Deck 14: Functions of Several Variables
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/92
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 14: Functions of Several Variables
1
Find the standard equation of the sphere whose center is and whose radius is 4.
A)
B)
C)
D)
E)
A)
B)
C)
D)
E)
2
Find if the midpoint of the line segment joining the two points and is .
A)
B)
C)
D)
E)
A)
B)
C)
D)
E)
3
Sketch the trace of the intersection of plane y = 4 with the sphere: .
A)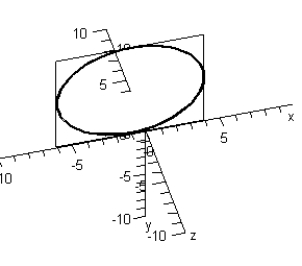
B)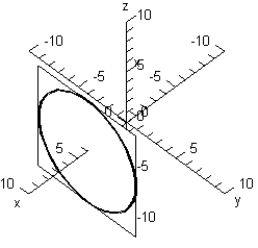
C)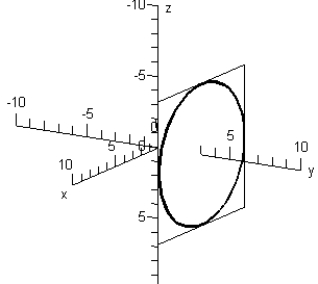
D)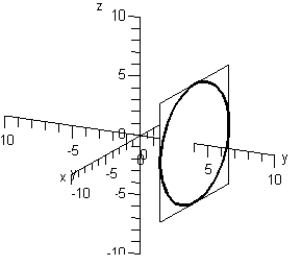
E)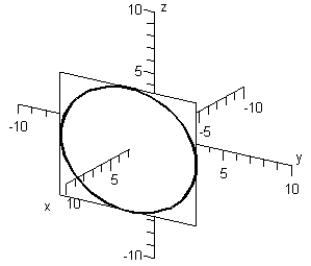
A)

B)

C)

D)

E)


4
Describe the trace of the surface given by the function below in the xz-plane.
A)circle
B)parabola
C)line
D)ellipse
E)hyperbola
A)circle
B)parabola
C)line
D)ellipse
E)hyperbola

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Find the center and radius of the sphere whose equation is . Round your answer to two decimal places, where applicable.
A)center: ; radius: 0.71
B)center: ; radius: 0.71
C)center: ; radius: 0.50
D)center: ; radius: 0.71
E)center: ; radius: 0.50
A)center: ; radius: 0.71
B)center: ; radius: 0.71
C)center: ; radius: 0.50
D)center: ; radius: 0.71
E)center: ; radius: 0.50

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Identify the quadric surface.
A)The graph is hyperboloid of two sheets.
B)The graph is an ellipsoid.
C)The graph is an elliptic cone.
D)The graph is an elliptic paraboloid.
E)The graph is a hyperboloid of one sheet.
A)The graph is hyperboloid of two sheets.
B)The graph is an ellipsoid.
C)The graph is an elliptic cone.
D)The graph is an elliptic paraboloid.
E)The graph is a hyperboloid of one sheet.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Sketch the yz-trace of the equation:
A)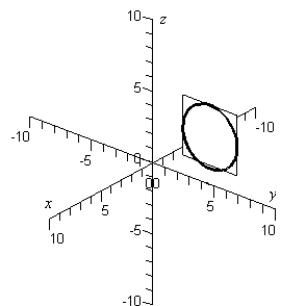
B)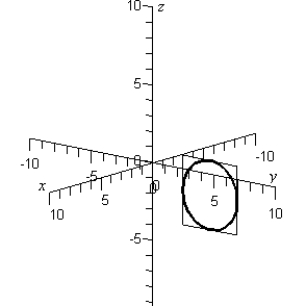
C)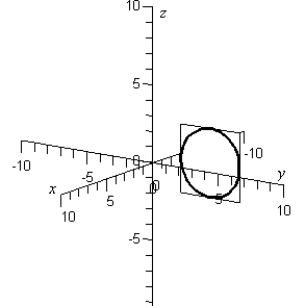
D)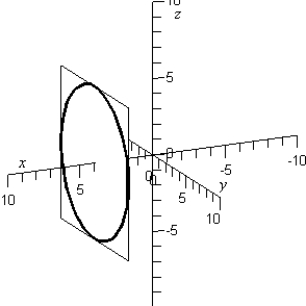
E)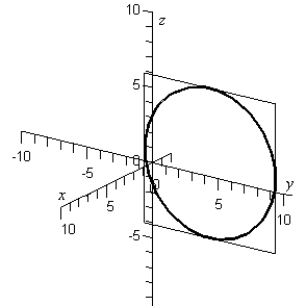
A)

B)

C)

D)

E)


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Evaluate the function at the given values of the independent variables.
A)
B)
C)
D)
E)
A)
B)
C)
D)
E)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Find the coordinates of the point that is located six units behind of the yz-plane, six units to the left of the xz-plane, and seven units below of the xy-plane.
A)
B)
C)
D)
E)
A)
B)
C)
D)
E)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Use the function to find
A)
B)
C)
D)
E)
A)
B)
C)
D)
E)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Describe the trace of the surface given by the function below in the xy-plane.
A)hyperbola
B)parabola
C)ellipse
D)line
E)circle
A)hyperbola
B)parabola
C)ellipse
D)line
E)circle

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Find the lengths of the sides of the triangle with the given vertices, and determine whether the triangle is a right triangle, an isosceles triangle, or neither.
A) ; obtuse triangle
B) ; right triangle
C) ; right triangle
D) ; acute triangle
E) ; acute triangle
A) ; obtuse triangle
B) ; right triangle
C) ; right triangle
D) ; acute triangle
E) ; acute triangle

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Find the intercepts of the plane given by .
A)The -intercept is .The -intercept is .
B)The -intercept is .The -intercept is .
C)The -intercept is .The -intercept is .
D)The -intercept is .The -intercept is .
E)The -intercept is .The -intercept is .
A)The -intercept is .The -intercept is .
B)The -intercept is .The -intercept is .
C)The -intercept is .The -intercept is .
D)The -intercept is .The -intercept is .
E)The -intercept is .The -intercept is .

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Identify the quadric surface.
A)The graph is an elliptic paraboloid.
B)The graph is an elliptic cone.
C)The graph is a hyperboloid of two sheet.
D)The graph is hyperboloid of one sheet.
E)The graph is an ellipsoid.
A)The graph is an elliptic paraboloid.
B)The graph is an elliptic cone.
C)The graph is a hyperboloid of two sheet.
D)The graph is hyperboloid of one sheet.
E)The graph is an ellipsoid.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Find the the distance between the two points and .
A)1 units
B)19 units
C) units
D)3 units
E)7 units
A)1 units
B)19 units
C) units
D)3 units
E)7 units

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Find the center and radius of the sphere.
A)Center: Radius:
B)Center: Radius:
C)Center: Radius:
D)Center: Radius:
E)Center: Radius:
A)Center: Radius:
B)Center: Radius:
C)Center: Radius:
D)Center: Radius:
E)Center: Radius:

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
The two planes and are parallel.
A)true
B)false
A)true
B)false

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Find the equation of the sphere that has the points and as end points of a diameter.
A)
B)
C)
D)
E)
A)
B)
C)
D)
E)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
The two planes and are perpendicular.
A)false
B)true
A)false
B)true

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Because of the forces caused by its rotation, a planet is actually an oblate ellipsoid rather than a sphere. The equatorial radius is 3961 miles and the polar radius is 3957 miles. Find an equation of the ellipsoid. Assume that the center of a planet is at the origin and the xy- trace corresponds to the equator.
A)
B)
C)
D)
E)
A)
B)
C)
D)
E)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Evaluate the function at
A)
B)
C)
D)
E)
A)
B)
C)
D)
E)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Evaluate and for the function at the point .
A) 330 and -132
B) 360 and -104
C) 330 and -104
D) 546 and 344
E) 330 and 112
A) 330 and -132
B) 360 and -104
C) 330 and -104
D) 546 and 344
E) 330 and 112

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Use the function to find
A)
B)
C)
D)
E)
A)
B)
C)
D)
E)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Find the first partial derivatives with respect to x, y, and z.
A)
B)
C)
D)
E)
A)
B)
C)
D)
E)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Find the domain and range of the function.
A)Domain: all point such that Range:
B)Domain: all point such that Range:
Range:
C)Domain: all point such that Range:
D)Domain: all point such that Range:
E)Domain: all point such that Range:
A)Domain: all point such that Range:
B)Domain: all point such that
 Range:
Range: C)Domain: all point such that Range:
D)Domain: all point such that Range:
E)Domain: all point such that Range:

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Find the slopes of the surface in the x- and y- directions at the point .
A)slope in x-direction: 29slope in y-direction: 17
B)slope in x-direction: 2slope in y-direction: 18
C)slope in x-direction: 17slope in y-direction: 29
D)slope in x-direction: 20slope in y-direction: 20
E)slope in x-direction: 18slope in y-direction: 2
A)slope in x-direction: 29slope in y-direction: 17
B)slope in x-direction: 2slope in y-direction: 18
C)slope in x-direction: 17slope in y-direction: 29
D)slope in x-direction: 20slope in y-direction: 20
E)slope in x-direction: 18slope in y-direction: 2

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
The utility function is a measure of utility (or satisfaction) derived by a person from the consumption of two products x and y. Suppose the utility function is . Determine the marginal utility of product x.
A)
B)
C)
D)
E)
A)
B)
C)
D)
E)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
For , find all values of x and y such that and simultaneously.
A)
B)
C)(0,0)
D)Both B and C
E)Both A and B
A)
B)
C)(0,0)
D)Both B and C
E)Both A and B

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Describe the level curves for the function for the c-values given by . 
A)
B)
C)
D)
E)

A)
B)
C)
D)
E)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Test for relative extrema and saddle points.
A)saddle point at
B)saddle point at
C)saddle point at
D)relative minimum at
E)relative minimum at
A)saddle point at
B)saddle point at
C)saddle point at
D)relative minimum at
E)relative minimum at

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
A company manufactures two types of wood-burning stoves: a freestanding model and a fireplace-insert model. The cost function for producing x freestanding and y fireplace-insert stoves is . Find the marginal costs ( and ) when and . Round your answers to two decimal places.
A)
B)
C)
D)
E)
A)
B)
C)
D)
E)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Describe the level curves of the function. Sketch the level curves for the given c-values. , c = 0, 2, 4, 6
A)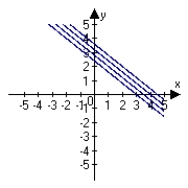
B)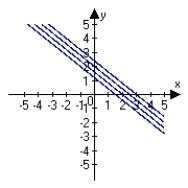
C)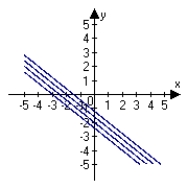
D)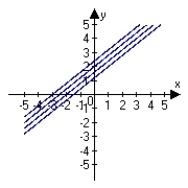
E)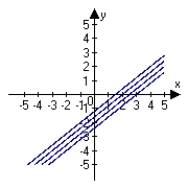
A)

B)

C)

D)

E)


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
The value of an investment of $4,000 after t years in an account for which the interest rate 100r% is compounded continuously is given by the function dollars. Write the partial derivative
A)
B)
C)
D)
E)
A)
B)
C)
D)
E)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
If find and
A)
B)
C)
D)
E)
A)
B)
C)
D)
E)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
If find
A)
B)
C)
D)
E)
A)
B)
C)
D)
E)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Sketch the level curves for the function below for the given values .
A)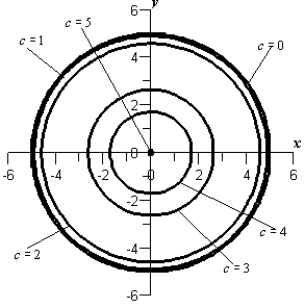
B)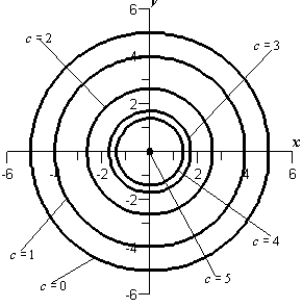
C)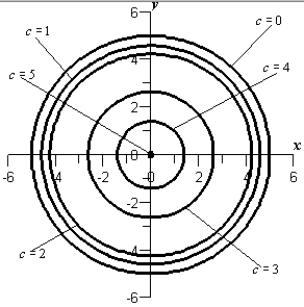
D)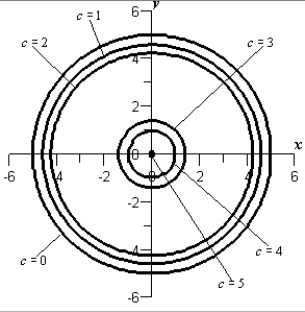
E)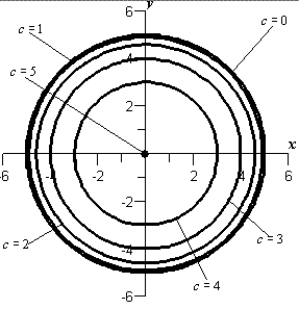
A)

B)

C)

D)

E)


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Describe the domain and range of the function.
A)domain: The disk range: The interval (0,7)
B)domain: The disk range: The interval [0,7]
C)domain: The disk range: The interval [0,7)
D)domain: The disk range: The interval [0,7]
E)domain: The disk range: The interval [0,7)
A)domain: The disk range: The interval (0,7)
B)domain: The disk range: The interval [0,7]
C)domain: The disk range: The interval [0,7)
D)domain: The disk range: The interval [0,7]
E)domain: The disk range: The interval [0,7)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Evaluate and for the function at the point . Round your answer to two decimal places.
A) 5.01 and 0.63
B) 4.51 and 0.63
C) 3.13 and 6.26
D) 5.01 and 0.13
E) 3.13 and 6.26.
A) 5.01 and 0.63
B) 4.51 and 0.63
C) 3.13 and 6.26
D) 5.01 and 0.13
E) 3.13 and 6.26.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
A manufacturer estimates the Cobb-Douglas production function to be given by . Estimate the production levels when and .
A)135,540 units
B)122,560 units
C)131,601 units
D)145,330 units
E)112,745 units
A)135,540 units
B)122,560 units
C)131,601 units
D)145,330 units
E)112,745 units

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Find the four second partial derivatives. Observe that the second mixed partials are equal.
A)
B)
C)
D)
E)
A)
B)
C)
D)
E)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
A company manufactures two types of sneakers: running shoes and basketball shoes. The total revenue from x1 units of running shoes and y1 units of basketball shoes is: , where x1 and x2 are in thousands of units. Find x1 and x2 so as to maximize the revenue.
A)
B)
C)
D)
E)
A)
B)
C)
D)
E)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Examine the function for relative extrema and saddle points.
A)saddle point: ; relative minimum:
B)relative minimum: ; relative maximum:
C)saddle points: ,
D)saddle point: ; relative minimum:
E)relative minimum: ; relative maximum:
A)saddle point: ; relative minimum:
B)relative minimum: ; relative maximum:
C)saddle points: ,
D)saddle point: ; relative minimum:
E)relative minimum: ; relative maximum:

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
Use Lagrange multipliers to find the minimum distance from the circle to the point Round your answer to the nearest tenth.
A)20.4
B)132.0
C)418.1
D)6.5
E)41.6
A)20.4
B)132.0
C)418.1
D)6.5
E)41.6

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
Examine the function given below for relative extrema and saddle points.
A)The function has a saddle point at .
B)The function has a relative maximum at .
C)The function has a relative minimum at .
D)The function has a saddle point at .
E)The function has a relative maximum at .
A)The function has a saddle point at .
B)The function has a relative maximum at .
C)The function has a relative minimum at .
D)The function has a saddle point at .
E)The function has a relative maximum at .

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Use Lagrange multipliers to find the given extremum. In each case, assume that and are positive. Maximize Constraint
A)
B)
C)
D)
E)
A)
B)
C)
D)
E)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
Use Lagrange multipliers to find the given extremum. Assume that and are positive. Minimize Constraint
A)
B)
C)
D)
E)
A)
B)
C)
D)
E)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
Find three positive numbers x, y, and z whose sum is 24 and the sum of the squares is a maximum.
A)x = y = z = 8
B)x = 4, y = 4, z = 16
C)x = 6, y = 6, z = 12
D)x = 3.2, y = 4.8, z = 8
E)x = 1.6, y = 9.6, z = 12.8
A)x = y = z = 8
B)x = 4, y = 4, z = 16
C)x = 6, y = 6, z = 12
D)x = 3.2, y = 4.8, z = 8
E)x = 1.6, y = 9.6, z = 12.8

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
A rectangular box is resting on the -plane with one vertex at the origin. The opposite lies in the plane Find the dimensions that maximize the volume. (Hint: Maximize subject to the constraint ).
A)15 units 12 units 5 units
B)11 units 9 units 5 units
C)10 units 9 units 6 units
D)15 units 10 units 6 units
E)12 units 11 units 7 units
A)15 units 12 units 5 units
B)11 units 9 units 5 units
C)10 units 9 units 6 units
D)15 units 10 units 6 units
E)12 units 11 units 7 units

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
Examine the function given below for relative extrema and saddle points.
A)The function has a relative minimum at .
B)The function has a relative maximum at
C)The function has a saddle point at .
D)The function has a saddle point at .
E)The function has a saddle point at
A)The function has a relative minimum at .
B)The function has a relative maximum at
C)The function has a saddle point at .
D)The function has a saddle point at .
E)The function has a saddle point at

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
Find three positive numbers x, y, and z whose sum is 33 and product is a maximum.
A)x = 5.5, y = 5.5, z = 22
B)x = y = z = 11
C)x = 8.25, y = 8.25, z = 16.5
D)x = 4.4, y = 6.6, z = 11
E)x = 2.2, y = 13.2, z = 17.6
A)x = 5.5, y = 5.5, z = 22
B)x = y = z = 11
C)x = 8.25, y = 8.25, z = 16.5
D)x = 4.4, y = 6.6, z = 11
E)x = 2.2, y = 13.2, z = 17.6

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
Examine the function for relative extrema.
A)saddle point at
B)relative minimum at
C)saddle point at
D)relative maximum at
E)saddle point at
A)saddle point at
B)relative minimum at
C)saddle point at
D)relative maximum at
E)saddle point at

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
The sum of the length (denote by z) and the girth (perimeter of a cross section) of packages carried by a delivery service cannot exceed 60 inches. Find the dimensions of the rectangular package of largest volume that may be sent.
A)x = 7.5, y = 7.5, z = 20
B)x = 5, y = 5, z = 40
C)x = 10 , y = 10 , z = 20
D)x = 4, y = 6, z = 40
E)x = 2, y = 12, z = 32
A)x = 7.5, y = 7.5, z = 20
B)x = 5, y = 5, z = 40
C)x = 10 , y = 10 , z = 20
D)x = 4, y = 6, z = 40
E)x = 2, y = 12, z = 32

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
Find the critical points of the function , and, from the form of the function, determine whether a relative maximum or a relative minimum occurs at each point.
A)relative minimum at
B)relative maximum at
C)relative minimum at
D)relative maximum at
E)no relative extrema
A)relative minimum at
B)relative maximum at
C)relative minimum at
D)relative maximum at
E)no relative extrema

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
A microbiologist must prepare a culture medium in which to grow a certain type of bacteria. The percent of salt contained in this medium is given by where and are the nutrient solutions to be mixed in the medium. For the bacteria to grow, the medium must be 13% salt. Nutrient solutions and cost $1, $2, and $3 per liter, respectively. How much of each nutrient solution should be used to minimize the cost of the culture medium?
A)
B)
C)
D)
E)
A)
B)
C)
D)
E)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
Determine whether there is a relative maximum, a relative minimum, a saddle point, or insufficient information to determine the nature of the function at the critical point . Given:
A) at
B) at
C) at
D) at
A) at
B) at
C) at
D) at

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
Find the critical points of the function , and, from the form of the function, determine whether a relative maximum or a relative minimum occurs at each point.
A)relative minima at , , , where and are arbitrary real numbers
B)relative maxima at , , , where and are arbitrary real numbers
C)relative minimum at
D)relative maximum at
E)no relative extrema
A)relative minima at , , , where and are arbitrary real numbers
B)relative maxima at , , , where and are arbitrary real numbers
C)relative minimum at
D)relative maximum at
E)no relative extrema

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
Examine the function for relative extrema.
A)relative at
B)relative at
C)relative at
D)relative at
E)no relative extrema
A)relative at
B)relative at
C)relative at
D)relative at
E)no relative extrema

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
Use Lagrange multipliers to minimize the function subject to the following constraint. Assume that x, y, and z are positive.
A)49
B)147
C)98
D)294
E)441
A)49
B)147
C)98
D)294
E)441

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
Use Lagrange multipliers to maximize the function subject to the following constraint: Assume that x, y, and z are positive.
A)
B)
C)
D)
E)no absolute maximum
A)
B)
C)
D)
E)no absolute maximum

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
Use Lagrange multipliers to find the given extremum. In each case, assume that and are positive. Maximize Constraints
A)
B)
C)
D)
E)
A)
B)
C)
D)
E)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
Evaluate the double integral .
A)
B)
C)
D)
E)
A)
B)
C)
D)
E)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
Determine whether the statement is true or false. If it is false, explain why or give an example that shows it is false. Data that are modeled by have a negative correlation.
A)True
B)False; The data modeled by have a positive correlation.
A)True
B)False; The data modeled by have a positive correlation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
Evaluate the double integral . Round your answer to two decimal places, where applicable.
A)-8.83
B)11.17
C)2.00
D)1.17
E)5.00
A)-8.83
B)11.17
C)2.00
D)1.17
E)5.00

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
A store manager wants to know the demand y for an energy bar as a function of price x. The daily sales for three different prices of the energy bar are shown in the table. Price, x
$ 1.02
$ 1.23
$ 1.54
Demand, y
410
365
280
(i) Use the regression capabilities of a graphing utility to find the least squares regression line for the data.
(ii) Use the model to estimate the demand when the price is $1.38.
A)(i) ; (ii)348.708392
B)(i) ; (ii)-416.059787
C)(i) ; (ii)505.287381
D)(i) ; (ii)-416.059787
E)none of the above
$ 1.02
$ 1.23
$ 1.54
Demand, y
410
365
280
(i) Use the regression capabilities of a graphing utility to find the least squares regression line for the data.
(ii) Use the model to estimate the demand when the price is $1.38.
A)(i) ; (ii)348.708392
B)(i) ; (ii)-416.059787
C)(i) ; (ii)505.287381
D)(i) ; (ii)-416.059787
E)none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
Evaluate the double integral .
A)134.00
B)144.00
C)154.00
D)42.00
E)24.00
A)134.00
B)144.00
C)154.00
D)42.00
E)24.00

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
Use the regression capabilities of a graphing utility or a spreadsheet to find the least squares regression line for the points . Round your answer to three decimal places.
A)
B)
C)
D)
E)
A)
B)
C)
D)
E)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
Sketch the region whose area is given by the following double integral.
A)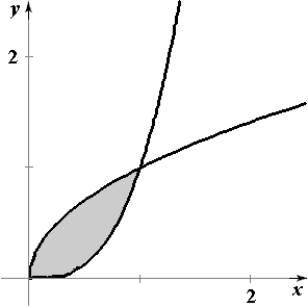
B)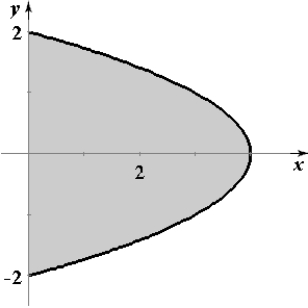
C)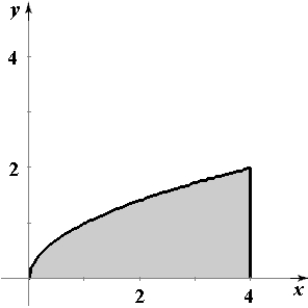
D)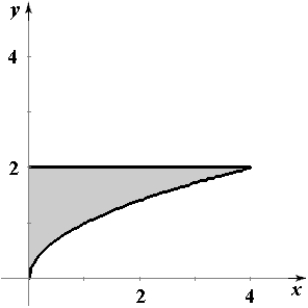
E)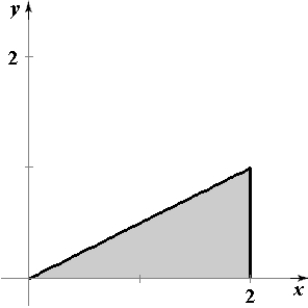
A)

B)

C)

D)

E)


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
A manufacturer has an order for 1100 units of fine paper that can be produced at two locations. Let and be the numbers of units produced at the two plants. Find the number of units that should be produced at each plant to minimize the cost if the cost function is given by .
A) units and units
B) units and units
C) units and units
D) units and units
E) units and units
A) units and units
B) units and units
C) units and units
D) units and units
E) units and units

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
Use the regression capabilities of a graphing utility or a spreadsheet to find the least squares regression line for the given points.
A)
B)
C)
D)
E)
A)
B)
C)
D)
E)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
Evaluate the double integral .
A)
B)
C)
D)
E)
A)
B)
C)
D)
E)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
Find the least squares regression line for the points (1,0) , (6,6) , (11,12).
A)
B)
C)
D)
E)none of the above
A)
B)
C)
D)
E)none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
Evaluate the following integral.
A)
B)
C)
D)
E)none of the above
A)
B)
C)
D)
E)none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
An agronomist used four test plots to determine the relationship between the wheat yield (in bushels per acre) and the amount of fertilizer (in pounds per acre). The results are shown in the table. (a) Use the regression capabilities of a graphing utility or a spreadsheet to find the least squares regression line for the data. (b) Estimate the yield for a fertilizer application of 160 pounds per acre.
A)
B)
C)
D)
E)
A)
B)
C)
D)
E)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
Evaluate the double integral . Round your answer to two decimal places, where applicable.
A)7.33
B)14.33
C)16.33
D)15.33
E)14.83
A)7.33
B)14.33
C)16.33
D)15.33
E)14.83

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
Find the sum of the squared errors for the linear model and the quadratic model using the given points.
A) ;
B) ;
C) ;
D) ;
E) ;
A) ;
B) ;
C) ;
D) ;
E) ;

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
Determine whether the statement is true or false. If it is false, explain why or give an example that shows it is false. A linear regression model with a positive correlation will have a slope that is greater than 0.
A)True
B)False
A)True
B)False

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
Determine whether the statement is true or false. If it is false, explain why or give an example that shows it is false. When the correlation coefficient is , the model is a good fit.
A)False
B)True
A)False
B)True

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
A rancher plans to use an existing stone wall and the side of a barn as a boundary for two adjacent rectangular corrals. Fencing for the perimeter costs 15 per foot. To separate the corrals, a fence that costs 6 per foot will divide the region. The total area of the two corrals is to be square feet. Use Lagrange multipliers to find the dimensions that will minimize the cost of the fencing. 
A)dimensions: feet by feet
B)dimensions: feet by feet
C)dimensions: feet by feet
D)dimensions: feet by feet
E)dimensions: feet by feet

A)dimensions: feet by feet
B)dimensions: feet by feet
C)dimensions: feet by feet
D)dimensions: feet by feet
E)dimensions: feet by feet

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
Use a double integral to find the area of the region bounded by the graphs of and .
A)
B)
C)
D)
E)
A)
B)
C)
D)
E)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
Find the least squares regression line for the given points. Then plot the points and sketch the regression line.
A)
B)
C)
D)
E)
A)
B)
C)
D)
E)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



