Deck 49: Excretory Systems and Salt and Water Balance
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/14
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 49: Excretory Systems and Salt and Water Balance
1
The excretory system found in insects is composed of
A) protonephridia.
B) metanephridia.
C) Malpighian tubules.
D) a filtration kidney.
E) a secretory kidney.
A) protonephridia.
B) metanephridia.
C) Malpighian tubules.
D) a filtration kidney.
E) a secretory kidney.
Insects have a unique excretory system. Instead of filtering wastes from the body, insects secrete waste into tubes called Malpighian tubules. Salts, uric acid, and water move into the tubules. From there, they are transported to the hindgut. In the hindgut, water and salt are reabsorbed into the body. The wastes exit the body through the anus. Insects do not have a kidneys, either filtration or secretory.
Flatworms use a protonephridia system of waste removal. Fluids flow through a series of tubules that have ciliated cells at the end of each tubule. These cells move the fluid through slits where the liquid is filtered. Most of the fluid is reabsorbed, but excess water and waste products are excreted through nephridiopores.
Annelids use the metanephridial system for waste removal. In this system, the organism has a metanephridia in each body segment. Inside of the metanephridia, there are nephrostomes which act as a filter. Nephrostomes are open to the body, so fluid can flow into them. As the fluid runs through the tubules, necessary particles are reabsorbed. Meanwhile, waste products continue until they are excreted through the nephridiopores.
Therefore, the correct answer is
 Malpighian tubules.
Malpighian tubules.
Flatworms use a protonephridia system of waste removal. Fluids flow through a series of tubules that have ciliated cells at the end of each tubule. These cells move the fluid through slits where the liquid is filtered. Most of the fluid is reabsorbed, but excess water and waste products are excreted through nephridiopores.
Annelids use the metanephridial system for waste removal. In this system, the organism has a metanephridia in each body segment. Inside of the metanephridia, there are nephrostomes which act as a filter. Nephrostomes are open to the body, so fluid can flow into them. As the fluid runs through the tubules, necessary particles are reabsorbed. Meanwhile, waste products continue until they are excreted through the nephridiopores.
Therefore, the correct answer is
 Malpighian tubules.
Malpighian tubules. 2
In the mammalian kidney, filtration is driven by
A) solute concentration in the tubular filtrate.
B) solute concentration in the blood.
C) water concentration in the blood.
D) water concentration in the tubular filtrate.
E) hydrostatic pressure in the blood vessels of the glomerulus.
A) solute concentration in the tubular filtrate.
B) solute concentration in the blood.
C) water concentration in the blood.
D) water concentration in the tubular filtrate.
E) hydrostatic pressure in the blood vessels of the glomerulus.
Filtration is driven by the dilation or constriction of the afferent arteriole. When this arteriole dilates, the glomerular filtration rate increases because more blood is entering the glomerulus. This might occur when an individual is well hydrated. Thus, more urine is created.
However, in the event that an individual is dehydrated, the afferent arteriole will constrict. Thus, less blood will flow into the glomerulus decreasing the glomerular filtration rate. In other words, less urine is generated.
When the afferent arteriole is dilated, more blood goes into the glomerulus. The increased blood volume causes an increase in the hydrostatic pressure. The reverse occurs when the arteriole is constricted. The dilation and constriction of the afferent arteriole is determined by the amount of water in the blood. Therefore, the amount of water in the blood controls the increases or decreases in the hydrostatic pressure.
When the water concentration in the blood is high, the solute concentration will be lower. Likewise, when the water concentration in the blood is low, the solute concentration will be higher. However, it is the water concentration that determines the flow of blood into the afferent arteriole because the blood's volume will be determined by the water quantity, not the solute quantity.
Think of it like making powdered lemon-aide. Even if you put just enough water to dissolve all of the powder, there is still more water than powder. Otherwise, the drink would be paste and not liquid. Blood is a liquid. It has more water than solute. Therefore, it is the water driving the filtration.
Once inside the tubules, water and solutes are either reabsorbed or excreted as waste. The rates at which this occurs depends on the body's needs. Therefore, the tubular filtrate concentrations of water or solutes do not determine the overall filtration rate.
Therefore, the correct answer is
 water concentration in the blood.
water concentration in the blood.
However, in the event that an individual is dehydrated, the afferent arteriole will constrict. Thus, less blood will flow into the glomerulus decreasing the glomerular filtration rate. In other words, less urine is generated.
When the afferent arteriole is dilated, more blood goes into the glomerulus. The increased blood volume causes an increase in the hydrostatic pressure. The reverse occurs when the arteriole is constricted. The dilation and constriction of the afferent arteriole is determined by the amount of water in the blood. Therefore, the amount of water in the blood controls the increases or decreases in the hydrostatic pressure.
When the water concentration in the blood is high, the solute concentration will be lower. Likewise, when the water concentration in the blood is low, the solute concentration will be higher. However, it is the water concentration that determines the flow of blood into the afferent arteriole because the blood's volume will be determined by the water quantity, not the solute quantity.
Think of it like making powdered lemon-aide. Even if you put just enough water to dissolve all of the powder, there is still more water than powder. Otherwise, the drink would be paste and not liquid. Blood is a liquid. It has more water than solute. Therefore, it is the water driving the filtration.
Once inside the tubules, water and solutes are either reabsorbed or excreted as waste. The rates at which this occurs depends on the body's needs. Therefore, the tubular filtrate concentrations of water or solutes do not determine the overall filtration rate.
Therefore, the correct answer is
 water concentration in the blood.
water concentration in the blood. 3
In the mammalian urinary system, the urine formed in the kidneys is carried to the urinary bladder by
A) the collecting duct.
B) the renal tubule.
C) the renal pelvis.
D) the ureters.
E) the urethra.
A) the collecting duct.
B) the renal tubule.
C) the renal pelvis.
D) the ureters.
E) the urethra.
Urine is formed in the kidney. Inside of the kidney, blood is filtered through renal tubules. From the tubules, urine is sent to collecting ducts. Next, the urine is amassed in the renal pelvis. After that, the urine flows to the urinary bladder through tubes called ureters. From the bladder, the urine travels through the urethra to exit the body.
Therefore, the correct answer is
 the ureters.
the ureters.
Therefore, the correct answer is
 the ureters.
the ureters. 4
Which of the following causes an increase in sodium reabsorption in the distal tubule
A) an increase in aldosterone concentrations
B) an increase in antidiuretic hormone concentrations
C) a decrease in aldosterone concentrations
D) a decrease in antidiuretic hormone concentrations
E) none of the above
A) an increase in aldosterone concentrations
B) an increase in antidiuretic hormone concentrations
C) a decrease in aldosterone concentrations
D) a decrease in antidiuretic hormone concentrations
E) none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 14 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Aquaporins are
A) ion channels.
B) water channels.
C) receptors for aldosterone.
D) small pores in the fenestrated capillaries of the glomerulus.
E) both a and c.
A) ion channels.
B) water channels.
C) receptors for aldosterone.
D) small pores in the fenestrated capillaries of the glomerulus.
E) both a and c.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 14 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Discuss two different types of filtration mechanisms found in invertebrates.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 14 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Define nitrogenous wastes, and list four types. What are some advantages and disadvantages of excreting different types of nitrogenous wastes

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 14 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
A change in salt (electrolyte) concentrations in the body may result in
A) altered membrane potentials that disrupt normal cell function.
B) disruption of certain biochemical processes that occur in the cell.
C) cell death.
D) a and b only.
E) a, b, and c.
A) altered membrane potentials that disrupt normal cell function.
B) disruption of certain biochemical processes that occur in the cell.
C) cell death.
D) a and b only.
E) a, b, and c.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 14 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Briefly discuss the parts and functions of the nephron in the mammalian kidney.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 14 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Nitrogenous wastes are the by-products of the metabolism of
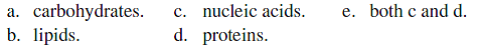
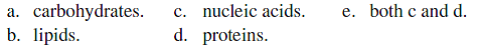

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 14 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
List and define the three processes involved in urine production. Do all three processes occur for every substance that enters an excretory organ such as the kidney

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 14 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Marine fishes avoid water balance problems by
A) producing a large volume of dilute urine.
B) not drinking water.
C) having gill epithelial cells that recapture lost ions from the environment.
D) producing small volumes of concentrated urine.
E) doing a, b, and c.
A) producing a large volume of dilute urine.
B) not drinking water.
C) having gill epithelial cells that recapture lost ions from the environment.
D) producing small volumes of concentrated urine.
E) doing a, b, and c.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 14 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Metabolic water is water
A) necessary to stimulate the process of cellular respiration.
B) found within cells.
C) produced during cellular respiration.
D) produced by sweat glands.
E) used by cells during the uptake of glucose.
A) necessary to stimulate the process of cellular respiration.
B) found within cells.
C) produced during cellular respiration.
D) produced by sweat glands.
E) used by cells during the uptake of glucose.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 14 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Animals that maintain a constant water balance despite changes in water concentrations in the environment are
A) osmoregulators.
B) osmoconformers.
A) osmoregulators.
B) osmoconformers.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 14 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



