Deck 6: Income or Loss From a Business
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/103
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 6: Income or Loss From a Business
1
What are the major types of income that make up Net Income For Tax Purposes?
The major types of income that make up Net Income For Tax Purposes are:
• Employment Income
• Business Income
• Property Income
• Capital Gains.
• Employment Income
• Business Income
• Property Income
• Capital Gains.
2
The Income Tax Act limits the deductions associated with the ownership of company cars. Describe these limitations.
There are two limits. CCA is limited to a maximum capital cost of $30,000. In addition, if the automobile is financed, interest costs are limited to $10 per day.
3
List and briefly describe three of the exceptions to the rule that only 50 percent of the cost of business meals and entertainment can be deducted in the determination of Net Income For Tax Purposes.
The text describes the following exceptions, any three of which would satisfy the requirements of the question:
• Long-haul truck drivers can deduct more than 80 percent of these costs.
• The costs incurred by hotels and restaurants in providing meals and entertainment to their clients are fully deductible.
• Meals and entertainment expenses relating to a fund raising event for a registered charity are fully deductible.
• Where the taxpayer is compensated by someone else for the cost of food, beverages, or entertainment, the amounts will be fully deductible against this compensation.
• When amounts are paid for meals or entertainment for employees and, either the payments create a taxable benefit for the employee, or the amounts do not create a taxable benefit because they are being provided at a remote work location, the amounts are fully deductible to the employer.
• When amounts are incurred by an employer for food, beverages, or entertainment that is generally available to all individuals employed by the taxpayer, the amounts are fully deductible. (Maximum of six such special events per year.)
• Meals included in the price of airline, bus, and rail tickets are viewed by the government as immaterial. The food component of the ticket price is deemed to be nil.
• Long-haul truck drivers can deduct more than 80 percent of these costs.
• The costs incurred by hotels and restaurants in providing meals and entertainment to their clients are fully deductible.
• Meals and entertainment expenses relating to a fund raising event for a registered charity are fully deductible.
• Where the taxpayer is compensated by someone else for the cost of food, beverages, or entertainment, the amounts will be fully deductible against this compensation.
• When amounts are paid for meals or entertainment for employees and, either the payments create a taxable benefit for the employee, or the amounts do not create a taxable benefit because they are being provided at a remote work location, the amounts are fully deductible to the employer.
• When amounts are incurred by an employer for food, beverages, or entertainment that is generally available to all individuals employed by the taxpayer, the amounts are fully deductible. (Maximum of six such special events per year.)
• Meals included in the price of airline, bus, and rail tickets are viewed by the government as immaterial. The food component of the ticket price is deemed to be nil.
4
Describe the restrictions that the Income Tax Act places on the deductibility of costs incurred to place advertising in foreign media.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 103 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
While business income and property income are covered in the same subdivision of the Income Tax Act, there are differences in the tax treatment of these two types of income. Briefly describe two of these differences.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 103 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Both employees and self-employed individuals can deduct the costs associated with maintaining a home office. Compare the items that can be deducted by an employee with those that can be deducted by a self-employed individual.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 103 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Both GAAP and income tax legislation require the allocation of the cost of depreciable assets to income over several years. Briefly describe how the accounting procedures used for this process differ from those required for income tax purposes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 103 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
The ability to use a reserve for unpaid amounts gives results that are similar to those that would result from using the cash basis of revenue recognition. However, there are constraints on the use of this reserve that prevent achieving results that are identical to those that result from using cash based revenue recognition. Describe these constraints.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 103 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Section 18 of the Income Tax Act lists a number of general limitations on the deductions that can be made in the determination of net business income. List four of these limitations.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 103 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
What is a reserve? Explain briefly the reserve system that is used in determining net business income.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 103 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
List three reserves that can be deducted in the determination of net business income.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 103 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
For tax purposes, the sale of inventories is treated differently than the sale of non-depreciable capital assets. Briefly describe the different treatments given to these two types of sales.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 103 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Describe the tax rules that apply to interest and property taxes on land.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 103 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Describe the alternative methods of inventory valuation that can be used for tax purposes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 103 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
ITA 67 indicates that no deduction is available for an outlay or expense, except to the extent that the outlay or expense was reasonable in the circumstances. Provide an example of an outlay or expense that would be disallowed by this provision.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 103 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Assets can be acquired for use in a business, for resale by a business, or as investments. For each of these classifications, indicate (1)how the income earned will be classified, and (2)how the income resulting from the sale of the asset would be classified.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 103 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Why is the distinction between capital gains and business income important?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 103 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
While there are many similarities between business income (for tax purposes)and accounting income as determined under GAAP, there are a number of differences. Indicate four such differences.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 103 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
List four criteria that can be used in distinguishing between business income and capital gains. Explanations are not required.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 103 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Compare the procedures used to determine bad debt expense under GAAP, with those used to determine the annual deduction for bad debts under the Income Tax Act.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 103 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
During 2020, a depreciable capital asset with a capital cost of $100,000 and a January 1 UCC balance of $79,400, is sold for $103,000. In the accounting records, the asset had a net book value of $83,400. What are the tax consequences of this sale?
A)Business income of $23,600.
B)A capital gain of $1,500.
C)A capital gain of $3,000 and business income of $20,600.
D)A capital gain of $23,600.
A)Business income of $23,600.
B)A capital gain of $1,500.
C)A capital gain of $3,000 and business income of $20,600.
D)A capital gain of $23,600.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 103 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
When a business ceases to operate and its inventories are disposed of, a gain on the inventories will be treated as a capital gain unless an election is made by the selling taxpayer.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 103 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Which of the following would be considered by the CRA to be business income rather than property income or capital gains?
A)Profits from the sale of assets that were used to produce business income
B)Profit from the sale of assets that were used to produce property income
C)Profit from the sale of inventory items
D)Both A and C
A)Profits from the sale of assets that were used to produce business income
B)Profit from the sale of assets that were used to produce property income
C)Profit from the sale of inventory items
D)Both A and C

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 103 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
A self-employed individual cannot deduct CCA on a home office in his principal residence unless it is used exclusively for income producing purposes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 103 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
In situations where a business ceases to operate and its assets are being sold, it is important that the parties to the transaction make the ITA 22 election with respect to the accounts receivable that are being transferred. Explain this importance.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 103 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
If an asset has been held for a considerable period of time, any gain on its disposition will be treated as business income.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 103 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
When property acquired for personal use is sold for more than its cost, there will be a taxable capital gain.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 103 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
The amounts charged to income for bad debts on accounts receivable will generally be the same for both tax and accounting purposes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 103 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Landscaping costs can be deducted in the determination of net business income, even if they involve items that would normally be considered capital assets.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 103 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
For the hobby farmer, deductible farming losses for a year are restricted to $2,500, plus one-half of the next $30,000.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 103 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
When an enterprise issues debt obligations, they may be sold at a discount from their maturity value. For accounting purposes, this discount is amortized to income as an addition to interest expense. What is the required treatment of such discount amounts for income tax purposes?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 103 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
In determining whether an individual can deduct farm losses against other sources of income, taxation authorities divide farmers into various categories. Describe these categories and indicate how the farm losses for each category are treated in the year they occur.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 103 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
If a reserve is deducted for accounting purposes, it can also be deducted for tax purposes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 103 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
The tax rules for determining business income are identical to those used for determining property income.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 103 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Compare the accounting treatment for estimated warranty costs with the required treatment for income tax purposes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 103 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
The deduction of CCA cannot be used to create or increase a net business loss.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 103 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
When a business makes payments that are unreasonable in the circumstances, they cannot be deducted in the calculation of either accounting Net Income or net business income.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 103 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
For tax purposes, inventories can be valued at aggregate market, which can mean replacement cost or net realizable value.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 103 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
When a business ceases to operate and its accounts receivable are disposed of with the other business assets, any loss on the receivables will be treated as a capital loss unless a joint election is made by the purchaser and seller.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 103 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Differences between business income for tax purposes and business income as determined under GAAP can be either permanent or temporary.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 103 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
With respect to determining net business income for tax purposes, which of the following statements is NOT correct?
A)A reserve that is deducted in the current taxation year, must be added back to income in the following taxation year.
B)Bad debts written off in the previous year for tax purposes that are recovered in the current year must be added to net business income for tax purposes for the current year.
C)Amounts received for goods to be delivered in the future must be included in the determination of net business income for tax purposes.
D)As long as some part of the proceeds for goods sold is not collectible until future periods, a reserve for uncollected amounts can be deducted.
A)A reserve that is deducted in the current taxation year, must be added back to income in the following taxation year.
B)Bad debts written off in the previous year for tax purposes that are recovered in the current year must be added to net business income for tax purposes for the current year.
C)Amounts received for goods to be delivered in the future must be included in the determination of net business income for tax purposes.
D)As long as some part of the proceeds for goods sold is not collectible until future periods, a reserve for uncollected amounts can be deducted.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 103 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Jean Brochet uses an automobile in his unincorporated business. It cost $53,000 in 2019, with maximum CCA being deducted in that year. The purchase was financed with a bank loan of $37,000. For 2020, the interest on this loan was $4,440. The automobile is used exclusively for business purposes, with the 2020 operating costs totaling $7,500. In determining his 2020 business income, his maximum automobile related deduction will be:
A)$16,100.
B)$16,890.
C)$24,665.
D)$19,875.
A)$16,100.
B)$16,890.
C)$24,665.
D)$19,875.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 103 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
Marvin purchased a large piece of land 5 years ago when a highway bypass was rumoured to have an exit being built nearby. He had planned to subdivide the land into building lots within 5 years, but has done no work on the land yet. He has rented the land each summer over the Labour Day weekend for $500. A local non-profit organization holds a huge neighbourhood garage sale on that weekend. A heart attack has convinced Marvin to slow down. As a result, he has advertised the land for sale online and an interested buyer is offering to purchase it at a price that would give him a large gain. That gain would be taxed as:
A)property income.
B)business income.
C)a capital gain.
D)a taxable capital gain.
A)property income.
B)business income.
C)a capital gain.
D)a taxable capital gain.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 103 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
In 2019, Marg's Antiques deducted a reserve for doubtful debts of $12,000. During 2020, she had actual write-offs of $12,500 and recoveries of previously written off debts of $1,500. At the end of 2020, she deducted a reserve for doubtful debts of $14,000. Marg's 2020 net deduction for bad debts would be:
A)$12,500.
B)$11,000.
C)$13,000.
D)$14,000.
A)$12,500.
B)$11,000.
C)$13,000.
D)$14,000.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 103 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Omar owns and manages an unincorporated business. During 2020, a car which he leases was driven 10,000 kilometers for business purposes and 12,000 kilometers for Omar's personal use. The total vehicle related expenses for 2020 were as follows:  For tax purposes, there is a:
For tax purposes, there is a:
A)business deduction of $4,318 and a taxable benefit of $0.
B)business deduction of $5,182 and a taxable benefit of $0.
C)business deduction of $9,500 and taxable benefit of $7,600.
D)business deduction of $9,500 and taxable benefit of $8,160.
 For tax purposes, there is a:
For tax purposes, there is a:A)business deduction of $4,318 and a taxable benefit of $0.
B)business deduction of $5,182 and a taxable benefit of $0.
C)business deduction of $9,500 and taxable benefit of $7,600.
D)business deduction of $9,500 and taxable benefit of $8,160.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 103 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
Which of the following items could NOT be deducted during the current year in the determination of net business income for tax purposes?
A)Premiums on a life insurance policy on a business owner's life that is required by the bank that has extended a loan to the business.
B)The cost of advertising on a U.S. television station that is attempting to attract customers in Florida.
C)Fees paid to the business owner's wife for keeping the accounting records of the business.
D)Parking fines incurred by delivery vehicles making deliveries in congested areas.
A)Premiums on a life insurance policy on a business owner's life that is required by the bank that has extended a loan to the business.
B)The cost of advertising on a U.S. television station that is attempting to attract customers in Florida.
C)Fees paid to the business owner's wife for keeping the accounting records of the business.
D)Parking fines incurred by delivery vehicles making deliveries in congested areas.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 103 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
Ed's Appliances Ltd (Ed's)sold a furnace to a customer in October, 2020 for $10,000. The mark-up on the $5,000 cost of the furnace was 100 percent. The customer paid 20 percent of the purchase price on delivery, with the remainder of the purchase price due in March 2021. What is the maximum reserve Ed's can claim for tax purposes for its November 30, 2020 year end?
A)$2,000.
B)$4,000.
C)$6,000.
D)$8,000.
E)None of the above.
A)$2,000.
B)$4,000.
C)$6,000.
D)$8,000.
E)None of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 103 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
A business may sometimes receive amounts of cash for goods or services to be delivered in a future taxation year. Under the requirements of the Income Tax Act, these amounts should be:
A)included in revenue when the goods or services are delivered.
B)included in revenue no later than 180 days after the end of the taxation year.
C)allocated to revenue over the period between the time the cash is received and the time the goods and services are delivered.
D)included in revenue when the cash is received.
A)included in revenue when the goods or services are delivered.
B)included in revenue no later than 180 days after the end of the taxation year.
C)allocated to revenue over the period between the time the cash is received and the time the goods and services are delivered.
D)included in revenue when the cash is received.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 103 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
Jon Bogen operates a consulting business out of a dedicated space in his home. It is his principal place of business. With respect to the items that he can deduct, which of the following statements is correct?
A)Jon can only deduct a pro rata share of operating costs and utilities.
B)Jon can only deduct a pro rata share of operating costs, utilities, and property taxes.
C)Jon can only deduct a pro rata share of operating costs, utilities, property taxes, and mortgage interest.
D)Jon can deduct a pro rata share of operating costs, utilities, property taxes, mortgage interest and CCA.
A)Jon can only deduct a pro rata share of operating costs and utilities.
B)Jon can only deduct a pro rata share of operating costs, utilities, and property taxes.
C)Jon can only deduct a pro rata share of operating costs, utilities, property taxes, and mortgage interest.
D)Jon can deduct a pro rata share of operating costs, utilities, property taxes, mortgage interest and CCA.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 103 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
Selected items from Mini Move Inc.'s December 31 audited financial statements are as follows: 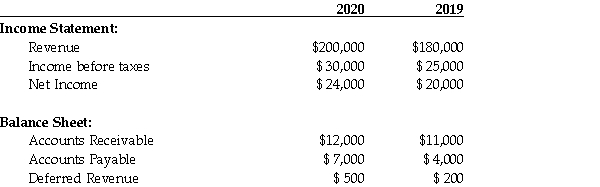 Mini Move's 2020 Net Income for Tax Purposes is:
Mini Move's 2020 Net Income for Tax Purposes is:
A)$24,300.
B)$30,300.
C)$31,000.
D)$31,300.
 Mini Move's 2020 Net Income for Tax Purposes is:
Mini Move's 2020 Net Income for Tax Purposes is:A)$24,300.
B)$30,300.
C)$31,000.
D)$31,300.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 103 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
Myrle Cocco owns a car that she uses both in her business and for personal use. The cost of the car was $28,000 and, on January 1, 2020, the UCC for the vehicle (it is the only asset in Class 10)was $11,662. During the year she drives the car a total of 42,000 kilometers of which 38,000 were related to her business activities. Her insurance for the year was $950 and her operating costs were $6,500. What is the amount of her maximum deduction for car costs during 2020?
A)$10,239.
B)$ 9,906.
C)$17,292.
D)$10,949.
A)$10,239.
B)$ 9,906.
C)$17,292.
D)$10,949.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 103 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
Fung Wo purchased vacant land on a remote island off the coast of British Columbia on January 1, 2017 for $50,000. She intended to re-sell it for a profit the next year but due to an oil spill, property values dropped. She was finally able to sell the vacant land for $45,000 on December 31, 2020. In the meantime, she paid property taxes of $500 each year. For 2020 tax purposes, Fung Wo has:
A)an allowable capital loss of $2,500.
B)an allowable capital loss of $3,500.
C)a net business loss of $5,000.
D)a net business loss of $7,000.
A)an allowable capital loss of $2,500.
B)an allowable capital loss of $3,500.
C)a net business loss of $5,000.
D)a net business loss of $7,000.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 103 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
Maxine is the proprietor of a home based business. She paid $25,000 to her editorial assistant, $8,000 to her son as her computer technician, and $32,000 to herself as salary. How much can she deduct as a business expense on her income tax return?
A)Nil.
B)$25,000.
C)$33,000.
D)$65,000.
A)Nil.
B)$25,000.
C)$33,000.
D)$65,000.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 103 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
Antonio Capellini is a successful self-employed accountant. He meets all of his clients in his office in the basement of his home. The office is 800 square feet and the house is 3,000 square feet. Antonio incurred the following costs during the current year:  What is the amount of the expenses deductible from Antonio's business income?
What is the amount of the expenses deductible from Antonio's business income?
A)$1,160
B)$2,888
C)$3,675
D)$4,835
 What is the amount of the expenses deductible from Antonio's business income?
What is the amount of the expenses deductible from Antonio's business income?A)$1,160
B)$2,888
C)$3,675
D)$4,835

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 103 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
For income tax purposes, X Co. can deduct life insurance premiums paid providing:
A)the life insurance policy is required as security on a loan from a financial institution.
B)the interest payable on the loan for which the life insurance is required is deductible by X Co. for tax purposes.
C)the premium paid is for insurance on the president of X Co.
D)Both A and B.
E)All of A, B, and C.
A)the life insurance policy is required as security on a loan from a financial institution.
B)the interest payable on the loan for which the life insurance is required is deductible by X Co. for tax purposes.
C)the premium paid is for insurance on the president of X Co.
D)Both A and B.
E)All of A, B, and C.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 103 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
Jerry collects baseball cards as a hobby. During the current year, he acquired twenty-five different items at a total cost of $29,550. During the year, he sold each of those items and received total proceeds of $55,900. What is the effect of these transactions on Jerry's Net Income For Tax Purposes?
A)Jerry has a taxable capital gain of $26,350.
B)Jerry has a taxable capital gain of 13,175.
C)Jerry has business income of $26,350.
D)Because the collection was a hobby, the gain does not have to be included in Net Income For Tax Purposes.
A)Jerry has a taxable capital gain of $26,350.
B)Jerry has a taxable capital gain of 13,175.
C)Jerry has business income of $26,350.
D)Because the collection was a hobby, the gain does not have to be included in Net Income For Tax Purposes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 103 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
In determining whether a gain resulting from a disposition of an asset is capital or business, various criteria have been used. Which of the following considerations would be least likely to affect the decision?
A)The length of time the asset is held.
B)Whether the transaction is related to the taxpayer's business.
C)The number and frequency of similar asset dispositions.
D)Whether the taxpayer knew the investment could be sold for a profit if the investment return was inadequate.
E)Whether the transaction resulted in a gain or loss.
A)The length of time the asset is held.
B)Whether the transaction is related to the taxpayer's business.
C)The number and frequency of similar asset dispositions.
D)Whether the taxpayer knew the investment could be sold for a profit if the investment return was inadequate.
E)Whether the transaction resulted in a gain or loss.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 103 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
Which of the following statements is NOT correct?
A)In determining property income, the deduction of CCA cannot be used to create or increase a loss.
B)Both business and property income are subject to the income attribution rules.
C)In determining business income, the deduction of CCA can be used to create or increase a loss.
D)Travel expenses cannot be deducted against property income.
A)In determining property income, the deduction of CCA cannot be used to create or increase a loss.
B)Both business and property income are subject to the income attribution rules.
C)In determining business income, the deduction of CCA can be used to create or increase a loss.
D)Travel expenses cannot be deducted against property income.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 103 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
Which of the following is correct?
A)In determining whether a disposition is capital or business in nature, the number and frequency of transactions is taken into account.
B)A taxpayer must include 50 percent of both business income and capital gains in their Taxable Income.
C)Amounts collected under an insurance policy are considered capital gains.
D)The sale of a depreciable asset can result in a capital gain or capital loss.
A)In determining whether a disposition is capital or business in nature, the number and frequency of transactions is taken into account.
B)A taxpayer must include 50 percent of both business income and capital gains in their Taxable Income.
C)Amounts collected under an insurance policy are considered capital gains.
D)The sale of a depreciable asset can result in a capital gain or capital loss.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 103 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
Which of the following expenses would be denied as a deduction under the Income Tax Act?
A)A speeding ticket received by a truck delivering goods for resale.
B)The costs of disability related building modifications.
C)Work space in a home costs for a self-employed contractor.
D)A reserve for doubtful accounts.
A)A speeding ticket received by a truck delivering goods for resale.
B)The costs of disability related building modifications.
C)Work space in a home costs for a self-employed contractor.
D)A reserve for doubtful accounts.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 103 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
Mary operates a proprietorship that generated $100,000 in income under GAAP. Included in this amount are:
• $7,000 of amortization expense;
• $4,000 for bad debt expense;
• $112,000 cost of goods sold; and
• $12,000 meals and entertainment with clients.
Mary's maximum CCA has been calculated at $10,000 for the year. How much is Mary's business income for tax purposes?
A)$113,000
B)$109,000
C)$107,000
D)$103,000
• $7,000 of amortization expense;
• $4,000 for bad debt expense;
• $112,000 cost of goods sold; and
• $12,000 meals and entertainment with clients.
Mary's maximum CCA has been calculated at $10,000 for the year. How much is Mary's business income for tax purposes?
A)$113,000
B)$109,000
C)$107,000
D)$103,000

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 103 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
Which of the following business expenses is deductible for tax purposes?
A)$25 late filing penalty charged by CRA.
B)$50 speeding ticket incurred while delivering goods to a customer.
C)$15 late payment interest charged by utility company.
D)$20 late payment interest charged by CRA.
A)$25 late filing penalty charged by CRA.
B)$50 speeding ticket incurred while delivering goods to a customer.
C)$15 late payment interest charged by utility company.
D)$20 late payment interest charged by CRA.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 103 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
Which of the following statements regarding farming income is correct?
A)A full time school teacher has income from his part-time farming activities. His farming income must be calculated on a cash basis.
B)A full time school teacher recognized a $9,500 loss this year from his part-time farming activities. The maximum deduction allowed this year from the farm loss is $6,000.
C)A full time school teacher recognized a $9,500 loss this year from his part-time farming activities. The maximum deduction allowed this year from the farm loss is $2,500.
D)A full time school teacher has income from his part-time farming activities. His farming income must be calculated on an accrual basis.
A)A full time school teacher has income from his part-time farming activities. His farming income must be calculated on a cash basis.
B)A full time school teacher recognized a $9,500 loss this year from his part-time farming activities. The maximum deduction allowed this year from the farm loss is $6,000.
C)A full time school teacher recognized a $9,500 loss this year from his part-time farming activities. The maximum deduction allowed this year from the farm loss is $2,500.
D)A full time school teacher has income from his part-time farming activities. His farming income must be calculated on an accrual basis.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 103 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
Old Time Company purchased a Class 10 truck many years ago for $8,000. The truck has now become a collectors' item and was sold on August 1, 2020 for $10,000. The net book value on that date was $500 and the Class 10 UCC balance was $11,525. There are other assets left in the class. Accounting net income before tax for the year ended December 31, 2020 was $24,000. Amortization of depreciable capital assets for accounting purposes is equal to the CCA deducted for tax purposes. Net income for tax purposes is:
A)$15,000.
B)$15,500.
C)$25,000.
D)$26,000.
A)$15,000.
B)$15,500.
C)$25,000.
D)$26,000.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 103 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
With respect to deductions in the determination of net business income for tax purposes, which of the following statements is correct?
A)A corporation can deduct the costs of issuing new common shares in the year in which the shares are issued.
B)Any premium on the sale of new debt securities by a corporation is amortized over the life of the securities.
C)Cost of sales can be determined using inventory valuation based on either replacement cost or net realizable value.
D)Landscaping costs are deductible in the year that they are accrued.
A)A corporation can deduct the costs of issuing new common shares in the year in which the shares are issued.
B)Any premium on the sale of new debt securities by a corporation is amortized over the life of the securities.
C)Cost of sales can be determined using inventory valuation based on either replacement cost or net realizable value.
D)Landscaping costs are deductible in the year that they are accrued.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 103 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
Which of the following is a deductible expense for an unincorporated business?
A)Donation made to the United Way.
B)Contribution made to the Federal Green Party.
C)Estimated cost of providing warranty services in future taxation years.
D)Reasonable salary paid to a relative.
A)Donation made to the United Way.
B)Contribution made to the Federal Green Party.
C)Estimated cost of providing warranty services in future taxation years.
D)Reasonable salary paid to a relative.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 103 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
Kyle purchased a large lot on a lake in anticipation of building his home there within 3 years. During the current year, Kyle paid $650 in property taxes and $2,500 of interest on the demand loan he obtained to purchase the lot. January to March he rented out the lot to a local snowmobile club for $1,500. Which of the following statements is correct?
A)Kyle cannot deduct any of the property taxes or interest paid for the vacant lot.
B)Kyle can deduct the $650 of property taxes paid, but none of the interest paid.
C)Kyle can deduct the $650 of property taxes paid and $850 of the interest paid.
D)Kyle can deduct all of the property taxes and interest paid.
A)Kyle cannot deduct any of the property taxes or interest paid for the vacant lot.
B)Kyle can deduct the $650 of property taxes paid, but none of the interest paid.
C)Kyle can deduct the $650 of property taxes paid and $850 of the interest paid.
D)Kyle can deduct all of the property taxes and interest paid.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 103 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
Several years ago, John Martin purchased a group of internet domain names at a cost of $1,000 each, hoping at some point that he could sell one or more at a later date. Until this year, none of the names have been sold. However, during this year, two of the names were sold for $25,000 each. Should the resulting gains be treated as capital gains or as business income? Justify your conclusion.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 103 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
Jon Avery starts an unincorporated business on December 1, 2020. Which of the following statements is correct with respect to Jon's taxation year end?
A)Jon must select December 31 as his taxation year end.
B)Jon must select November 30 as his taxation year end.
C)Jon can choose any date for his year end. However, if Jon chooses a non-calendar year end he will have to adjust his income by an amount referred to as "additional business income".
D)Jon can choose any date for his year end. However, if Jon chooses a non-calendar year end he will have to report income for his first two fiscal years in his 2021 tax return.
A)Jon must select December 31 as his taxation year end.
B)Jon must select November 30 as his taxation year end.
C)Jon can choose any date for his year end. However, if Jon chooses a non-calendar year end he will have to adjust his income by an amount referred to as "additional business income".
D)Jon can choose any date for his year end. However, if Jon chooses a non-calendar year end he will have to report income for his first two fiscal years in his 2021 tax return.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 103 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
Maria has her own accounting practice in Victoria, B.C. During 2020 she paid $1,650 to attend the following conventions: • $400 for a 2 day convention on "Tax issues for the owner/manager" held at Vancouver, B.C.
• $500 for a 3 day convention on "Attracting new clients" held at Kelowna, B.C.
• $750 for a 5 day convention on "IFRS implementation" held at Whistler, B.C.
The fees included all meals served during the convention. Maria's total deductible convention expense for tax purposes is:
A)$1,650.
B)$1,250.
C)$1,050.
D)$825.
• $500 for a 3 day convention on "Attracting new clients" held at Kelowna, B.C.
• $750 for a 5 day convention on "IFRS implementation" held at Whistler, B.C.
The fees included all meals served during the convention. Maria's total deductible convention expense for tax purposes is:
A)$1,650.
B)$1,250.
C)$1,050.
D)$825.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 103 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
During 2020, an individual sells his incorporated business for its fair market value. At the time of the sale the business has accounts receivable of $123,000. The vendor of the business and the purchaser agree on a fair market value for these receivables of $118,500. In 2019, the vendor had deducted a reserve for estimated bad debts of $6,800. Which of the following statements is correct?
A)If no election is made, the vendor will have an addition to net business income for tax purposes of $2,300.
B)If no election is made, the vendor will have an addition to net business income for tax purposes of $4,550.
C)If an election is made under ITA 22, the vendor will have a deduction in the determination of net business income for tax purposes of $2,300.
D)If an election is made under ITA 22, the vendor will have a deduction in the determination of net business income for tax purposes of $4,500.
A)If no election is made, the vendor will have an addition to net business income for tax purposes of $2,300.
B)If no election is made, the vendor will have an addition to net business income for tax purposes of $4,550.
C)If an election is made under ITA 22, the vendor will have a deduction in the determination of net business income for tax purposes of $2,300.
D)If an election is made under ITA 22, the vendor will have a deduction in the determination of net business income for tax purposes of $4,500.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 103 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
Martin Elwood has purchased the rights to a group of songs written by the Ringtones. He estimates that these songs will produce royalties of about $100,000 per year for at least 5 years. He does not have plans to acquire additional song rights. Explain whether the royalties he receives would be treated as business income or property income. In addition, indicate how any gain or loss on their disposition would be taxed.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 103 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
Tomas began his unincorporated business on January 1, 2020. During 2020, he received $40,000 cash in revenues and paid $33,000 for operating expenses. On December 31, 2020 one of his customers owed him $1,200 and Tomas owed one of his suppliers $2,300. In addition to the operating expenses, Tomas can also deduct one-third of his house costs since he operates his business out of the ground floor of his rented 3-storey home. Total house costs for 2020 were: rent of $19,200; insurance of $800; utilities of $2,100. Tomas' maximum work space in the home expense deduction for 2020 is:
A)$5,900.
B)$7,000.
C)$7,100.
D)$7,367.
A)$5,900.
B)$7,000.
C)$7,100.
D)$7,367.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 103 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
Which of the following items is NOT deductible in calculating net business income for the current taxation year?
A)An $11,000 legal fee paid for services rendered in conjunction with a new issue of the company's common stock.
B)A $125,000 management bonus paid 125 days after the end of the corporation's current taxation year.
C)An amount of $25,000 paid for planting large maple trees in various locations on the grounds of the company's facilities.
D)A $10,000 contribution to a company pension fund.
A)An $11,000 legal fee paid for services rendered in conjunction with a new issue of the company's common stock.
B)A $125,000 management bonus paid 125 days after the end of the corporation's current taxation year.
C)An amount of $25,000 paid for planting large maple trees in various locations on the grounds of the company's facilities.
D)A $10,000 contribution to a company pension fund.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 103 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
For tax purposes, the cost of the end of period inventory can be determined in a variety of ways. Which of the following approaches CANNOT be used?
A)Last-In, First-Out.
B)First-In, First-Out.
C)Specific Identification.
D)Average Cost.
A)Last-In, First-Out.
B)First-In, First-Out.
C)Specific Identification.
D)Average Cost.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 103 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
Widget Production Ltd. has a fiscal year end of June 30. In February 2018, the Company borrowed $750,000 to fund an expansion. The Company paid $21,000 to obtain this financing. In January 2019, the Company repaid $250,000 of the principal and in June 2020, it repaid the remaining $500,000. All repayments were made from cash flow from operations. For tax purposes, which one of the following schedule of claims represents the most rapid method of claiming the costs of obtaining this financing?
A)$4,200 in each of fiscal 2018 through 2022.
B)$4,200 in each of 2018 and 2019, and the remaining $12,600 in 2020.
C)$4,200 in 2018, $8,400 in 2019, and $8,400 in 2020.
D)$7,000 in 2019 and $14,000 in 2020.
A)$4,200 in each of fiscal 2018 through 2022.
B)$4,200 in each of 2018 and 2019, and the remaining $12,600 in 2020.
C)$4,200 in 2018, $8,400 in 2019, and $8,400 in 2020.
D)$7,000 in 2019 and $14,000 in 2020.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 103 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
Quality Homes Ltd. (Quality)has a December 31, 2020 year end. The controller has calculated the Company's 2020 income as $50,000. However, in arriving at this amount, the controller deducted $30,000 of salary to an employee who is the sole shareholder of the Company and $5,000 of salary to an arm's length employee. Both of these amounts were paid on June 30, 2021. Which one of the following represents Quality's 2020 Net Income For Tax Purposes?
A)$50,000.
B)$55,000.
C)$80,000.
D)$85,000.
A)$50,000.
B)$55,000.
C)$80,000.
D)$85,000.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 103 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
Busy Company incurred the following meal costs during 2020:  The total deductible meal expense for tax purposes is:
The total deductible meal expense for tax purposes is:
A)$11,100.
B)$11,850.
C)$13,300.
D)$13,900.
 The total deductible meal expense for tax purposes is:
The total deductible meal expense for tax purposes is:A)$11,100.
B)$11,850.
C)$13,300.
D)$13,900.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 103 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
888 Company leased a car throughout 2020 for $950 per month, $75 of which was for insurance. There was no down payment or refundable deposit. The manufacturer's suggested list price for the car is $38,000. Other costs incurred for the vehicle during 2020 were $1,600 for gas and $420 for repairs. The maximum tax deduction for 2020 vehicle expenses is:
A)$11,753.
B)$12,653.
C)$12,672.
D)$13,420.
A)$11,753.
B)$12,653.
C)$12,672.
D)$13,420.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 103 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
William Lemay acquired a six unit apartment building for $315,000 with the intention of operating it as a rental property. Three weeks after his purchase, he received an unexpected offer to purchase the building for $387,000. He accepts the offer. Should the $72,000 be treated as a capital gain or as business income? Justify your conclusion.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 103 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



