Deck 2: Motion in One Dimension
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/48
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 2: Motion in One Dimension
1
A ball is thrown vertically upward with an initial speed of 20 m/s. Two seconds later, a stone is thrown vertically (from the same initial height as the ball) with an initial speed of 24 m/s. At what height above the release point will the ball and stone pass each other?
A)17 m
B)21 m
C)18 m
D)27 m
E)31 m
A)17 m
B)21 m
C)18 m
D)27 m
E)31 m
17 m
2
An automobile moving along a straight track changes its velocity from 40 m/s to 80 m/s in a distance of 200 m. What is the (constant) acceleration of the vehicle during this time?
A)8.0 m/s
B)9.6 m/s
C)12 m/s
D)6.9 m/s
E)0.20 m/s
A)8.0 m/s
B)9.6 m/s
C)12 m/s
D)6.9 m/s
E)0.20 m/s
12 m/s
3
A ball thrown vertically from ground level is caught 3.0 s later when it is at its highest point by a person on a balcony that is 14 m above the ground. Determine the initial speed of the ball.
A)19 m/s
B)4.7 m/s
C)10 m/s
D)34 m/s
E)17 m/s
A)19 m/s
B)4.7 m/s
C)10 m/s
D)34 m/s
E)17 m/s
19 m/s
4
An object moving on the x axis with a constant acceleration increases its x coordinate by 80 m in a time of 5.0 s and has a velocity of +20 m/s at the end of this time. Determine the acceleration of the object during this motion.
A)(-1.6 m/s2)
B)+6.4 m/s2
C)+1.6 m/s2
D)(-2.0 m/s2)
E)(-6.4 m/s2)
A)(-1.6 m/s2)
B)+6.4 m/s2
C)+1.6 m/s2
D)(-2.0 m/s2)
E)(-6.4 m/s2)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
An object is thrown downward with an initial (t = 0) speed of 10 m/s from a height of 60 m above the ground. At the same instant (t = 0), a second object is propelled vertically upward from ground level with a speed of 40 m/s. At what height above the ground will the two objects pass each other?
A)53 m
B)41 m
C)57 m
D)46 m
E)37 m
A)53 m
B)41 m
C)57 m
D)46 m
E)37 m

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Vx is the velocity of a particle moving along the x axis as shown. If x = 2.0 m at t = 1.0 s, what is the position of the particle at t = 6.0 s? 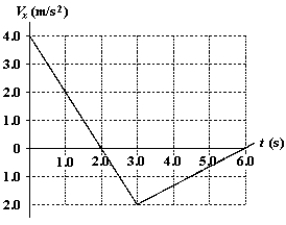
A)(-2.0 m)
B)+2.0 m
C)+1.0 m
D)(-1.0 m)
E)6.0 m

A)(-2.0 m)
B)+2.0 m
C)+1.0 m
D)(-1.0 m)
E)6.0 m

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
The velocity at the midway point of a ball able to reach a height y when thrown with velocity vi at the origin is:
A)
B)
C)
D)
E)gy
A)
B)
C)
D)
E)gy

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
An electron, starting from rest and moving with a constant acceleration, travels 2.0 cm in 5.0 m/s. What is the magnitude of this acceleration?
A)2.5 km/s2
B)0.80 km/s2
C)1.6 km/s2
D)1.3 km/s2
E)3.2 km/s2
A)2.5 km/s2
B)0.80 km/s2
C)1.6 km/s2
D)1.3 km/s2
E)3.2 km/s2

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
The position of a particle as it moves along the x axis is given for t > 0 by x = (t3 - 3t2 + 6t) m, where t is in s. Where is the particle when it achieves its minimum speed (after t = 0)?
A)3 m
B)4 m
C)8 m
D)2 m
E)7 m
A)3 m
B)4 m
C)8 m
D)2 m
E)7 m

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
At t = 0, a particle is located at x = 25 m and has a velocity of 15 m/s in the positive x direction. The acceleration of the particle varies with time as shown in the diagram. What is the position of the particle at t = 5.0 s? 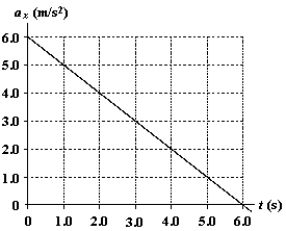
A)175 m
B)125 m
C)138 m
D)154 m
E)165 m

A)175 m
B)125 m
C)138 m
D)154 m
E)165 m

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
A particle moving with a constant acceleration has a velocity of 20 cm/s when its position is x = 10 cm. Its position 7.0 s later is x = -30 cm. What is the acceleration of the particle?
A)(-7.3 cm/s2)
B)(-8.9 cm/s2)
C)(-11 cm/s2)
D)(-15 cm/s2)
E)(-13 cm/s2)
A)(-7.3 cm/s2)
B)(-8.9 cm/s2)
C)(-11 cm/s2)
D)(-15 cm/s2)
E)(-13 cm/s2)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Imagine that you are working at the Woomera rocket range. A rocket, initially at rest, is fired vertically with an upward acceleration of 10 m/s2. At an altitude of 0.50 km, the engine of the rocket cuts off. What is the maximum altitude it achieves?
A)1.9 km
B)1.3 km
C)1.6 km
D)1.0 km
E)2.1 km
A)1.9 km
B)1.3 km
C)1.6 km
D)1.0 km
E)2.1 km

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
A particle moving along the x axis has a position given by x = (24t - 2.0t3) m, where t is measured in s. What is the magnitude of the acceleration of the particle at the instant when its velocity is zero?
A)24 m/s2
B)zero
C)12 m/s2
D)48 m/s2
E)36 m/s2
A)24 m/s2
B)zero
C)12 m/s2
D)48 m/s2
E)36 m/s2

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
A particle confined to motion along the x axis moves with constant acceleration from x = 2.0 m to x = 8.0 m during a 2.5-s time interval. The velocity of the particle at x = 8.0 m is 2.8 m/s. What is the acceleration during this time interval?
A)0.48 m/s2
B)0.32 m/s2
C)0.64 m/s2
D)0.80 m/s2
E)0.57 m/s2
A)0.48 m/s2
B)0.32 m/s2
C)0.64 m/s2
D)0.80 m/s2
E)0.57 m/s2

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
A stone is thrown from the top of a building with an initial velocity of 20 m/s downward. The top of the building is 60 m above the ground. How much time elapses between the instant of release and the instant of impact with the ground?
A)2.0 s
B)6.1 s
C)3.5 s
D)1.6 s
E)1.0 s
A)2.0 s
B)6.1 s
C)3.5 s
D)1.6 s
E)1.0 s

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
The position of a particle moving along the x axis is given by x = 6.0t2 -1.0t3, where x is in metres and t in seconds. What is the position of the particle when it achieves its maximum speed in the positive x direction?
A)24 m
B)12 m
C)32 m
D)16 m
E)2.0 m
A)24 m
B)12 m
C)32 m
D)16 m
E)2.0 m

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
The position of a particle as it moves along the x axis is given by x = 15e-2t m, where t is in s. What is the acceleration of the particle at t = 1.0 s?
A)22 m/s
B)60 m/s
C)8.1 m/s
D)15 m/s
E)35 m/s
A)22 m/s
B)60 m/s
C)8.1 m/s
D)15 m/s
E)35 m/s

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
The position of a particle moving along the x axis is given by x = (21 + 22t - 6.0t2)m, where t is in s. What is the average velocity during the time interval t = 1.0 s to t = 3.0 s?
A)(-6.0 m/s)
B)(-4.0 m/s)
C)(-2.0 m/s)
D)(-8.0 m/s)
E)8.0 m/s
A)(-6.0 m/s)
B)(-4.0 m/s)
C)(-2.0 m/s)
D)(-8.0 m/s)
E)8.0 m/s

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
A rock is thrown downward from an unknown height above the ground with an initial speed of 10 m/s. It strikes the ground 3.0 s later. Determine the initial height of the rock above the ground.
A)44 m
B)14 m
C)74 m
D)30 m
E)60 m
A)44 m
B)14 m
C)74 m
D)30 m
E)60 m

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Holden claims that its latest Commodore sedan will, starting from rest, travel 0.40 km in 9.0 s. What is the magnitude of the constant acceleration required to do this?
A)9.9 m/s2
B)8.9 m/s2
C)6.6 m/s2
D)5.6 m/s2
E)4.6 m/s2
A)9.9 m/s2
B)8.9 m/s2
C)6.6 m/s2
D)5.6 m/s2
E)4.6 m/s2

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
The position of an object at equal time intervals is shown below:  Which graph below correctly represents position versus time for this object?
Which graph below correctly represents position versus time for this object?
A)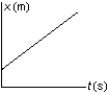
B)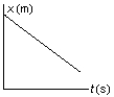
C)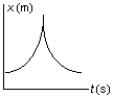
D)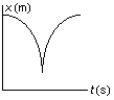
E)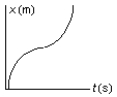
 Which graph below correctly represents position versus time for this object?
Which graph below correctly represents position versus time for this object?A)

B)

C)

D)

E)


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Five motion diagrams in which points represent the positions of an object at equal time intervals are shown below. Which statement is correct? 
A)A has the greatest speed and the greatest acceleration.
B)C has decreasing speed.
C)D slows down and then speeds up.
D)D speeds up and then slows down.
E)E has a greater speed than A.

A)A has the greatest speed and the greatest acceleration.
B)C has decreasing speed.
C)D slows down and then speeds up.
D)D speeds up and then slows down.
E)E has a greater speed than A.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Driver A is cruising along enjoying the autumn colours. Driver B starts her car at the instant he passes her. Their velocities are shown as functions of time in the graph below. At what instants in time on the graph are drivers A and B side by side? 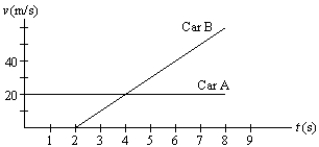
A)0 s, 2 s
B)0 s, 4 s
C)2 s, 4 s
D)2 s, 6 s
E)4 s, 6 s

A)0 s, 2 s
B)0 s, 4 s
C)2 s, 4 s
D)2 s, 6 s
E)4 s, 6 s

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Two identical balls are at rest side by side at the bottom of a hill. Some time after ball A is kicked up the hill, ball B is given a kick up the hill. Ball A is headed downhill when it passes ball B headed up the hill. At the instant when ball A passes ball B,
A)it has the same position and velocity as ball B.
B)it has the same position and acceleration as ball B.
C)it has the same velocity and acceleration as ball B.
D)it has the same displacement and velocity as ball B.
E)it has the same position, displacement and velocity as ball B.
A)it has the same position and velocity as ball B.
B)it has the same position and acceleration as ball B.
C)it has the same velocity and acceleration as ball B.
D)it has the same displacement and velocity as ball B.
E)it has the same position, displacement and velocity as ball B.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
A skier leaves a ski jump with a horizontal velocity of 29.4 m/s. The instant before she lands three seconds later, the magnitudes of the horizontal and vertical components of her velocity are:
A)0; 29.4 m/s.
B)29.4 m/s; 0.
C)29.4 m/s; 29.4 m/s.
D)29.4 m/s; 41.6 m/s.
E)41.6 m/s; 41.6 m/s.
A)0; 29.4 m/s.
B)29.4 m/s; 0.
C)29.4 m/s; 29.4 m/s.
D)29.4 m/s; 41.6 m/s.
E)41.6 m/s; 41.6 m/s.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
The small circles in the diagram below represent the positions along the x axis of a body at equal time intervals. Assume the body moves in a straight line.  This diagram is most likely to describe:
This diagram is most likely to describe:
A)a swimmer swimming laps.
B)an exercise on a rowing machine.
C)a person on a treadmill.
D)a tennis ball during a volley.
E)a runner who tripped, fell, rose, and continued racing.
 This diagram is most likely to describe:
This diagram is most likely to describe:A)a swimmer swimming laps.
B)an exercise on a rowing machine.
C)a person on a treadmill.
D)a tennis ball during a volley.
E)a runner who tripped, fell, rose, and continued racing.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Jane says that any change in velocity is directly proportional to the time interval over which the change took place. Dana says that is true only when the acceleration is constant. Which one, if either, is correct?
A)Dana, because it is true only when the acceleration is constant.
B)Jane, because we can define ax, avg so that vx = ax, avg t.
C)Jane, because ax, avg always is equal to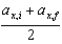 .
.
D)All the other statements are correct.
E)None of the other statements are correct.
A)Dana, because it is true only when the acceleration is constant.
B)Jane, because we can define ax, avg so that vx = ax, avg t.
C)Jane, because ax, avg always is equal to
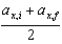 .
.D)All the other statements are correct.
E)None of the other statements are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
The area under a graph of ax vs t from t = ti to t = tf represents:
A)xf - xi.
B)vf - vi.
C)xavg.
D)vavg.
E)aavg.
A)xf - xi.
B)vf - vi.
C)xavg.
D)vavg.
E)aavg.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
When Jim and Rob ride bicycles, Jim can only accelerate at three-quarters the acceleration of Rob. Both start from rest at the bottom of a long straight road with a constant upward slope. If Rob takes 5.0 minutes to reach the top, how much earlier should Jim start to reach the top at the same time as Rob?
A)25 s
B)40 s
C)46 s
D)55 s
E)75 s
A)25 s
B)40 s
C)46 s
D)55 s
E)75 s

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
The speed of an object is given by where v is in m/s and t is in s. What is the acceleration of the object at t = 2.00 s?
A)5.00 m/s2
B)9.00 m/s2
C)10.0 m/s2
D)14.0 m/s2
E)20.0 m/s2
A)5.00 m/s2
B)9.00 m/s2
C)10.0 m/s2
D)14.0 m/s2
E)20.0 m/s2

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Two children start at one end of a street, the origin, run to the other end, then head back. On the way back Joan is ahead of Mike. At this moment in time, which statement is correct about the distances run and the displacements from the origin?
A)Joan has run a greater distance and her displacement is greater than Mike's.
B)Mike has run a greater distance and his displacement is greater than Joan's.
C)Joan has run a greater distance, but her displacement is less than Mike's.
D)Mike has run a greater distance, but his displacement is less than Joan's.
E)Mike has run a shorter distance, and his displacement is less than Joan's.
A)Joan has run a greater distance and her displacement is greater than Mike's.
B)Mike has run a greater distance and his displacement is greater than Joan's.
C)Joan has run a greater distance, but her displacement is less than Mike's.
D)Mike has run a greater distance, but his displacement is less than Joan's.
E)Mike has run a shorter distance, and his displacement is less than Joan's.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
A particle moving along the x axis has a position given by x = 54t - 2.0t3 m. At the time t = 3.0 s, the speed of the particle is zero. Which statement is correct?
A)The particle remains at rest after t = 3.0 s.
B)The particle no longer accelerates after t = 3.0 s.
C)The particle can be found at positions x < 0 m only when t < 0 s.
D)All of the above are correct.
E)None of the above is correct.
A)The particle remains at rest after t = 3.0 s.
B)The particle no longer accelerates after t = 3.0 s.
C)The particle can be found at positions x < 0 m only when t < 0 s.
D)All of the above are correct.
E)None of the above is correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
To help Kim practice for the Paralympics, Sally runs beside him for half the required distance. She runs the remaining distance at her regular speed and arrives 90 seconds ahead of Kim. What is the ratio of Sally's regular speed to Kim's speed? Use tKim for Kim's total time.
A)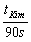
B)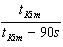
C)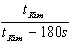
D)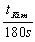
E)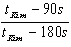
A)
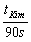
B)
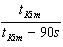
C)
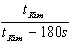
D)
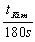
E)
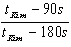

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
The graph below shows the velocity versus time graph for a ball. Which explanation best fits the motion of the ball as shown by the graph? 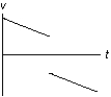
A)The ball is falling, is caught, and is thrown down with greater velocity.
B)The ball is rolling, stops, and then continues rolling.
C)The ball is rising, hits the ceiling, and falls down.
D)The ball is falling, hits the floor, and bounces up.
E)The ball is rising, is caught, and then is thrown down.

A)The ball is falling, is caught, and is thrown down with greater velocity.
B)The ball is rolling, stops, and then continues rolling.
C)The ball is rising, hits the ceiling, and falls down.
D)The ball is falling, hits the floor, and bounces up.
E)The ball is rising, is caught, and then is thrown down.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Two identical balls are at rest and side by side at the top of a hill. You let one ball, A, start rolling down the hill. A little later you start the second ball, B, down the hill by giving it a shove. The second ball rolls down the hill along a line parallel to the path of the first ball and passes it. At the instant ball B passes ball A:
A)it has the same position and the same velocity as A.
B)it has the same position and the same acceleration as A.
C)it has the same velocity and the same acceleration as A.
D)it has the same displacement and the same velocity as A.
E)it has the same position, displacement and velocity as A.
A)it has the same position and the same velocity as A.
B)it has the same position and the same acceleration as A.
C)it has the same velocity and the same acceleration as A.
D)it has the same displacement and the same velocity as A.
E)it has the same position, displacement and velocity as A.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
The equation that solves a problem is . The problem is:
A)What is the initial velocity of a car that goes from rest to 18 m/s in 3.0 s?
B)What is the final velocity of a car that goes from rest to 18 m/s in 3.0 s?
C)What is the initial velocity of a car that accelerates at 18 m/s for 3.0 s?
D)What is the final velocity of a car that accelerates at 3.0 m/s2 over a 6.0 m distance?
E)What is the final velocity of a car that accelerates at 3.0 m/s2 over a 3.0 m distance?
A)What is the initial velocity of a car that goes from rest to 18 m/s in 3.0 s?
B)What is the final velocity of a car that goes from rest to 18 m/s in 3.0 s?
C)What is the initial velocity of a car that accelerates at 18 m/s for 3.0 s?
D)What is the final velocity of a car that accelerates at 3.0 m/s2 over a 6.0 m distance?
E)What is the final velocity of a car that accelerates at 3.0 m/s2 over a 3.0 m distance?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
The position of a particle moving along the y axis has a position given by: Is there any time interval during which the particle is not moving?
A)Yes, from 0.60 s to 1.00 s.
B)Yes, from 0.795 s to 0.805 s.
C)Yes, at the time t = 0.80 s.
D)No, the velocity is never zero.
E)No, an instant is not the same as a time interval.
A)Yes, from 0.60 s to 1.00 s.
B)Yes, from 0.795 s to 0.805 s.
C)Yes, at the time t = 0.80 s.
D)No, the velocity is never zero.
E)No, an instant is not the same as a time interval.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
A boy on a skate board skates off a horizontal bench at a velocity of 10 m/s. One tenth of a second after he leaves the bench, to two significant figures, the magnitudes of his velocity and acceleration are:
A)10 m/s; 9.8 m/s2.
B)9.0 m/s; 9.8 m/s2.
C)9.0 m/s; 9.0 m/s2.
D)1.0 m/s; 9.0 m/s2.
E)1.0 m/s; 9.8 m/s2.
A)10 m/s; 9.8 m/s2.
B)9.0 m/s; 9.8 m/s2.
C)9.0 m/s; 9.0 m/s2.
D)1.0 m/s; 9.0 m/s2.
E)1.0 m/s; 9.8 m/s2.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
In 20 minutes, Lucy ran 2.40 km on a treadmill facing due east. Relative to the gym, what were her displacement and average velocity during this time interval?
A)0; 0
B)0; 2.00 m/s
C)2.40 km, east; 0
D)2.40 km, east; 2.00 m/s, east
E)2.40 km, west; 2.00 m/s, west
A)0; 0
B)0; 2.00 m/s
C)2.40 km, east; 0
D)2.40 km, east; 2.00 m/s, east
E)2.40 km, west; 2.00 m/s, west

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
When starting from rest at the bottom of a straight road with constant upward slope, Joan bicycles to the top 50.0 s ahead of Sally, whose travel time is 5.00 minutes. What is the ratio of Joan's acceleration to Sally's acceleration?
A)0.694
B)0.833
C)1.20
D)1.44
E)6.00
A)0.694
B)0.833
C)1.20
D)1.44
E)6.00

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
A particle is moving at constant velocity. Its position at t = 1.0 s is 3.0 m and its position at t = 4.0 s is 15.0 m. What is the slope of the position-time graph for this particle?
A)0, since this is a constant velocity situation.
B)4.0 m/s
C)4.0 m/s2
D)9.0 m/s
E)12 m/s2
A)0, since this is a constant velocity situation.
B)4.0 m/s
C)4.0 m/s2
D)9.0 m/s
E)12 m/s2

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Starting from rest, a car travels 1350 metres in 1.00 minute. It accelerated at 1.0 m/s2 until it reached its cruising speed. Then it drove the remaining distance at constant velocity. What was its cruising speed?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
A car originally travelling at 30 m/s manages to brake for 5.0 seconds while travelling 125 m downhill. At that point the brakes fail. After an additional 5.0 seconds it travels an additional 150 m down the hill. What was the acceleration of the car after the brakes failed?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
A cyclist starts down a hill with an initial speed of 2.0 m/s. She moves down the hill with a constant acceleration, arriving at the bottom of the hill with a speed of 8.0 m/s. If the hill is 12 m long, how long did it take the bicyclist to travel down the hill?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
A speedy tortoise can run with a velocity of 10.0 cm/s and a hare can run 20.0 times as fast. In a race, they both start at the same time, but the hare stops to rest for 2.00 minutes. The tortoise wins by a shell (20.0 cm). What was the length of the race?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
A wedge-tailed eagle dives at a myna. The eagle starts with zero downward velocity and falls with the acceleration of gravity. If the myna is 76.0 m below the initial height of the eagle, how long does it take the eagle to intercept the myna?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
A boat moves at 10.0 m/s relative to the water. If the boat is on the Brisbane river where the current is 2.0 m/s, how long does it take the boat to make a complete round trip of 1.00 km upstream followed by a 1.00 km trip downstream?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
A 50-gram superball travelling at 25.0 m/s is bounced off a brick wall and rebounds at 22.0 m/s. A high-speed camera records this event. If the ball is in contact with the wall for 3.50 ms, what is the average acceleration of the ball during this time interval?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



