Deck 13: Decision Rights: Bundling Tasks Into Jobs and Subunits
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/19
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 13: Decision Rights: Bundling Tasks Into Jobs and Subunits
1
ANALYZING MANAGERIAL DECISIONS: Jog PCS
Jog PCS is a wireless telephone company. It sells cell phones to three customer groups: (1) business users, (2) high-volume individual users, and (3) low-volume individual users. Currently, the company is functionally organized. Primary functions include product development, marketing, sales, and customer service. The organizational chart is as follows:
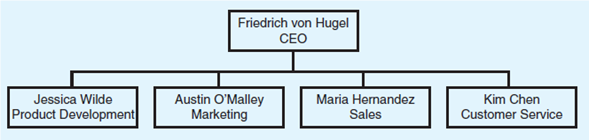
Discuss the pros and cons of the proposed reorganization, relative to the current structure.
Jog PCS is a wireless telephone company. It sells cell phones to three customer groups: (1) business users, (2) high-volume individual users, and (3) low-volume individual users. Currently, the company is functionally organized. Primary functions include product development, marketing, sales, and customer service. The organizational chart is as follows:

Discuss the pros and cons of the proposed reorganization, relative to the current structure.
The company currently follows a functional organizational structure, but the CEO of the company is considering shifting to an organizational structure that will be around the customer type groups that the company deals with.
The current structure offers advantages such as less coordination cost, and offers a simple structure to comply with but also has some drawbacks attached to it.
The structure that the company wishes to opt for in the future also has its pros and cons in comparison to the current structure.
Pros: -
• As per the new division company can easily check up on the functions of each customer group individually and thus would be easy for the upper management to formulate strategies targeting different customers group type, unlike the previous system where the differentiation would have been tough.
• It will allow specialization of the work resulting in an efficient and effective outcome, unlike the previous structure where a department has to oversee multiple groups.
• The autonomy within the departments would allow each group to coordinate easily with sub-departments internally without any upper management interference whereas in the current structure there was a lack of autonomy.
Cons: -
• While the internal coordination would improve but coordination cost for the overall company is likely to increase as there are now multiple departments.
• Decentralization of authority and autonomy with the departments can sometimes lead to distancing the upper management from the day to day operational activities making it difficult for them to keep a track of regular activities.
The current structure offers advantages such as less coordination cost, and offers a simple structure to comply with but also has some drawbacks attached to it.
The structure that the company wishes to opt for in the future also has its pros and cons in comparison to the current structure.
Pros: -
• As per the new division company can easily check up on the functions of each customer group individually and thus would be easy for the upper management to formulate strategies targeting different customers group type, unlike the previous system where the differentiation would have been tough.
• It will allow specialization of the work resulting in an efficient and effective outcome, unlike the previous structure where a department has to oversee multiple groups.
• The autonomy within the departments would allow each group to coordinate easily with sub-departments internally without any upper management interference whereas in the current structure there was a lack of autonomy.
Cons: -
• While the internal coordination would improve but coordination cost for the overall company is likely to increase as there are now multiple departments.
• Decentralization of authority and autonomy with the departments can sometimes lead to distancing the upper management from the day to day operational activities making it difficult for them to keep a track of regular activities.
2
ANALYZING MANAGERIAL DECISIONS: Bagby Copy Company
Bagby Copy Company is a worldwide producer of copy machines. It manufactures 10 different copiers, ranging from low-end desktop copiers that sell for a few hundred dollars to high-volume document machines that retail for over $200,000.
Each copy machine requires a wiring bundle. Each bundle contains several hundred wires and connectors that provide circuits connecting the paper-flow units, scanner, and photoreceptor to the internal computer logic. The wire harness is plugged into various components during the assembly process. It is possible to assign each major task in this process to different employees. For example, a given employee might focus on one of the many connectors or on testing the completed wire harness. Alternatively, one individual might be assigned the task of producing and testing a completed harness.
In either case, there is a group of employees that is assigned individual tasks to produce a wire harness for a particular copier. In total, there are 10 subgroups of wire harness makers. One alternative is to place all 10 groups in one wire harness department. Another alternative is that each of these 10 subgroups can be assigned to and report to a manager responsible for a particular copier.
Bagby operates in five European countries. Currently, it has separate subunits in each country, where a country manager handles the manufacturing and marketing of all 10 copiers. The company is considering two alternatives. One would be to organize its foreign operations around products. In this case, there would be 10 international product managers with decision rights for managing the manufacturing and sale of a particular copier throughout Europe. The company also is considering a matrix organization, organized around product and country.
What are the trade-offs between these two methods of grouping wire harness makers into subgroups
Bagby Copy Company is a worldwide producer of copy machines. It manufactures 10 different copiers, ranging from low-end desktop copiers that sell for a few hundred dollars to high-volume document machines that retail for over $200,000.
Each copy machine requires a wiring bundle. Each bundle contains several hundred wires and connectors that provide circuits connecting the paper-flow units, scanner, and photoreceptor to the internal computer logic. The wire harness is plugged into various components during the assembly process. It is possible to assign each major task in this process to different employees. For example, a given employee might focus on one of the many connectors or on testing the completed wire harness. Alternatively, one individual might be assigned the task of producing and testing a completed harness.
In either case, there is a group of employees that is assigned individual tasks to produce a wire harness for a particular copier. In total, there are 10 subgroups of wire harness makers. One alternative is to place all 10 groups in one wire harness department. Another alternative is that each of these 10 subgroups can be assigned to and report to a manager responsible for a particular copier.
Bagby operates in five European countries. Currently, it has separate subunits in each country, where a country manager handles the manufacturing and marketing of all 10 copiers. The company is considering two alternatives. One would be to organize its foreign operations around products. In this case, there would be 10 international product managers with decision rights for managing the manufacturing and sale of a particular copier throughout Europe. The company also is considering a matrix organization, organized around product and country.
What are the trade-offs between these two methods of grouping wire harness makers into subgroups
The trade-off between the two lies based on the cost involved while choosing the method.
• If Bagboy chooses the first alternative i.e. to decides to place all groups of harness under a single department it will result in lower the company's cost of coordination and cost of communication between the groups and the manager. But in this type of method, employees lack incentive and will underperform. The manager can face difficulties in managing different groups as he has to now trained for multiple functions and handle multiple groups under his supervision.
• Now, if Bagboy goes for another alternative it will have to divide all subgroups with each different manager. Doing this would help the company to exploit its comparative advantage and motivate the employees to perform well. This will further also result in effective communication between the group and the manager. But the choice of this division method would result in coordination costs across the groups and the company.
Therefore, the choice between either of the methods depends upon the weight of the benefits and cost attached to the method.
• If Bagboy chooses the first alternative i.e. to decides to place all groups of harness under a single department it will result in lower the company's cost of coordination and cost of communication between the groups and the manager. But in this type of method, employees lack incentive and will underperform. The manager can face difficulties in managing different groups as he has to now trained for multiple functions and handle multiple groups under his supervision.
• Now, if Bagboy goes for another alternative it will have to divide all subgroups with each different manager. Doing this would help the company to exploit its comparative advantage and motivate the employees to perform well. This will further also result in effective communication between the group and the manager. But the choice of this division method would result in coordination costs across the groups and the company.
Therefore, the choice between either of the methods depends upon the weight of the benefits and cost attached to the method.
3
Define the following: functional organizations, product organization, geographic organization, matrix organization, and network organization.
Functional organization:
The concept of functional organization was given by F.W. Taylor. In functional organization, the organization is divided to put the people with special abilities at the top level. In this type of organization, the functional departments are made to deal with the problems at business level. The authority in this case is limited to providing guidance to different departments. This maintains the quality and functions are performed uniformly throughout the organization. In this the organization is divided into various functions in order to operate the business and management.
Product organization:
In product organization, the organization structure is based on the particular product or service. These departments are allowed to operate independently. In this structure, the grouping is done based on the product line of the business. The sales and purchases are divided accordingly. This organization is used when the business has different product lines and it needs a special expertise for its distribution and promotion. This organization provides better coordination among managers. It reduces communication barriers among the managers who deal in same product and services.
Geographical organization:
In this type of organization, the organizational structure of the company is bifurcated on the basis of the geographical locations the business deals. Such an organization is headed from the head office under centralized organization structure. This kind of organization understands, identifies and fulfills the needs of the certain people located in a specific location.
Matrix organization:
In matrix organization, each individual manager reports to more than one senior manager or supervisor, leader. The reporting responsibilities under this organization are set up as a grid, or a matrix. The managers have a dual reporting responsibility. They report to product manager as well as functional manager. It has a rapid inflow of information, resources are efficiently used, and the morale and spirit of the team is high. Sometimes, dual reporting responsibilities lead to project manager caught in middle, the complexity in organizational structure and an increased overhead cost of management.
Network organization:
Network organization is the organizational structure that is built around the central organization. The subsidiaries of the company are connected to the head office of the organization through the network organization. This organization works on the cooperation and coordination of the network organization. The central organization makes all the decisions and then passes it on to the network organizations. The information is shared with the other organization very easily.
The concept of functional organization was given by F.W. Taylor. In functional organization, the organization is divided to put the people with special abilities at the top level. In this type of organization, the functional departments are made to deal with the problems at business level. The authority in this case is limited to providing guidance to different departments. This maintains the quality and functions are performed uniformly throughout the organization. In this the organization is divided into various functions in order to operate the business and management.
Product organization:
In product organization, the organization structure is based on the particular product or service. These departments are allowed to operate independently. In this structure, the grouping is done based on the product line of the business. The sales and purchases are divided accordingly. This organization is used when the business has different product lines and it needs a special expertise for its distribution and promotion. This organization provides better coordination among managers. It reduces communication barriers among the managers who deal in same product and services.
Geographical organization:
In this type of organization, the organizational structure of the company is bifurcated on the basis of the geographical locations the business deals. Such an organization is headed from the head office under centralized organization structure. This kind of organization understands, identifies and fulfills the needs of the certain people located in a specific location.
Matrix organization:
In matrix organization, each individual manager reports to more than one senior manager or supervisor, leader. The reporting responsibilities under this organization are set up as a grid, or a matrix. The managers have a dual reporting responsibility. They report to product manager as well as functional manager. It has a rapid inflow of information, resources are efficiently used, and the morale and spirit of the team is high. Sometimes, dual reporting responsibilities lead to project manager caught in middle, the complexity in organizational structure and an increased overhead cost of management.
Network organization:
Network organization is the organizational structure that is built around the central organization. The subsidiaries of the company are connected to the head office of the organization through the network organization. This organization works on the cooperation and coordination of the network organization. The central organization makes all the decisions and then passes it on to the network organizations. The information is shared with the other organization very easily.
4
ANALYZING MANAGERIAL DECISIONS: Jog PCS
Jog PCS is a wireless telephone company. It sells cell phones to three customer groups: (1) business users, (2) high-volume individual users, and (3) low-volume individual users. Currently, the company is functionally organized. Primary functions include product development, marketing, sales, and customer service. The organizational chart is as follows:
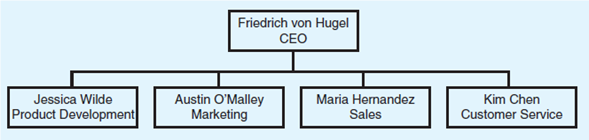
Jessica Wilde, vice president of product development, suggests that a matrix organization might be better. Draw the organization chart implied by her proposal.
Jog PCS is a wireless telephone company. It sells cell phones to three customer groups: (1) business users, (2) high-volume individual users, and (3) low-volume individual users. Currently, the company is functionally organized. Primary functions include product development, marketing, sales, and customer service. The organizational chart is as follows:

Jessica Wilde, vice president of product development, suggests that a matrix organization might be better. Draw the organization chart implied by her proposal.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 19 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
ANALYZING MANAGERIAL DECISIONS: Bagby Copy Company
Bagby Copy Company is a worldwide producer of copy machines. It manufactures 10 different copiers, ranging from low-end desktop copiers that sell for a few hundred dollars to high-volume document machines that retail for over $200,000.
Each copy machine requires a wiring bundle. Each bundle contains several hundred wires and connectors that provide circuits connecting the paper-flow units, scanner, and photoreceptor to the internal computer logic. The wire harness is plugged into various components during the assembly process. It is possible to assign each major task in this process to different employees. For example, a given employee might focus on one of the many connectors or on testing the completed wire harness. Alternatively, one individual might be assigned the task of producing and testing a completed harness.
In either case, there is a group of employees that is assigned individual tasks to produce a wire harness for a particular copier. In total, there are 10 subgroups of wire harness makers. One alternative is to place all 10 groups in one wire harness department. Another alternative is that each of these 10 subgroups can be assigned to and report to a manager responsible for a particular copier.
Bagby operates in five European countries. Currently, it has separate subunits in each country, where a country manager handles the manufacturing and marketing of all 10 copiers. The company is considering two alternatives. One would be to organize its foreign operations around products. In this case, there would be 10 international product managers with decision rights for managing the manufacturing and sale of a particular copier throughout Europe. The company also is considering a matrix organization, organized around product and country.
Which trade-offs does Bagby face in choosing among the country, product, and matrix forms of organizing its international operations
Bagby Copy Company is a worldwide producer of copy machines. It manufactures 10 different copiers, ranging from low-end desktop copiers that sell for a few hundred dollars to high-volume document machines that retail for over $200,000.
Each copy machine requires a wiring bundle. Each bundle contains several hundred wires and connectors that provide circuits connecting the paper-flow units, scanner, and photoreceptor to the internal computer logic. The wire harness is plugged into various components during the assembly process. It is possible to assign each major task in this process to different employees. For example, a given employee might focus on one of the many connectors or on testing the completed wire harness. Alternatively, one individual might be assigned the task of producing and testing a completed harness.
In either case, there is a group of employees that is assigned individual tasks to produce a wire harness for a particular copier. In total, there are 10 subgroups of wire harness makers. One alternative is to place all 10 groups in one wire harness department. Another alternative is that each of these 10 subgroups can be assigned to and report to a manager responsible for a particular copier.
Bagby operates in five European countries. Currently, it has separate subunits in each country, where a country manager handles the manufacturing and marketing of all 10 copiers. The company is considering two alternatives. One would be to organize its foreign operations around products. In this case, there would be 10 international product managers with decision rights for managing the manufacturing and sale of a particular copier throughout Europe. The company also is considering a matrix organization, organized around product and country.
Which trade-offs does Bagby face in choosing among the country, product, and matrix forms of organizing its international operations

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 19 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Discuss the circumstances under which you think functional organizations will work best.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 19 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
ANALYZING MANAGERIAL DECISIONS: Jog PCS
Jog PCS is a wireless telephone company. It sells cell phones to three customer groups: (1) business users, (2) high-volume individual users, and (3) low-volume individual users. Currently, the company is functionally organized. Primary functions include product development, marketing, sales, and customer service. The organizational chart is as follows:
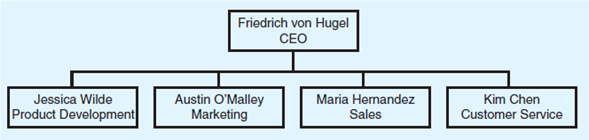
Discuss the pros and cons of the matrix proposal relative to the multidivisional proposal.
Jog PCS is a wireless telephone company. It sells cell phones to three customer groups: (1) business users, (2) high-volume individual users, and (3) low-volume individual users. Currently, the company is functionally organized. Primary functions include product development, marketing, sales, and customer service. The organizational chart is as follows:

Discuss the pros and cons of the matrix proposal relative to the multidivisional proposal.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 19 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Discuss the pluses and minuses of matrix organizations.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 19 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Why do you think many US firms have reorganized their international divisions from a country focus to matrix organizations focusing on both country and product

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 19 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
In the early 1990s, Chrysler Corporation placed nearly all decisions about the development of a new vehicle in the hands of a single, cross functional product team. In contrast, General Motors used an approach that placed a stronger emphasis on functional specialties. Small teams were established that consisted of experts from the same functional field. Each team was charged with a particular assignment that related to its area of specialization. For example, one team might have had the primary responsibility for the design of the body of the vehicle, whereas another team might have been charged with developing the drive train. The teams worked simultaneously on their specific tasks. Some individuals on these teams also served on additional cross functional teams that were charged with coordinating the development process across the functional areas. Discuss the relative advantages and disadvantages of these two approaches to product development.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 19 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Johnson Johnson ( J J) is one of the largest medical products companies in the world. In 1994, it had 33 major lines of business, with 168 operating companies in 53 countries. Decision rights in J J were quite decentralized. For instance, in 1993, the baby oil manager in Italy ran his own factory and got to decide such things as package size, pricing, and advertising. Similarly, other country managers had considerable discretionary authority for similar products sold in their countries. This type of decentralized decision making has served J J well: Its returns to shareholders have been very good. Significant changes, however, are occurring in J J's environment. In particular, trade barriers have been significantly reduced in Europe.
a. Describe the advantages of J J's decentralized decision making that have helped to explain the success of the company.
b. What organizational changes do you think J J should consider given the change in the environment Explain. Draw a new organizational chart for J J's international operations (based on your suggestions).
a. Describe the advantages of J J's decentralized decision making that have helped to explain the success of the company.
b. What organizational changes do you think J J should consider given the change in the environment Explain. Draw a new organizational chart for J J's international operations (based on your suggestions).

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 19 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
AutoMart Repair Shop is currently organized as follows: a repair manager meets with the customer to discuss the problems with the car. A repair order is completed. The mechanics specialize in particular types of repairs (for example, air conditioning, body work, etc.). Typically, a car in the shop requires work by several specialists. The manager plans the sequence of service among the specialists. The car is then serviced by each of the necessary specialists in turn. Discuss how AutoMart's Repair Shop might look if it reorganized around the process of fixing an automobile. Discuss the pluses and minuses of the current structure compared to the more product oriented structure.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 19 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Many companies are making increased use of telecommuting, which consists of employees working out of their homes, linked to the central office by telephone, computer, and fax machine. Discuss the benefits and costs of telecommuting. What types of occupations are likely to be best suited for telecommuting Explain why.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 19 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
ANALYZING MANAGERIAL DECISIONS: Jog PCS
Jog PCS is a wireless telephone company. It sells cell phones to three customer groups: (1) business users, (2) high-volume individual users, and (3) low-volume individual users. Currently, the company is functionally organized. Primary functions include product development, marketing, sales, and customer service. The organizational chart is as follows:
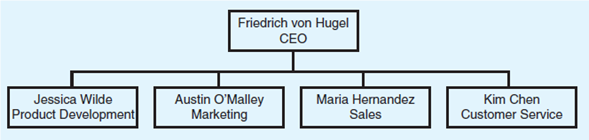
The CEO, von Hugel, is considering reorganizing the company as a multidivisional firm organized around customer type. Draw the revised organizational chart.
Jog PCS is a wireless telephone company. It sells cell phones to three customer groups: (1) business users, (2) high-volume individual users, and (3) low-volume individual users. Currently, the company is functionally organized. Primary functions include product development, marketing, sales, and customer service. The organizational chart is as follows:

The CEO, von Hugel, is considering reorganizing the company as a multidivisional firm organized around customer type. Draw the revised organizational chart.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 19 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Evaluate the following statement: "It is usually best to organize as a matrix organization. Matrix organizations combine the best of both worlds, functional excellence and product focus."

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 19 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
ANALYZING MANAGERIAL DECISIONS: Bagby Copy Company
Bagby Copy Company is a worldwide producer of copy machines. It manufactures 10 different copiers, ranging from low-end desktop copiers that sell for a few hundred dollars to high-volume document machines that retail for over $200,000.
Each copy machine requires a wiring bundle. Each bundle contains several hundred wires and connectors that provide circuits connecting the paper-flow units, scanner, and photoreceptor to the internal computer logic. The wire harness is plugged into various components during the assembly process. It is possible to assign each major task in this process to different employees. For example, a given employee might focus on one of the many connectors or on testing the completed wire harness. Alternatively, one individual might be assigned the task of producing and testing a completed harness.
In either case, there is a group of employees that is assigned individual tasks to produce a wire harness for a particular copier. In total, there are 10 subgroups of wire harness makers. One alternative is to place all 10 groups in one wire harness department. Another alternative is that each of these 10 subgroups can be assigned to and report to a manager responsible for a particular copier.
Bagby operates in five European countries. Currently, it has separate subunits in each country, where a country manager handles the manufacturing and marketing of all 10 copiers. The company is considering two alternatives. One would be to organize its foreign operations around products. In this case, there would be 10 international product managers with decision rights for managing the manufacturing and sale of a particular copier throughout Europe. The company also is considering a matrix organization, organized around product and country.
What are the trade-offs that Bagby faces in choosing between specialized and broad task assignment
Bagby Copy Company is a worldwide producer of copy machines. It manufactures 10 different copiers, ranging from low-end desktop copiers that sell for a few hundred dollars to high-volume document machines that retail for over $200,000.
Each copy machine requires a wiring bundle. Each bundle contains several hundred wires and connectors that provide circuits connecting the paper-flow units, scanner, and photoreceptor to the internal computer logic. The wire harness is plugged into various components during the assembly process. It is possible to assign each major task in this process to different employees. For example, a given employee might focus on one of the many connectors or on testing the completed wire harness. Alternatively, one individual might be assigned the task of producing and testing a completed harness.
In either case, there is a group of employees that is assigned individual tasks to produce a wire harness for a particular copier. In total, there are 10 subgroups of wire harness makers. One alternative is to place all 10 groups in one wire harness department. Another alternative is that each of these 10 subgroups can be assigned to and report to a manager responsible for a particular copier.
Bagby operates in five European countries. Currently, it has separate subunits in each country, where a country manager handles the manufacturing and marketing of all 10 copiers. The company is considering two alternatives. One would be to organize its foreign operations around products. In this case, there would be 10 international product managers with decision rights for managing the manufacturing and sale of a particular copier throughout Europe. The company also is considering a matrix organization, organized around product and country.
What are the trade-offs that Bagby faces in choosing between specialized and broad task assignment

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 19 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Stable Inc. is in a relatively stable environment in terms of technology, competition, and regulation. Variance Inc. is in a relatively unstable environment with more frequent changes in technology, competition, and regulation. Both produce the same number of products. Which firm is more likely to be functionally organized Explain why.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 19 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Discuss the costs and benefits of specialized task assignment relative to broad task assignment. What variables are likely to be particularly important in determining the optimal choice between these two alternatives

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 19 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Professors Brickley and Smith are writing two chapters for a new book. Two primary tasks are involved. First, someone has to write each of the chapters. Second, someone has to copyedit the chapters. The second step involves making sure that the writing is good, that there are no typographical errors, etc. They are considering two alternative ways to organize the work. In one case, one of the professors would write both chapters, and the other professor would copyedit both chapters. In the other case, each professor would select one chapter and be responsible for all writing and copyediting. The two professors have equal abilities and knowledge. Discuss the trade-offs between these two methods of organizing the work. What factors do you think will be most important in deciding how to organize

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 19 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



