Deck 6: The Human Population and Urbanization
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/26
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 6: The Human Population and Urbanization
1
The chart below shows selected population data for two different countries, A and B. Study the chart and answer the questions that follow.
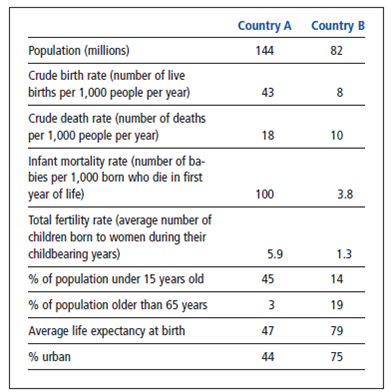
Describe where each of the two countries might be in the stages of demographic transition (Figure 6.10). Discuss factors that could hinder either country from progressing to later stages in the demographic transition.

Describe where each of the two countries might be in the stages of demographic transition (Figure 6.10). Discuss factors that could hinder either country from progressing to later stages in the demographic transition.
The demographic transition defined as the development of hypothesis of population change. The five stage of demographic transition is fowling.
•Preindustrial.
•Transitional.
•Industrial.
•Postindustrial.
The factor could hinder is age of scientist, engineer, skilled worker insufficient financial capital large foreign debt factor are making this transition. Family planning is provides educational knowledge and clinical services by which helped people how many child they have.
•Preindustrial.
•Transitional.
•Industrial.
•Postindustrial.
The factor could hinder is age of scientist, engineer, skilled worker insufficient financial capital large foreign debt factor are making this transition. Family planning is provides educational knowledge and clinical services by which helped people how many child they have.
2
What is the key concept for this section? Distinguish between compact and dispersed cities, and give an example of each. What are the major advantages and disadvantages of using motor vehicles? List four ways to reduce dependence on motor vehicles. List the major advantages and disadvantages of relying more on (a) bicycles, (b) bus rapid-transit systems, (c) mass-transit rail systems within urban areas, and (d) rapid-rail systems between urban areas.
The key concept of this section is that environmental impacts due to transportation and urbanization. Cites with high density of population depend on the walking, biking, rail and bus system for the transportation are called compact cities. Examples of compact cities are:
•China
•Hong Kong
•Japan
•Tokyo
Cites with high density of population depend on the motor vehicles for the transportation are called dispersed cities. Examples of dispersed cities are:
•Canada
•Australia
•United States
The major advantage of using motor vehicles is fast and reliable transportation and the major disadvantage is air pollution. The ways to reduce the dependence on motor vehicles are:
•Walking
•Using bicycles
•Transportation by rail and bus systems
(a)The advantages of using bicycles are usage of low resources for building and no need to use fossil fuels. No pollution and need very less parking place. The disadvantages of bicycles are long trips would not possible and has less protection against weather and accidents.
(b)The advantages of using bus-rapid transport system are less air pollution. Cheap than rail system and can be rerouted as needed. The disadvantages of bus-rapid transport system limited transportation schedules and more affordable prices for poor people and may get caught in traffic.
(c)The advantages of mass transit rail are less air pollution and fewer deaths caused than the cars. Require very less and fixed parking lot. The disadvantages of mass transit rail are transport schedule, high cost and limited to most urban cities.
(d)The advantages of rapid rail system are more efficiency than cars and buses. Less air pollution and less parking area required than cars and buses. The disadvantages of rapid rail system are noise and vibration pollution and need more cost to run and maintain.
•China
•Hong Kong
•Japan
•Tokyo
Cites with high density of population depend on the motor vehicles for the transportation are called dispersed cities. Examples of dispersed cities are:
•Canada
•Australia
•United States
The major advantage of using motor vehicles is fast and reliable transportation and the major disadvantage is air pollution. The ways to reduce the dependence on motor vehicles are:
•Walking
•Using bicycles
•Transportation by rail and bus systems
(a)The advantages of using bicycles are usage of low resources for building and no need to use fossil fuels. No pollution and need very less parking place. The disadvantages of bicycles are long trips would not possible and has less protection against weather and accidents.
(b)The advantages of using bus-rapid transport system are less air pollution. Cheap than rail system and can be rerouted as needed. The disadvantages of bus-rapid transport system limited transportation schedules and more affordable prices for poor people and may get caught in traffic.
(c)The advantages of mass transit rail are less air pollution and fewer deaths caused than the cars. Require very less and fixed parking lot. The disadvantages of mass transit rail are transport schedule, high cost and limited to most urban cities.
(d)The advantages of rapid rail system are more efficiency than cars and buses. Less air pollution and less parking area required than cars and buses. The disadvantages of rapid rail system are noise and vibration pollution and need more cost to run and maintain.
3
The campus where you go to school is something like an urban community. Choose five eco-city characteristics (p. 122) and apply them to your campus. For each characteristic:
Do some research and rate your campus for each characteristic.
Write a proposed plan for how the campus could improve its ratings.
Do some research and rate your campus for each characteristic.
Write a proposed plan for how the campus could improve its ratings.
Not Answer
4
Define smart growth and explain its benefits. Describe the eco-city model. Give five examples of how Curitiba, Brazil, has attempted to become an eco-city. What are this chapter's three big ideas ? Explain how Portland, Oregon, and other cities are applying the six principles of sustainability to become more sustainable urban areas.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 26 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
What are the two key concepts for this section? List three variables that affect the growth and decline of human populations. How can we calculate the population change of an area? Define the total fertility rate (TFR). How has the global TFR changed since 1955? Summarize the story of population growth in the United States. About how much of the annual U.S. population growth is due to legal immigration? List six changes in lifestyles that have taken place in the United States during the 20th century, leading to a rise in per capita resource use.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 26 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
If you could say hello to a new person every second without taking a break and working around the clock, how many years would it take you to greet the 85 million people who were added to the world's population in 2013? (Hint: start by dividing 85 million seconds by 60 to find the number of minutes, and go from there to find the number of years.) How many years would it take for you to greet 7.1 billion people?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 26 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
The chart below shows selected population data for two different countries, A and B. Study the chart and answer the questions that follow.
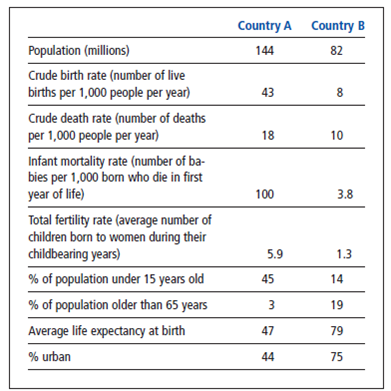
Explain how the percentages of people under age 15 in each country could affect its per capita and total ecological footprints.

Explain how the percentages of people under age 15 in each country could affect its per capita and total ecological footprints.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 26 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
The campus where you go to school is something like an urban community. Choose five eco-city characteristics (p. 122) and apply them to your campus. For each characteristic:
Write an explanation of your research process and why you chose each rating.
Write a proposed plan for how the campus could improve its ratings.
Write an explanation of your research process and why you chose each rating.
Write a proposed plan for how the campus could improve its ratings.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 26 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
List nine factors that affect birth rates and fertility rates. Define life expectancy and infant mortality rate and explain how they affect the population size of a country. What is migration ? What factors can promote migration?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 26 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Identify a major local, national, or global environmental problem, and describe the role that population growth plays in this problem.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 26 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Explain how Portland, Oregon has attempted to become a more sustainable city.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 26 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
What is the key concept for this section? What is the age structure of a population? Explain how age structure affects population growth and economic growth. Describe the American baby boom and some of its economic and social effects. What are some problems related to rapid population decline due to an aging population?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 26 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Portland, Oregon ( Core Case Study ) has made significant progress in becoming a more environmentally sustainable and desirable place to live. If you live in an urban area, what steps, if any, has your community taken toward becoming more environmentally sustainable? What further steps could be taken?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 26 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Some people think that our most important environmental goal should be to sharply reduce the rate of population growth in less-developed countries, where at least 92% of the world's population growth is expected to take place between now and 2050. Others argue that the most serious environmental problems stem from high levels of resource consumption per person in more-developed countries, which have much larger ecological footprints per person than do less-developed countries. What is your view on this issue? Explain.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 26 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
The chart below shows selected population data for two different countries, A and B. Study the chart and answer the questions that follow.
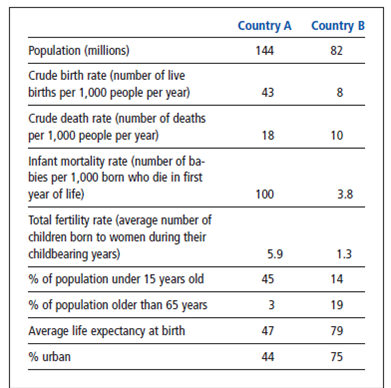
Calculate the rates of natural increase (due to births and deaths, not counting immigration) for the populations of country A and country B. Based on these calculations and the data in the table, for each of the countries, suggest whether it is a more-developed country or a less-developed country and explain the reasons for your answers.

Calculate the rates of natural increase (due to births and deaths, not counting immigration) for the populations of country A and country B. Based on these calculations and the data in the table, for each of the countries, suggest whether it is a more-developed country or a less-developed country and explain the reasons for your answers.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 26 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
What is the key concept for this section? What is the demographic transition and what are its four stages? Explain how the reduction of poverty and empowerment of women can help countries to slow their population growth. What is family planning and how can it help to stabilize populations? Describe India's efforts to control its population growth. Describe China's population control program and compare it with that of India.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 26 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
The campus where you go to school is something like an urban community. Choose five eco-city characteristics (p. 122) and apply them to your campus. For each characteristic:
Create a scale of 1 to 10 in order to rate the campus on how well it does in having that characteristic. (For example, how well does it do in giving students options for getting around, other than by using a car? A rating of 1 could be not at all, while a rating of 10 could be excellent. )
Write a proposed plan for how the campus could improve its ratings.
Create a scale of 1 to 10 in order to rate the campus on how well it does in having that characteristic. (For example, how well does it do in giving students options for getting around, other than by using a car? A rating of 1 could be not at all, while a rating of 10 could be excellent. )
Write a proposed plan for how the campus could improve its ratings.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 26 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
If you own a car or hope to own one, what conditions, if any, would encourage you to rely less on your car and to travel to school or work by bicycle, on foot, by mass transit, or by carpool?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 26 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Find three different projections for the size of the global population in 2050 ( Core Case Study ). Explain how the projections were made. To do this, try to find out the assumptions behind each of the projections with regard to total fertility rates, crude death rates, infant mortality rates, life expectancies, and other factors. Based on your reading, choose the projection that you believe to be the closest to reality, and explain why you chose this projection.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 26 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
What is the key concept for this section? What percentage of the world's people lives in urban areas? List two ways in which urban areas grow. List three trends in global urban growth. Describe the three phases of urban growth in the United States. What is urban sprawl ? List five factors that have promoted urban sprawl in the United States. List five undesirable effects of urban sprawl.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 26 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
HOW LONG CAN THE HUMAN POPULATION KEEP GROWING?
Are there physical limits to human population growth and economic growth on a finite planet? Some say yes. Others say no.
The debate over possible limits to the growth of human populations and economies has been going on for more than 200 years. Meanwhile, natural capital degradation (Figure 6.2) has occurred widely and grown more intense. The earth's life-support system has been resilient enough to withstand such widespread disturbances.
However, at some point, we could reach one or more planetary boundaries or ecological tipping points (see Figure 3.A, p. 58). Exceeding such boundaries could lead to damaging long-term changes and the possibility of a sharp decline in the human population due to increasing death rates.
To some analysts, the key problem is the large and rapidly growing number of people in less-developed countries (see Table 1.1, p. 13). To others, the key factor is overconsumption in affluent, more-developed countries because of their high rates of resource use per person. Thus, they debate over which is more important for shrinking the human ecological footprint: slowing population growth or reducing resource consumption. Some call for doing both.
Another view of population growth is that, so far, technological advances have allowed us to overcome the environmental limits that all populations of other species face and that this has had the effect of increasing the earth's carrying capacity for our species. Proponents of this view point out that average life expectancy in most of the world has been steadily rising, despite warnings that we are seriously degrading our life-support system.
Some of these analysts argue that because of our technological ingenuity, there are few, if any, limits to human population growth and resource use per person. They believe that we can continue ever-increasing economic growth and avoid serious damage to our life-support systems by making technological advances in areas such as food production and medicine, and by finding substitutes for resources that we are depleting. As a result, they see no need to slow population growth or resource consumption.
Proponents of slowing and eventually stopping population growth point out that in addition to degrading our life-support system, we are failing to provide the basic necessities for about 1.4 billion people-one of every five on the planet-who struggle to survive on the equivalent of about $1.25 per day. This raises a serious question: How will we meet the basic needs of the additional 2.6 billion people projected to be added between 2013 and 2050?
No one knows how close we are to environmental limits that some analysts say eventually will reduce the size of the human population primarily by sharply increasing the human death rate. These analysts call for us to confront this vital scientific, political, economic, and ethical issue.
Critical Thinking
Do you think there are environmental limits to human population growth? If so, how close do you think we are to such limits? Very close, moderately close, or far away? Explain.
Are there physical limits to human population growth and economic growth on a finite planet? Some say yes. Others say no.
The debate over possible limits to the growth of human populations and economies has been going on for more than 200 years. Meanwhile, natural capital degradation (Figure 6.2) has occurred widely and grown more intense. The earth's life-support system has been resilient enough to withstand such widespread disturbances.
However, at some point, we could reach one or more planetary boundaries or ecological tipping points (see Figure 3.A, p. 58). Exceeding such boundaries could lead to damaging long-term changes and the possibility of a sharp decline in the human population due to increasing death rates.
To some analysts, the key problem is the large and rapidly growing number of people in less-developed countries (see Table 1.1, p. 13). To others, the key factor is overconsumption in affluent, more-developed countries because of their high rates of resource use per person. Thus, they debate over which is more important for shrinking the human ecological footprint: slowing population growth or reducing resource consumption. Some call for doing both.
Another view of population growth is that, so far, technological advances have allowed us to overcome the environmental limits that all populations of other species face and that this has had the effect of increasing the earth's carrying capacity for our species. Proponents of this view point out that average life expectancy in most of the world has been steadily rising, despite warnings that we are seriously degrading our life-support system.
Some of these analysts argue that because of our technological ingenuity, there are few, if any, limits to human population growth and resource use per person. They believe that we can continue ever-increasing economic growth and avoid serious damage to our life-support systems by making technological advances in areas such as food production and medicine, and by finding substitutes for resources that we are depleting. As a result, they see no need to slow population growth or resource consumption.
Proponents of slowing and eventually stopping population growth point out that in addition to degrading our life-support system, we are failing to provide the basic necessities for about 1.4 billion people-one of every five on the planet-who struggle to survive on the equivalent of about $1.25 per day. This raises a serious question: How will we meet the basic needs of the additional 2.6 billion people projected to be added between 2013 and 2050?
No one knows how close we are to environmental limits that some analysts say eventually will reduce the size of the human population primarily by sharply increasing the human death rate. These analysts call for us to confront this vital scientific, political, economic, and ethical issue.
Critical Thinking
Do you think there are environmental limits to human population growth? If so, how close do you think we are to such limits? Very close, moderately close, or far away? Explain.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 26 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Do you think the United States (or the country in which you live) should develop a comprehensive and integrated mass-transit system over the next 20 years, including an efficient rapid-rail network for travel within and between its major cities? Explain. If so, how would you pay for such a system?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 26 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
What is the key concept for this section? List three factors that account for the rapid increase in the world's human population over the past 200 years. Summarize the three major population growth trends recognized by demographers. About how many people are added to the world's population each year? List eight major ways in which we have altered the earth's ecosystem services to meet our needs. Summarize the debate over whether and how long the human population can keep growing.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 26 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
What are the major advantages and disadvantages of urbanization? Define noise pollution. Explain why most urban areas are unsustainable systems. Describe the major aspects of poverty in urban areas. Summarize Mexico City's major urban and environmental problems and what government officials are doing about them.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 26 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Do you think that the global population of 7.1 billion is too large? Explain. If your answer was yes, what do you think should be done to slow human population growth? If your answer was no, do you believe that there is a population size that would be too big? Explain. Do you think that the population of the country where you live is too large? Explain.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 26 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Consider the characteristics of an eco-city listed on p. 122. How close to this eco-city model is the city in which you live or the city nearest to where you live? Pick what you think are the five most important characteristics of an eco-city and, for each of these characteristics, describe a way in which your city could attain it.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 26 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



