Deck 13: Fiscal Policy, Deficits, and Debt
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/401
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 13: Fiscal Policy, Deficits, and Debt
1
Assume the economy is at full employment and that investment spending declines dramatically. If the goal is to restore full employment, government fiscal policy should be directed toward
A) an equality of tax receipts and government expenditures.
B) an excess of tax receipts over government expenditures.
C) an excess of government expenditures over tax receipts.
D) a reduction of subsidies and transfer payments and an increase in tax rates.
A) an equality of tax receipts and government expenditures.
B) an excess of tax receipts over government expenditures.
C) an excess of government expenditures over tax receipts.
D) a reduction of subsidies and transfer payments and an increase in tax rates.
an excess of government expenditures over tax receipts.
2
Suppose that the economy is in the midst of a recession. Which of the following policies would most likely end the recession and stimulate output growth?
A) A congressional proposal to incur a federal surplus to be used for the retirement of public debt.
B) Reductions in agricultural subsidies and veterans' benefits.
C) Postponement of a highway construction program.
D) Reductions in federal tax rates on personal and corporate income.
A) A congressional proposal to incur a federal surplus to be used for the retirement of public debt.
B) Reductions in agricultural subsidies and veterans' benefits.
C) Postponement of a highway construction program.
D) Reductions in federal tax rates on personal and corporate income.
Reductions in federal tax rates on personal and corporate income.
3
If the MPC in an economy is 0.8, government could shift the aggregate demand curve rightward by $100 billion by
A) increasing government spending by $25 billion.
B) increasing government spending by $80 billion.
C) decreasing taxes by $25 billion.
D) decreasing taxes by $100 billion.
A) increasing government spending by $25 billion.
B) increasing government spending by $80 billion.
C) decreasing taxes by $25 billion.
D) decreasing taxes by $100 billion.
decreasing taxes by $25 billion.
4
If the MPC in an economy is 0.75, government could shift the aggregate demand curve leftward by $60 billion by
A) reducing government expenditures by $12 billion.
B) reducing government expenditures by $60 billion.
C) increasing taxes by $15 billion.
D) increasing taxes by $20 billion.
A) reducing government expenditures by $12 billion.
B) reducing government expenditures by $60 billion.
C) increasing taxes by $15 billion.
D) increasing taxes by $20 billion.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 401 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
In a certain year the aggregate amount demanded at the existing price level consists of $100 billion of consumption, $40 billion of investment, $10 billion of net exports, and $20 billion of government
Purchases. Full-employment GDP is $200 billion. To obtain full employment under these conditions, the
Government should
A) encourage personal saving by increasing the interest rate on government bonds.
B) decrease government expenditures.
C) reduce tax rates and/or increase government spending.
D) discourage private investment by increasing corporate income taxes.
Purchases. Full-employment GDP is $200 billion. To obtain full employment under these conditions, the
Government should
A) encourage personal saving by increasing the interest rate on government bonds.
B) decrease government expenditures.
C) reduce tax rates and/or increase government spending.
D) discourage private investment by increasing corporate income taxes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 401 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
In a certain year, the aggregate amount demanded at the existing price level consists of $100 billion of consumption, $40 billion of investment, $10 billion of net exports, and $20 billion of government
Purchases. Full-employment GDP is $120 billion. To obtain price-level stability under these conditions,
The government should
A) increase tax rates and/or reduce government spending.
B) discourage personal saving by reducing the interest rate on government bonds.
C) increase government expenditures.
D) encourage private investment by reducing corporate income taxes.
Purchases. Full-employment GDP is $120 billion. To obtain price-level stability under these conditions,
The government should
A) increase tax rates and/or reduce government spending.
B) discourage personal saving by reducing the interest rate on government bonds.
C) increase government expenditures.
D) encourage private investment by reducing corporate income taxes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 401 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Discretionary fiscal policy will likely cause budget
A) surpluses during recessions and deficits during periods of demand-pull inflation.
B) deficits during recessions and surpluses during periods of demand-pull inflation.
C) surpluses during both recessions and periods of demand-pull inflation.
D) deficits during both recessions and periods of demand-pull inflation.
A) surpluses during recessions and deficits during periods of demand-pull inflation.
B) deficits during recessions and surpluses during periods of demand-pull inflation.
C) surpluses during both recessions and periods of demand-pull inflation.
D) deficits during both recessions and periods of demand-pull inflation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 401 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
If the MPS in an economy is 0.4, government could shift the aggregate demand curve leftward by $50 billion by
A) reducing government expenditures by $125 billion.
B) reducing government expenditures by $20 billion.
C) increasing taxes by $50 billion.
D) increasing taxes by $250 billion.
A) reducing government expenditures by $125 billion.
B) reducing government expenditures by $20 billion.
C) increasing taxes by $50 billion.
D) increasing taxes by $250 billion.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 401 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
An appropriate fiscal policy for a severe recession is
A) a decrease in government spending.
B) a decrease in tax rates.
C) appreciation of the dollar.
D) an increase in interest rates.
A) a decrease in government spending.
B) a decrease in tax rates.
C) appreciation of the dollar.
D) an increase in interest rates.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 401 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
The group of three economists who provide fiscal policy recommendations to the president is the
A) Council of Economic Advisers.
B) Joint Economic Committee.
C) Bureau of Economic Analysis.
D) Federal Reserve Board of Governors.
A) Council of Economic Advisers.
B) Joint Economic Committee.
C) Bureau of Economic Analysis.
D) Federal Reserve Board of Governors.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 401 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
In an aggregate demand-aggregate supply diagram, equal decreases in government spending and taxes will
A) shift the AD curve to the right.
B) increase the equilibrium GDP.
C) not affect the AD curve.
D) shift the AD curve to the left.
A) shift the AD curve to the right.
B) increase the equilibrium GDP.
C) not affect the AD curve.
D) shift the AD curve to the left.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 401 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Discretionary fiscal policy is so named because it
A) is undertaken at the option of the nation's central bank.
B) occurs automatically as the nation's level of GDP changes.
C) involves specific changes in taxes and government spending undertaken expressly for stabilization at the option of Congress.
D) is invoked secretly by the Council of Economic Advisers.
A) is undertaken at the option of the nation's central bank.
B) occurs automatically as the nation's level of GDP changes.
C) involves specific changes in taxes and government spending undertaken expressly for stabilization at the option of Congress.
D) is invoked secretly by the Council of Economic Advisers.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 401 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
If the MPS in an economy is 0.1, government could shift the aggregate demand curve rightward by $40 billion by
A) increasing government spending by $4 billion.
B) increasing government spending by $40 billion.
C) decreasing taxes by $4 billion.
D) increasing taxes by $4 billion.
A) increasing government spending by $4 billion.
B) increasing government spending by $40 billion.
C) decreasing taxes by $4 billion.
D) increasing taxes by $4 billion.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 401 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Contractionary fiscal policy is so named because it
A) involves a contraction of the nation's money supply.
B) necessarily reduces the size of government.
C) is aimed at reducing aggregate demand and thus achieving price stability.
D) is expressly designed to expand real GDP.
A) involves a contraction of the nation's money supply.
B) necessarily reduces the size of government.
C) is aimed at reducing aggregate demand and thus achieving price stability.
D) is expressly designed to expand real GDP.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 401 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Which of the following represents the most expansionary fiscal policy?
A) a $10 billion tax cut
B) a $10 billion increase in government spending
C) a $10 billion tax increase
D) a $10 billion decrease in government spending
A) a $10 billion tax cut
B) a $10 billion increase in government spending
C) a $10 billion tax increase
D) a $10 billion decrease in government spending

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 401 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Discretionary fiscal policy will stabilize the economy most when
A) deficits are incurred during recessions and surpluses during inflations.
B) the budget is balanced each year.
C) deficits are incurred during inflations and surpluses during recessions.
D) budget surpluses are continuously incurred.
A) deficits are incurred during recessions and surpluses during inflations.
B) the budget is balanced each year.
C) deficits are incurred during inflations and surpluses during recessions.
D) budget surpluses are continuously incurred.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 401 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Expansionary fiscal policy is so named because it
A) involves an expansion of the nation's money supply.
B) necessarily expands the size of government.
C) is aimed at achieving greater price stability.
D) is designed to expand real GDP.
A) involves an expansion of the nation's money supply.
B) necessarily expands the size of government.
C) is aimed at achieving greater price stability.
D) is designed to expand real GDP.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 401 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Discretionary fiscal policy refers to
A) any change in government spending or taxes that destabilizes the economy.
B) the authority that the president has to change personal income tax rates.
C) intentional changes in taxes and government expenditures made by Congress to stabilize the economy.
D) the changes in taxes and transfers that occur as GDP changes.
A) any change in government spending or taxes that destabilizes the economy.
B) the authority that the president has to change personal income tax rates.
C) intentional changes in taxes and government expenditures made by Congress to stabilize the economy.
D) the changes in taxes and transfers that occur as GDP changes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 401 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Fiscal policy refers to
A) deliberate changes in government spending and taxes to promote economic growth, full employment, and price level stability.
B) deliberate changes in government spending and taxes to achieve greater equality in the distribution of income.
C) altering of the interest rate to change aggregate demand.
D) fact that equal increases in government spending and taxation will be contractionary.
A) deliberate changes in government spending and taxes to promote economic growth, full employment, and price level stability.
B) deliberate changes in government spending and taxes to achieve greater equality in the distribution of income.
C) altering of the interest rate to change aggregate demand.
D) fact that equal increases in government spending and taxation will be contractionary.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 401 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
An appropriate fiscal policy for severe demand-pull inflation is
A) an increase in government spending.
B) depreciation of the dollar.
C) a reduction in interest rates.
D) a tax rate increase.
A) an increase in government spending.
B) depreciation of the dollar.
C) a reduction in interest rates.
D) a tax rate increase.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 401 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
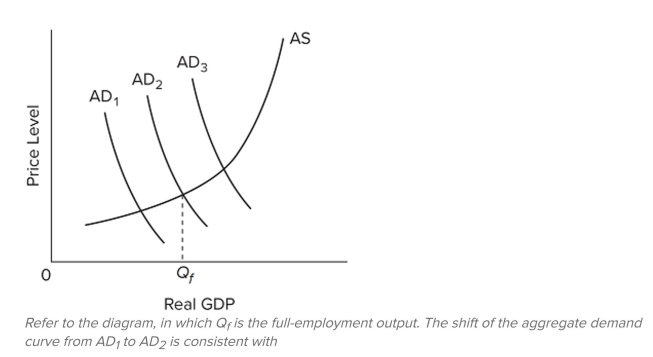
A) expansionary fiscal policy.
B) a major recession.
C) contractionary fiscal policy.
D) severe demand-pull inflation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 401 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
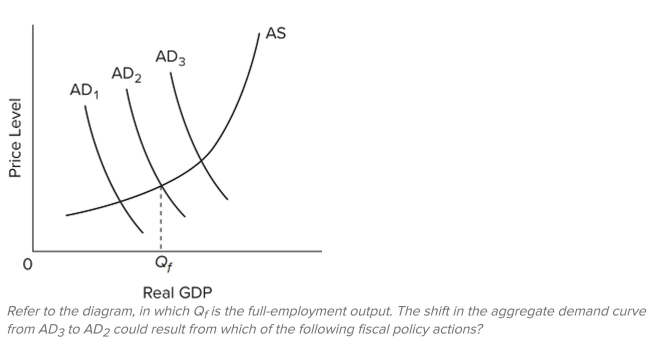
A) a tax reduction
B) a tax reduction accompanied by an even larger reduction in government spending
C) a tax increase accompanied by an even larger increase in government spending
D) an increase in government spending

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 401 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
A tax reduction of a specific amount will be more expansionary the
A) smaller is the economy's MPC.
B) larger is the economy's MPC.
C) smaller is the economy's multiplier.
D) less is the economy's built-in stability.
A) smaller is the economy's MPC.
B) larger is the economy's MPC.
C) smaller is the economy's multiplier.
D) less is the economy's built-in stability.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 401 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
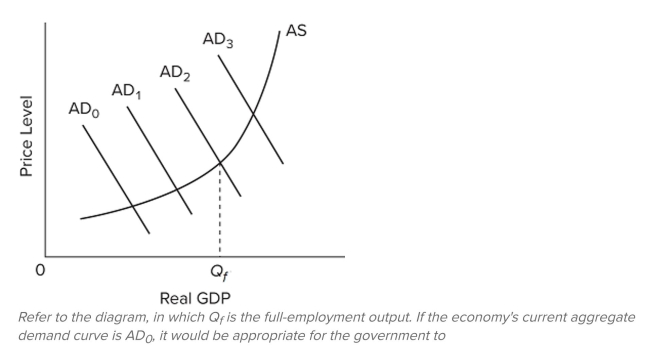
24
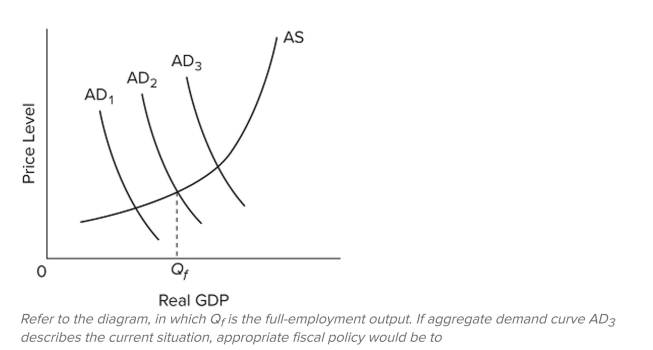
A) do nothing since the economy appears to be achieving full-employment real output.
B) increase taxes and reduce government spending to shift the aggregate demand curve leftward from AD
, assuming downward price ?exibility.
C) increase taxes on businesses to shift the aggregate supply curve rightward to reduce the price level.
D) increase taxes and reduce government spending to shift the aggregate demand curve from

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 401 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
The effect of contractionary fiscal policy is shown as a
A) rightward shift in the economy's aggregate demand curve.
B) rightward shift in the economy's aggregate supply curve.
C) movement along an existing aggregate demand curve.
D) leftward shift in the economy's aggregate demand curve.
A) rightward shift in the economy's aggregate demand curve.
B) rightward shift in the economy's aggregate supply curve.
C) movement along an existing aggregate demand curve.
D) leftward shift in the economy's aggregate demand curve.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 401 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
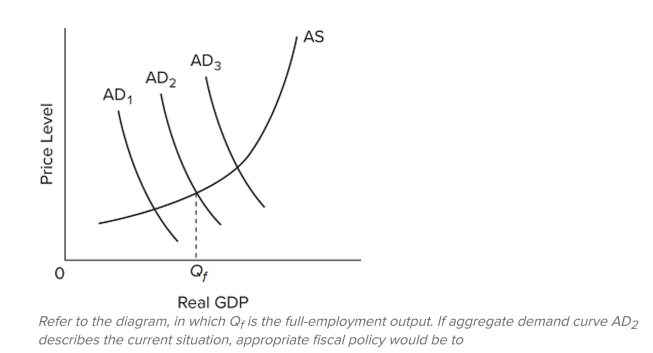
A) do nothing since the economy appears to be achieving full-employment real output.
B) increase taxes and reduce government spending to shift the aggregate demand curve rightward from AD
C) increase taxes on businesses to shift the aggregate supply curve rightward to reduce the price level.
D) reduce taxes and increase government spending to shift the aggregate demand curve from

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 401 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
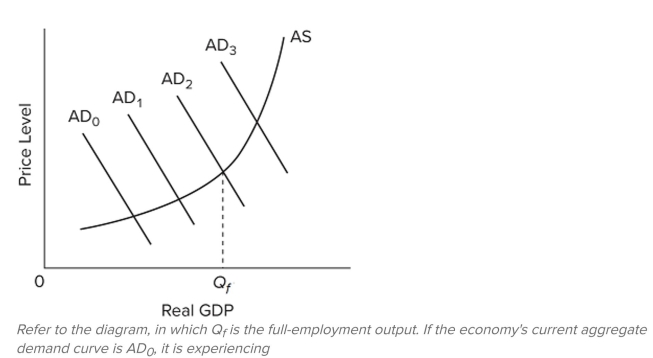
A) a positive GDP gap.
B) a negative GDP gap.
C) inflation.
D) an adverse supply shock.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 401 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Which of the following represents the most contractionary fiscal policy?
A) a $30 billion tax cut
B) a $30 billion increase in government spending
C) a $30 billion tax increase
D) a $30 billion decrease in government spending
A) a $30 billion tax cut
B) a $30 billion increase in government spending
C) a $30 billion tax increase
D) a $30 billion decrease in government spending

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 401 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
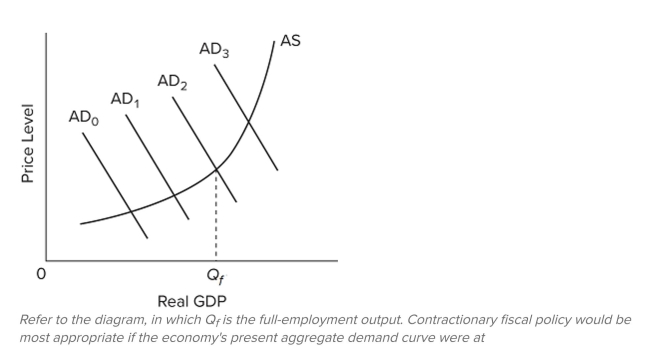
A)
B)
C)
D)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 401 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
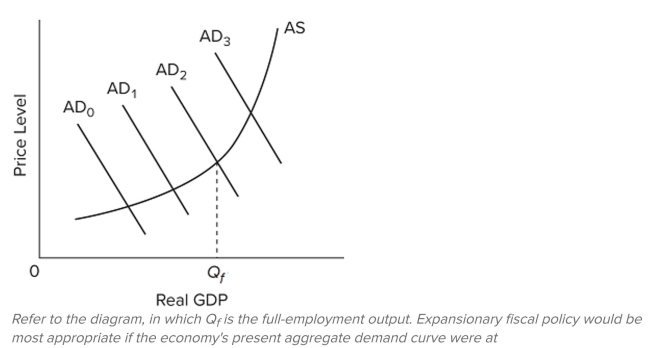
A)
B)
C)
D)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 401 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
The effect of expansionary fiscal policy is shown as a
A) rightward shift in the economy's aggregate demand curve.
B) movement along an existing aggregate demand curve.
C) leftward shift in the economy's aggregate supply curve.
D) leftward shift in the economy's aggregate demand curve.
A) rightward shift in the economy's aggregate demand curve.
B) movement along an existing aggregate demand curve.
C) leftward shift in the economy's aggregate supply curve.
D) leftward shift in the economy's aggregate demand curve.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 401 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Suppose the price level is fixed, the MPC is 0.5, and the GDP gap is a negative $100 billion. To achieve full-employment output (exactly), government should
A) increase government expenditures by $100 billion.
B) increase government expenditures by $50 billion.
C) reduce taxes by $50 billion.
D) reduce taxes by $200 billion.
A) increase government expenditures by $100 billion.
B) increase government expenditures by $50 billion.
C) reduce taxes by $50 billion.
D) reduce taxes by $200 billion.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 401 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
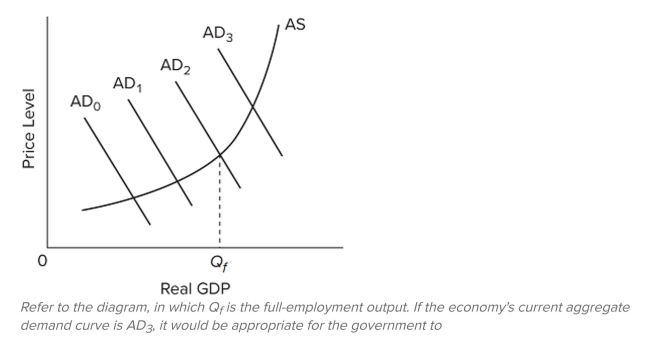
A) reduce government expenditures and taxes by equal-size amounts.
B) reduce government expenditures or increase taxes.
C) increase government expenditures or reduce taxes.
D) reduce unemployment compensation benefits.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 401 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
A specific reduction in government spending will dampen demand-pull inflation by a greater amount the
A) smaller is the economy's MPC.
B) flatter is the economy's aggregate supply curve.
C) smaller is the economy's MPS.
D) less is the economy's built-in stability.
A) smaller is the economy's MPC.
B) flatter is the economy's aggregate supply curve.
C) smaller is the economy's MPS.
D) less is the economy's built-in stability.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 401 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
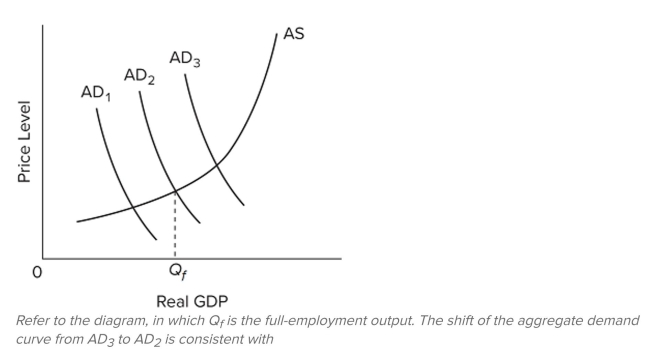
A) expansionary fiscal policy.
B) a major recession.
C) contractionary fiscal policy.
D) demand-pull inflation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 401 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
A) reduce government expenditures and taxes by equal-size amounts.
B) reduce government expenditures or increase taxes.
C) increase government expenditures or reduce taxes.
D) reduce unemployment compensation benefits.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 401 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
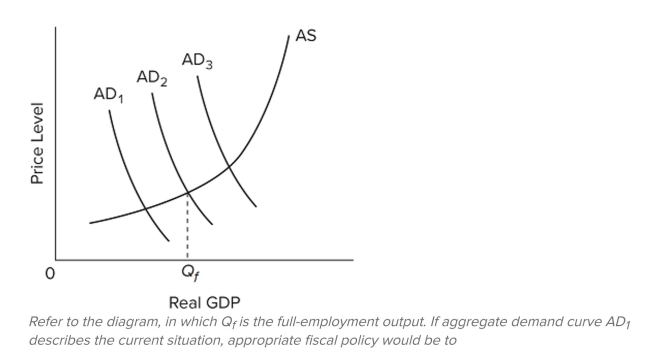
A) increase taxes and reduce government spending to shift the aggregate demand curve rightward to AD
B) reduce taxes on businesses to shift the aggregate supply curve leftward.
C) reduce taxes and increase government spending to shift the aggregate demand curve from
D) do nothing since the economy appears to be achieving full-employment real GDP.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 401 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Suppose the price level is fixed, the MPC is 0.5, and the GDP gap is a negative $80 billion. To achieve full-employment output (exactly), government should
A) increase government expenditures by $80 billion.
B) reduce government expenditures by $40 billion.
C) reduce taxes by $40 billion.
D) reduce taxes by $80 billion.
A) increase government expenditures by $80 billion.
B) reduce government expenditures by $40 billion.
C) reduce taxes by $40 billion.
D) reduce taxes by $80 billion.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 401 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
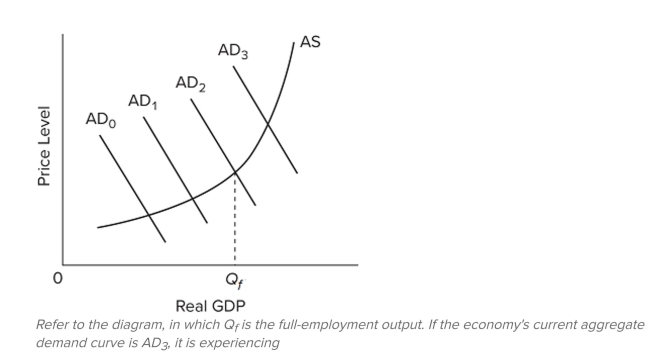
A) an inflationary GDP gap.
B) a recessionary GDP gap.
C) a recession.
D) cost-push inflation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 401 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
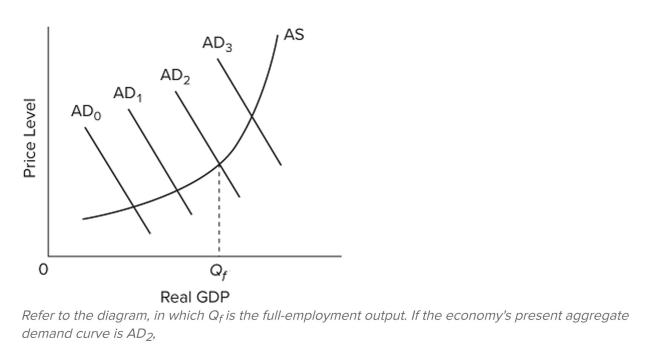
A) the most appropriate fiscal policy is an increase of government expenditures or a reduction of taxes.
B) the most appropriate fiscal policy is a reduction of government expenditures or an increase of taxes.
C) government should undertake neither expansionary nor contractionary fiscal policy.
D) the economy is achieving its maximum possible output.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 401 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
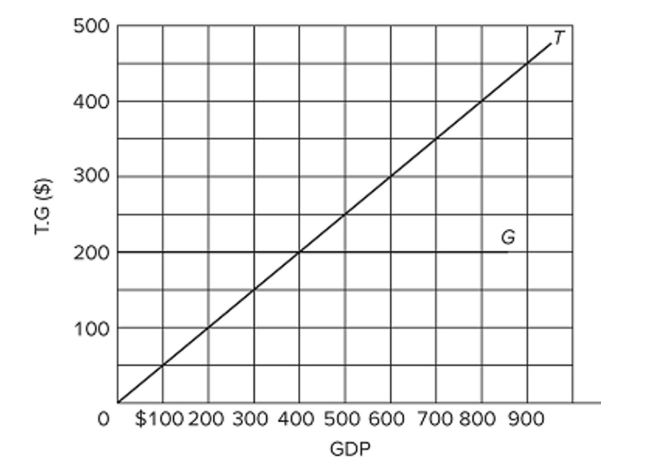 Refer to the diagram, in which T is tax revenues and G is government expenditures. All figures are in billions. This diagram portrays the idea of
Refer to the diagram, in which T is tax revenues and G is government expenditures. All figures are in billions. This diagram portrays the idea ofA) progressive taxation.
B) built-in stability.
C) the multiplier.
D) discretionary fiscal policy.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 401 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
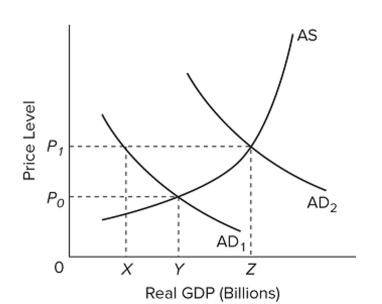 Refer to the ?gure. Suppose that the economy is currently operating at the intersection of AS and AD and that the full-employment level of output is Y. If contractionary ?scal policy and accompanying
Refer to the ?gure. Suppose that the economy is currently operating at the intersection of AS and AD and that the full-employment level of output is Y. If contractionary ?scal policy and accompanyingMultiplier effects move aggregate demand from AD
, what will be the effect on real GDP and the
Price level?
A) Real GDP will fall to Y and the price level will fall to , assuming in?exible prices.
B) Real GDP will fall to X and the price level will remain unchanged, assuming prices are in?exible downward.
C) Real GDP will fall to X and the price level will fall to , assuming in?exible prices.
D) Real GDP will fall to Y and the price level will remain unchanged, assuming in?exible prices.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 401 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
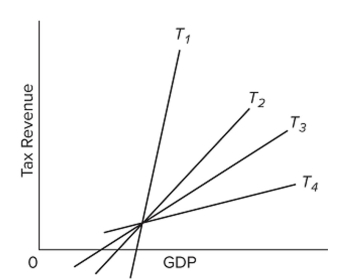 Refer to the diagram. Which tax system will generate the largest cyclical de?cits?
Refer to the diagram. Which tax system will generate the largest cyclical de?cits?A)
B)
C)
D)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 401 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
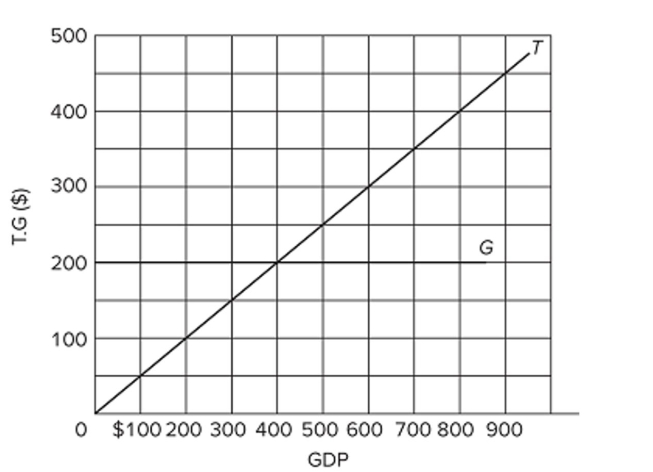 Refer to the diagram, in which T is tax revenues and G is government expenditures. All figures are in billions. The budget will entail a deficit
Refer to the diagram, in which T is tax revenues and G is government expenditures. All figures are in billions. The budget will entail a deficitA) at all levels of GDP.
B) at any level of GDP above $400.
C) at any level of GDP below $400.
D) only when GDP is stable.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 401 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
The accompanying table is the before-tax consumption schedule for a closed economy. If a lump-sum tax (the same tax amount at each level of GDP) of $40 is now imposed in this economy, the consumption
Schedule will be
A)
B)
C)
D)
Schedule will be
A)
B)
C)
D)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 401 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
The accompanying table is the before-tax consumption schedule for a closed economy. If a lump-sum tax (the same tax amount at each level of GDP) of $40 is imposed in this economy, the tax system
A) is regressive.
B) is proportional.
C) is progressive.
D) may be either proportional or progressive.
A) is regressive.
B) is proportional.
C) is progressive.
D) may be either proportional or progressive.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 401 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
Built-in stability means that
A) an annually balanced budget will offset the procyclical tendencies created by state and local finance and thereby stabilize the economy.
B) with given tax rates and expenditures policies, a rise in domestic income will reduce a budget deficit or produce a budget surplus, while a decline in income will result in a deficit or a lower
Budget surplus.
C) Congress will automatically change the tax structure and expenditure programs to correct upswings and downswings in business activity.
D) government expenditures and tax receipts automatically balance over the business cycle, though they may be out of balance in any single year.
A) an annually balanced budget will offset the procyclical tendencies created by state and local finance and thereby stabilize the economy.
B) with given tax rates and expenditures policies, a rise in domestic income will reduce a budget deficit or produce a budget surplus, while a decline in income will result in a deficit or a lower
Budget surplus.
C) Congress will automatically change the tax structure and expenditure programs to correct upswings and downswings in business activity.
D) government expenditures and tax receipts automatically balance over the business cycle, though they may be out of balance in any single year.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 401 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
A major advantage of the built-in or automatic stabilizers is that they
A) simultaneously stabilize the economy and reduce the absolute size of the public debt.
B) automatically produce surpluses during recessions and deficits during inflations.
C) require no legislative action by Congress to be made effective.
D) guarantee that the federal budget will be balanced over the course of the business cycle.
A) simultaneously stabilize the economy and reduce the absolute size of the public debt.
B) automatically produce surpluses during recessions and deficits during inflations.
C) require no legislative action by Congress to be made effective.
D) guarantee that the federal budget will be balanced over the course of the business cycle.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 401 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
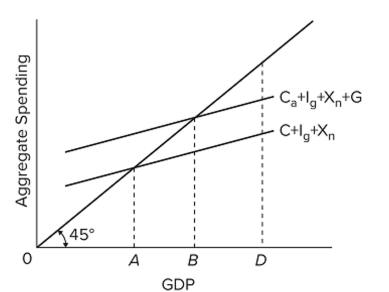
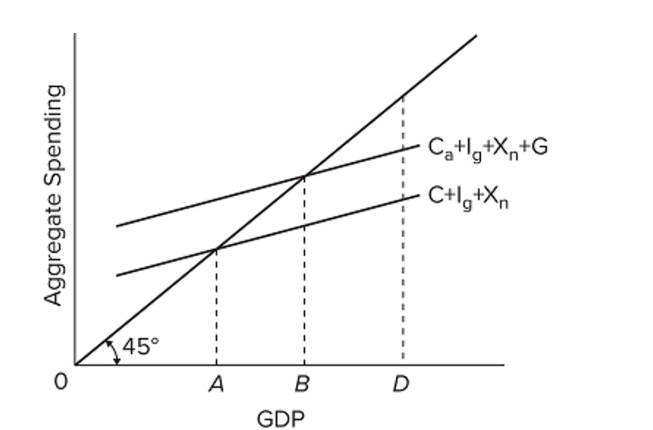 Refer to the diagram. If the full-employment level of GDP is D, then it would be appropriate fiscal policy for government to
Refer to the diagram. If the full-employment level of GDP is D, then it would be appropriate fiscal policy for government toA) decrease spending and increase taxes.
B) decrease spending and decrease taxes.
C) increase spending and increase taxes.
D) increase spending and decrease taxes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 401 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
The accompanying table is the before-tax consumption schedule for a closed economy. If a lump-sum tax (the same tax amount at each level of GDP) of $40 is imposed in this economy, the marginal
Propensity to consume is
A) 0.8 before taxes and 0.6 after taxes.
B) 0.8 both before and after taxes.
C) 0.6 before taxes and 0.8 after taxes.
D) 0.8 before taxes and 0.4 after taxes.
Propensity to consume is
A) 0.8 before taxes and 0.6 after taxes.
B) 0.8 both before and after taxes.
C) 0.6 before taxes and 0.8 after taxes.
D) 0.8 before taxes and 0.4 after taxes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 401 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
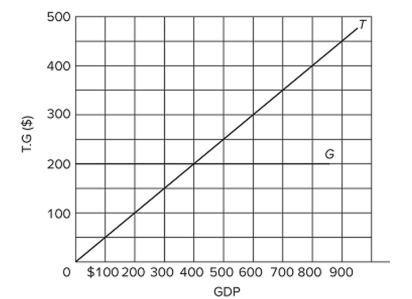 Refer to the diagram, in which T is tax revenues and G is government expenditures. All figures are in billions. If GDP is $400,
Refer to the diagram, in which T is tax revenues and G is government expenditures. All figures are in billions. If GDP is $400,A) there will be a budget deficit.
B) there will be a budget surplus.
C) the budget will be balanced.
D) the macroeconomy will necessarily be in equilibrium.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 401 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
If Congress adjusted the U.S. tax system so that the MPC was reduced, the
A) economy would become more inflation prone.
B) economy would become less stable.
C) stability of the economy would be unaffected.
D) economy would become more stable.
A) economy would become more inflation prone.
B) economy would become less stable.
C) stability of the economy would be unaffected.
D) economy would become more stable.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 401 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
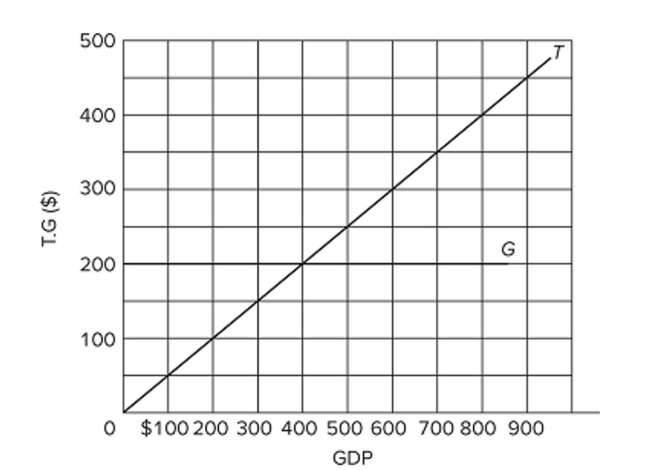 Refer to the diagram, in which T is tax revenues and G is government expenditures. All figures are in billions. In this economy,
Refer to the diagram, in which T is tax revenues and G is government expenditures. All figures are in billions. In this economy,A) tax revenues and government spending both vary directly with GDP.
B) tax revenues vary directly with GDP, but government spending is independent of GDP.
C) tax revenues and government spending both vary inversely with GDP.
D) government spending varies directly with GDP, but tax revenues are independent of GDP.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 401 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
Suppose the price level is fixed, the MPC is 0.8, and the GDP gap is a negative $200 billion. To achieve full-employment output (exactly), government should
A) increase government expenditures by $200 billion.
B) reduce taxes by $200 billion.
C) increase government expenditures by $40 billion.
D) reduce taxes by $160 billion.
A) increase government expenditures by $200 billion.
B) reduce taxes by $200 billion.
C) increase government expenditures by $40 billion.
D) reduce taxes by $160 billion.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 401 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
Which of the following best describes the built-in stabilizers as they function in the United States?
A) The size of the multiplier varies inversely with the level of GDP.
B) Personal and corporate income tax collections automatically fall and transfers and subsidies automatically rise as GDP rises.
C) Personal and corporate income tax collections and transfers and subsidies all automatically vary inversely with the level of GDP.
D) Personal and corporate income tax collections automatically rise and transfers and subsidies automatically decline as GDP rises.
A) The size of the multiplier varies inversely with the level of GDP.
B) Personal and corporate income tax collections automatically fall and transfers and subsidies automatically rise as GDP rises.
C) Personal and corporate income tax collections and transfers and subsidies all automatically vary inversely with the level of GDP.
D) Personal and corporate income tax collections automatically rise and transfers and subsidies automatically decline as GDP rises.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 401 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
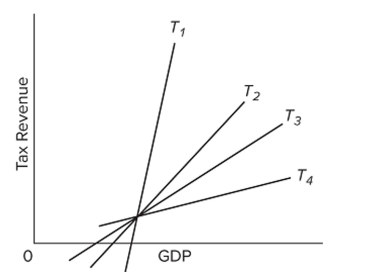 Refer to the diagram. Which tax system has the most built-in stability?
Refer to the diagram. Which tax system has the most built-in stability?A)
B)
C)
D)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 401 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
The accompanying table is the before-tax consumption schedule for a closed economy. If a lump-sum tax (the same tax amount at each level of GDP) of $40 is imposed in this economy, we can conclude that
The tax
A) enhances the economy's built-in stability.
B) reduces the economy's built-in stability.
C) neither increases nor decreases built-in stability.
D) increases the MPC and therefore increases the size of the multiplier.
The tax
A) enhances the economy's built-in stability.
B) reduces the economy's built-in stability.
C) neither increases nor decreases built-in stability.
D) increases the MPC and therefore increases the size of the multiplier.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 401 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
Which of the following statements is correct?
A) Built-in stability only partially offsets fluctuations in economic activity.
B) Built-in stability works in halting inflation, but it cannot alleviate unemployment.
C) Built-in stability can be relied on to eliminate completely any fluctuation in economic activity.
D) Built-in stability has eliminated the need for discretionary fiscal policy.
A) Built-in stability only partially offsets fluctuations in economic activity.
B) Built-in stability works in halting inflation, but it cannot alleviate unemployment.
C) Built-in stability can be relied on to eliminate completely any fluctuation in economic activity.
D) Built-in stability has eliminated the need for discretionary fiscal policy.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 401 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
 Refer to the diagram. If the full-employment level of GDP is A, then it would be appropriate fiscal policy for government to
Refer to the diagram. If the full-employment level of GDP is A, then it would be appropriate fiscal policy for government toA) decrease spending and increase taxes.
B) decrease spending and decrease taxes.
C) increase spending and increase taxes.
D) increase spending and decrease taxes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 401 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
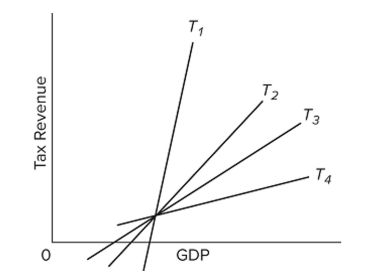 Refer to the diagram. Which tax system has the least built-in stability?
Refer to the diagram. Which tax system has the least built-in stability?A)
B)
C)
D)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 401 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
The cyclically adjusted budget refers to
A) the inflationary impact that the automatic stabilizers have in a full-employment economy.
B) that portion of a full-employment GDP that is not consumed in the year it is produced.
C) the size of the federal government's budgetary surplus or deficit when the economy is operating at full employment.
D) the number of workers who are underemployed when the level of unemployment is 4 to 5 percent.
A) the inflationary impact that the automatic stabilizers have in a full-employment economy.
B) that portion of a full-employment GDP that is not consumed in the year it is produced.
C) the size of the federal government's budgetary surplus or deficit when the economy is operating at full employment.
D) the number of workers who are underemployed when the level of unemployment is 4 to 5 percent.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 401 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
Refer to the table for a ?ctional economy. The changes in the budget conditions between Year 3 and 4 best re?ect
A) demand-pull in?ation.
B) cost-push in?ation.
C) an expansion of real GDP and an automatic increase in tax revenues.
D) a contractionary ?scal policy.
A) demand-pull in?ation.
B) cost-push in?ation.
C) an expansion of real GDP and an automatic increase in tax revenues.
D) a contractionary ?scal policy.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 401 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
Suppose the government purposely changes the economy's cyclically adjusted budget from a deficit of 0 percent of real GDP to a deficit of 3 percent of real GDP. The government is engaging in a(n)
A) expansionary fiscal policy.
B) contractionary fiscal policy.
C) neutral fiscal policy.
D) low-interest-rate policy.
A) expansionary fiscal policy.
B) contractionary fiscal policy.
C) neutral fiscal policy.
D) low-interest-rate policy.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 401 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
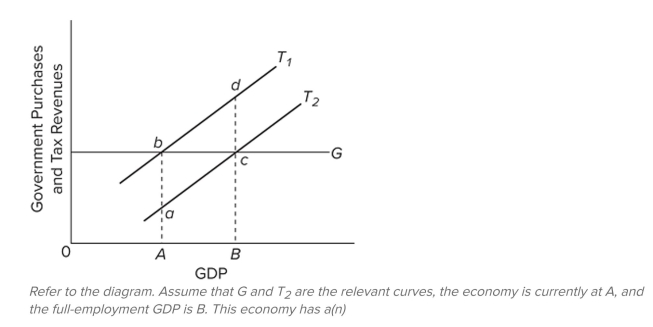
A) cyclically adjusted budget surplus.
B) actual budget deficit.
C) cyclically adjusted budget deficit.
D) actual budget surplus.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 401 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
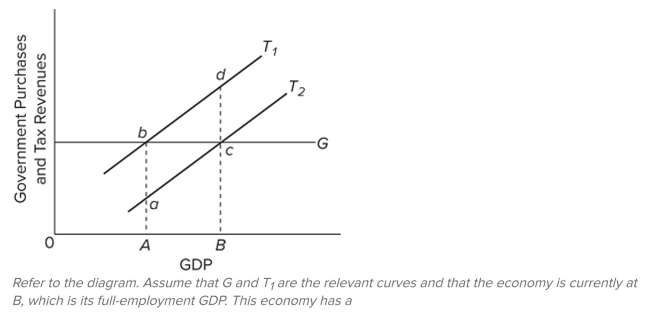
A) cyclically adjusted budget surplus only.
B) cyclically adjusted budget deficit only.
C) cyclically adjusted budget surplus and an actual budget surplus.
D) cyclically adjusted deficit and an actual budget deficit.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 401 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
When current government expenditures exceed current tax revenues and the economy is achieving full employment,
A) the cyclically adjusted budget has neither a deficit nor a surplus.
B) the cyclically adjusted budget has a deficit.
C) fiscal policy is contractionary.
D) the cyclically adjusted budget has a surplus.
A) the cyclically adjusted budget has neither a deficit nor a surplus.
B) the cyclically adjusted budget has a deficit.
C) fiscal policy is contractionary.
D) the cyclically adjusted budget has a surplus.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 401 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
The cyclically adjusted budget tells us
A) that in a full-employment economy, the federal budget should be in balance.
B) that tax revenues should vary inversely with GDP.
C) what the size of the federal budget deficit or surplus would be if the economy was at full employment.
D) the actual budget deficit or surplus realized in any given year.
A) that in a full-employment economy, the federal budget should be in balance.
B) that tax revenues should vary inversely with GDP.
C) what the size of the federal budget deficit or surplus would be if the economy was at full employment.
D) the actual budget deficit or surplus realized in any given year.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 401 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
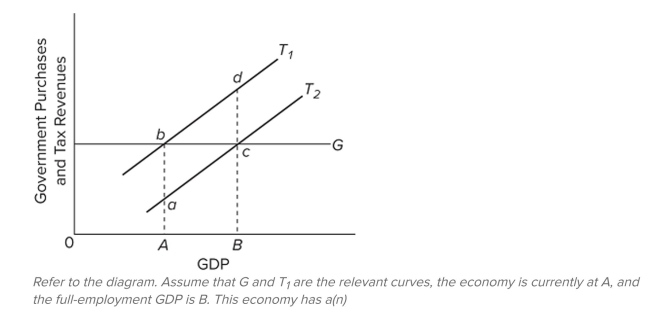
A) cyclically adjusted budget surplus.
B) cyclically adjusted budget deficit.
C) actual budget deficit.
D) actual budget surplus.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 401 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
The actual budget deficit of the federal government in 2018 was about $3.9 percent of GDP. On the basis of this information, it
A) can be concluded that the economy was faced with serious inflation in 2018.
B) cannot be determined whether the government engaged in expansionary or contractionary fiscal policy in 2018.
C) can be concluded that fiscal policy was contractionary in 2018.
D) can be concluded that fiscal policy was expansionary in 2018.
A) can be concluded that the economy was faced with serious inflation in 2018.
B) cannot be determined whether the government engaged in expansionary or contractionary fiscal policy in 2018.
C) can be concluded that fiscal policy was contractionary in 2018.
D) can be concluded that fiscal policy was expansionary in 2018.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 401 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
When current government expenditures equal current tax revenues and the economy is achieving full employment,
A) the cyclically adjusted budget has neither a deficit nor a surplus.
B) the cyclically adjusted budget may have either a deficit or a surplus.
C) fiscal policy is contractionary.
D) nominal GDP and real GDP are equal.
A) the cyclically adjusted budget has neither a deficit nor a surplus.
B) the cyclically adjusted budget may have either a deficit or a surplus.
C) fiscal policy is contractionary.
D) nominal GDP and real GDP are equal.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 401 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
Refer to the table for a ?ctional economy. The changes in the budget conditions between Year 4 and 5 best re?ect a(n)
A) recession.
B) expansionary ?scal policy.
C) tax increase.
D) contractionary ?scal policy.
A) recession.
B) expansionary ?scal policy.
C) tax increase.
D) contractionary ?scal policy.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 401 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
If the economy has a cyclically adjusted budget surplus, this means that
A) the public sector is exerting an expansionary impact on the economy.
B) tax revenues would exceed government expenditures if full employment were achieved.
C) the actual budget is necessarily also in surplus.
D) the economy is actually operating at full employment.
A) the public sector is exerting an expansionary impact on the economy.
B) tax revenues would exceed government expenditures if full employment were achieved.
C) the actual budget is necessarily also in surplus.
D) the economy is actually operating at full employment.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 401 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
When current tax revenues exceed current government expenditures and the economy is achieving full employment,
A) the cyclically adjusted budget has neither a deficit nor a surplus.
B) the cyclically adjusted budget may have either a deficit or a surplus.
C) the cyclically adjusted budget has a surplus.
D) the government is engaging in an expansionary fiscal policy.
A) the cyclically adjusted budget has neither a deficit nor a surplus.
B) the cyclically adjusted budget may have either a deficit or a surplus.
C) the cyclically adjusted budget has a surplus.
D) the government is engaging in an expansionary fiscal policy.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 401 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
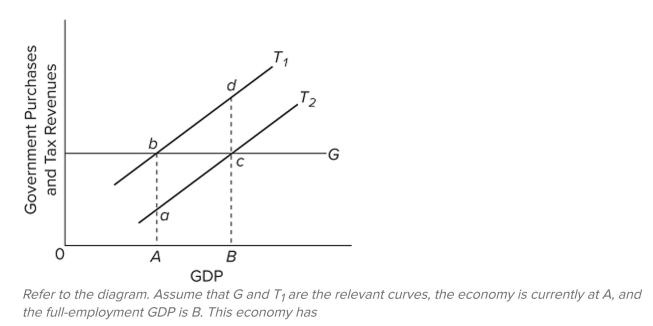
A) a cyclically adjusted budget deficit.
B) an actual budget deficit.
C) an actual budget surplus.
D) neither a surplus nor deficit in the actual budget.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 401 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
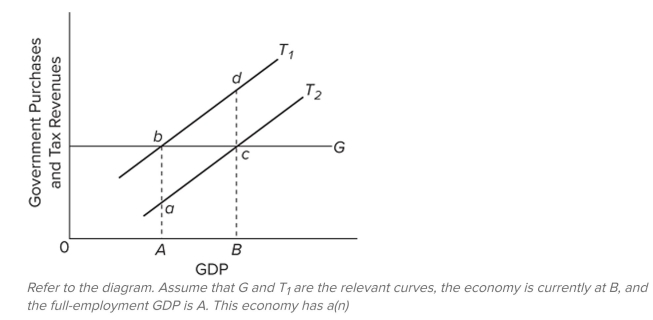
A) cyclically adjusted budget surplus.
B) actual budget deficit.
C) cyclically adjusted budget deficit.
D) actual budget surplus.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 401 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
Which of the following statements is correct?
A) The cyclically adjusted budget and the actual budget differ because the latter does not take government transfer payments into account.
B) The cyclically adjusted budget is less likely to show a deficit than is the actual budget.
C) The cyclically adjusted budget and the actual budget will show the same size deficit or surplus in any given fiscal year.
D) The cyclically adjusted budget is more likely to show a deficit than is the actual budget.
A) The cyclically adjusted budget and the actual budget differ because the latter does not take government transfer payments into account.
B) The cyclically adjusted budget is less likely to show a deficit than is the actual budget.
C) The cyclically adjusted budget and the actual budget will show the same size deficit or surplus in any given fiscal year.
D) The cyclically adjusted budget is more likely to show a deficit than is the actual budget.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 401 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
Suppose the government cuts taxes to keep the economy's cyclically adjusted budget in balance when the economy is expanding. The government is engaging in a(n)
A) contractionary fiscal policy.
B) expansionary fiscal policy.
C) low-interest-rate policy.
D) neutral fiscal policy.
A) contractionary fiscal policy.
B) expansionary fiscal policy.
C) low-interest-rate policy.
D) neutral fiscal policy.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 401 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
Suppose the government purposely changes the economy's cyclically adjusted budget from a deficit of 3 percent of real GDP to a surplus of 1 percent of real GDP. The government is engaging in a(n)
A) expansionary fiscal policy.
B) contractionary fiscal policy.
C) neutral fiscal policy.
D) high-interest-rate policy.
A) expansionary fiscal policy.
B) contractionary fiscal policy.
C) neutral fiscal policy.
D) high-interest-rate policy.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 401 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
Refer to the data for a ?ctional economy. The changes in the budget conditions between Year 1 and 2 best re?ect
A) demand-pull in?ation.
B) an expansionary ?scal policy.
C) a recession.
D) a contractionary ?scal policy.
A) demand-pull in?ation.
B) an expansionary ?scal policy.
C) a recession.
D) a contractionary ?scal policy.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 401 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
Refer to the data for a ?ctional economy. The changes in the budget conditions between Year 2 and 3 best re?ect
A) demand-pull in?ation.
B) an expansionary ?scal policy.
C) a tax increase.
D) a contractionary ?scal policy.
A) demand-pull in?ation.
B) an expansionary ?scal policy.
C) a tax increase.
D) a contractionary ?scal policy.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 401 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



