Deck 23: Ecological Economics
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/22
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 23: Ecological Economics
1
The human development index (HDI) is a measure created by the United Nations Development Programme to track social progress. HDI incorporates life expectancy, adult literacy, children s education, and standard of living indicators to measure human development. The 2006 report draws on statistics from 175 countries. While there has been encouraging progress in most world regions, the index shows that widening inequality is taking a toll on global human development.
The graph shows trends in the HDI by world region. Study this graph carefully, and answer the following questions: ( Note: you may have to search online to find some answers.)
Which region has the highest HDI rating
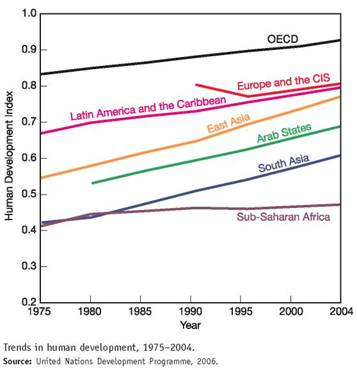
The graph shows trends in the HDI by world region. Study this graph carefully, and answer the following questions: ( Note: you may have to search online to find some answers.)
Which region has the highest HDI rating

The human development index (HDI) is a measure to calculate the expectancy of the life span of human beings, the education rate, and the income of every individual. There are three indicators to check the HDI-
• The expectancy of life at birth- average years citizens are expected to live and the maximum value is 85
• Expected years and average years of learning- the education index is calculated and is expected that the mean years of schooling are 15 and the upper limit of expected years of schooling is 18 which is required to complete the master's degree
• Gross national income is total household and overseas production demanded by the citizens of the country.
It is estimated that the country with higher HDI will have citizens with a higher life span, higher education index, and high income.
Europe and the CIS region have the highest HDI that is around 0.8. Europe and other independent states got separated from the USSR in 1991 and thus the HDI of Europe and CIS was calculated after 199. The HDI of the USSR was almost 0.8 in 1991 but got declined between 1990 and 1995 and then increased from 1995 to 2004.
Thus, lifespan, education, and income of people in Europe and CIS are high compared to other regions of the world.
• The expectancy of life at birth- average years citizens are expected to live and the maximum value is 85
• Expected years and average years of learning- the education index is calculated and is expected that the mean years of schooling are 15 and the upper limit of expected years of schooling is 18 which is required to complete the master's degree
• Gross national income is total household and overseas production demanded by the citizens of the country.
It is estimated that the country with higher HDI will have citizens with a higher life span, higher education index, and high income.
Europe and the CIS region have the highest HDI that is around 0.8. Europe and other independent states got separated from the USSR in 1991 and thus the HDI of Europe and CIS was calculated after 199. The HDI of the USSR was almost 0.8 in 1991 but got declined between 1990 and 1995 and then increased from 1995 to 2004.
Thus, lifespan, education, and income of people in Europe and CIS are high compared to other regions of the world.
2
Describe how cost-benefit ratios are determined and how they are used in natural resource management.
Various ecological values are received from the ecosystem but are free of cost and the ecological values are-
• Use value- the price that is paid for utilizing the resources
• Option value- the resources that are preserved in stock for the future
• Existence value- the resources that exist in nature, but cannot be used or see them
• Aesthetic value- the beauty of nature
• Cultural values- the culture that is connected to nature
• Scientific and educational value- the knowledge and information that is searched and used for the invention of new technology
The value or price is not paid for many of the values and cannot be evaluated, but the estimated value of the ecological services in a year is around $ 33.3 trillion, which is about 75% of the combined GNP of every 195 nations on the earth.
Cost-benefit analysis is a way to evaluate the price and the advantages obtained from the public project. This analysis method tags the prices of the resources obtained from the nature of the project and also tags the price on the effects that are generated by the project on nature and society and also on the effects that are indirectly generated by the project.
Ecological economics has a main framework of CBA for evaluating the resources and the services that are received by the leaders or the industries for starting the project for public benefits on the cost of the environment. The steps followed in this analysis are as follows-
• The analysis starts by doing a survey based on the following questions-
• Who or what might be affected by the project
• Potential outcomes and results of the project
• The alternative actions that can be considered
• After the questionnaire is done, then the economic expenditure and advantages are assigned to each factor
• The final analysis is made based on a factor that who have to face the costs and who will have the advantages as due to the project the beauty of the place, the water for the fishes and swimming will be affected so these are considered as monetary costs
• The results of the analysis are finalized by comparing the expenses and reimbursement of the project, and whether the project is defensible or any alternative is possible at lower costs.
The cost-benefit ratios are used in the management of the natural resources as based on the analysis done by the decision-makers the projects are approved by estimating the value of the harm to be done on the environment and society and if the project is not justified according to the subsidiary cost and benefits then the projects are disqualified. Thus the CBA manages the resources obtained from nature and all the resources that are unaccountable and the values cannot be calculated because they are freely available and unlimited.
• Use value- the price that is paid for utilizing the resources
• Option value- the resources that are preserved in stock for the future
• Existence value- the resources that exist in nature, but cannot be used or see them
• Aesthetic value- the beauty of nature
• Cultural values- the culture that is connected to nature
• Scientific and educational value- the knowledge and information that is searched and used for the invention of new technology
The value or price is not paid for many of the values and cannot be evaluated, but the estimated value of the ecological services in a year is around $ 33.3 trillion, which is about 75% of the combined GNP of every 195 nations on the earth.
Cost-benefit analysis is a way to evaluate the price and the advantages obtained from the public project. This analysis method tags the prices of the resources obtained from the nature of the project and also tags the price on the effects that are generated by the project on nature and society and also on the effects that are indirectly generated by the project.
Ecological economics has a main framework of CBA for evaluating the resources and the services that are received by the leaders or the industries for starting the project for public benefits on the cost of the environment. The steps followed in this analysis are as follows-
• The analysis starts by doing a survey based on the following questions-
• Who or what might be affected by the project
• Potential outcomes and results of the project
• The alternative actions that can be considered
• After the questionnaire is done, then the economic expenditure and advantages are assigned to each factor
• The final analysis is made based on a factor that who have to face the costs and who will have the advantages as due to the project the beauty of the place, the water for the fishes and swimming will be affected so these are considered as monetary costs
• The results of the analysis are finalized by comparing the expenses and reimbursement of the project, and whether the project is defensible or any alternative is possible at lower costs.
The cost-benefit ratios are used in the management of the natural resources as based on the analysis done by the decision-makers the projects are approved by estimating the value of the harm to be done on the environment and society and if the project is not justified according to the subsidiary cost and benefits then the projects are disqualified. Thus the CBA manages the resources obtained from nature and all the resources that are unaccountable and the values cannot be calculated because they are freely available and unlimited.
3
Define economics and distinguish the emphasis of classical, neoclassical, and ecological economics.
Economics is a subject that concerns with the resources that are produced, distributed, sold, or bought of those resources so that money can be earned for better living standards. This subject deals with the idea of using the resources to satisfy needs and earn the profits from those resources for their better future either individually or collaboratively. Economics is an important means of gaining knowledge and using resources effectively. There are three branches of economics-
• Classical economics
• Neoclassical economics
• Ecological economics
Classical Economics-
This economics is concerned with how the interest of the resources in citizens and values of the resources crisscross with the larger social goal. The main idea given in classical economics is-
• The values earned by the people in the market increase the value of their nation automatically
• This theory assumes that the value of the product is earned from the price of the material used in the product and the price of the people who worked for the production of that product.
• The balance in the market for the product is created from the supply of the product and the demand for the product.
• If the value of the product is increased than the supply is increased, but the demand for the product is reduced
• If the value of the product is decreased, then the supply is also decreased, but the demand for that product is increased
• The word demand emphasizes on the amount of the product that the people can buy or are agreeable to buy
• The word supply emphasizes the sum of product that is accessible for trade at different prices
• Thus, the classical economic states that there is a direct and reciprocal relationship between supply and demand.
Neoclassical economy-
This model of economics highlights the flow of goods, services, and factors of production like soil, employment, and wealth between businesses, workers, and consumers.
• This model emphasizes the growth through supply and demand of the product
• The nature of exchange occurs only when the market equilibrium prices are reached
• This emphasizes on personal, security, and social requirements of the workers
• This focuses on the emotional and human qualities of the workers in an organization
• This focuses on the long term and is primarily determined by aggregate supply
• The assumptions of this theory are-
• Rational decisions are taken on the issues of economics based on the absolute data of the manufactured goods and its uses
• The goods are compared by the consumers and then the decision is taken based on the perceived utility
• The main objective of the consumers is to fund the satisfaction received by using the product
• The necessary and desirable focus in neoclassical economics is the continued growth in the economy.
Ecological economics-
Ecological economics is based on nature and the resources that are received from the natural system.
• In this model, the economists calculate the cost of the pollutants that are absorbed by the climate, water that absorbs the wastes, bacteria that decomposes the waste and the wind that carry away the smoke
• The resources or advantages that re received from nature is considered as external costs as it is not added to the accounting system by the classical or neoclassical economists
• In this economics, matter and energy are consumed as raw materials and rejected as wastes. Materials are recycled by the ecological cycles and heat is ejected back into space.
• Generally, it is considered that the natural resources are abundant, so the value of the natural endowments is cheap, but according to the ecological economists the natural resources are limited and so are more valuable than the products that are produced in the manufacturing units.
• The ecological economists make the account that includes social costs and the costs of the waste produced from the product or services provided by the environment
• Classical economics
• Neoclassical economics
• Ecological economics
Classical Economics-
This economics is concerned with how the interest of the resources in citizens and values of the resources crisscross with the larger social goal. The main idea given in classical economics is-
• The values earned by the people in the market increase the value of their nation automatically
• This theory assumes that the value of the product is earned from the price of the material used in the product and the price of the people who worked for the production of that product.
• The balance in the market for the product is created from the supply of the product and the demand for the product.
• If the value of the product is increased than the supply is increased, but the demand for the product is reduced
• If the value of the product is decreased, then the supply is also decreased, but the demand for that product is increased
• The word demand emphasizes on the amount of the product that the people can buy or are agreeable to buy
• The word supply emphasizes the sum of product that is accessible for trade at different prices
• Thus, the classical economic states that there is a direct and reciprocal relationship between supply and demand.
Neoclassical economy-
This model of economics highlights the flow of goods, services, and factors of production like soil, employment, and wealth between businesses, workers, and consumers.
• This model emphasizes the growth through supply and demand of the product
• The nature of exchange occurs only when the market equilibrium prices are reached
• This emphasizes on personal, security, and social requirements of the workers
• This focuses on the emotional and human qualities of the workers in an organization
• This focuses on the long term and is primarily determined by aggregate supply
• The assumptions of this theory are-
• Rational decisions are taken on the issues of economics based on the absolute data of the manufactured goods and its uses
• The goods are compared by the consumers and then the decision is taken based on the perceived utility
• The main objective of the consumers is to fund the satisfaction received by using the product
• The necessary and desirable focus in neoclassical economics is the continued growth in the economy.
Ecological economics-
Ecological economics is based on nature and the resources that are received from the natural system.
• In this model, the economists calculate the cost of the pollutants that are absorbed by the climate, water that absorbs the wastes, bacteria that decomposes the waste and the wind that carry away the smoke
• The resources or advantages that re received from nature is considered as external costs as it is not added to the accounting system by the classical or neoclassical economists
• In this economics, matter and energy are consumed as raw materials and rejected as wastes. Materials are recycled by the ecological cycles and heat is ejected back into space.
• Generally, it is considered that the natural resources are abundant, so the value of the natural endowments is cheap, but according to the ecological economists the natural resources are limited and so are more valuable than the products that are produced in the manufacturing units.
• The ecological economists make the account that includes social costs and the costs of the waste produced from the product or services provided by the environment
4
Explain how scarcity and technological progress can extend resource availability and extend the carrying capacity of the environment.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 22 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
How can intangible resources be infinite and exhaustible at the same time Isn't this a contradiction in terms Can you find other similar paradoxes in this chapter

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 22 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Describe how GNP is calculated and explain why this may fail to adequately measure human welfare and environmental quality. Discuss some alternative measures of progress.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 22 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
The human development index (HDI) is a measure created by the United Nations Development Programme to track social progress. HDI incorporates life expectancy, adult literacy, children s education, and standard of living indicators to measure human development. The 2006 report draws on statistics from 175 countries. While there has been encouraging progress in most world regions, the index shows that widening inequality is taking a toll on global human development.
The graph shows trends in the HDI by world region. Study this graph carefully, and answer the following questions: ( Note: you may have to search online to find some answers.)
What does OECD stand for
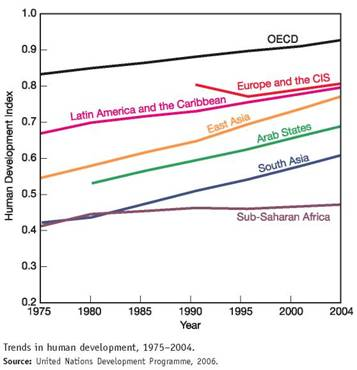
The graph shows trends in the HDI by world region. Study this graph carefully, and answer the following questions: ( Note: you may have to search online to find some answers.)
What does OECD stand for


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 22 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
What is microlending, and what are its benefits

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 22 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Define resources and give some examples of renewable, non-renewable, and intangible resources.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 22 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
List some of the characteristics of an eco-efficient economic system.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 22 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
What would be the effect on the developing countries of the world if we were to change to a steady-state economic system How could we achieve a just distribution of resource benefits while still protecting environmental quality and future resource use

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 22 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
The human development index (HDI) is a measure created by the United Nations Development Programme to track social progress. HDI incorporates life expectancy, adult literacy, children s education, and standard of living indicators to measure human development. The 2006 report draws on statistics from 175 countries. While there has been encouraging progress in most world regions, the index shows that widening inequality is taking a toll on global human development.
The graph shows trends in the HDI by world region. Study this graph carefully, and answer the following questions: ( Note: you may have to search online to find some answers.)
Which region has made the greatest progress over the past 30 years, and how much has its HDI increased
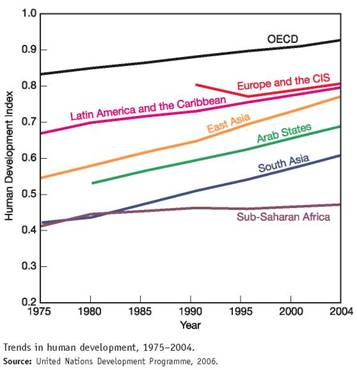
The graph shows trends in the HDI by world region. Study this graph carefully, and answer the following questions: ( Note: you may have to search online to find some answers.)
Which region has made the greatest progress over the past 30 years, and how much has its HDI increased


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 22 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Describe the relationship between supply and demand.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 22 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Resource use policies bring up questions of intergenerational justice. Suppose you were asked: "What has posterity ever done for me " How would you answer

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 22 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
The human development index (HDI) is a measure created by the United Nations Development Programme to track social progress. HDI incorporates life expectancy, adult literacy, children s education, and standard of living indicators to measure human development. The 2006 report draws on statistics from 175 countries. While there has been encouraging progress in most world regions, the index shows that widening inequality is taking a toll on global human development.
The graph shows trends in the HDI by world region. Study this graph carefully, and answer the following questions: ( Note: you may have to search online to find some answers.)
Which region has shown the least progress in human development
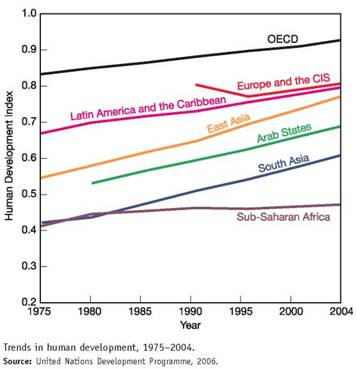
The graph shows trends in the HDI by world region. Study this graph carefully, and answer the following questions: ( Note: you may have to search online to find some answers.)
Which region has shown the least progress in human development


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 22 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
What do we mean by "externalizing costs" Give several examples.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 22 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
If you were doing a cost-benefit study, how would you assign a value to the opportunity for good health or the existence of rare and endangered species in faraway places Is there a danger or cost in simply saying some things are immeasurable and priceless and therefore off limits to discussion

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 22 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
The human development index (HDI) is a measure created by the United Nations Development Programme to track social progress. HDI incorporates life expectancy, adult literacy, children s education, and standard of living indicators to measure human development. The 2006 report draws on statistics from 175 countries. While there has been encouraging progress in most world regions, the index shows that widening inequality is taking a toll on global human development.
The graph shows trends in the HDI by world region. Study this graph carefully, and answer the following questions: ( Note: you may have to search online to find some answers.)
What historic events could explain the reduction in Europe and the CIS between 1990 and 1995
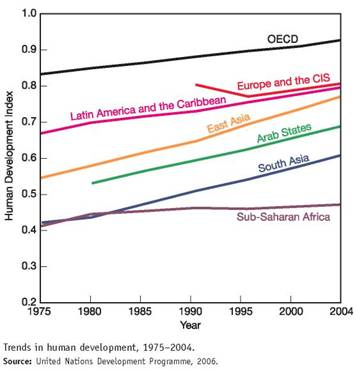
The graph shows trends in the HDI by world region. Study this graph carefully, and answer the following questions: ( Note: you may have to search online to find some answers.)
What historic events could explain the reduction in Europe and the CIS between 1990 and 1995


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 22 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Identify some important ecological services on which our economy depends.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 22 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
If natural capitalism or eco-efficiency has been so good for some entrepreneurs, why haven't all businesses moved in this direction

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 22 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
When the ecologist warns that we are using up irreplaceable natural resources and the economist rejoins that ingenuity and enterprise will find substitutes for most resources, what underlying premises and definitions shape their arguments

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 22 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
The human development index (HDI) is a measure created by the United Nations Development Programme to track social progress. HDI incorporates life expectancy, adult literacy, children s education, and standard of living indicators to measure human development. The 2006 report draws on statistics from 175 countries. While there has been encouraging progress in most world regions, the index shows that widening inequality is taking a toll on global human development.
The graph shows trends in the HDI by world region. Study this graph carefully, and answer the following questions: ( Note: you may have to search online to find some answers.)
How much lower is the HDI ranking of sub-Saharan Africa from the OECD
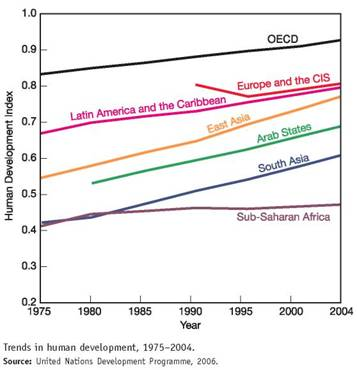
The graph shows trends in the HDI by world region. Study this graph carefully, and answer the following questions: ( Note: you may have to search online to find some answers.)
How much lower is the HDI ranking of sub-Saharan Africa from the OECD


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 22 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



