C)zero because at every point on the surface the electric field has no component perpendicular to the surface.
D)zero because the electric field is zero at every point on the surface.
E)none of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 44 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
The electric field in the region of space shown is given by N/C where y is in m.What is the magnitude of the electric flux through the top face of the cube shown? 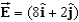
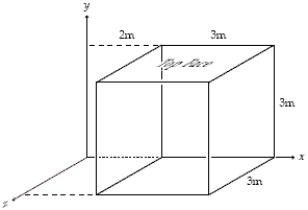
A)90 N . m2/C
B)6.0 N.m2/C
C)54 N . m2/C
D)12 N . m2/C
E)126 N.m2/C
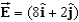

A)90 N . m2/C
B)6.0 N.m2/C
C)54 N . m2/C
D)12 N . m2/C
E)126 N.m2/C

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 44 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Two infinite parallel surfaces carry uniform charge densities of 0.20 nC/m2 and -0.60 nC/m2.What is the magnitude of the electric field at a point between the two surfaces?
A)34 N/C
B)23 N/C
C)45 N/C
D)17 N/C
E)90 N/C
A)34 N/C
B)23 N/C
C)45 N/C
D)17 N/C
E)90 N/C

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 44 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
A uniform electric field is present in the region between the infinite parallel planes of charge A and B, and a uniform electric field is present in the region between the infinite parallel planes of charge B and C.When the planes are vertical and the fields are both non-zero: 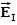
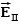
A)and are both directed to the right.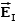
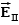
B)and are both directed to the left.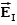
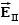
C)points to the right and to the left.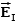
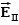
D)points to the left and to the right.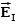
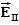
E)Any one of the above is possible.
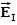
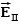
A)and are both directed to the right.
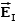
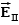
B)and are both directed to the left.
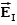
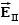
C)points to the right and to the left.
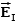
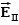
D)points to the left and to the right.
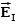
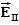
E)Any one of the above is possible.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 44 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
An astronaut is in an all-metal chamber outside the space station when a solar storm results in the deposit of a large positive charge on the station.Which statement is correct?
A)The astronaut must abandon the chamber immediately to avoid being electrocuted.
B)The astronaut will be safe only if she is wearing a spacesuit made of non-conducting materials.
C)The astronaut does not need to worry: the charge will remain on the outside surface.
D)The astronaut must abandon the chamber if the electric field on the outside surface becomes greater than the breakdown field of air.
E)The astronaut must abandon the chamber immediately because the electric field inside the chamber is non-uniform.
A)The astronaut must abandon the chamber immediately to avoid being electrocuted.
B)The astronaut will be safe only if she is wearing a spacesuit made of non-conducting materials.
C)The astronaut does not need to worry: the charge will remain on the outside surface.
D)The astronaut must abandon the chamber if the electric field on the outside surface becomes greater than the breakdown field of air.
E)The astronaut must abandon the chamber immediately because the electric field inside the chamber is non-uniform.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 44 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
You are told that summed over both the surface areas of sphere A and sphere B below totals to .You can conclude that: 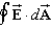
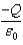

A)Sphere A contains charge qin = -Q.
B)Sphere B contains charge qin = -Q.
C)Sphere B contains charge qin = +Q.
D)Each sphere contains charge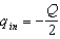
E)The sum of the charges contained in both spheres is -Q.
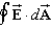
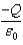

A)Sphere A contains charge qin = -Q.
B)Sphere B contains charge qin = -Q.
C)Sphere B contains charge qin = +Q.
D)Each sphere contains charge
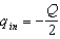
E)The sum of the charges contained in both spheres is -Q.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 44 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Which one of the following is not an expression for electric charge?
A)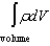
B)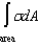
C)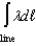
D)
E)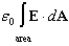
A)
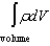
B)
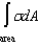
C)
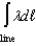
D)

E)
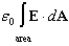

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 44 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
A positive point charge q is placed off centre inside an uncharged metal sphere insulated from the ground as shown.Where is the induced charge density greatest in magnitude and what is its sign? 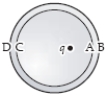
A)A; negative.
B)A; positive.
C)B; negative.
D)B; positive.
E)C; negative.

A)A; negative.
B)A; positive.
C)B; negative.
D)B; positive.
E)C; negative.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 44 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
The electric field just outside the surface of a hollow conducting sphere of radius 20 cm has a magnitude of 500 N/C and is directed outward.An unknown charge Q is introduced into the centre of the sphere and it is noted that the electric field is still directed outward but has decreased to 100 N/C.What is the magnitude of the charge Q?
A)1.5 nC
B)1.8 nC
C)1.3 nC
D)1.1 nC
E)2.7 nC
A)1.5 nC
B)1.8 nC
C)1.3 nC
D)1.1 nC
E)2.7 nC

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 44 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
A constant electric field, N/C, goes through a surface with area m2.(This surface can also be expressed as an area of 10 m2 with the direction of the unit vector ().What is the magnitude of the electric flux through this area? 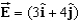
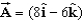
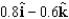
A)24 N . m2/C
B)48 N. m2/C
C)0.24 N . m2/C
D)0.48 N . m2/C
E)0
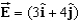
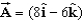
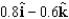
A)24 N . m2/C
B)48 N. m2/C
C)0.24 N . m2/C
D)0.48 N . m2/C
E)0

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 44 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Three infinite planes of charge, A, B and C, are vertical and parallel to one another.There is a uniform electric field to the left of plane A and a uniform electric field to the right of plane C.The field points to the left and the field points to the right.The signs of the charges on plates A, B and C may be: 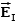
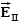
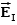
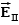
A)(-, -, -.)
B)+, -, -.
C)+, -, +.
D)+, +, +.
E)any one of the above.
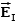
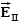
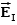
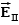
A)(-, -, -.)
B)+, -, -.
C)+, -, +.
D)+, +, +.
E)any one of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 44 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
If the electric field just outside a thin conducting sheet is equal to 1.5 N/C, determine the surface charge density on the conductor.
A)53 pC/m2
B)27 pC/m2
C)35 pC/m2
D)13 pC/m2
E)6.6 pC/m2
A)53 pC/m2
B)27 pC/m2
C)35 pC/m2
D)13 pC/m2
E)6.6 pC/m2

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 44 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Whitney says that Gauss's Law can be used to find the electric field of a sufficiently symmetrical distribution of charge as long as over the whole Gaussian surface.Algie says that the electric field must be a constant vector over the entire Gaussian surface.Which one, if either, is correct? 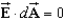
A)Whitney, because that means no charge is enclosed within the Gaussian surface.
B)Algie, because a constant electric field means that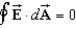
C)Both, because the conditions in (a) and (b) are equivalent.
D)Neither, because the electric field can be found from Gauss's law only if holds only over a portion of the Gaussian surface.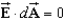
E)Neither, because the charge distribution must be symmetric if anywhere on the surface.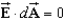
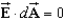
A)Whitney, because that means no charge is enclosed within the Gaussian surface.
B)Algie, because a constant electric field means that
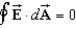
C)Both, because the conditions in (a) and (b) are equivalent.
D)Neither, because the electric field can be found from Gauss's law only if holds only over a portion of the Gaussian surface.
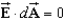
E)Neither, because the charge distribution must be symmetric if anywhere on the surface.
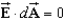

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 44 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
If we define the gravitational field , where is a unit radial vector, then Gauss's Law for gravity is: 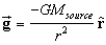
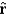
A)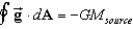
B)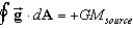
C)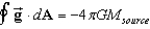
D)
E)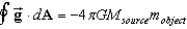
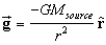
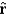
A)
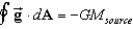
B)
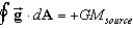
C)
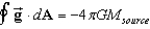
D)

E)
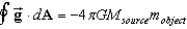

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 44 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
A positive point charge q is placed at the centre of an uncharged metal sphere insulated from the ground.The outside of the sphere is then grounded as shown.Then the ground wire is removed.A is the inner surface and B is the outer surface.Which statement is correct? 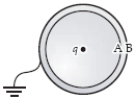
A)The charge on A is -q; that on B is +q.
B)The charge on B is -q; that on A is +q.
C)The charge is on A and on B.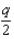
D)There is no charge on either A or B.
E)The charge on A is -q; there is no charge on B.

A)The charge on A is -q; that on B is +q.
B)The charge on B is -q; that on A is +q.
C)The charge is on A and on B.
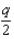
D)There is no charge on either A or B.
E)The charge on A is -q; there is no charge on B.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 44 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
An uncharged spherical conducting shell surrounds a charge -q at the centre of the shell.Then charge +3q is placed on the outside of the shell.When static equilibrium is reached, the charges on the inner and outer surfaces of the shell are respectively:
A)+q, -q.
B)(-q, +q.)
C)+q, +2q.
D)+2q, +q.
E)+3q, 0.
A)+q, -q.
B)(-q, +q.)
C)+q, +2q.
D)+2q, +q.
E)+3q, 0.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 44 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
A small metal sphere is suspended from the conducting cover of a conducting metal ice bucket by a non-conducting thread.The sphere is given a negative charge before the cover is placed on the bucket.The bucket is tilted by means of a non-conducting material so that the charged sphere touches the inside of the bucket.Which statement is correct?
A)The negative charge remains on the metal sphere.
B)The negative charge spreads over the outside surface of the bucket and cover.
C)The negative charge spreads over the inside surface of the bucket and cover.
D)The negative charge spreads equally over the inside and outside surfaces of the bucket and cover.
E)The negative charge spreads equally over the sphere and the inside and outside surfaces of the bucket and cover.
A)The negative charge remains on the metal sphere.
B)The negative charge spreads over the outside surface of the bucket and cover.
C)The negative charge spreads over the inside surface of the bucket and cover.
D)The negative charge spreads equally over the inside and outside surfaces of the bucket and cover.
E)The negative charge spreads equally over the sphere and the inside and outside surfaces of the bucket and cover.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 44 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
A point charge of 6.0 nC is placed at the centre of a hollow spherical conductor (inner radius = 1.0 cm, outer radius = 2.0 cm) which has a net charge of -4.0 nC.Determine the resulting charge density on the inner surface of the conducting sphere.
A)+4.8 C/m2
B)(-4.8 C/m2)
C)(-9.5 C/m2)
D)+9.5 C/m2
E)(-8.0 C/m2)
A)+4.8 C/m2
B)(-4.8 C/m2)
C)(-9.5 C/m2)
D)+9.5 C/m2
E)(-8.0 C/m2)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 44 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
An uncharged spherical conducting shell surrounds a charge -q at the centre of the shell.The charges on the inner and outer surfaces of the shell are respectively:
A)(-q, -q.)
B)(-q, +q.)
C)+q, -q.
D)+q, +q.
E)+q, 0.
A)(-q, -q.)
B)(-q, +q.)
C)+q, -q.
D)+q, +q.
E)+q, 0.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 44 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
A student has made the statement that the electric flux through one half of a Gaussian surface is always equal and opposite to the flux through the other half of the Gaussian surface.This is:
A)never true.
B)never false.
C)true whenever enclosed charge is symmetrically located at a centre point, or on a centre line or centrally placed plane.
D)true whenever no charge is enclosed within the Gaussian surface.
E)true only when no charge is enclosed within the Gaussian surface.
A)never true.
B)never false.
C)true whenever enclosed charge is symmetrically located at a centre point, or on a centre line or centrally placed plane.
D)true whenever no charge is enclosed within the Gaussian surface.
E)true only when no charge is enclosed within the Gaussian surface.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 44 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Gino says that the analogue of Gauss's law for the flow of an incompressible fluid of density at constant velocity is for an imaginary surface within the fluid.Lorenzo says that it is true only if the area where the fluid enters the surface and the area where it leaves the surface are both perpendicular to the velocity of the fluid.Which one, if either, is correct? 
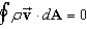
A)Gino, because as much fluid leaves as enters.
B)Lorenzo, because is not equal to zero if the fluid enters or exits at angles other than 90 .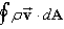
C)Lorenzo, because this is true only when the fluid executes rotational motion.
D)Gino, because it is true only when the fluid is enclosed on all sides, not when it is flowing.
E)Lorenzo, because it is true only when the fluid is enclosed on all sides, not when it is flowing.
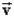
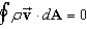
A)Gino, because as much fluid leaves as enters.
B)Lorenzo, because is not equal to zero if the fluid enters or exits at angles other than 90 .
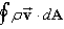
C)Lorenzo, because this is true only when the fluid executes rotational motion.
D)Gino, because it is true only when the fluid is enclosed on all sides, not when it is flowing.
E)Lorenzo, because it is true only when the fluid is enclosed on all sides, not when it is flowing.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 44 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Two planes of charge with no thickness, A and B, are parallel and vertical.The electric field in region I to the left of plane A has magnitude and points to the left.The electric field in the region to the right of B has magnitude and points to the right.The electric field in the region between the two planes has magnitude and points to the right.The surface charge density on planes A and B respectively is:
A)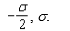
B),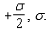
C)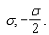
D)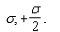
E)2 , .
A)
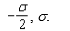
B),
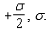
C)
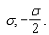
D)
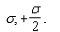
E)2 , .

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 44 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
An uncharged metal sphere is placed on an insulating puck on a frictionless table.While being held parallel to the table, a rod with a charge q is brought close to the sphere, but does not touch it.As the rod is brought in, the sphere:
A)remains at rest.
B)moves toward the rod.
C)moves away from the rod.
D)moves perpendicular to the velocity vector of the rod.
E)moves upward off the puck.
A)remains at rest.
B)moves toward the rod.
C)moves away from the rod.
D)moves perpendicular to the velocity vector of the rod.
E)moves upward off the puck.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 44 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
At the point of fission a nucleus of U-238 with 92 protons is divided into two smaller spheres each with 46 protons and a radius of 5.9 * 10-15 m.What is the repulsive force pushing the two spheres apart when they are just touching one another? (The mass of the U-238 nucleus is 3.98 * 10-25 kg.)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 44 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
The nucleus of lead-208, , has 82 protons within a sphere of radius 6.34 * 10-15.Each electric charge has a value of 1.60 *10-19 C.Assuming that the protons create a spherically symmetric distribution of charge, calculate the electric field at the surface of the nucleus. 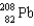
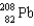

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 44 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
The nucleus of a hydrogen atom, a proton, sets up an electric field.The distance between the proton and electron is about 5.1 *10-11 m.What is the magnitude of the electric field at this distance from the proton? [The charge on the proton is +1.6 *10-19 C.]

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 44 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
A Geiger counter is like an electroscope that discharges whenever ions formed by a radioactive particle produce a conducting path.A typical Geiger counter consists of a thin conducting wire of radius 0.002 cm stretched along the axis of a conducting cylinder of radius 2.0 cm.The wire and the cylinder carry equal and opposites charges of 8.0 *10-10 C all along their length of 10.0 cm.What is the magnitude of the electric field at the surface of the wire?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 44 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



